The global circumcision devices market, which includes clamp-based solutions like the Gomco clamp, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2023 to 2030, driven by rising newborn circumcision rates, increasing awareness of hygiene-related health benefits, and expanded use in adult male circumcision programs, particularly in regions with high HIV prevalence (Grand View Research, 2023). As demand for safe, efficient, and standardized circumcision tools rises, Gomco clamps—long recognized for their durability and precision—remain a dominant choice in both clinical and outreach settings. This growing market has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers, leading to advancements in design, material quality, and production standards. Based on market presence, regulatory compliance, and distribution reach, the top four Gomco clamp manufacturers—Crane Healthcare, Apex Medical Corporation, Adamlevine Medical, and MedMox—have distinguished themselves through consistent product performance and adherence to international quality benchmarks.
Top 4 Clamp Gomco Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ALLIED HEALTHCARE PRODUCTS INC. GOMCO CIRCUMCISION …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: accessdata.fda.gov
Key Highlights: The gomco clamp instruction state the following: “warning: use only component parts manufactured by “gomco” when assembling this device.” warning notices have ……
#2 Gomco Clamp Technique
Domain Est. 1985
Website: med.stanford.edu
Key Highlights: The Gomco clamp is the most commonly used circumcision device in our nursery. It has the advantages of a steel bell which protects the glans penis during the ……
#3 Gomco Circumcision Clamp
Domain Est. 1987
Website: embryo.asu.edu
Key Highlights: The Gomco circumcision clamp is a metal device that medical practitioners use to perform circumcision, or the removal of the foreskin of the ……
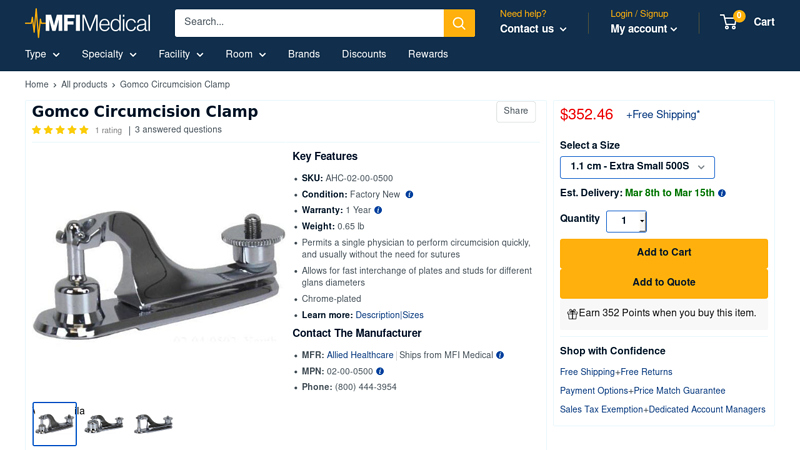
#4 Gomco Circumcision Clamp
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mfimedical.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (1) The Gomco Circumcision Clamp is chrome-plated and designed for a single physician to perform circumcision quickly, and usually without the need for suture…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Clamp Gomco
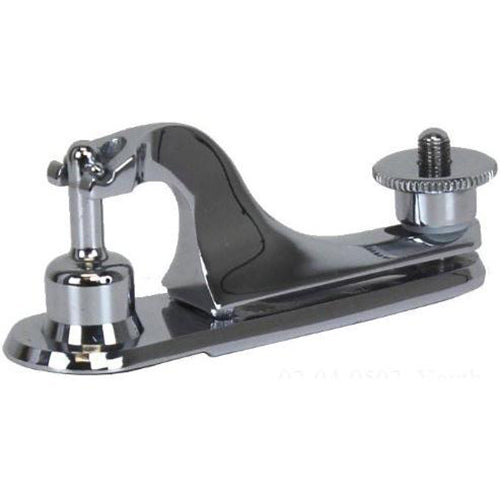

H2: Market Trends Analysis for Clamp Gomco in 2026
As the global medical device industry evolves rapidly, Clamp Gomco—a historically recognized brand in surgical instrumentation, particularly in urological and circumcision clamps—faces a dynamic market landscape in 2026. While the brand’s legacy remains strong, especially in regions with established use of traditional circumcision devices, several macroeconomic, technological, and regulatory trends are shaping its market position and growth potential.
1. Shift Toward Minimally Invasive and Disposable Devices
In 2026, there is a pronounced global shift toward disposable, single-use surgical instruments to reduce infection risks and streamline clinical workflows. Traditionally, Gomco clamps have been reusable, requiring sterilization between uses. However, concerns over cross-contamination and the rising cost of reprocessing are driving demand for disposable alternatives. Competitors have introduced single-use versions of circumcision clamps, putting pressure on Clamp Gomco to innovate or risk losing market share, particularly in high-volume settings like neonatal care units and mass circumcision programs.
2. Growth in Global Circumcision Markets
Demand for male circumcision remains strong in key markets:
– Sub-Saharan Africa: Ongoing public health initiatives supported by WHO and PEPFAR continue to promote voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) as an HIV prevention strategy. In 2026, these programs represent a significant volume opportunity, but preference is increasingly shifting toward safer, faster, and less painful devices such as the Shang Ring and PrePex, which are more operator-friendly than traditional clamps.
– Middle East and South Asia: Cultural and religious circumcision drives steady demand. However, adoption of newer devices and increasing access to trained healthcare providers may reduce reliance on traditional tools like the Gomco clamp.
3. Technological Innovation and Competition
By 2026, newer circumcision technologies offering reduced procedure time, lower complication rates, and minimal training requirements—such as automated stapling devices and energy-based systems—are gaining traction, especially in private healthcare and outpatient clinics. Gomco’s mechanical design, while reliable, is perceived as more technically demanding and time-consuming compared to modern alternatives. Unless Clamp Gomco introduces updated or hybrid models (e.g., disposable components or ergonomic enhancements), it risks being viewed as outdated.
4. Regulatory and Safety Scrutiny
Medical device regulations are tightening globally, particularly in the U.S. (FDA) and EU (MDR). There is increased focus on post-market surveillance, adverse event reporting, and user training. Clamp Gomco must ensure ongoing compliance and demonstrate safety and efficacy data to maintain market access. Any reported complications related to improper use could trigger regulatory scrutiny and impact brand reputation.
5. Market Consolidation and Brand Legacy
Clamp Gomco is now part of larger medical device portfolios (currently under CooperSurgical, a subsidiary of The Cooper Companies). In 2026, this integration provides distribution strength and R&D resources, but also means the product must compete internally for investment. The brand benefits from decades of trust among experienced urologists and pediatric surgeons, particularly in North America. However, younger practitioners are more inclined to adopt newer technologies, posing a generational adoption challenge.
6. Sustainability and Cost Pressures
Hospitals and public health programs are increasingly cost-conscious and environmentally aware. While reusable clamps like Gomco are more sustainable in theory, the labor and resource costs of sterilization are rising. In contrast, single-use devices offer predictable costs and reduced logistical burden. This economic trade-off is influencing procurement decisions, particularly in resource-constrained settings.
Conclusion: Strategic Outlook for Clamp Gomco in 2026
Clamp Gomco remains a trusted name in surgical circumcision, but its market position in 2026 is under pressure from innovation, shifting clinical preferences, and competitive alternatives. To remain relevant, the brand should consider:
– Introducing a disposable or hybrid Gomco model to meet infection control demands.
– Enhancing training and digital support tools to reduce learning curves and complications.
– Leveraging its brand heritage and clinical trust in marketing, especially among experienced surgeons.
– Exploring emerging markets where cost-effective, durable instruments are still valued.
Without strategic modernization, Clamp Gomco risks transitioning from a standard of care to a legacy tool in select niches. However, with targeted innovation and positioning, it can sustain a meaningful presence in the 2026 surgical landscape.
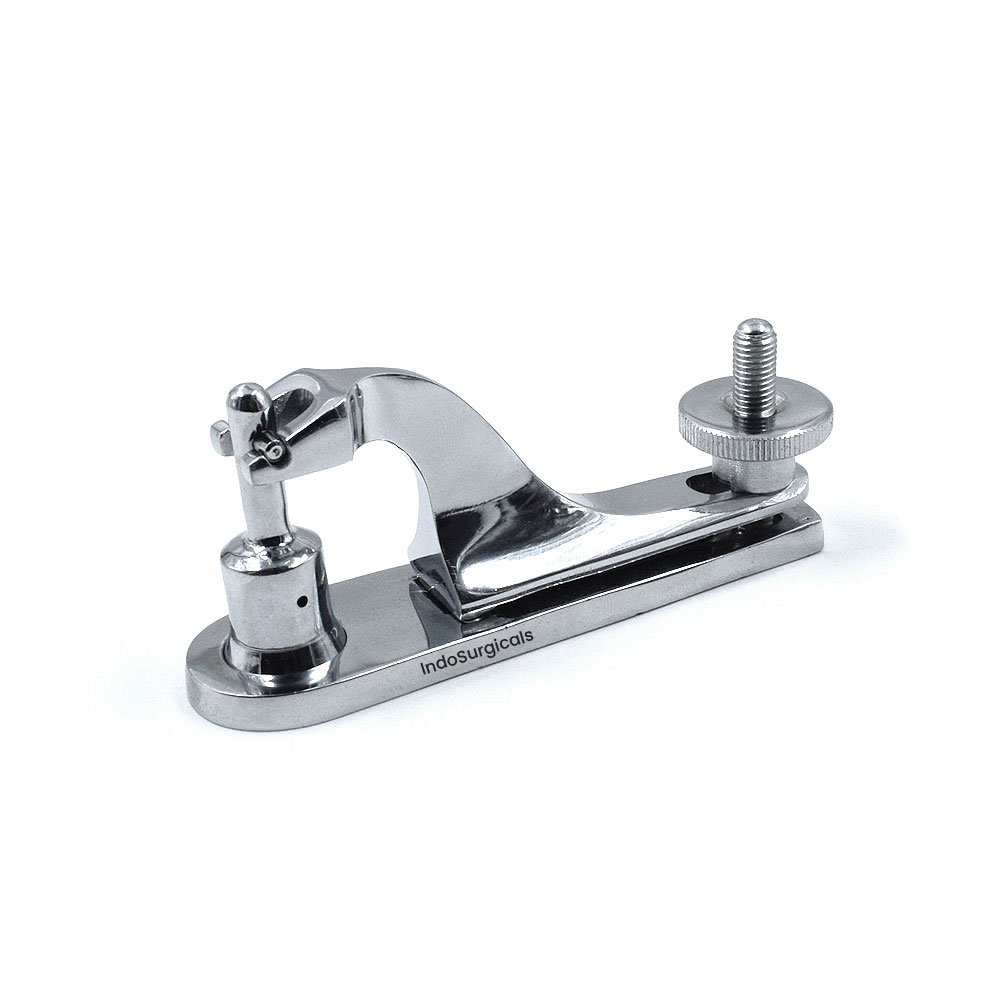

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Clamp Gomco (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Clamp Gomco devices—commonly used in neonatal circumcision procedures—can present significant challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Falling into these pitfalls can lead to legal risks, patient safety issues, and reputational damage.
Quality Concerns with Non-OEM or Counterfeit Products
One of the most prevalent pitfalls is the availability of low-quality or counterfeit Clamp Gomco devices in the global supply chain. These imitations often fail to meet the stringent safety and performance standards of the original equipment manufactured by Gomco (a CooperSurgical brand). Risks include:
- Substandard Materials: Inferior metals or plastics that may corrode or break during use, increasing the risk of surgical complications.
- Inconsistent Manufacturing: Poor tolerances or imprecise dimensions can lead to improper clamping, causing tissue damage or ineffective circumcision.
- Lack of Sterilization Compliance: Non-compliant devices may not support standard hospital sterilization protocols (e.g., autoclaving), raising infection risks.
- Absence of Regulatory Approval: Many counterfeit or copy versions lack FDA clearance, CE marking, or other regulatory approvals, making their use legally and clinically risky.
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or unverified suppliers increases the likelihood of receiving such subpar products.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
The Gomco Clamp is a patented medical device, and its design, branding, and associated trademarks are protected under intellectual property law. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers often involves IP violations, leading to several risks:
- Legal Liability: Distributors, hospitals, or clinics using counterfeit or infringing devices may face legal action from CooperSurgical for contributory infringement.
- Brand Damage: Institutions associated with counterfeit medical devices may suffer reputational harm and loss of patient trust.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Seizures by customs authorities or legal injunctions can interrupt the availability of devices, affecting clinical operations.
- Voided Warranties and Support: IP-infringing devices do not qualify for manufacturer support, training, or warranty coverage, leaving users without recourse in case of failure.
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should verify supplier authenticity, request documentation (e.g., certificates of authenticity, regulatory clearances), and source directly from authorized distributors or the manufacturer. Due diligence is essential to ensure both patient safety and legal compliance.
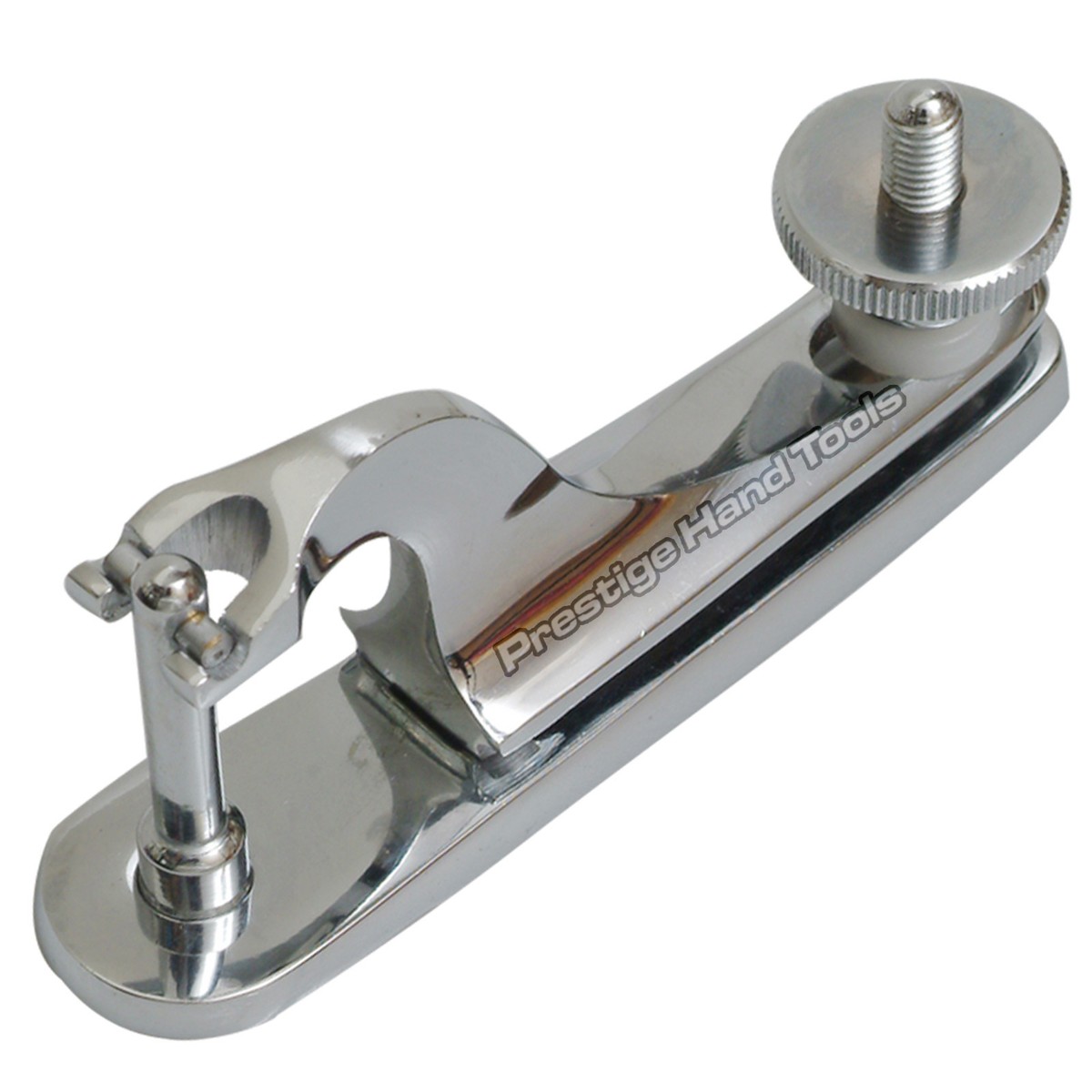

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Clamp Gomco
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, storing, and using Clamp Gomco devices in accordance with regulatory standards and best practices.
Regulatory Classification and Approvals
Clamp Gomco devices are classified as medical devices and are subject to regulatory oversight by authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other national regulatory bodies. These devices are typically categorized under Class I or Class II medical devices, depending on jurisdiction and intended use. Ensure that all Clamp Gomco units are CE-marked (for EU markets), FDA-cleared (for U.S. markets), and comply with local regulations in the destination country. Documentation, including the Declaration of Conformity and 510(k) clearance (if applicable), must accompany shipments and be retained for audit purposes.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
All Clamp Gomco devices must be shipped in validated, tamper-evident packaging that protects against physical damage, moisture, and contamination. Labels must include:
– Product name and model number
– Lot or serial number
– Expiration date (if applicable)
– Manufacturer and distributor information
– Regulatory markings (e.g., CE, FDA)
– Single-Use or Reusable designation
– Biohazard symbols (if applicable)
– Directional and handling icons (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
Labeling must be in the official language(s) of the destination country and comply with country-specific requirements under regulations such as the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745.
Storage Conditions
Clamp Gomco devices must be stored in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment. Recommended storage conditions are:
– Temperature: 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F)
– Relative Humidity: 30% to 60%
Avoid direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and exposure to solvents or corrosive chemicals. Reusable clamps should be stored in sealed, sterile packaging until reprocessing. Single-use devices must remain sealed until point of use.
Transportation and Distribution
Transportation of Clamp Gomco devices must comply with International Air Transport Association (IATA) and local regulations for medical goods. Use carriers experienced in medical device logistics. Maintain the cold chain (if required) and monitor environmental conditions using data loggers when appropriate. For international shipments:
– Ensure Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DAP) are clearly defined in contracts
– Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes for customs clearance
– Submit required import documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, and certificates of origin and conformity
Import/Export Compliance
Export of medical devices may be subject to export control regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), though Clamp Gomco devices generally fall outside ITAR scope. Verify export license requirements based on destination country and end-user. For imports, comply with local medical device registration requirements (e.g., China NMPA, Health Canada, TGA in Australia). Engage local regulatory partners when necessary.
Reprocessing and Reuse Compliance (Reusable Models)
For reusable Clamp Gomco models, strict adherence to reprocessing protocols is mandatory. Follow the manufacturer’s validated cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization instructions. Use only approved sterilization methods (e.g., steam autoclaving at specified temperature and duration). Document all reprocessing cycles and perform regular maintenance and inspection for wear or damage. Facilities must comply with standards such as ISO 17664 and AAMI ST79.
Single-Use Device Handling
Single-use Clamp Gomco devices must not be reprocessed or reused under any circumstances. Clearly label waste streams and dispose of used devices according to local biomedical waste regulations (e.g., incineration, autoclaving, and landfill protocols as permitted). Ensure staff are trained to recognize and segregate single-use items.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Maintain comprehensive records for a minimum of 10 years (or as required by local law), including:
– Device lot and serial numbers
– Distribution records (ship-to/ship-from details)
– Complaints and adverse event reports
– Reprocessing logs (for reusable models)
– Calibration and maintenance records
Implement a robust Unique Device Identification (UDI) system to support traceability throughout the supply chain, as mandated by FDA UDI requirements and EU MDR.
Adverse Event Reporting
In the event of device malfunction, injury, or death related to Clamp Gomco use, report incidents promptly to relevant regulatory authorities. In the U.S., submit reports via the FDA’s MedWatch program (Form 3500A) within required timeframes. In the EU, use the EUDAMED system per MDR Article 87. Internal investigations and root cause analyses must be conducted and documented.
Training and Personnel Compliance
Ensure all personnel involved in handling, storing, distributing, or using Clamp Gomco devices receive appropriate training on:
– Product-specific handling and use
– Infection control practices
– Regulatory compliance requirements
– Adverse event reporting procedures
Maintain training records and conduct periodic refresher sessions.
Audits and Quality Management
Regular internal and external audits must be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 13485, FDA Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820), and other applicable standards. Address non-conformances promptly and implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) as needed.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure the safe, legal, and effective distribution and use of Clamp Gomco devices worldwide.
Conclusion for Sourcing Gomco Clamps:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, quality standards, regulatory compliance, and cost-efficiency, sourcing Gomco clamps from reputable medical device manufacturers or certified distributors is essential to ensure product safety, reliability, and performance in clinical settings. Gomco clamps are widely recognized for their precision and durability in surgical procedures, particularly circumcision, making it critical to procure them from authorized or high-quality sources that adhere to international medical device regulations such as ISO 13485 and FDA standards.
Primary considerations in the sourcing process should include product authenticity, sterility (if pre-sterilized), material quality (typically surgical-grade stainless steel), and compliance with healthcare facility requirements. While cost is a factor, prioritizing quality and patient safety over price alone will lead to better clinical outcomes and reduced risk of complications.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy involves partnering with trusted suppliers—whether original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), certified medical distributors, or global healthcare procurement platforms—that provide verifiable certifications, consistent supply, and after-sales support. This ensures the integrity of the surgical process and supports high standards of patient care.