The global leather goods market continues to demonstrate resilient growth, driven by rising consumer demand for premium materials in fashion, automotive, and upholstery applications. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global leather goods market size was valued at USD 447.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Chrome-tanned leather, known for its softness, durability, and resistance to shrinkage, accounts for over 80% of global leather production, making it the dominant tanning method in modern manufacturing. This surge in demand has elevated the prominence of specialized chrome leather manufacturers who combine scalability with sustainable practices, particularly amid tightening environmental regulations. As industries seek consistent quality and ethical sourcing, identifying leading producers becomes critical. The following analysis highlights the top eight chrome leather manufacturers shaping the global supply chain through innovation, capacity, and compliance with international standards.
Top 8 Chrome Leather Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
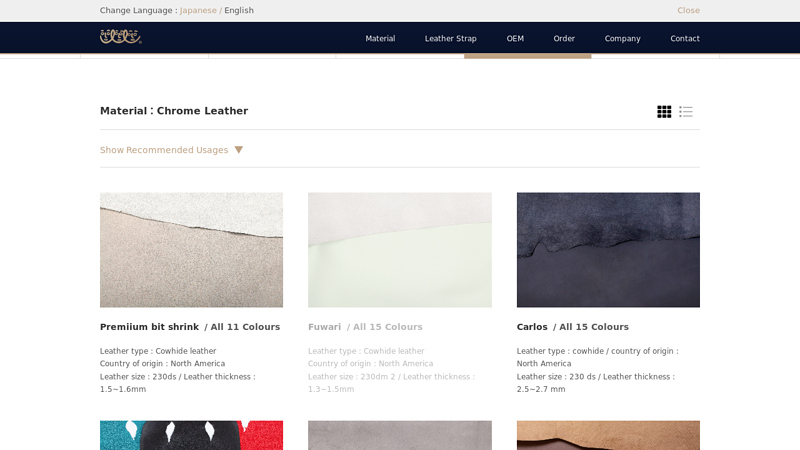
#1 Material:Chrome Leather
Domain Est. 2016
Website: hashimotoindustry.com
Key Highlights: Chrome Leather | HASHIMOTO INDUSTRY Co.,Ltd. [L Factory] Manufacture and sale of leather products / Manufacture and sales of various leather tapes….
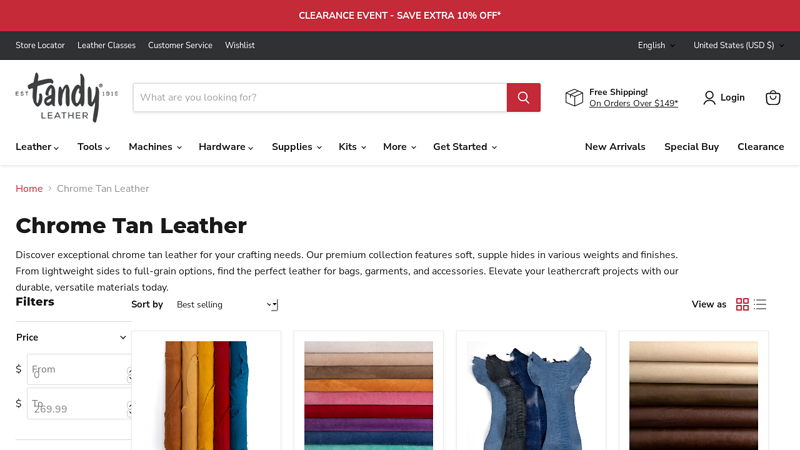
#2 Shop Chrome Tan Leather at Tandy
Domain Est. 1996
#3 Chrome Industries
Domain Est. 2001
Website: chromeindustries.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $100 · 30-day returnsWhat began decades ago with our iconic messenger bag has grown into a skilled heritage brand that lives at the intersection of movement and…
#4 Chrome Tanned Leather
Domain Est. 2012
#5 Weaver Leather Supply
Domain Est. 2013
Website: weaverleathersupply.com
Key Highlights: Start your next leather crafting project with top quality leather, leatherworking tools, machinery and hardware from Weaver Leather Supply….
#6 Chrome
Domain Est. 2014
Website: rmleathersupply.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery · 30-day returnsEurope. Cordovan Calf – Luxury Calfskin Leather “Finished like Shell Cordovan” (HIDES). Price. From $ 239.99. View options….
#7 Chrome Free Leather
Domain Est. 2020
Website: neratanning.com
Key Highlights: Zeology, our zeolite based leather tanning agent, is chrome free, heavy metal free and aldehyde free and does not compromise on leather performance….
#8 Chrome Leather Company
Website: chromeleathercompany.com
Key Highlights: Chrome Leather Company is a leading exporter committed to providing exceptional services to businesses across all industries….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Chrome Leather
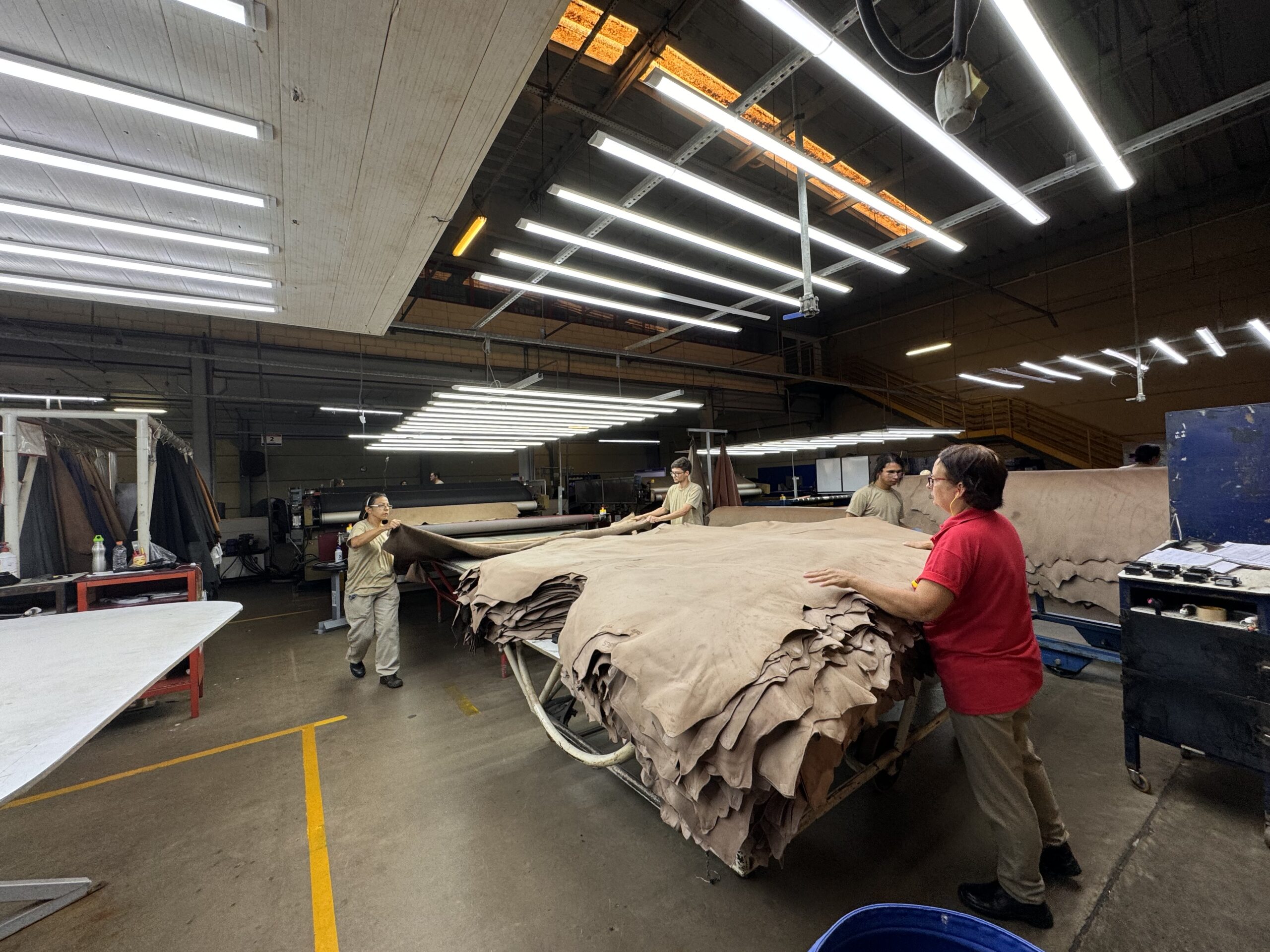

2026 Market Trends for Chrome Leather
Rising Demand in Luxury and Sustainable Fashion
By 2026, chrome-tanned leather is expected to maintain a strong foothold in the luxury fashion sector due to its softness, durability, and vibrant dye retention. However, consumer demand for transparency and environmental responsibility will push brands to adopt cleaner production methods. Leading manufacturers are anticipated to invest in closed-loop water systems and non-toxic alternatives to traditional chromium salts, aligning chrome leather production with circular economy principles.
Regulatory Pressures and Shift Toward Eco-Certifications
Stringent environmental regulations, particularly in the EU under REACH and the upcoming Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability, will reshape chrome leather manufacturing. By 2026, compliance with low hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) emissions will be mandatory, driving innovation in tanning chemistry. Increased adoption of certifications such as LWG (Leather Working Group) Gold Rating will become a competitive necessity, influencing sourcing decisions across automotive and apparel industries.
Growth in Automotive and Upholstery Applications
The automotive sector—especially electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers—will continue to favor chrome leather for premium interiors due to its comfort, aesthetic appeal, and performance under varying climates. By 2026, demand is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2%, with a shift toward semi-aniline and low-impact chrome-tanned leathers that balance luxury with reduced environmental impact.
Competition from Alternative Materials
Chrome leather will face intensified competition from bio-based and lab-grown leathers, as well as improved synthetic alternatives like Piñatex and Mylo. However, its superior tactile qualities and established supply chains will sustain its market position, especially in high-end segments. The key differentiator by 2026 will be traceability and verifiable sustainability claims integrated through blockchain-enabled supply chains.
Regional Production Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia, particularly India and China, will remain dominant in chrome leather production, but with increased investment in wastewater treatment infrastructure to meet export standards. Meanwhile, nearshoring trends in Europe and North America may lead to a resurgence of smaller, specialized tanneries focusing on high-value, low-volume chrome leather goods with full lifecycle accountability.
Conclusion
By 2026, chrome leather will persist as a material of choice in premium markets, but its future success hinges on innovation in eco-friendly tanning, regulatory compliance, and transparent sourcing. The convergence of performance, aesthetics, and sustainability will define the next generation of chrome-tanned leather products.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Chrome Leather: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing chrome-tanned leather offers benefits like softness, durability, and consistent appearance, but buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) issues. Being aware of these pitfalls can help mitigate risks and ensure a reliable supply chain.
Inconsistent Quality Standards
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing chrome leather is variability in quality. Suppliers—especially in regions with less stringent oversight—may deliver products that do not meet specified thickness, finish, or grain uniformity standards. This inconsistency can stem from differences in raw hide sourcing, tanning processes, or finishing techniques. Buyers may receive shipments with color mismatches, surface defects, or poor dye fastness, leading to production delays and increased rejection rates.
Hidden Defects and Lack of Transparency
Chrome leather may appear high-quality on the surface but conceal hidden flaws such as scar tissue, insect bites, or uneven tannage. Without rigorous inspection protocols or access to traceable supply chains, buyers risk receiving substandard material. Some suppliers may also blend lower-grade hides into premium batches without disclosure, undermining product integrity.
Misrepresentation of Leather Type and Origin
Suppliers may falsely label corrected grain or bonded leather as “top-grain” or “full-grain” chrome leather, misleading buyers about the product’s quality and value. Additionally, the geographic origin of the leather may be misrepresented to imply higher quality (e.g., claiming European origin when the product is sourced from less-regulated markets). This mislabeling can damage brand reputation and lead to compliance issues.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing chrome leather from third-party manufacturers increases the risk of unintentional IP violations. Some suppliers may offer leathers with embossed patterns, textures, or finishes that replicate patented or trademarked designs (e.g., signature exotic prints or brand-specific finishes). Using such materials—even unknowingly—can expose the buyer to legal liability, including cease-and-desist orders or financial damages.
Lack of Certification and Compliance Documentation
Reputable chrome leather sourcing requires adherence to environmental and safety standards, such as REACH, OEKO-TEX, or ZDHC. However, some suppliers may provide falsified or incomplete certifications, exposing buyers to regulatory risk. Absence of proper documentation also raises concerns about chemical usage (e.g., hexavalent chromium) and ethical sourcing practices.
Inadequate Traceability and Supply Chain Visibility
Many suppliers lack end-to-end traceability, making it difficult to verify animal welfare practices, environmental impact, or adherence to labor standards. This opacity not only affects sustainability goals but also increases vulnerability to reputational risks, especially as consumers demand greater transparency.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, including on-site audits, sample testing, and legal review of design specifications. Establishing long-term partnerships with certified, transparent suppliers and incorporating strict quality control clauses into contracts can significantly reduce both quality and IP risks when sourcing chrome leather.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Chrome Leather
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, and regulating chrome-tanned leather. Chrome leather—tanned using chromium(III) sulfate—requires special attention due to environmental, safety, and international trade regulations.
Regulatory Compliance
REACH & RoHS Compliance
Chrome leather must comply with the EU’s REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) regulations. Specifically, total chromium content and the presence of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) must be monitored. Cr(VI) levels must not exceed 3 ppm in finished leather goods under REACH Annex XVII.
Proposition 65 (California, USA)
Products containing chrome leather must comply with California’s Proposition 65 if sold in the state. This requires clear labeling if hexavalent chromium is present above safe harbor levels.
Customs & Import Regulations
Importers must provide detailed product documentation, including material composition, country of origin, and compliance certifications. Tariff classifications (HS Code 4107 for tanned bovine leather) must be accurately declared to avoid delays or penalties.
Environmental & Safety Standards
Waste Management
Residual chrome liquors and trimmings from production are classified as hazardous waste in many jurisdictions. Proper treatment, neutralization, and disposal per local environmental protection agency (EPA or equivalent) guidelines are mandatory.
Worker Safety
Handling chrome-tanned leather requires protective equipment (gloves, masks) to prevent skin contact and inhalation of dust, especially during cutting or finishing. Employers must comply with OSHA (or local equivalent) standards for chemical exposure.
Transportation & Packaging
Domestic and International Shipping
Chrome leather should be packed in moisture-resistant, breathable materials to prevent mold and staining. Use of desiccants is recommended for long-distance or maritime transport.
Avoid direct contact with wood packaging materials treated with chromated copper arsenate (CCA), as this can lead to contamination.
IATA & IMDG Compliance
While finished chrome leather is generally not classified as dangerous goods, shipments containing residual chromium salts may require hazard declarations. Always verify classification under IATA (air) and IMDG (sea) regulations based on chemical content.
Documentation Requirements
Certificates of Conformity
Suppliers must provide Certificates of Conformity (CoC) confirming compliance with REACH, Oeko-Tex Standard 100 (if applicable), and other relevant standards.
Traceability & Due Diligence
Maintain full traceability from raw hide source to finished product. Implement due diligence systems to ensure supply chain transparency and prevent sourcing from regions with poor environmental or labor practices.
Storage & Handling
Warehouse Conditions
Store chrome leather in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Maintain relative humidity between 50–60% to prevent drying or mold growth.
Segregation
Store finished leather separately from raw materials and chemicals to prevent cross-contamination.
Audits & Monitoring
Regular Testing
Conduct periodic testing for hexavalent chromium and pH levels, especially before export. Third-party lab certification enhances credibility with buyers and regulators.
Compliance Audits
Schedule internal and third-party audits to verify adherence to environmental, safety, and customs compliance protocols. Maintain audit records for a minimum of five years.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for chrome leather depend on strict adherence to chemical safety, environmental protection, and international trade regulations. Proactive documentation, testing, and supply chain management are key to ensuring smooth operations and market access.
Conclusion for Sourcing Chrome-Tanned Leather
Sourcing chrome-tanned leather presents a balance of advantages and responsibilities. As one of the most widely used methods in the leather industry, chrome tanning offers efficiency, durability, and a consistent, soft finish highly valued in fashion, automotive, and furniture applications. Its faster processing time and lower cost compared to vegetable tanning make it an attractive option for large-scale manufacturers.
However, the environmental and health impacts associated with chromium (particularly hexavalent chromium) necessitate careful supplier selection and adherence to sustainability standards. Responsible sourcing involves partnering with tanneries that follow strict wastewater treatment protocols, employ chrome recycling systems, and comply with international regulations such as REACH and ZDHC. Certifications like LWG (Leather Working Group) provide valuable guidance in identifying environmentally responsible suppliers.
In conclusion, while chrome-tanned leather remains a practical and economical choice for many industries, sustainable sourcing requires due diligence, transparency, and a commitment to minimizing environmental impact. Companies that prioritize ethical procurement and invest in cleaner production technologies will not only reduce their ecological footprint but also strengthen brand reputation and meet growing consumer demand for responsible manufacturing practices.