The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing automation, rising demand for precision manufacturing, and the widespread adoption of laser technologies across automotive, electronics, and medical device industries. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 5.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady growth in the sector, citing advancements in fiber laser technology and growing investments in electric vehicle (EV) production as key drivers. With China accounting for over 60% of global industrial laser equipment production—per China’s Laser Industry Development Report—the country has emerged as a dominant force in laser manufacturing. Within this competitive landscape, a select group of Chinese laser welder manufacturers have risen to the forefront, combining innovation, cost efficiency, and scalability to capture significant market share both domestically and internationally. The following list highlights the top eight Chinese companies shaping the future of laser welding through technological excellence and strategic market positioning.
Top 8 Chinese Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Demark (Wuhan) Technology Co., Ltd.
Website: demarkchina.cn
Key Highlights: Demark (Wuhan) Technology Co.,ltd has focused on laser technology for over 20 years in China, including laser marking, laser engraving, laser welding and laser ……
#2 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now become the flagship of Chinese national laser ……
#3 China Laser Welding
Website: laserchina.com
Key Highlights: LASERCHINA is a China-based laser manufacturer that specializes in developing and manufacturing laser machine, parts, custom solutions and repair service….
#4 Wuhan Raycus Fiber Laser Technologies Co., Ltd.
Website: en.raycuslaser.com
Key Highlights: (hereinafter referred to as “Wuhan Raycus”) is the first Chinese enterprise engaged in the research, development and scale production of high-power fiber lasers ……
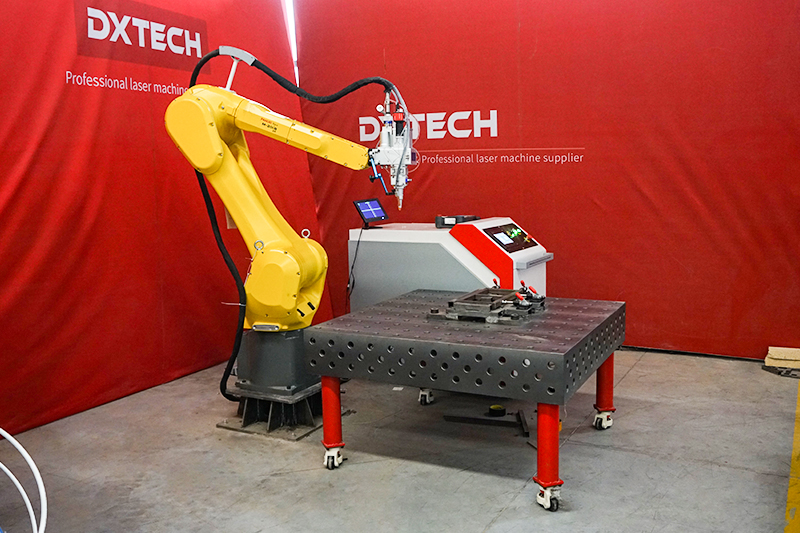
#5 DXTECH Official
Website: dxtech.com
Key Highlights: DXTECH, as the advanced CNC laser machine manufacturer, mainly manufactures and supplies the laser cutting machines, laser welding machines, laser engraving ……
#6 Chinese laser welder Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Website: laserdmk.com
Key Highlights: The DMK chinese laser welding machine that has been Chinese welder supplies an advanced level of accuracy, making sure their welds is newly made. Their ……
#7 Laser Welding Machine
Website: yihailasers.com
Key Highlights: Laser Welding Machine ; Favourite Portable Air Cooled Fiber Laser Welding Machine · 5,500.00 ; Surprise Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine Manufacturer in China….
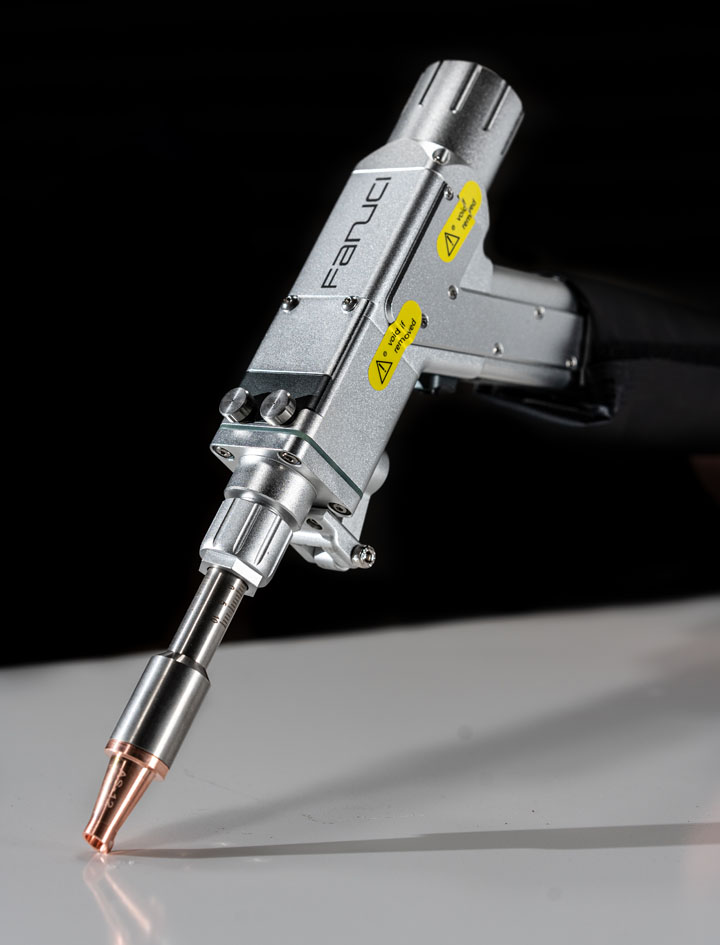
#8 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Chinese Laser Welder

H2: Market Trends in the Chinese Laser Welder Industry (2026 Outlook)
By 2026, the Chinese laser welder market is expected to experience robust growth, driven by technological innovation, rising automation demand, and strong government support for advanced manufacturing. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Accelerated Adoption in High-Growth Industries
The electric vehicle (EV), battery manufacturing, and renewable energy sectors are major drivers of laser welding demand. As China strengthens its position as the world’s largest EV producer, precision welding for battery packs, powertrains, and lightweight vehicle components will push demand for high-speed, high-accuracy laser welders. By 2026, integration of laser welding in battery production lines is projected to grow at over 20% CAGR. -
Shift Toward High-Power and Ultrafast Lasers
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting high-power fiber lasers (6 kW–30 kW) and ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers for superior weld quality, reduced heat-affected zones, and increased throughput. Domestic laser source producers such as IPG Photonics (with Chinese operations), Raycus, and Max Photonics are advancing indigenous capabilities, reducing reliance on imports and lowering system costs. -
Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Integration
Laser welding systems are being embedded with AI-driven process monitoring, real-time quality control, and IoT connectivity. By 2026, over 60% of new laser welders sold in China are expected to feature smart diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities, aligning with China’s “Made in China 2025” initiative to promote intelligent manufacturing. -
Localization and Supply Chain Resilience
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions are accelerating domestic substitution of core components, including laser sources, optics, and control systems. Chinese companies are investing heavily in R&D to achieve self-reliance, reducing import dependency and enhancing cost competitiveness in both domestic and export markets. -
Expansion in SME Adoption
Falling equipment prices and modular, user-friendly systems are enabling small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt laser welding for precision applications in electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods. Government subsidies and financing programs are further lowering entry barriers. -
Rising Exports and Global Competitiveness
Chinese laser welder manufacturers are expanding overseas, particularly in Southeast Asia, India, and Eastern Europe, offering cost-effective, high-performance solutions. By 2026, China is projected to account for over 35% of global laser welding equipment exports, up from approximately 25% in 2022. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
As environmental regulations tighten, energy-efficient laser systems with lower carbon footprints are gaining favor. Fiber lasers, known for their high wall-plug efficiency, are displacing older CO₂ and lamp-pumped systems across industries.
In conclusion, the 2026 Chinese laser welder market will be characterized by technological sophistication, broad industrial integration, and growing global influence. Domestic innovation, policy support, and expanding applications will solidify China’s role as a central hub in the global laser processing ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Chinese Laser Welders (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser welders from China can offer significant cost advantages, but it comes with notable risks, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these common pitfalls is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Quality Inconsistencies and Substandard Components
One of the most prevalent challenges is the wide variance in build quality and component selection among Chinese suppliers. While some manufacturers produce high-end, reliable machines, many prioritize cost-cutting over performance and durability. Key issues include:
- Inferior Optics and Lasers: Low-quality laser sources (e.g., unbranded or recycled diodes/fiber lasers) and optics can result in inconsistent weld penetration, reduced beam quality, and frequent failures.
- Poor Mechanical Construction: Chassis and motion systems made from subpar materials or with imprecise assembly lead to misalignment, vibration, and reduced accuracy over time.
- Inadequate Cooling and Thermal Management: Overheating due to undersized or inefficient cooling systems can shorten laser lifespan and cause downtime.
- Lack of Standardization: Even within the same model, batch-to-batch variations are common due to inconsistent manufacturing processes and lax quality control.
Purchasers often discover these flaws only after deployment, resulting in increased maintenance costs and production delays.
Misleading Specifications and Performance Gaps
Many Chinese suppliers exaggerate technical specifications to win contracts. Common misrepresentations include:
- Overstated Laser Power: Advertised power ratings may reflect peak or theoretical output rather than sustained, real-world performance.
- Inflated Duty Cycles: Claims of continuous operation at maximum power may not be achievable due to thermal limitations.
- False Certification Claims: Some suppliers falsely state compliance with international safety or quality standards (e.g., CE, ISO) without proper verification.
Without independent testing or third-party validation, buyers risk acquiring equipment that fails to meet production requirements.
Intellectual Property Risks and Technology Replication
Sourcing advanced laser welding technology from China poses serious IP concerns:
- Reverse Engineering: Suppliers may deconstruct purchased equipment to replicate proprietary designs, control algorithms, or integration features.
- Unauthorized Resale or Rebranding: There are documented cases of original equipment being copied and sold under different brands, including back into the buyer’s home market.
- Weak Contract Enforcement: Even with NDAs and IP clauses, enforcing IP rights in cross-border disputes is often time-consuming and costly, with limited legal recourse in some jurisdictions.
This risk is especially high when purchasing custom or semi-custom systems where unique engineering elements are exposed.
Limited After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Post-purchase support is often inadequate:
- Delayed Technical Assistance: Time zone differences, language barriers, and understaffed support teams lead to prolonged downtimes.
- Spare Parts Shortages: Critical components may be out of stock or require long lead times, disrupting operations.
- Firmware and Software Lock-ins: Some suppliers restrict access to control software updates or parameters, limiting customization and troubleshooting capabilities.
This lack of support undermines the total cost of ownership, negating initial price savings.
Inadequate Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Not all Chinese laser welders meet international safety standards:
- Missing Safety Interlocks: Essential features like emergency stops, door interlocks, or beam enclosures may be absent or poorly implemented.
- Non-Compliant Laser Classifications: Equipment may be improperly labeled, posing safety and regulatory risks in markets like the EU or North America.
- Electrical Safety Deficiencies: Improper grounding, substandard wiring, or lack of EMI shielding can create fire or operational hazards.
Buyers must independently verify compliance with local regulations, as supplier-provided documentation may be unreliable.
Mitigation Strategies
To reduce these risks:
– Conduct factory audits and request third-party quality inspections (e.g., SGS, TÜV).
– Require performance testing under real operating conditions before final payment.
– Use escrow services and phased payments tied to milestones.
– Work with legal counsel to draft robust IP protection clauses and jurisdiction-specific contracts.
– Prioritize suppliers with international certifications, established global service networks, and verifiable customer references.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Chinese Laser Welder
Import Regulations and Documentation
Ensure compliance with destination country regulations when importing a laser welder from China. Required documentation typically includes a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or air waybill, and a certificate of origin. In many countries, laser equipment is subject to safety and radiation standards—verify that the laser welder meets local requirements such as FDA compliance in the United States (21 CFR 1040.10) or CE marking in the European Union under the Machinery Directive and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive. Request a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) from the manufacturer.
Product Classification and Tariff Codes
Accurately classify the laser welder using the Harmonized System (HS) code to determine applicable tariffs and import duties. Typical HS codes for industrial laser welding machines fall under 8456.20 (Electrical discharge machines, laser, or other electro-thermic machines for working metal). Confirm the correct code with your customs broker, as misclassification can lead to delays, fines, or unexpected costs. Check for any preferential trade agreements (e.g., RCEP) that may reduce tariffs on Chinese-origin equipment.
Shipping and Handling Considerations
Choose between sea, air, or express freight based on urgency, cost, and equipment size. Sea freight is cost-effective for heavy machinery but takes longer (30–45 days); air freight is faster (5–10 days) but more expensive. Ensure the laser welder is securely crated with shock-absorbing materials, especially for sensitive optical and electronic components. Clearly label the package with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include internal documentation in case external labels are damaged.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Prepare for customs clearance by submitting all required documents to the local customs authority. Provide technical specifications of the laser welder, including power output, wavelength, and intended use, as this may affect classification and compliance verification. Pay attention to valuation—customs may assess duties based on the transaction value, including freight and insurance (CIF). Factor in potential customs bonds, handling fees, and import VAT or GST, which vary by country.
Safety and Technical Compliance
Verify that the laser welder complies with international safety standards such as IEC 60825 (laser safety) and IEC 60204 (safety of machinery). The equipment should include proper labeling, interlocks, and emergency stops. Request test reports or third-party certifications from the manufacturer. For industrial use, ensure integration with local power supply standards (e.g., voltage, frequency) and include necessary adapters or transformers if required.
After-Sales Support and Warranty
Confirm the availability of technical support, spare parts, and warranty services from the Chinese manufacturer or an authorized local distributor. Understand the warranty terms, including duration, coverage, and process for claiming service. Consider service contracts or extended warranties to minimize downtime. Retain all purchase and compliance documents for future service or regulatory audits.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Be aware of environmental regulations related to the disposal of laser components, particularly batteries, optics, and electronic waste. Ensure end-of-life handling complies with local laws such as WEEE in the EU or EPA guidelines in the U.S. Some components may require special recycling procedures due to hazardous materials.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Chinese Laser Welder
Sourcing a laser welder from China offers significant advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, technological advancement, and a wide range of choices. The Chinese manufacturing sector has made tremendous strides in recent years, producing high-quality laser welding machines that meet international standards and cater to various industrial applications. Competitive pricing, combined with improvements in build quality, automation integration, and technical support, makes Chinese laser welders an attractive option for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities without incurring the high costs associated with Western or European brands.
However, successful sourcing requires due diligence. Buyers should carefully evaluate suppliers based on certifications (such as CE, ISO), after-sales support, warranty terms, and technical expertise. Engaging with reputable manufacturers, requesting product demonstrations or samples, and using secure payment methods can mitigate risks related to quality and reliability. Additionally, considering logistics, import regulations, and potential language barriers is essential for a smooth procurement process.
In summary, sourcing a laser welder from China can be a strategic decision that delivers advanced technology at a competitive price, provided it is approached with careful research and clear communication. When done correctly, it offers a strong return on investment and supports long-term manufacturing efficiency.