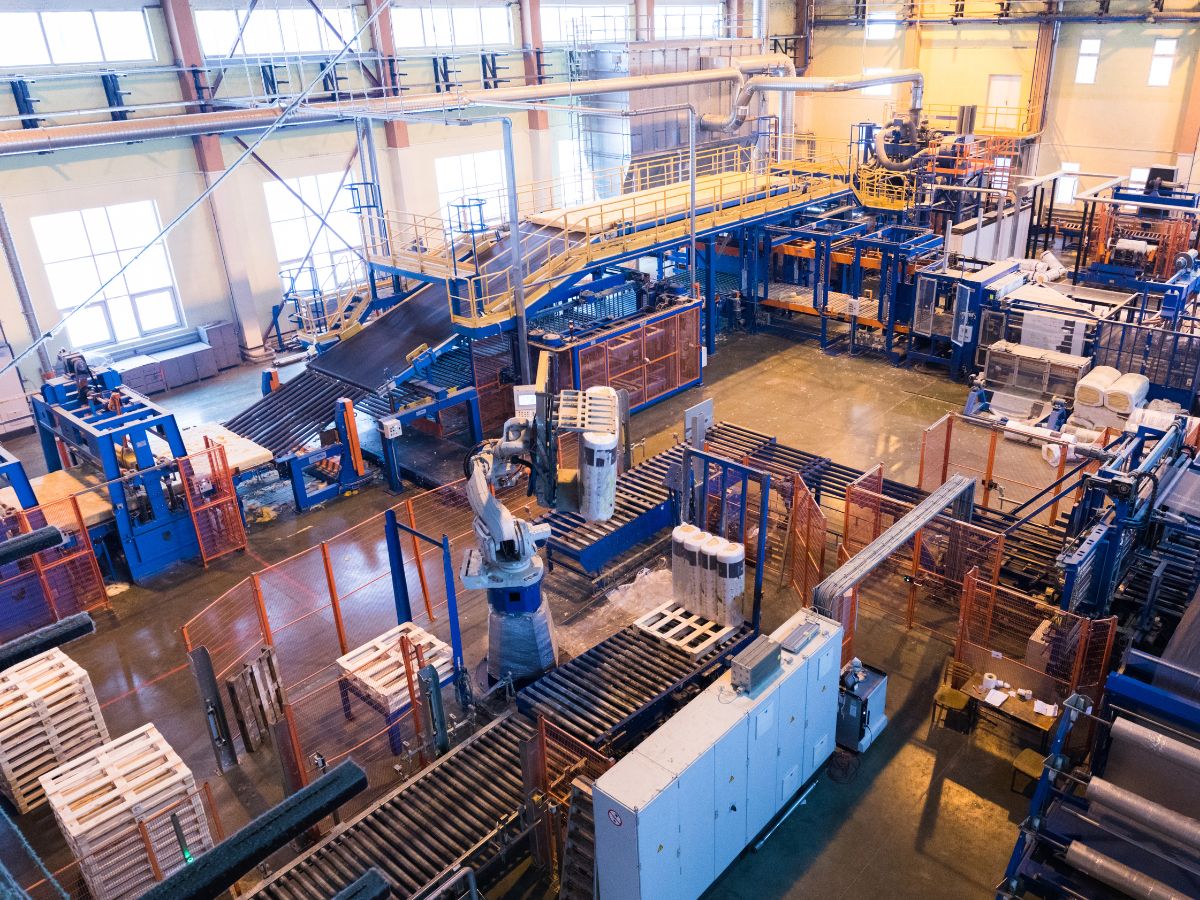
The manufacturing sector in China continues to dominate global supply chains, driven by technological advancements, scale, and cost efficiency. According to Mordor Intelligence, the China manufacturing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by increasing automation, government support under initiatives like “Made in China 2025,” and rising demand in high-tech industries such as electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy. Grand View Research further highlights that China accounted for more than 30% of global manufacturing output in 2022, maintaining its position as the world’s largest manufacturing hub. With exports surpassing $3.5 trillion in 2023, Chinese manufacturers are not only scaling production but also advancing in innovation and quality. This data-driven landscape sets the stage for identifying the top nine Chinese manufacturing companies that exemplify industrial excellence, operational scale, and global impact.
Top 9 China Manufacturing Companies Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Hand Tools Manufacturers, Suppliers & Exporters, Wholesale …
Domain Est. 2007
Website: sinotools.com
Key Highlights: China leading manufacturer & exporter of hand tools, garden tools & agriculture tools, main products include industrial hand tools, garden hand tools, ……
#2 HKTDC Sourcing
Domain Est. 2000
Website: sourcing.hktdc.com
Key Highlights: Source quality products online from reliable China and Hong Kong wholesale suppliers & Chinese manufacturers on HKTDC Online Marketplace, a leading HKTDC ……
#3 China Manufacturers On B2BChinaSources.Com For China …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: b2bchinasources.com
Key Highlights: Leading B2B China manufacturers directory for global buyers to buy Taiwan quality at Chinese prices. Efficient in China products sourcing….
#4 China Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2006
Website: sourcingallies.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.9 (33) This read will walk you through how to find a manufacturer in China. You first need to build a shortlist of Chinese suppliers who manufacture the product you ……
#5 China Quality Manufacturers, China Products & China Suppliers on …
Domain Est. 2011
Website: everychina.com
Key Highlights: EveryChina.com is the leading China product sourcing and supplier discovery platform connecting China manufacturers and suppliers with worldwide buyers from ……
#6 Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited
Domain Est. 1993 | Founded: 1987
Website: tsmc.com
Key Highlights: TSMC has been the world’s dedicated semiconductor foundry since 1987, and we support a thriving ecosystem of global customers and partners with the ……
#7 Global Supply Chain Success with ITI Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2007
Website: itimanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: ITI provides turnkey global manufacturing services with partners in The Americas, China, Vietnam, South Korea, Taiwan, India and elsewhere, with proven ……
#8 WuXi AppTec
Domain Est. 2008
Website: wuxiapptec.com
Key Highlights: WuXi AppTec is a trusted partner and contributor to the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries, providing R&D and manufacturing services that help advance ……
#9 China LESSO Group
Domain Est. 2008
Website: en.lesso.com
Key Highlights: It offers a wide range of products such as pipes, photovoltaics, plumbing and sanitary ware, integral kitchen materials, integral doors and windows, aluminum ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for China Manufacturing Companies
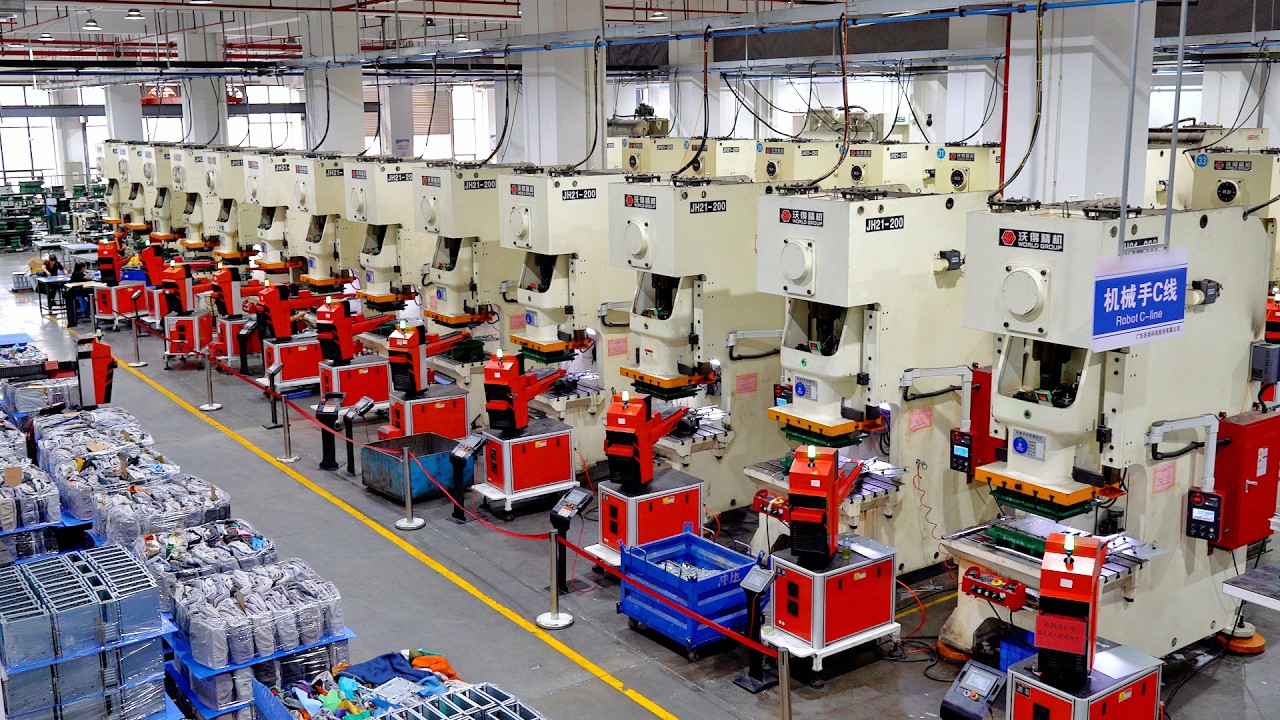

H2: Market Trends Shaping China’s Manufacturing Sector in 2026
As China progresses toward its strategic economic goals under the 14th Five-Year Plan and broader “Made in China 2025” vision, the manufacturing sector is undergoing a profound transformation. By 2026, several key trends are defining the trajectory of Chinese manufacturing companies, driven by technological innovation, policy direction, global dynamics, and shifting consumer demands.
1. Accelerated Adoption of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Technologies
By 2026, Chinese manufacturers are increasingly integrating advanced digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and big data analytics into production processes. Smart factories are becoming the norm, especially in electronics, automotive, and high-tech equipment sectors. Government incentives, including subsidies and pilot programs, have catalyzed investments in automation and digital twins, improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and enabling mass customization.
2. Resilience and Diversification of Supply Chains
In response to geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, and post-pandemic disruptions, Chinese manufacturers are reconfiguring global supply chains. While China remains a central hub, companies are adopting a “China +1” strategy—expanding production into Southeast Asia, Mexico, and Eastern Europe to mitigate risks. Domestically, there is a strong push to localize critical components (e.g., semiconductors, rare earth materials) to reduce foreign dependency and enhance supply chain resilience.
3. Green Manufacturing and Carbon Neutrality Goals
China’s commitment to peak carbon emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 is reshaping manufacturing practices. By 2026, stricter environmental regulations and carbon pricing mechanisms are compelling manufacturers to adopt green technologies, energy-efficient processes, and circular economy models. Solar panel, wind turbine, and electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers are leading this transition, supported by state-led investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
4. Rising Focus on High-Value and Innovation-Driven Production
China is shifting from low-cost, labor-intensive manufacturing to high-value-added industries. In 2026, sectors such as advanced semiconductors, biopharmaceuticals, aerospace, and new materials are receiving significant R&D investment. Domestic innovation is being prioritized, with companies like Huawei, BYD, and SMIC driving breakthroughs. Intellectual property protection has improved, encouraging both domestic and foreign firms to innovate within China.
5. Expansion of Domestic and Global Market Access
With global trade headwinds, Chinese manufacturers are increasingly tapping into the vast domestic consumer market, fueled by rising middle-class demand for premium, sustainable, and smart products. Simultaneously, exports are diversifying—moving beyond traditional markets to the Middle East, Africa, Latin America, and ASEAN nations. E-commerce platforms and cross-border digital trade (via platforms like Alibaba and JD) are enabling SMEs to reach international customers efficiently.
6. Workforce Transformation and Talent Development
As automation reduces demand for low-skilled labor, manufacturers are investing in upskilling workers in robotics operation, data analysis, and engineering. Vocational education reforms and industry-academia collaborations are enhancing the talent pipeline. However, labor shortages in certain regions and sectors persist, prompting further automation and regional rebalancing of manufacturing zones.
7. Geopolitical and Regulatory Challenges
Despite growth, Chinese manufacturers face increased scrutiny abroad, particularly in the U.S. and EU, over national security, data privacy, and unfair trade practices. Export controls on advanced technologies and de-risking strategies by Western nations are pushing Chinese firms to strengthen self-reliance and explore alternative markets. Compliance with international standards (e.g., ESG, product safety) has become essential for global competitiveness.
Conclusion
By 2026, China’s manufacturing landscape is more technologically advanced, sustainable, and strategically positioned than ever before. While challenges remain, the sector’s adaptability, robust policy support, and innovation-driven mindset are solidifying its role as a global manufacturing powerhouse—evolving from the “world’s factory” to a leader in smart, green, and high-tech production.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing from Chinese Manufacturing Companies
Quality Control Challenges
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing from China is inconsistent product quality. Many suppliers may provide excellent samples but fail to maintain the same standards during mass production. Differences in raw materials, worker training, and oversight between sample and production runs can lead to subpar outputs. Without independent third-party inspections or an on-the-ground quality assurance team, buyers risk receiving defective or non-compliant goods that can damage brand reputation and result in costly returns or recalls.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Protecting intellectual property is a major concern when working with Chinese manufacturers. Despite legal frameworks, enforcement can be inconsistent, and there have been documented cases of design theft, unauthorized production (also known as “ghost production”), and reverse engineering. Suppliers may replicate your product for other clients or sell it under their own brand. To mitigate this risk, companies should register IP in China, use robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limit the sharing of sensitive design details, and work with trusted partners verified through due diligence.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for China Manufacturing Companies
Understanding China’s Export Regulatory Framework
China’s export landscape is governed by multiple regulatory bodies, including the General Administration of Customs (GAC), State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), and Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM). Manufacturers must comply with national laws such as the Export Control Law (effective 2020), which regulates dual-use items, technologies, and sensitive goods. Familiarity with export control lists and licensing requirements is essential to avoid penalties and shipment delays.
Export Licensing and Documentation Requirements
Most exports from China require proper documentation, including a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and export declaration. Certain goods—such as electronics, chemicals, and machinery—may require export licenses or certificates of origin. The Automated System for Customs Data (ASCD) is used for electronic customs declarations. Accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification is critical to determine duties, restrictions, and eligibility for trade agreements.
Product Standards and Certification Compliance
Manufacturers must ensure products meet both Chinese mandatory standards (China Compulsory Certification, or CCC) and the regulatory requirements of destination countries. For example, electronics exported to the EU need CE marking, while U.S.-bound goods may require FCC or UL certification. Non-compliance can result in shipment rejection, fines, or market bans. Regular audits and third-party testing help maintain compliance.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
China enforces strict environmental laws under the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE), particularly for industries involving chemicals, textiles, and electronics. Exporters must comply with regulations on hazardous substance restrictions (e.g., RoHS China), waste disposal, and carbon emissions reporting. Additionally, workplace safety standards set by the应急管理部 (MEM) must be followed to maintain export facility certifications.
Intellectual Property Protection
Manufacturers must safeguard their own intellectual property (IP) and avoid infringing on others’. Registering patents, trademarks, and designs with the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) is crucial. Customs can detain shipments suspected of IP violations under the IP Recordal System. Proactive IP management minimizes legal risks and strengthens international competitiveness.
Logistics Infrastructure and Supply Chain Management
China boasts a vast logistics network, including world-leading ports (e.g., Shanghai, Shenzhen), rail links under the Belt and Road Initiative, and extensive air cargo hubs. Choosing between sea, air, rail, or multimodal transport depends on cost, speed, and destination. Partnering with licensed freight forwarders and utilizing bonded warehouses can streamline customs clearance and reduce lead times.
Free Trade Zones and Bonded Logistics
Free Trade Zones (FTZs) such as Shanghai Pudong and Guangdong offer preferential policies, including simplified customs procedures, tax exemptions, and foreign investment facilitation. Goods stored in bonded warehouses can be re-exported without paying Chinese import duties. Leveraging these zones enhances supply chain flexibility and cost efficiency for export-oriented manufacturers.
Incoterms and International Contracts
Using standardized Incoterms® 2020 (e.g., FOB, CIF, EXW) clarifies responsibilities for transportation, insurance, and risk transfer between buyer and seller. Clear contracts should specify delivery terms, payment methods (e.g., letters of credit), quality standards, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Legal review of export contracts helps prevent misunderstandings and financial losses.
Anti-Bribery and Trade Sanctions Compliance
Chinese manufacturers must adhere to the PRC Anti-Unfair Competition Law and international standards like the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and UK Bribery Act when conducting overseas business. Additionally, companies must screen business partners against global sanctions lists (e.g., OFAC, EU) to avoid dealings with restricted entities, especially in sensitive regions.
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance Training
Regulations in China and foreign markets evolve frequently. Establishing a compliance management system—including regular staff training, internal audits, and updates from legal advisors—ensures ongoing adherence. Subscribing to official government alerts and trade association bulletins helps manufacturers stay ahead of regulatory changes.
Final Recommendations
To thrive globally, Chinese manufacturing companies should integrate logistics and compliance into core operations. Investing in digital tools for customs filing, supply chain tracking, and compliance management enhances transparency and efficiency. Building strong relationships with customs brokers, legal experts, and logistics partners further supports sustainable international growth.
In conclusion, sourcing from Chinese manufacturing companies offers significant advantages, including competitive pricing, vast production capabilities, and access to a wide range of industries and suppliers. However, success in this endeavor requires careful supplier vetting, clear communication, quality control measures, and an understanding of logistics, intellectual property protection, and cultural differences. By leveraging tools such as audits, third-party inspections, and trusted platforms like Alibaba, businesses can mitigate risks and build reliable, long-term partnerships. When managed strategically, sourcing from China remains a powerful option for companies aiming to scale efficiently and maintain cost-effective operations in the global market.