The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, efficient joining solutions across industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the rising adoption of automation and advanced manufacturing technologies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, where China has emerged as both a manufacturing powerhouse and a key innovator in laser technology. With domestic policies like “Made in China 2025” promoting the shift toward intelligent manufacturing, Chinese laser welder manufacturers are rapidly advancing in technological capabilities, cost efficiency, and global competitiveness. As a result, the country now hosts a growing number of suppliers offering innovative, high-performance laser welding systems that cater to both local and international markets. This data-driven momentum underscores the importance of identifying the top players shaping the future of laser welding from China.
Top 10 China Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Machine – Laser Equipment Manufacturer
Website: dplaser.com
Key Highlights: DPLASER is a leading manufacturer & factory of industrial laser welding, laser cutting, laser marking and laser cleaning machines….
#2 Demark (Wuhan) Technology Co., Ltd.
Website: demarkchina.cn
Key Highlights: Demark (Wuhan) Technology Co.,ltd has focused on laser technology for over 20 years in China, including laser marking, laser engraving, laser welding and laser ……
#3 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now become the flagship of Chinese national laser ……
#4 HJZ Laser
Website: laserwuhan.com
Key Highlights: HJZ Laser is a China Industrial laser machines manufacturer and Solutions Provider of Automatic laser equipment for more than 12 years….
#5 China Laser Welding
Website: laserchina.com
Key Highlights: LASERCHINA is a China-based laser manufacturer that specializes in developing and manufacturing laser machine, parts, custom solutions and repair service….
#6 Wuhan Raycus Fiber Laser Technologies Co., Ltd.
Website: en.raycuslaser.com
Key Highlights: (hereinafter referred to as “Wuhan Raycus”) is the first Chinese enterprise engaged in the research, development and scale production of high-power fiber lasers ……
#7 DXTECH Official
Website: dxtech.com
Key Highlights: DXTECH, as the advanced CNC laser machine manufacturer, mainly manufactures and supplies the laser cutting machines, laser welding machines, laser engraving ……
#8 China Laser Machine Manufacturer
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: We have over 20 years of expertise in designing and manufacturing laser machines. Our products include laser cleaning machines, welding machines, laser marking ……
#9 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#10 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
Expert Sourcing Insights for China Laser Welder
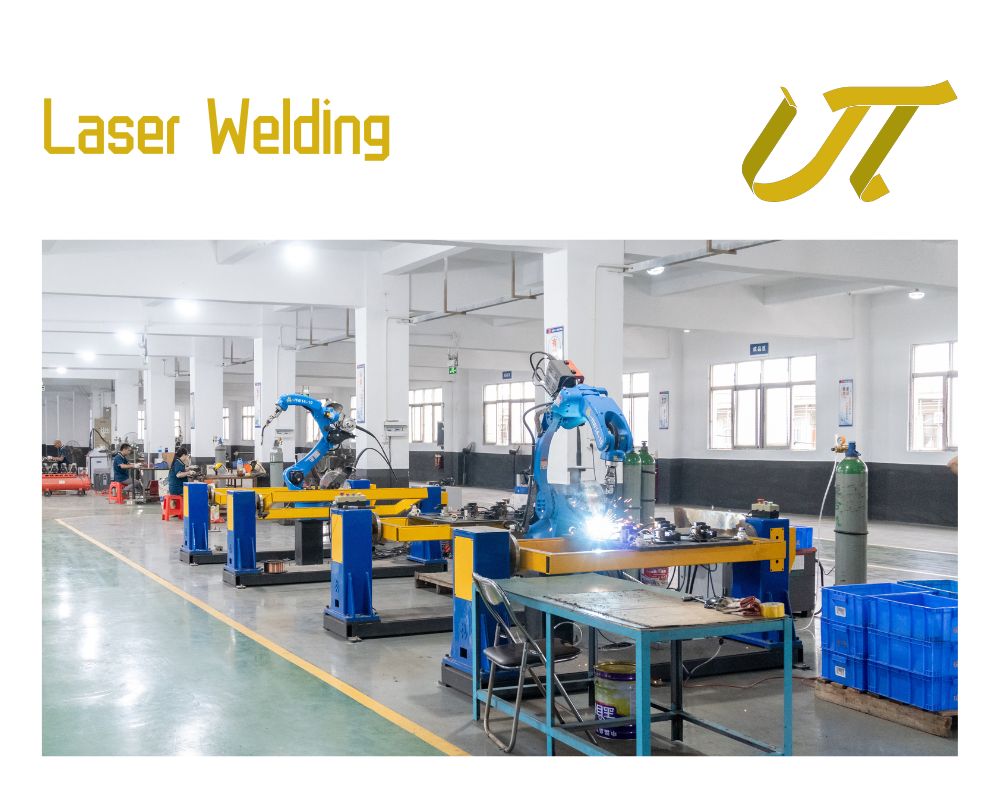

H2: 2026 Market Trends for China Laser Welder Industry
By 2026, the China laser welder market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, rising industrial automation, and strong government support for high-end manufacturing. This analysis explores key trends shaping the sector, including technological innovation, market demand shifts, competitive dynamics, and policy influences.
1. Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Chinese manufacturers are increasingly investing in R&D to develop high-power, high-precision fiber laser welders with improved energy efficiency and integration capabilities. By 2026, hybrid laser-arc welding and smart welding systems equipped with AI and IoT connectivity are expected to dominate industrial applications. These innovations enable real-time monitoring, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance—enhancing productivity and reducing downtime in automotive, electronics, and aerospace manufacturing.
2. Rising Demand from Key End-Use Sectors
The automotive and new energy vehicle (NEV) industries remain primary drivers of laser welder demand. With China’s aggressive push toward electric mobility, battery manufacturing—particularly for lithium-ion cells—requires precision welding solutions, boosting the need for specialized laser systems. Additionally, the electronics sector, including consumer electronics and semiconductors, continues to demand miniaturized and high-accuracy laser welding technologies.
3. Localization and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities have accelerated efforts to localize core components such as laser generators, optical fibers, and control systems. By 2026, domestic Chinese firms like Han’s Laser, Maxphotonics, and JPT Opto-electronics are expected to capture over 70% of the domestic market for mid-to-high-end laser sources, reducing reliance on imported components from Europe and the U.S.
4. Expansion into Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional manufacturing, laser welding is gaining traction in emerging fields such as renewable energy (e.g., solar panel assembly), medical devices, and 3D printing. These niche but high-growth segments are creating new revenue streams for Chinese laser equipment providers, fostering diversification and innovation.
5. Intensifying Competition and Market Consolidation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with a growing number of domestic players offering cost-effective solutions. Price pressures are prompting consolidation, with larger firms acquiring smaller innovators to expand product portfolios and enhance technical capabilities. By 2026, the top five Chinese laser welder manufacturers are projected to hold over 50% market share.
6. Government Policy and Industry 4.0 Integration
China’s “Made in China 2025” initiative and the broader push for intelligent manufacturing are providing strong policy and financial support for laser technology adoption. Subsidies, tax incentives, and national R&D programs are accelerating the deployment of laser welding in smart factories, aligning with the goals of Industry 4.0.
7. Export Growth and Global Market Penetration
Chinese laser welder manufacturers are expanding internationally, particularly in Southeast Asia, India, and Eastern Europe. Competitive pricing, improved product quality, and localized service networks are enabling Chinese brands to challenge established Western and Japanese competitors in global markets.
Conclusion
By 2026, the China laser welder market will be characterized by rapid innovation, strong domestic demand, and growing global influence. Fueled by strategic industrial policies and technological self-reliance, Chinese manufacturers are well-positioned to lead in both volume and value, reshaping the global laser welding landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welders from China
Sourcing laser welders from China can offer cost advantages, but it comes with significant risks if not managed carefully. Two major areas of concern are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) vulnerabilities.
Quality Inconsistencies and Lack of Standardization
One of the most prevalent challenges is the wide variation in product quality among Chinese manufacturers. While some suppliers offer high-performance, reliable machines, others may cut corners on components, assembly, or calibration. Buyers often encounter discrepancies between product specifications provided during sales negotiations and the actual performance of delivered units. Issues such as unstable beam output, poor weld penetration, or premature component failure (e.g., laser sources, cooling systems) are common. Additionally, inconsistent quality control processes—especially among smaller or less established factories—can result in unit-to-unit variability, making it difficult to ensure reliability in production environments. Without clear adherence to international standards (e.g., CE, ISO, or FDA for medical applications), buyers may receive equipment that fails to meet safety or performance benchmarks.
Intellectual Property Risks and Technology Exposure
Sourcing advanced laser welding technology from China poses significant intellectual property (IP) concerns. Sharing technical requirements, custom configurations, or proprietary designs with suppliers increases the risk of IP misappropriation, including unauthorized replication, reverse engineering, or resale of your specifications to competitors. Some manufacturers may use provided designs to develop their own branded versions, undermining your market position. Furthermore, weak enforcement of IP rights in certain jurisdictions can make legal recourse difficult and costly. Even with non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) in place, enforcement may be inconsistent. Buyers must also be cautious when allowing factory audits or sharing detailed technical documentation, as these can expose sensitive innovation to potential misuse.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for China Laser Welder
Overview
Importing a laser welder from China involves navigating complex logistics and regulatory requirements. This guide outlines key steps, documentation, compliance standards, and best practices to ensure smooth and legal shipment and operation.
Classification and HS Code
Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the laser welder, typically falling under:
– 8515.21 – Resistance welding machines, including laser welding equipment.
Accurate classification is essential for determining import duties, taxes, and regulatory controls. Confirm the code with your customs broker or local customs authority.
Export Regulations from China
Ensure the Chinese supplier complies with China’s export controls:
– Verify the equipment does not require an export license due to dual-use or technology restrictions.
– Confirm the manufacturer provides a valid Commercial Invoice, Packing List, and Bill of Lading/Air Waybill.
– Request a Certificate of Origin (preferably Form A for preferential tariff treatment under certain trade agreements).
Import Regulations in Destination Country
Compliance varies by country; common requirements include:
– Customs Declaration: Submit full documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading.
– Duties and Taxes: Pay applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on the landed cost (product + shipping + insurance).
– Product Standards: Ensure the laser welder meets local electrical, safety, and EMC standards (e.g., CE in EU, UL/ETL in USA, CCC in China if re-exported).
Laser Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser welders are subject to strict safety regulations due to radiation hazards:
– FDA Registration (USA): Laser products must comply with 21 CFR 1040.10 and be reported to the FDA. Importers may need to file an Initial Importer Report (Form FDA 2877).
– IEC 60825 Compliance: Verify the equipment meets international laser safety standards (Class 1, 4, etc.).
– Local Workplace Safety Laws: Comply with OSHA (USA), HSE (UK), or equivalent regulations for laser use in industrial settings.
Shipping and Logistics
Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in machinery shipments:
– Incoterms: Agree with the supplier on terms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
– Packaging: Ensure the laser welder is crated securely with shock absorption and moisture protection.
– Transport Mode: Sea freight (FCL/LCL) is cost-effective for heavy machinery; air freight for urgent, smaller units.
– Insurance: Obtain all-risk cargo insurance to cover damage or loss during transit.
Customs Clearance
Prepare for efficient clearance:
– Provide accurate product description, value, and technical specifications.
– Include user manuals and technical drawings if requested.
– Assign a licensed customs broker to handle documentation and duties.
After-Import Requirements
Post-arrival steps include:
– Inspection: Some countries require physical inspection by customs or standards bodies.
– Installation and Commissioning: Follow manufacturer guidelines and ensure qualified personnel perform setup.
– Training and Documentation: Maintain operation manuals, safety data sheets, and compliance certificates on-site for audits.
Risk Mitigation and Best Practices
- Conduct due diligence on the Chinese supplier (verify business license, export history).
- Use Letters of Credit (LC) or escrow for secure payment.
- Retain all documentation for at least 5 years for audit purposes.
- Stay updated on changes in trade policies, tariffs, or sanctions affecting China-origin goods.
Conclusion
Successfully importing a laser welder from China requires meticulous planning in logistics, compliance, and safety. Partnering with experienced suppliers, freight forwarders, and regulatory consultants ensures timely delivery and legal operation in your market.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Welder from China:
Sourcing a laser welder from China can offer significant advantages, including cost-effectiveness, access to advanced manufacturing technology, and a wide range of suppliers with varying levels of expertise and specialization. Chinese manufacturers have made substantial advancements in recent years, producing high-quality laser welding machines that meet international standards and cater to diverse industrial applications.
However, successful sourcing requires due diligence. Key considerations include verifying the supplier’s credibility through certifications, customer reviews, and on-site factory audits if possible, ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards (such as CE, ISO, or FDA), and understanding the total cost of ownership—including shipping, import duties, after-sales service, and technical support.
Establishing clear communication, negotiating warranty terms, and securing technical training or installation assistance can mitigate potential risks and ensure seamless integration into your production process. Additionally, building a strong, long-term relationship with a reliable supplier can provide ongoing benefits, including product upgrades and faster response times.
In summary, sourcing a laser welder from China is a strategic option for businesses seeking high-quality, competitively priced equipment—provided it is approached with careful planning, thorough supplier evaluation, and attention to post-purchase support. When executed properly, it can deliver a significant return on investment and enhance manufacturing capabilities.