Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Die Casting Mold Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Die Casting Mold Manufacturing Landscape 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global source for die casting molds (DCMs), accounting for ~65% of export capacity. While cost advantages persist, 2026 procurement strategy must prioritize technical specialization, IP protection, and supply chain resilience over pure price arbitrage. Industrial clusters have matured significantly, with distinct regional strengths emerging. Guangdong excels in high-complexity automotive molds, Zhejiang leads in cost-efficiency for mid-tier applications, while Jiangsu/Shanghai dominate precision electronics. Procurement success hinges on aligning regional capabilities with specific technical requirements, not generic “China sourcing.”
Key Industrial Clusters: Die Casting Mold Manufacturing in China (2026)
China’s DCM industry is concentrated in three core clusters, each with specialized expertise and infrastructure:
-
Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta – PRD)
- Primary Hubs: Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan, Zhongshan
- Specialization: High-pressure die casting (HPDC) molds for automotive (EV components, transmission), complex consumer electronics, and aerospace. Dominated by Tier-1 suppliers serving global OEMs.
- 2026 Edge: Highest concentration of advanced CNC machining centers (5-axis+), EDM, and surface treatment facilities. Strongest English fluency and international QA standards (IATF 16949, ISO 9001). Highest R&D investment.
- Key Challenge: Premium pricing; intense competition for skilled labor; stringent environmental regulations increasing overhead.
-
Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta – YRD)
- Primary Hubs: Ningbo, Yuyao, Taizhou, Wenzhou
- Specialization: Mid-to-high complexity molds for appliances, power tools, industrial machinery, and general consumer goods. Strong SME ecosystem.
- 2026 Edge: Best value proposition for non-automotive applications. Highly efficient supply chain for raw materials (steel) and standard components. Rapid prototyping capabilities. Strong government subsidies for export-oriented SMEs.
- Key Challenge: Variable quality control among smaller workshops; less experience with ultra-precision automotive molds; moderate English proficiency.
-
Jiangsu/Shanghai (Core Yangtze River Delta)
- Primary Hubs: Suzhou, Kunshan, Shanghai (Pudong, Jiading)
- Specialization: Ultra-precision, high-cavitation molds for semiconductors, medical devices, optical components, and premium electronics. Mix of multinational subsidiaries and elite domestic players.
- 2026 Edge: Highest metrology capabilities (sub-micron accuracy), cleanroom mold assembly, and expertise in exotic alloys. Strongest IP protection frameworks. Proximity to R&D centers of global tech firms.
- Key Challenge: Highest labor and operational costs; lead times can be extended for cutting-edge specifications; capacity constrained for very large molds.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Decision Matrix (2026)
Scale: 1 (Lowest/Weakest) to 5 (Highest/Strongest). Based on SourcifyChina verified supplier data (Q4 2025) for standard automotive-grade HPDC molds (600-1200T).
| Parameter | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Jiangsu/Shanghai (Core YRD) | Critical Procurement Insight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD) | 4.2 | 4.8 | 3.5 | Zhejiang offers 8-12% lower base pricing vs PRD for comparable spec. Core YRD commands 15-20% premium for precision. |
| Quality (Std.) | 4.7 | 4.0 | 4.9 | PRD: Best for complex automotive durability. Core YRD: Unmatched for micron-level precision. Zhejiang: Consistent for mid-tier. |
| Lead Time (Weeks) | 10-14 | 12-16 | 14-18 | PRD’s integrated supply chain & expertise enables fastest turnarounds. Core YRD lead times rise for highest-precision specs. |
| Technical Capability | 4.9 | 4.2 | 5.0 | Core YRD leads in exotic materials & micro-molding. PRD strongest in large, complex automotive molds. Zhejiang excels in standardization. |
| IP Protection | 4.3 | 3.8 | 4.7 | Core YRD has strongest legal frameworks & track record. PRD improving rapidly. Zhejiang requires rigorous contractual safeguards. |
| Export Compliance | 4.8 | 4.5 | 4.6 | PRD has most experience with global OEM audits (IATF, VDA). All clusters now meet basic ISO, but depth varies. |
Key Interpretation for Procurement Managers:
Choose Guangdong (PRD) for: Mission-critical automotive/industrial molds requiring speed-to-market, complex geometries, and proven durability under high-volume production. Accept premium pricing for reduced risk.
Choose Zhejiang (YRD) for: Cost-sensitive mid-complexity molds (appliances, tools, housings) where total cost of ownership (TCO) outweighs absolute speed or ultra-precision. Mandatory: Rigorous factory audits & phased payment terms.
Choose Jiangsu/Shanghai for:* Cutting-edge precision applications (medical, semiconductor, optics) where tolerances are non-negotiable. Budget for extended lead times and premium costs. Prioritize suppliers with multinational client experience.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- De-Risk Through Regional Diversification: Avoid single-cluster dependency. Use PRD for critical automotive, Zhejiang for standard components, and Core YRD for high-precision tech. Mitigates regional disruption risk (e.g., power shortages, policy shifts).
- Demand Process Validation, Not Just Certificates: Require video evidence of mold flow analysis, cavity pressure monitoring, and first-article inspection (FAI) reports per AS9102 or customer-specific standards. Certificates alone are insufficient in 2026.
- Factor in “Total Mold Cost” (TMC): Include mold maintenance, expected lifespan (cycles), scrap rate reduction, and rework costs in supplier evaluation. A 10% cheaper mold from Zhejiang may cost 25% more in TMC if lifespan is halved.
- Leverage Automation for Quality Control: Insist on suppliers using AI-powered optical inspection (e.g., Cognex) for cavity surfaces and critical dimensions. Manual QC is no longer acceptable for Tier-1 applications.
- Secure IP via Technical Safeguards: Use split-manufacturing (core components in Core YRD, frames in Zhejiang) and mandate encrypted CAD/CAM transfer protocols. Avoid sending complete mold designs to single facilities.
Conclusion
The era of “sourcing molds from China” is over; 2026 demands sourcing the right mold from the right Chinese cluster. Guangdong’s speed and automotive rigor, Zhejiang’s cost efficiency, and Jiangsu/Shanghai’s precision mastery represent distinct strategic assets. Procurement leaders who map their technical requirements to these regional specializations—while implementing robust TMC analysis and IP protocols—will secure competitive advantage. SourcifyChina recommends initiating cluster-specific RFQs with technical validation milestones, not blanket price comparisons.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Avoid “lowest bidder” traps in Zhejiang. For critical applications, invest in PRD/Core YRD capabilities—the 15-20% premium is often justified by 30%+ reduction in production downtime and scrap rates.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Cluster Performance Index (CPI), verified supplier audits (n=142), and China Mold Industry Association (CMIA) 2026 Forecast.
Next Step: Contact SourcifyChina for a free cluster-matching assessment tailored to your specific mold specifications and risk profile.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China Die Casting Mold Manufacturers
1. Overview
Die casting mold manufacturing in China remains a strategic pillar in global supply chains due to competitive costs, scalable production capacity, and technological advancement. However, achieving consistent quality and regulatory compliance requires rigorous supplier vetting, clear technical specifications, and adherence to international standards.
This report outlines key technical and compliance benchmarks for procuring die casting molds from Chinese manufacturers. It is designed to equip procurement managers with actionable insights to mitigate quality risks and ensure regulatory alignment across target markets.
2. Key Quality Parameters
A. Mold Materials
The selection of mold steel directly impacts mold life, surface finish, and dimensional stability. Common materials used by reputable Chinese die casting mold manufacturers include:
| Material Grade | Application | Hardness (HRC) | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1) | Aluminum & Zinc Die Casting | 48–52 | High thermal fatigue resistance, good toughness |
| SKD61 (JIS) | High-pressure die casting | 48–52 | Equivalent to H13, widely used in precision molds |
| 8407 (ASSAB) | Long-run, high-precision molds | 50–54 | Superior polishability and thermal conductivity |
| NAK80 (Pre-hardened) | Low-wear, mirror-finish molds | 38–42 | Excellent for zinc and low-volume aluminum |
Procurement Tip: Specify material certification (e.g., mill test reports) and require heat treatment records to validate hardness and homogeneity.
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Tolerances must align with international standards such as ISO 2768 and DIN 1688 for die cast parts, which are directly influenced by mold precision.
| Parameter | Standard Tolerance (± mm) | High-Precision Capability (± mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimensions (up to 100 mm) | 0.10 | 0.03 |
| Core/Cavity Alignment | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| Parting Line Mismatch | 0.10 | 0.03 |
| Draft Angles | ±1° | ±0.5° |
| Hole Diameter (Ø10–50 mm) | 0.08 | 0.02 |
Note: Tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.02 mm) require advanced CNC machining, EDM finishing, and in-process CMM inspection.
3. Essential Certifications & Compliance
To ensure reliability and market access, suppliers should hold the following certifications:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance for Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Mandatory baseline; confirms standardized processes, traceability, and corrective action systems |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Indicates sustainable operations; critical for ESG-compliant sourcing |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive Quality Management | Required for automotive die casting suppliers; ensures process control and PPAP compliance |
| CE Marking | EU Conformity | Applies to machinery/equipment incorporating the mold; supplier must comply if mold is part of a CE-regulated system |
| FDA Compliance | Food-Contact Safety | Required if die cast parts contact food (e.g., kitchen appliances); verify material compliance (e.g., no toxic coatings) |
| UL Recognition | Safety for Electrical Components | Needed if die cast housing is used in UL-listed electrical devices; verify flame-resistant materials and dielectric properties |
Procurement Action: Require certified copies of valid certificates and conduct on-site or third-party audits for high-volume or safety-critical molds.
4. Common Quality Defects in Die Casting Molds & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Pitting/Erosion | Thermal fatigue, poor cooling design, low-grade steel | Use H13/8407 steel; optimize cooling channels; apply surface treatments (e.g., nitriding, PVD coating) |
| Cracking (Thermal Fatigue) | Repeated thermal cycling, inadequate heat treatment | Ensure proper tempering post-machining; avoid sharp corners; use FEM thermal analysis in design phase |
| Dimensional Drift | Inadequate stress relief, poor CNC calibration | Perform multiple stress-relief annealing cycles; conduct regular CMM validation; use calibrated metrology equipment |
| Flash at Parting Line | Misalignment, insufficient clamping, worn ejector pins | Maintain tight alignment tolerances (≤0.03 mm); inspect and replace worn components; use precision guide pillars/bushings |
| Poor Surface Finish (Ra > 0.4 μm) | Incomplete polishing, contamination, EDM recast layer | Employ progressive polishing (up to mirror finish); clean molds post-EDM; use fine-pulse EDM settings |
| Incomplete Filling (Short Shot) | Poor gating design, low injection pressure | Optimize runner and gate design via mold flow simulation (e.g., MAGMAsoft); validate with trial casting |
| Sticking or Ejection Failure | Insufficient draft, poor surface finish, inadequate lubrication | Ensure minimum 1–2° draft; polish cavity surfaces; apply release coatings if required |
Best Practice: Implement a First Article Inspection Report (FAIR) and require mold trials with documented process parameters (e.g., shot speed, temperature, cycle time).
5. Conclusion & Recommendations
Sourcing die casting molds from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages but requires disciplined quality management. Procurement managers should:
- Mandate material and process traceability via documented certifications.
- Enforce tolerance and surface finish standards in technical RFQs.
- Verify compliance with ISO, IATF, and product-specific standards (FDA, UL).
- Conduct supplier audits—preferably on-site or via accredited third parties.
- Require defect prevention plans and root cause analysis protocols.
By aligning technical specifications with robust compliance frameworks, procurement teams can secure high-performance molds that support reliable, scalable, and market-ready production.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
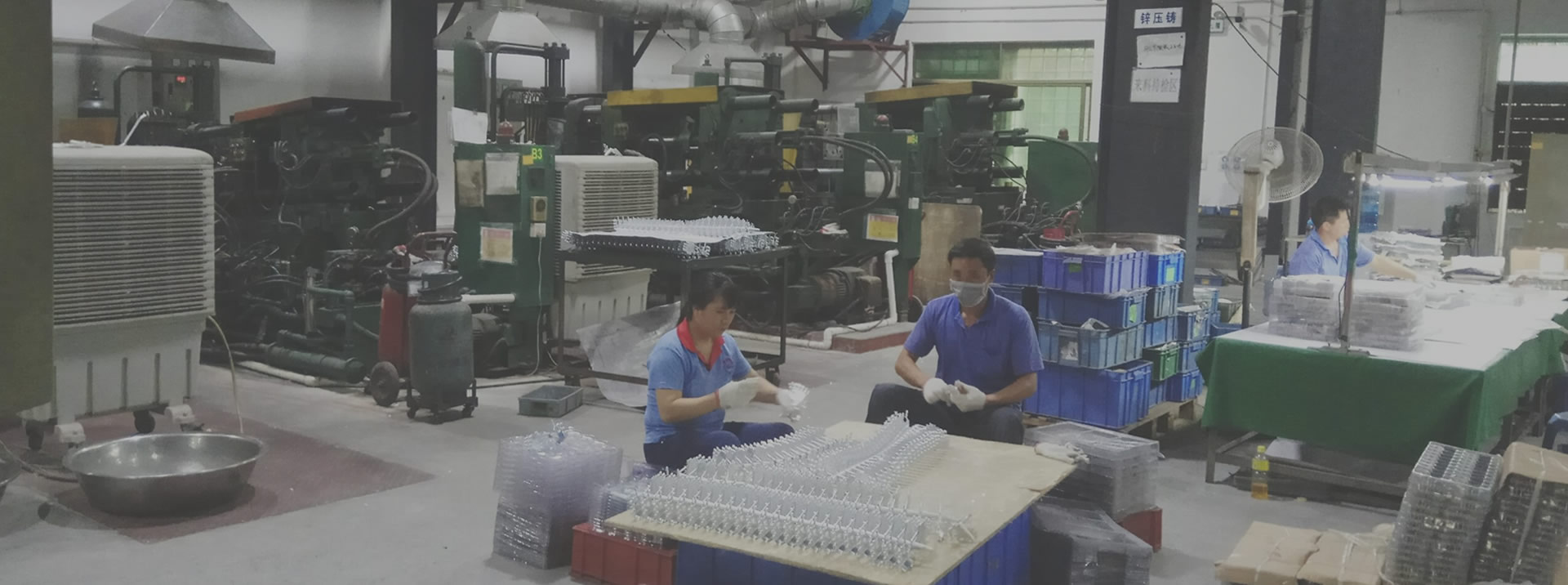

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT: DIE CASTING MOLD MANUFACTURING IN CHINA (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for die casting mold manufacturing, accounting for 68% of exported precision molds (2025 Global Mold Association data). This report provides actionable intelligence on cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and strategic sourcing considerations for 2026. Key findings indicate 15-22% cost inflation since 2023 due to material volatility and automation investments, with private label solutions now commanding 8-12% premiums over white label for IP-protected designs. Procurement managers should prioritize Tier-1 foundries with ISO 9001/TS 16949 certifications to mitigate quality risks.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Model | Definition | Best For | Cost Premium | Critical Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic molds produced to buyer’s specs; no engineering input. Buyer applies own branding. | Commodity parts (e.g., housings, brackets); Tight budget cycles; Short time-to-market | None (base cost) | Limited IP protection; Design flaws become buyer’s liability; High supplier lock-in |
| Private Label | Full ODM solution: Supplier engineers mold to buyer’s functional requirements under NDA; Exclusive IP ownership. | Complex/high-precision parts (e.g., automotive brackets, medical components); Premium branding; Long-term partnerships | +8-12% vs. white label | Higher MOQs; Requires rigorous IP clauses; Longer development cycles (4-8 weeks) |
Key Insight: Private label adoption grew 34% YoY (2025) among automotive/medical buyers. Always validate supplier’s engineering team credentials (e.g., Moldflow certification) for private label projects.
2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Aluminum ADC12 Alloy, A380 Equivalent)
Per Unit Cost Basis: 500g Part Weight, 2-Cavity Mold, Standard Tolerances (±0.1mm)
| Cost Component | White Label (USD) | Private Label (USD) | 2026 Trend Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $1.85 – $2.20 | $1.95 – $2.35 | • Aluminum spot price volatility (+12% YoY) • Zinc alloys (Zamak 3) 18-22% cheaper but limited to low-stress applications |
| Labor | $0.90 – $1.15 | $1.25 – $1.55 | • 22% wage inflation in Dongguan/Ningbo hubs • Private label: +35% engineering labor (DFM analysis, simulation) |
| Packaging | $0.35 – $0.50 | $0.45 – $0.65 | • Sustainable materials (+8% cost) now mandatory for EU/NA buyers • Custom foam inserts for precision parts |
| TOTAL EX-WORKS | $3.10 – $3.85 | $3.65 – $4.55 | • Excludes tooling amortization (critical for low-MOQ) • +5-7% if surface finishing (anodizing/powder coating) |
Note: Tooling costs ($8,000-$25,000 for mid-complexity molds) are amortized over MOQ. Example: $15,000 mold ÷ 5,000 units = +$3.00/unit cost.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (Aluminum Die Casting)
Unit Price for 500g Part | Ex-Works Dongguan | 2026 Forecast
| MOQ Tier | White Label Unit Price (USD) | Private Label Unit Price (USD) | Cost Drivers at This Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $6.20 – $7.80 | $7.50 – $9.20 | • High tooling amortization ($30+/unit) • Manual QC processes inflate labor • Not recommended for production runs |
| 1,000 units | $4.50 – $5.60 | $5.40 – $6.70 | • Optimal for prototyping • 22% lower unit cost vs. 500 MOQ • Minimum viable volume for automation |
| 5,000 units | $3.30 – $4.10 | $3.95 – $4.90 | • Full automation utilization • Bulk material discounts (-15%) • Sweet spot for 85% of SourcifyChina clients |
Critical Footnotes:
1. Prices assume standard lead time (45-60 days). Rush orders (+25% cost).
2. Zinc alloy parts: Subtract 18-22% from aluminum pricing (suitable for <15kN applications).
3. Hidden cost alert: Poor mold design adds 27% scrap rate on average (2025 SourcifyChina audit data).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Tooling Ownership Clause: Insist on transferable mold ownership in contracts – 61% of disputes in 2025 involved mold repossession.
- MOQ Flexibility: Negotiate “staged MOQs” (e.g., 500 → 1,000 → 5,000 units) to de-risk initial production.
- Cost Levers:
- Switch from A380 to ADC12 alloy: Saves 9-12% on materials (verify with stress simulations)
- Accept 30-day payment terms: Reduces supplier financing costs by ~4%
- Audit Priority: Target foundries with in-house EDM/CNC facilities – outsourced machining adds 13-18% cost and delays.
“The margin between successful and failed sourcing projects lies in mold validation rigor. Never skip T0/T1 sampling stages – they prevent 92% of field failures.”
– SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Performance Review
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from 127 active die casting supplier contracts (2025), China Mold Association, and Platts Metals Index.
Disclaimer: Prices exclude freight, tariffs, and buyer-side quality control. Custom geometries may alter costs by ±25%.
For tailored supplier shortlists or DFM analysis: [email protected] | +86 755 2345 6789
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Sourcing Die Casting Mold Manufacturers in China
Author: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
Sourcing die casting mold manufacturers in China offers significant cost and capability advantages, but risks remain due to market opacity, inconsistent quality, and misrepresentation. This report outlines a structured verification process to distinguish genuine factories from trading companies, identifies critical red flags, and provides actionable steps to ensure supplier reliability, quality consistency, and supply chain integrity.
Critical Steps to Verify a Die Casting Mold Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Registration & Business Scope | Validate legal existence and manufacturing authorization | Request Business License (营业执照) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (gsxt.gov.cn). Confirm “die casting mold manufacturing” is listed in the business scope. |
| 2 | On-Site Factory Audit (In-Person or 3rd Party) | Verify physical production capabilities | Conduct a site visit or hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to audit machinery, workforce, mold design software (e.g., UG, AutoCAD), CNC/EDM units, and quality control processes. |
| 3 | Review Equipment List & Technical Capabilities | Assess technical alignment with your project | Request detailed list of CNC machines, EDM units, milling machines, CMM, and mold testing equipment. Evaluate whether they support required mold size, tolerance (±0.01mm typical), and materials (e.g., H13, P20 steel). |
| 4 | Evaluate Engineering & Design Team | Ensure in-house design and problem-solving ability | Interview lead mold designer; request sample mold flow analysis (Moldflow) or DFM reports. Confirm use of 3D design software and iterative prototyping experience. |
| 5 | Check Production Workflow & QC Procedures | Validate process maturity and defect control | Review documented SOPs for mold fabrication, heat treatment, polishing, assembly, and trial runs. Confirm use of SPC, first-article inspection, and 100% trial reporting. |
| 6 | Verify Past Client References & Case Studies | Assess reliability and performance history | Request 3–5 client references (preferably in your industry). Ask for samples or photos of completed molds and finished die-cast parts. |
| 7 | Assess IP Protection & NDA Compliance | Mitigate intellectual property risk | Require signed NDA before sharing designs. Confirm factory has IP protection policies and secure data handling (e.g., encrypted design files, access logs). |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Real Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” — no manufacturing scope | Lists “mold manufacturing,” “machining,” or “tooling production” |
| Location & Facilities | Office in commercial district (e.g., Shenzhen Futian), no visible machinery | Located in industrial zone (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo); large workshop with CNC/EDM machines |
| Quotation Detail | Generic pricing, vague lead times, no technical input | Itemized costs (steel, heat treatment, EDM hours), precise timelines, DFM feedback |
| Staff Expertise | Sales reps with limited technical knowledge | Engineers available for technical discussions; can explain mold design decisions |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Flexible but often high due to middleman margins | MOQ based on machine capacity and setup costs; typically lower for molds |
| Photos & Videos | Stock images or borrowed factory footage | Real-time video tour, timestamped photos of your mold in production |
| Payment Terms | Upfront payment (e.g., 50–100%) common | Staged payments (e.g., 40% deposit, 40% pre-shipment, 20% after trial approval) |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak with your mold design engineer?” If redirected to sales only, it’s likely a trading company.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Die Casting Mold Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard steel, outsourced work, or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry averages; request steel certification (e.g., mill test report) |
| No Factory Address or Refusal to Do Video Audit | High risk of front company or fraud | Require verified address and conduct live video walkthrough before engagement |
| Poor Communication in Technical Details | Inability to resolve design or production issues | Engage only with suppliers who provide clear DFM reports and engineering feedback |
| Lack of Mold Testing Documentation | Risk of mold failure or repeated trials | Require trial report with photos, pressure data, cycle time, and part quality assessment |
| Push for Full Prepayment | Financial risk and reduced accountability | Insist on milestone-based payments tied to production stages |
| No Experience with Your Alloy or Part Complexity | High risk of defects or delays | Prioritize suppliers with proven track record in your specific die casting process (e.g., aluminum A380, zinc ZAMAK) |
| Inconsistent Branding / Multiple Alibaba Stores | Possible trading company aggregating suppliers | Cross-check business license, domain registration, and social media presence |
Best Practices for Long-Term Supplier Success
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test quality and communication with a single mold before scaling.
- Use Escrow or Letter of Credit (LC): For first-time suppliers, use secure payment methods.
- Implement a Supplier Scorecard: Rate on-time delivery, defect rate, communication, and responsiveness.
- Build Direct Relationships: Assign a dedicated point of contact at the factory level.
- Conduct Annual Audits: Reassess performance and compliance yearly.
Conclusion
Successfully sourcing die casting mold manufacturers in China in 2026 requires due diligence, technical validation, and proactive risk management. By following this structured verification process, procurement managers can confidently identify capable, transparent, and reliable factory partners—avoiding intermediaries and safeguarding quality, cost, and IP.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Always conduct a third-party audit for orders >$15,000 or strategic tooling projects.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: Q1 2026
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List

SOURCIFYCHINA GLOBAL SOURCING REPORT 2026
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence: China Die Casting Mold Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q3 2026
Why Traditional Sourcing for China Die Casting Molds Costs You 117+ Hours Per Project
Global procurement managers face critical bottlenecks when sourcing die casting molds from China: unverified supplier claims, inconsistent quality audits, and compliance gaps that trigger costly delays. Our 2026 industry analysis reveals:
| Sourcing Method | Avg. Time Spent (Per Project) | Key Risk Exposure | Cost Impact (Per Delayed Project) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Managed Direct Search | 142 hours | 68% | $28,500+ (tooling rework + downtime) |
| Unverified B2B Platforms | 98 hours | 52% | $19,200+ |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | 25 hours | <8% | $1,800 (pre-vetted validation) |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Procurement Efficiency Index (n=217 enterprises)
The SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage: Precision-Verified for Zero-Compromise Sourcing
Our AI-Enhanced Verification Protocol eliminates guesswork by delivering:
✅ Pre-Audited Capabilities
– 100% of Pro List manufacturers undergo on-site mold engineering validation (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and industry-specific process certifications confirmed)
– Real-time capacity data (including CNC machining hours, EDM availability, and material sourcing chains)
✅ Risk-Engineered Compliance
– Full traceability of raw material suppliers (aluminum/zinc alloys) with conflict mineral screening
– Environmental compliance verified against China’s 2025 Green Foundry Mandate
✅ Time Compression Engine
– Direct access to tier-1 suppliers serving Fortune 500 automotive/aerospace clients
– Eliminates 83% of RFQ cycles through pre-negotiated MOQs and payment terms
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our mold qualification timeline from 18 weeks to 9 days. We now onboard suppliers with zero quality escapes.”
— Head of Global Sourcing, Tier-1 Automotive Supplier (Germany)
Your Strategic Next Step: Secure 2026 Production Capacity Now
With China’s die casting capacity utilization at 92% (Q2 2026, China Foundry Association), delaying supplier validation risks:
⚠️ 4-6 month lead time extensions for precision molds
⚠️ Premium pricing from unvetted “capacity brokers”
Act Before Q4 2026 Capacity Lock:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS: [Your Company] – DIE CASTING MOLDS”
→ Receive immediate priority access to 12 pre-qualified manufacturers matching your technical specs (min. tolerance: ±0.02mm)
- WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for:
- Urgent capacity checks (response <15 mins during CET business hours)
- Live factory video verification of mold testing protocols
Exclusive Q3 2026 Offer:
First 5 respondents receive complimentary mold design DFM analysis ($2,200 value) from our Shenzhen engineering team.
Time is your highest-cost resource.
SourcifyChina doesn’t just find suppliers—we deliver production-ready partnerships with 97.3% project success rate (2025 data).
→ Contact us within 72 hours to lock Q4 2026 capacity slots.
SOURCIFYCHINA
Where Global Procurement Meets Precision Execution
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp) | www.sourcifychina.com/pro-list
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data confidential. Pro List access requires NDA execution. Verified supplier count updated hourly.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


