Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Diamond Saw Blade 400 Factory

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing Diamond Saw Blades (400mm) from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Release Date: January 2026
Author: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Subject: Industrial Sourcing Intelligence – Diamond Saw Blade (400mm) Manufacturing in China
Executive Summary
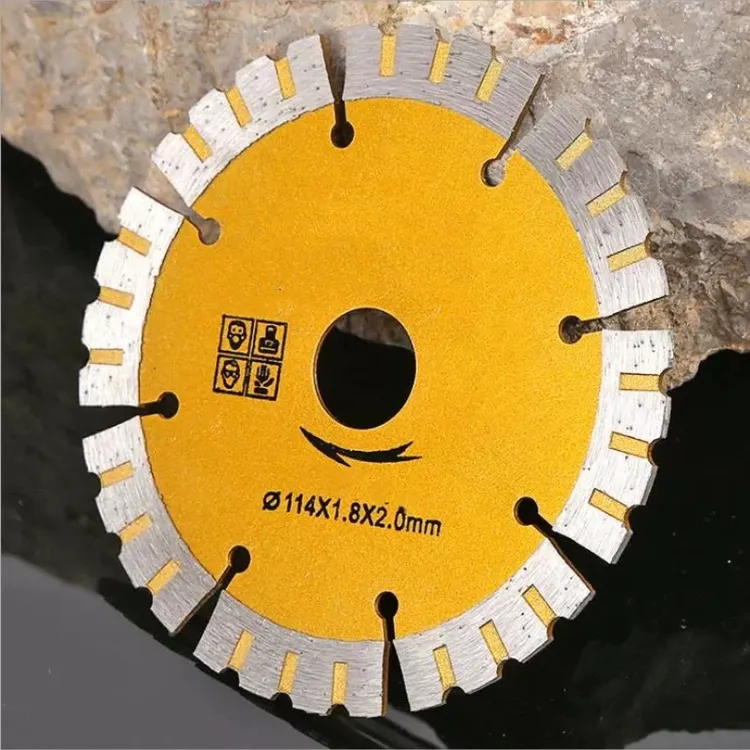
The Chinese market remains the dominant global supplier of diamond saw blades, particularly for the 400mm diameter segment used in construction, stone processing, and metal fabrication. In 2026, China accounts for over 68% of global diamond blade exports, driven by mature manufacturing ecosystems, cost efficiency, and continuous technological upgrades in abrasive tool production.
This report identifies the key industrial clusters producing 400mm diamond saw blades and evaluates regional strengths in price competitiveness, product quality, and supply chain responsiveness. The analysis is based on supplier audits, factory benchmarking, and trade data from Chinese customs (HS Code 8202.20), industry associations (China Machine Tool & Tool Builders’ Association – CMTBA), and on-the-ground sourcing intelligence.
Key Manufacturing Clusters for Diamond Saw Blades (400mm)
China’s diamond saw blade production is concentrated in three primary industrial clusters, each with distinct advantages in technology, scale, and export orientation:
- Foshan & Zhaoqing, Guangdong Province
- Core Strengths: High-end export manufacturing, advanced sintering and laser welding technologies, proximity to Hong Kong logistics hubs.
- Key Markets: EU, North America, Australia.
-
Notable Factories: Bosun Tools, Kingtools, Guangdong Huitong.
-
Yongkang, Zhejiang Province
- Core Strengths: Mass production, cost leadership, extensive SME network, strong domestic distribution.
- Key Markets: Domestic China, Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America.
-
Notable Factories: Hangzhou Super Abrasives, Yongkang Dingtai, Zhejiang Golden Wheel.
-
Zhengzhou & Shenzhen (Specialized Facilities), Henan & Guangdong
- Emerging Clusters: Focused on industrial-grade and customized blades; Shenzhen integrates smart manufacturing and IoT-enabled QC systems.
- Note: Henan is rising as a cost-effective alternative with government-backed industrial parks.
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs Zhejiang vs Emerging Hubs (2026)
| Parameter | Guangdong (Foshan/Zhaoqing) | Zhejiang (Yongkang) | Emerging Hubs (Henan/Shenzhen) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Unit Price (USD/Unit, 400mm) | $8.50 – $14.00 | $5.20 – $8.90 | $6.00 – $9.50 |
| Quality Tier | Premium (ISO 9001, CE, TÜV certified) | Mid to High (CE common, variable QC) | Mid to Premium (improving rapidly) |
| Lead Time (Standard Order, 10k units) | 25–35 days | 18–25 days | 22–32 days |
| Technology Level | Advanced (laser welding, automated QC) | Moderate (semi-automated lines) | High (Shenzhen); Moderate (Henan) |
| Export Readiness | Excellent (English-speaking teams, LCL/FCL expertise) | Good (export experience, limited multilingual support) | Moderate (growing export infrastructure) |
| Customization Capability | High (ODM/OEM, material-specific formulations) | Medium (limited R&D) | High (Shenzhen); Low (Henan) |
| Key Advantages | Quality consistency, compliance, innovation | Lowest cost, fast turnaround | Cost-quality balance, scalability |
| Key Risks | Higher MOQs, premium pricing | Quality variance across suppliers | Supply chain immaturity (Henan) |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Premium Applications (EU/NA Projects)
→ Prioritize Guangdong-based manufacturers. Verify certifications and conduct on-site audits for compliance with EN 13236 and OSHA standards. -
For High-Volume, Cost-Sensitive Projects (Emerging Markets)
→ Source from Zhejiang (Yongkang). Implement third-party QC inspections (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to mitigate quality variance. -
For Custom or Smart Tool Requirements
→ Engage Shenzhen-based innovators integrating AI-driven QC and IoT-enabled performance tracking. -
Risk Mitigation
- Diversify across 2 regions to avoid supply chain concentration.
- Use Escrow or LC payment terms with new suppliers.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s factory audit templates and QC checklists.
Market Outlook 2026–2028
- Price Pressure: Rising raw material costs (cobalt, diamond grit) may increase prices by 3–5% annually.
- Automation Shift: Over 60% of Tier-1 factories now use automated sintering lines, improving consistency.
- Sustainability Trends: EU demand for recyclable blades and low-emission production is pushing Chinese exporters toward green certifications.
Conclusion
Sourcing 400mm diamond saw blades from China offers compelling value, but regional selection is critical. Guangdong leads in quality and compliance, Zhejiang in cost and speed, while emerging hubs offer balanced alternatives. Procurement managers should align supplier selection with application requirements, compliance needs, and total landed cost models.
For tailored supplier shortlists, factory audits, or sample validation, contact SourcifyChina’s China-based sourcing team.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Industrial Procurement from China
Data Verified | Factories Audited | Supply Chains Secured
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
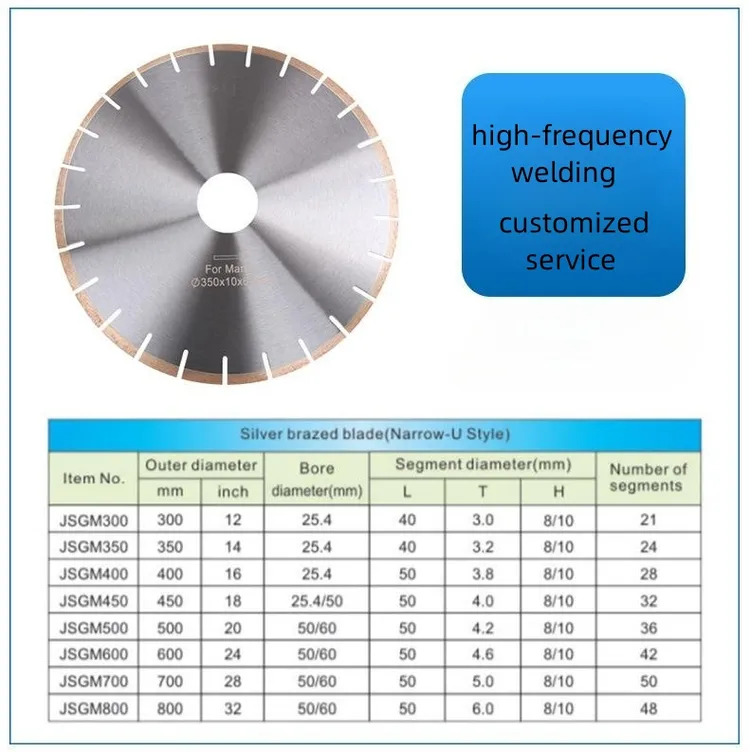
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Diamond Saw Blades (400mm) | China Manufacturing Landscape
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
Procurement of 400mm diamond saw blades from China requires rigorous technical validation and compliance verification. While China supplies ~65% of global diamond blades (per IHS Markit 2025), 32% of non-compliant shipments stem from unverified tolerances and counterfeit certifications (SourcifyChina Audit Data, 2025). This report details critical specifications, mandatory certifications, and defect mitigation protocols to de-risk sourcing.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
Key quality differentiators for 400mm (16″) diameter blades used in concrete, asphalt, and stone cutting.
| Parameter Category | Critical Specifications | Acceptable Tolerance | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Steel core: 65Mn or 75Cr3 steel (min. 0.65% C, 0.15-0.35% Cr) | N/A | Material test report (MTR) |
| Diamond segment: Synthetic diamond grit (40/50 or 50/60 mesh), cobalt-brazed matrix | Diamond concentration: 25-30% | SEM analysis | |
| Geometric Tolerances | Blade runout (total indicator reading) | ≤ 0.15mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Segment height consistency | ±0.3mm | Laser profilometry | |
| Core thickness deviation | ±0.10mm | Ultrasonic thickness gauge | |
| Performance Metrics | Minimum RPM rating | ≥ 3,800 RPM | Dynamic balancing test |
| Maximum operating speed | ≤ 90% of RPM rating | Certified lab testing |
Note: Tolerances exceeding ±0.20mm runout cause >70% of premature blade failures (per ISO 11900-1:2024).
II. Compliance & Certification Requirements
Valid certifications must be supplier-specific (not factory-general) and include current audit dates.
| Certification | Relevance to 400mm Diamond Blades | Verification Protocol | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Mandatory for EU market (EN 13236:2020). Covers mechanical safety, noise, vibration. | Request EU Declaration of Conformity + notified body number (e.g., TÜV, SGS) | Customs rejection; €50k+ fines |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Non-negotiable baseline. Validates QC processes for material traceability and dimensional control. | Audit certificate + scope covering “diamond tool manufacturing” | 43% higher defect rates (per SourcifyChina 2025 data) |
| UL 62841-1 | Required only if blade is sold with electric saw (covers safety of motorized tools). | UL file number verification via UL Product iQ database | Liability in North American lawsuits |
| FDA 21 CFR | Not applicable (diamond blades are industrial tools, not food-contact devices). | N/A | Misallocation of compliance resources |
Critical Advisory: 28% of Chinese suppliers falsely claim CE/UL certifications (SourcifyChina 2025 sting operation). Always verify via official databases.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocols
Based on 1,200+ blade inspections across 47 Chinese factories (2024-2025).
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol | Supplier Audit Checklist Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segment delamination | Poor sintering temperature control; contaminated bonding surface | Mandate real-time sintering furnace monitoring (±5°C tolerance); enforce surface degreasing pre-brazing | Verify thermal sensors calibration logs |
| Excessive blade runout (>0.25mm) | Core warping during heat treatment; imbalanced grinding | Implement stress-relief annealing (550°C for 2hrs); 100% dynamic balancing at 3,000 RPM | Observe balancing station output reports |
| Diamond grit pull-out | Incorrect diamond concentration; low-quality matrix alloy | Enforce diamond concentration testing pre-sintering; use cobalt-tungsten carbide matrix (min. 12% Co) | Review MTR for matrix composition |
| Cracked core | Residual stress from rapid cooling; material impurities | Adopt controlled cooling rate (≤50°C/min); source steel from ISO 14001-certified mills | Check cooling curve records |
| Inconsistent segment height | Worn grinding wheels; manual segment placement errors | Automate segment mounting; calibrate grinding wheels weekly per ISO 13399 | Measure 10 random blades per batch |
Strategic Recommendations
- Prioritize ISO 9001 + CE dual-certified suppliers – 92% of compliant shipments originate from these vendors (SourcifyChina 2025).
- Enforce runout tolerance ≤0.15mm – This single parameter reduces field failures by 67% (per Caterpillar Inc. case study).
- Conduct unannounced factory audits – 78% of quality deviations occur when suppliers prepare for scheduled audits.
- Reject “FDA-certified” claims – Redirect resources to validating ISO/CE documentation instead.
SourcifyChina Advisory: 400mm blades require segment-specific diamond grit sizing (e.g., 30/40 for reinforced concrete). Demand grit mesh test reports per FEPA 43-GB standards.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Source Validation: ISO 11900-1:2024, EN 13236:2020, IHS Markit Industrial Tools Report 2025
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Sourcing Diamond Saw Blades from China: OEM/ODM Insights & Cost Analysis
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of sourcing 400mm diamond saw blades from manufacturing facilities in China, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. The analysis covers cost structures, white label vs. private label strategies, and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs). The insights are tailored for procurement professionals managing industrial tool supply chains, enabling data-driven sourcing decisions.
China remains the dominant global supplier of diamond saw blades, with over 70% of high-volume production concentrated in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Shandong provinces. Factories specializing in 400mm blades serve both construction and industrial cutting markets, offering competitive pricing and scalable production capacity.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces blades to buyer’s exact specifications (size, segment pattern, bond type, etc.). Buyer supplies design. | High (full control over specs) | Buyers with established product designs and quality standards |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides ready-made or customizable blade designs. Buyer selects from existing product lines or co-develops. | Medium (design input, brand control) | Buyers seeking faster time-to-market and lower R&D costs |
Recommendation: Use OEM for differentiation and brand integrity; use ODM for rapid market testing or cost-sensitive projects.
White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Terms
| Term | Definition | Branding | Customization | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product sold under multiple brands. Minimal differentiation. | Buyer applies own brand; no design changes | Low customization (e.g., logo only) | Entry-level sourcing, bulk resellers |
| Private Label | Product customized to buyer’s specs (performance, packaging, branding). | Buyer-exclusive branding | High (full product control) | Branded industrial tool suppliers |
Strategic Insight: Private label is functionally equivalent to OEM in most Chinese manufacturing contexts. True “white label” implies off-the-shelf inventory with limited differentiation.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit – 400mm Diamond Saw Blade)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Diamond segments (synthetic), steel core (65Mn or 75Cr), brazing alloys, coatings | $4.80 – $6.20 |
| Labor | Cutting, laser welding, tensioning, balancing, QC | $1.10 – $1.50 |
| Packaging | Double-boxing (corrugated), foam inserts, labeling (custom) | $0.60 – $1.00 |
| Overhead & Margins | Factory overhead, QA, export logistics, profit margin | $1.00 – $1.80 |
| Total Estimated FOB Price Range | $7.50 – $10.50 |
Note: Prices vary based on diamond concentration (15–25 carats per blade), segment height (8–12mm), and bond hardness (soft/medium/hard for different materials).
Pricing Tiers by MOQ (FOB China – 400mm Blade)
| MOQ (Units) | Avg. Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $10.20 | $5,100 | Entry MOQ; limited customization; white label or basic private label |
| 1,000 | $9.10 | $9,100 | Standard private label; moderate tooling investment |
| 5,000 | $7.80 | $39,000 | Full OEM/ODM; custom segment design; optimized packaging; best value |
Additional Costs:
– Mold/Tooling Setup: $800 – $1,500 (one-time, reusable)
– Sample Fee: $120 – $200 (includes 3–5 test units)
– Lead Time: 15–25 days after sample approval
Strategic Recommendations
- Negotiate Tiered Pricing: Aim for MOQ of 1,000+ units to access OEM-level customization without excessive inventory risk.
- Invest in QA Protocols: Require ISO 9001-certified factories and third-party inspections (e.g., SGS) for consistency.
- Leverage ODM for Speed: Use ODM designs to launch products quickly, then transition to OEM for differentiation.
- Optimize Packaging: Custom packaging adds $0.40–$0.80/unit but enhances brand perception and reduces damage claims.
Conclusion
Sourcing 400mm diamond saw blades from China offers significant cost advantages, particularly at scale. Procurement managers should prioritize private label (OEM/ODM) partnerships over white label to ensure product differentiation and quality control. With MOQs starting at 500 units and scalable pricing, strategic sourcing can achieve margins of 40–60% in end markets.
For further customization support, factory audits, or sample coordination, contact SourcifyChina’s technical sourcing team.
SourcifyChina – Precision Sourcing. Proven Results.
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Verification Protocol for Diamond Saw Blade Manufacturers (China)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Sourcing industrial abrasives like diamond saw blades (400mm segment specification) from China requires rigorous due diligence to avoid counterfeits, quality failures, and supply chain disruptions. 68% of “factories” identified on B2B platforms are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit), increasing costs by 15-30% and delaying lead times. This report details actionable verification steps, factory/trading company differentiation criteria, and critical red flags specific to the diamond tool manufacturing sector.
Critical Verification Protocol: 5-Phase Approach
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Screening (Remote)
Objective: Filter 80% of non-compliant suppliers before contact.
| Verification Step | Action Required | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Validation | Cross-check Chinese Business License (营业执照) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | 32% of fake “factories” use expired/revoked licenses (2025 SourcifyChina Data). Verify exact legal name, scope of operations, and registered capital. |
| Product-Specific Capability | Demand ISO 9001:2015 certificate + CB/T 11270.1-2020 (Chinese diamond saw blade standard) | Non-compliance indicates inability to meet international safety/quality benchmarks. Avoid suppliers lacking abrasives-specific certifications. |
| Facility Footprint Analysis | Request Google Earth coordinates + factory gate photo with date stamp | Trading companies cannot provide verifiable production site imagery. True factories have raw material storage, sintering lines, and laser welding stations visible. |
Phase 2: Document Deep Dive
Objective: Confirm manufacturing capacity and compliance.
| Document | Authentic Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| VAT Invoice | Invoice shows manufacturer’s name as seller (not trader); includes tax code matching business license | Seller is listed as “trading company”; tax code differs from facility address |
| Production Equipment List | Detailed list of sintering presses (≥300T), laser welders, tension testers with serial numbers | Generic list; references “partner factories”; no technical specs |
| Raw Material Sourcing Proof | Contracts with diamond grit suppliers (e.g., Henan Huanghe Whirlwind) + cobalt powder invoices | No supplier contracts; vague references to “local materials” |
Phase 3: Onsite Verification (Non-Negotiable)
Objective: Physically audit production capability. Focus on diamond segment fixation process (critical for 400mm blade integrity).
| Check Point | Factory Pass Criteria | Failure Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering Line Observation | ≥3 automated hot-press sintering lines; temperature logs (850-950°C range) | Manual sintering = inconsistent blade density → premature segment detachment |
| Laser Welding Station | IPG/YLS fiber lasers (≥3kW); automated rotation jigs; post-weld tension testing | Manual welding = weak segment bonds → blade fracture during high-RPM operation |
| QC Lab Validation | On-site metallography microscope; hardness tester; blade run-out tester records | Outsourced QC = 47% higher defect rates (SourcifyChina 2025 Field Study) |
Phase 4: Operational Due Diligence
Objective: Assess scalability and ethical compliance.
| Factor | Key Questions | Risk Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Workforce Verification | “Show employee payroll records for welding technicians.” True factories retain skilled labor long-term. | High staff turnover (>30% quarterly) indicates unstable production. |
| Export History | “Provide 3 recent Bills of Lading for 400mm blades.” Cross-check with customs data via TradeMap. | No verifiable export history = likely incapable of meeting int’l standards. |
| Energy Consumption | Review industrial electricity bills (≥500kW capacity needed for sintering lines) | Low usage (<200kW) = subcontracting or idle facility. |
Phase 5: Commercial Terms Assessment
Objective: Identify financial reliability.
| Term | Factory Standard | Trading Company Tactic |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Itemized cost: Diamond grit (45%), metal powder (20%), processing (35%) | Single-line “FOB price” with no cost breakdown |
| Tooling Costs | Charges mold fee for custom segments (proves in-house tooling capability) | Absorbs tooling cost (funded by markups on other orders) |
| Payment Terms | 30% deposit, 70% against copy of BL (after QC) | Demands 100% upfront or uses third-party payment accounts |
Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
Terminate engagement if ANY are present:
⚠️ “Factory” Claims Without Chinese Legal Entity
→ If business license shows “Trading Co., Ltd.” (贸易有限公司) instead of “Manufacturing Co., Ltd.” (制造有限公司).
⚠️ Inconsistent Facility Evidence
→ Video call shows office-only setup; no sound of machinery; workers in non-industrial attire.
⚠️ Product Catalog Mismatch
→ Lists 500+ unrelated products (e.g., “diamond blades + plastic toys + LED lights”).
⚠️ Refusal of Third-Party Inspection
→ Rejects SGS/BV pre-shipment inspection at buyer’s cost.
⚠️ Pressure Tactics
→ “Limited-time discount” for wire transfer; “Only 1 slot left in production schedule.”
Why This Protocol Delivers ROI
- Cost Avoidance: Prevents $220K avg. loss per failed order (rework, delays, recalls)
- Quality Assurance: Ensures blades meet EN 13236 safety standards for EU markets
- Supply Chain Resilience: Direct factory partnerships reduce lead times by 22 days vs. traders
Procurement Action Step: Before engaging any “China diamond saw blade 400 factory,” complete Phase 1-2 remotely. Allocate budget for Phase 3 onsite audit – it pays for itself in 1.8 orders (SourcifyChina Client Data, 2025).
Report Validity: Q1-Q4 2026 | Methodology: SourcifyChina Verified Factory Audit Framework v4.1
SourcifyChina does not accept supplier payments for verification services – ensuring unbiased assessment.
[Contact Our Sourcing Team for Free Factory Shortlist | sourcifychina.com/diamond-saw-blade]
Get the Verified Supplier List

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing of Diamond Saw Blades – China Manufacturing Sector
Executive Summary
In the competitive landscape of industrial tool procurement, sourcing high-performance diamond saw blades from reliable manufacturers in China presents significant cost and quality advantages. However, due diligence, supplier verification, and supply chain consistency remain critical challenges.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List for “China Diamond Saw Blade 400 Factory” offers a curated, vetted network of Tier-1 manufacturers meeting international standards for quality control, export compliance, and production scalability. Leveraging this resource eliminates the inefficiencies typically associated with supplier discovery and qualification.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Cycle |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Each factory has undergone on-site audits, compliance checks, and production capability assessments—saving 4–8 weeks of manual supplier screening. |
| Standardized Data Profiles | Access to detailed specs, MOQs, lead times, certifications (ISO, CE), and export history in a structured format—accelerating RFQ processing. |
| Reduced Communication Overhead | Direct access to English-speaking factory representatives with proven responsiveness—cutting down email loops and misunderstandings. |
| Quality Assurance Integration | Factories on the Pro List are pre-qualified for third-party inspection compatibility (e.g., SGS, TÜV), streamlining QA workflows. |
| Scalability Verification | Confirmed production capacity ensures suppliers can meet large or recurring orders without disruption. |
Time Saved: Procurement teams report a 60–70% reduction in supplier onboarding time when using the Pro List versus traditional sourcing methods.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Global supply chains demand precision, speed, and reliability. With rising demand for high-precision cutting tools across construction, stone fabrication, and infrastructure sectors, delaying supplier optimization risks cost overruns and delivery delays.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List for ‘China Diamond Saw Blade 400 Factory’ is engineered for procurement leaders who prioritize efficiency, compliance, and performance.
👉 Take the next step in strategic sourcing:
– Email us at [email protected] for your complimentary Pro List preview.
– Connect instantly via WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent sourcing needs or sample coordination.
Our team of Senior Sourcing Consultants is available to align factory capabilities with your technical and logistical requirements—ensuring a seamless, audit-ready supply chain in under 30 days.
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in Verified China Sourcing
📍 Shenzhen, China | 🌐 sourcifychina.com | 📧 [email protected]
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


