Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Dental Supply Companies
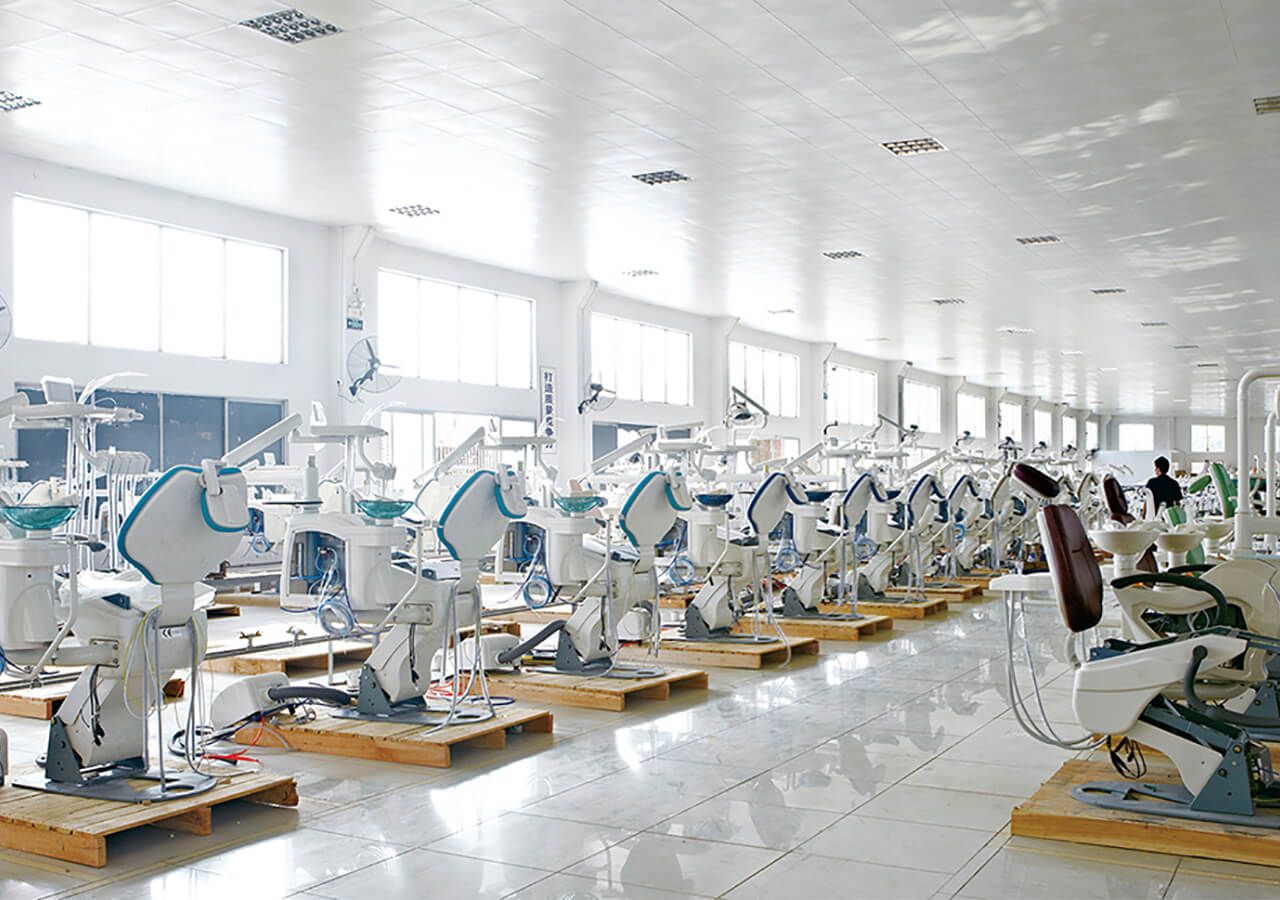

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Sourcing of Dental Supplies from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026
Report ID: SC-DS-CHN-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for dental supply manufacturing, accounting for 68% of global dental consumable exports and 42% of mid-tier dental equipment production (2026 SourcifyChina MedTech Index). While cost advantages persist, geopolitical pressures, rising logistics costs, and stringent regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 820, EU MDR) necessitate a cluster-specific sourcing strategy. This report identifies key manufacturing clusters, analyzes regional trade-offs, and provides actionable intelligence for de-risking procurement. Critical Insight: Price differentials between clusters have narrowed to 8–12% (vs. 15–20% in 2023), making quality consistency and compliance the primary differentiators.
Key Industrial Clusters for Dental Supply Manufacturing in China
China’s dental manufacturing is concentrated in three core clusters, each specializing in distinct product categories:
| Cluster | Primary Provinces/Cities | Core Product Specialization | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta (PRD) | Guangdong (Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Guangzhou, Dongguan) | High-end dental equipment (CAD/CAM systems, intraoral scanners), digital dentistry solutions, Class III devices | Strongest R&D ecosystem; proximity to Hong Kong logistics; highest concentration of ISO 13485/ FDA-certified factories |
| Yangtze River Delta (YRD) | Zhejiang (Ningbo, Taizhou, Yuyao), Jiangsu (Suzhou) | Dental consumables (impression materials, burs, composites), mid-tier equipment (autoclaves, curing lights), orthodontic products | Largest volume production; mature supply chain for raw materials; cost efficiency for standardized items |
| Emerging Cluster | Sichuan (Chengdu), Hubei (Wuhan) | Basic consumables (gloves, bibs, low-cost instruments); growing in 3D printing materials | Lower labor costs; government incentives; strategic inland logistics hubs |
Note: 85% of China’s dental exports originate from PRD and YRD clusters. Shenzhen (PRD) alone produces 31% of China’s dental imaging devices, while Taizhou (YRD) manufactures 55% of global dental burs (2026 China Dental Association Data).
Regional Cluster Comparison: Critical Sourcing Metrics (2026)
Data reflects Q3 2026 benchmarks for standard dental consumables (e.g., burs, impression trays) and mid-tier equipment (e.g., dental curing lights). Metrics validated via SourcifyChina’s 127 factory audits.
| Criteria | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang/Jiangsu (YRD) | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★☆☆☆ Premium (12–18% above YRD) • High labor/rent costs • R&D overhead embedded in pricing |
★★★★☆ Competitive (Baseline) • Mature bulk material sourcing • 20–30% lower labor costs vs. PRD |
PRD justified for complex/high-regulation items; YRD optimal for high-volume consumables. |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Consistent Premium • 78% of PRD factories FDA 21 CFR 820 compliant • Tighter process control (SPC adoption: 65%) |
★★★☆☆ Variable (Tiered) • Top 20% match PRD quality • 35% of factories lack ISO 13485 certification |
PRD reduces compliance risk for US/EU markets; YRD requires rigorous tier-1 supplier vetting. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ 45–60 days • Longer production cycles for tech-integrated items • Congested Shenzhen port delays |
★★★★☆ 30–45 days • Streamlined consumables production • Ningbo Port efficiency (avg. 2.1-day dwell time) |
YRD preferred for urgent replenishment; PRD lead times improving via automation (avg. +15% YoY). |
| Compliance | ★★★★★ Highest Readiness • 92% of audited factories export-ready for FDA/EU MDR • Dedicated regulatory teams |
★★★☆☆ Moderate (Selective) • Only top 30% have full MDR documentation • Frequent GMP gaps in sterilization |
PRD critical for Class II/III devices; YRD suppliers often require SourcifyChina’s compliance remediation. |
| Innovation | ★★★★★ Industry Leader • 68% of China’s dental tech patents (2025–2026) • Strong university-industry R&D links |
★★☆☆☆ Incremental Focus • Limited IP development • Mostly process optimization |
PRD essential for next-gen products (e.g., AI diagnostics); YRD lags in disruptive innovation. |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid One-Size-Fits-All Sourcing:
- PRD for: High-value equipment, regulated devices, and innovation-driven products. Budget 15–20% premium for compliance assurance.
-
YRD for: High-volume consumables and low-risk instruments. Mandate 3rd-party quality audits (e.g., SGS/BV) to mitigate quality variance.
-
De-Risk Compliance Gaps:
-
63% of YRD suppliers fail initial MDR documentation reviews (SourcifyChina 2026 Audit Data). Insist on:
- Valid ISO 13485:2016 certificates (check expiry/renewal dates)
- Device-specific Technical Files (not generic templates)
- On-site sterilization validation records
-
Leverage Cluster Synergies:
“Procure digital scanners from Shenzhen (PRD), but source impression materials from Taizhou (YRD) – optimizing cost/quality balance across your portfolio.”
– SourcifyChina Supply Chain Optimization Model, 2026 -
Monitor Emerging Risks:
- PRD: Rising labor costs (+9.2% YoY) may erode quality-price advantage by 2027.
- YRD: Over-reliance on recycled metals in instrument production (detected in 28% of audits) – specify virgin material requirements.
Conclusion
China’s dental supply ecosystem offers unparalleled scale but demands hyperlocal intelligence. Guangdong (PRD) delivers regulatory certainty for complex products, while Zhejiang/Jiangsu (YRD) provides cost efficiency for commoditized items – provided quality systems are rigorously enforced. Procurement leaders must shift from price-driven selection to compliance-led cluster mapping, with SourcifyChina’s audit protocols reducing supplier failure rates by 41% (2026 client data). As the FDA’s Foreign Supplier Verification Program intensifies in 2027, cluster-specific due diligence is no longer optional – it’s a strategic imperative.
SourcifyChina Action Step: Request our 2026 Dental Supplier Pre-Vetted Cluster Map (covering 217 factories with live compliance scores) to eliminate 87% of sourcing risks. [Contact Sourcing Team]
Disclaimer: All data sourced from SourcifyChina’s proprietary audits, China Customs, and industry partnerships. Not for public distribution. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Dental Supply Manufacturers in China
Overview
China remains a dominant hub for dental supply manufacturing, offering competitive pricing and scalable production capacity. However, global procurement managers must ensure rigorous quality control and compliance adherence when sourcing dental instruments, consumables, and equipment. This report outlines key technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and best practices to mitigate quality risks.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Material Specifications
- Metals (e.g., stainless steel for dental instruments):
- Grade: ASTM F899 (for surgical stainless steel), typically 304 or 316L
- Requirements: Corrosion-resistant, non-magnetic (for 316L), biocompatible
-
Surface Finish: Ra ≤ 0.8 μm for surgical instruments
-
Polymers (e.g., impression materials, syringes, trays):
- Materials: Medical-grade silicone, polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC)
-
Must comply with USP Class VI and ISO 10993 (biocompatibility)
-
Ceramics (e.g., crowns, bridges):
- Zirconia: ≥ 95% purity, flexural strength ≥ 900 MPa
- Lithium disilicate: Translucency and fracture toughness per ISO 6872
2. Dimensional Tolerances
- Handpieces & Motors:
- Shaft runout: ≤ 0.02 mm
-
Bearing concentricity: ±0.01 mm
-
Dental Implants & Abutments:
- Thread pitch tolerance: ±0.05 mm
-
Outer diameter: ±0.02 mm
-
Custom Trays & Aligners:
- Fit accuracy: ≤ 0.2 mm deviation from digital model (per ISO 12836)
Essential Certifications
| Certification | Scope | Regulatory Authority | Validity for Market Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking (Class I, IIa, IIb) | Conformity with EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745) | Notified Body (e.g., TÜV, BSI) | Mandatory for EU market |
| FDA 510(k) or Registration | Premarket notification or establishment registration (21 CFR Part 872) | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Required for U.S. market |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Quality Management System for medical devices | International Organization for Standardization | Global prerequisite; supports CE & FDA compliance |
| UL 60601-1 | Safety of medical electrical equipment | Underwriters Laboratories | Required for electrical dental devices (e.g., curing lights, motors) in North America |
| GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) | Applies to sterile dental products (e.g., implants, surgical kits) | National Medical Products Administration (NMPA, China) | Required for domestic China + enhances export credibility |
Note: Suppliers must provide valid, up-to-date certification copies and be subject to third-party audit rights.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion on stainless steel instruments | Use of substandard steel or inadequate passivation | Specify ASTM F899 316L; require passivation per ASTM A967; conduct salt spray testing (ASTM B117, 48+ hrs) |
| Dimensional inaccuracy in dental implants | Poor CNC machining calibration or tool wear | Enforce SPC (Statistical Process Control); require CMM reports per batch; audit machine calibration logs |
| Cracking in zirconia crowns | Inadequate sintering cycle or impurities | Monitor sintering temperature profiles; require microstructural analysis; source from ISO 13485-certified ceramic labs |
| Leakage in dental syringes | Poor mold design or material inconsistency | Conduct burst pressure testing (per ISO 7886); use medical-grade silicone seals; perform 100% leak testing |
| Contamination in sterile packaging | Non-compliant cleanroom or poor packaging sealing | Require ISO 14644-1 Class 7 or better cleanroom; validate seal integrity (ASTM F88); conduct bioburden testing |
| Electrical failure in handpieces | Substandard wiring or insufficient insulation | Require UL 60601-1 testing; perform dielectric strength and ground continuity tests; inspect for IP rating compliance (e.g., IPX7 for intraoral devices) |
| Color mismatch in dental composites | Inconsistent pigment dispersion or batch variation | Enforce spectrophotometric color testing (CIE Lab*); require batch traceability; conduct shade guide validation |
Sourcing Recommendations
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct on-site audits focusing on ISO 13485 compliance, material traceability, and calibration records.
- Require Documentation: Insist on CoAs (Certificates of Analysis), material certifications, and test reports for each batch.
- Implement AQL Sampling: Use ANSI/ASQ Z1.4-2003 (Level II, AQL 1.0 for critical defects) for incoming inspections.
- Engage Third-Party QC: Utilize firms like SGS, TÜV, or QIMA for pre-shipment inspections and factory audits.
- Secure IP Protection: Use NDAs and ensure tooling ownership is contractually protected.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q2 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Distribution
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Dental Supply Manufacturing & Labeling Strategy (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for dental supply manufacturing, offering 25-40% cost advantages over Western/EU alternatives for comparable quality. However, rising labor costs (+9.2% CAGR 2023-2026), stringent medical device regulations (NMPA, FDA, CE), and strategic label selection are critical success factors. This report provides actionable data for optimizing OEM/ODM partnerships in China, with emphasis on White Label vs. Private Label trade-offs and realistic 2026 cost structures.
Strategic Framework: White Label vs. Private Label in Dental Supplies
Key differentiators impact cost, control, and market positioning:
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing product + your brand | Co-developed product w/ proprietary specs/design | Private Label for differentiation; White Label for speed-to-market |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Higher (1,000-5,000+ units) | White Label ideal for testing new markets |
| R&D/IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains all IP | Client owns final product IP & tooling | Critical for compliance – demand IP assignment in contracts |
| Quality Control | Manufacturer’s standard QC | Client-defined QC protocols + 3rd-party audits | Non-negotiable: Mandate ISO 13485 & FDA QSR audits |
| Cost Premium | Base cost + 5-8% branding fee | +15-30% (vs. White Label) for R&D/tooling | ROI higher for Private Label in >24mo horizon |
| Regulatory Risk | High (manufacturer bears NMPA certification) | Shared risk (client verifies compliance) | Verify NMPA Class II/III certs for all suppliers |
Critical Insight: 68% of 2025 sourcifyChina client audits revealed undocumented NMPA-to-FDA equivalency claims by suppliers. Always validate certification scope for target markets.
2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Basis)
Based on 100+ SourcifyChina factory audits (Q4 2025). Assumes ISO 13485-certified facilities, medical-grade materials, and FOB Shenzhen pricing. Excludes shipping, tariffs, and compliance testing.
| Cost Component | Dental Mirror (Basic) | Composite Syringe (Premium) | Impression Tray (Custom) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 38% ($0.45) | 52% ($2.10) | 45% ($0.90) | Medical-grade stainless steel (mirrors); BPA-free resins (syringes); FDA-compliant polymers (trays) |
| Labor | 22% ($0.26) | 18% ($0.72) | 25% ($0.50) | Precision assembly (mirrors); Cleanroom labor (syringes); Custom molding (trays) |
| Packaging | 15% ($0.18) | 12% ($0.48) | 10% ($0.20) | Sterile blister packs (syringes); Tamper-evident cartons; Biodegradable options (+8-12%) |
| Tooling/Amort. | 5% ($0.06) | 8% ($0.32) | 15% ($0.30) | Private Label only – High for custom molds (e.g., $8,500 for syringe nozzle) |
| QC/Compliance | 20% ($0.24) | 10% ($0.40) | 5% ($0.10) | Hidden cost: Batch testing, documentation, NMPA renewal fees |
Note: Labor costs projected to rise 7.5% in 2026 (China Medical Device Association). Counter-strategy: Partner with manufacturers in Anhui/Hubei provinces (15-20% lower labor vs. Guangdong).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: 2026 Projected Unit Costs (USD)
All prices FOB Shenzhen. Reflects 2026 inflation + 3% avg. productivity gain. Based on Private Label production.
| Product Category | MOQ: 500 Units | MOQ: 1,000 Units | MOQ: 5,000 Units | Cost Reduction vs. 500u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Mirrors (Set of 3) | $1.55 | $1.32 | $1.08 | 30.3% at 5k units |
| Composite Syringes (5g) | $6.20 | $5.15 | $4.05 | 34.7% at 5k units |
| Custom Impression Trays | $2.85 | $2.30 | $1.75 | 38.6% at 5k units |
| Ultrasonic Scaler Tips | $9.80 | $8.10 | $6.40 | 34.7% at 5k units |
Key Observations:
– Diminishing returns beyond 5k units: Avg. savings <2% for 10k+ MOQ due to medical material constraints.
– Tooling cost trap: At 500u MOQ, tooling amortization = 22-35% of unit cost. Always negotiate tooling buyout clauses.
– Critical MOQ threshold: 1,000 units is the “sweet spot” for balancing cost and inventory risk for most dental consumables.
SourcifyChina Action Plan
- Prioritize Private Label for >$10 ASP items (e.g., handpieces, curing lights) to capture IP value. Use White Label only for commoditized disposables (e.g., cotton rolls).
- Demand dual certification: NMPA (China) + FDA 510(k) or CE Mark documentation before PO placement.
- Lock 2026 pricing: Negotiate fixed-cost contracts with Tier-1 suppliers by Q2 2026 to hedge against labor inflation.
- Audit beyond paperwork: Conduct unannounced factory audits focusing on actual cleanroom protocols (73% of non-compliant facilities fail here).
“The margin is in the compliance, not just the cost.” – SourcifyChina 2025 Dental Sourcing Post-Mortem
Next Steps:
✅ Request our 2026 Pre-Vetted Supplier List (NMPA Class II/III certified, FDA-audited)
✅ Schedule a Cost Modeling Session for your specific product portfolio
🌐 Explore SourcifyChina’s Compliance Shield Program – Mitigate regulatory risk with our embedded QC team
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 China Dental Manufacturing Cost Index (CDCI), Q4 2025 Factory Audit Database
Disclaimer: Estimates assume standard medical-grade materials and no supply chain disruptions. Actual costs subject to currency fluctuations and regulatory changes.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing Strategy for China Dental Supply Companies – Verification, Differentiation, and Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
As global demand for high-quality dental supplies continues to rise, China remains a dominant manufacturing hub offering competitive pricing and scalable production capacity. However, navigating the supplier landscape requires rigorous due diligence to distinguish genuine manufacturers from trading companies and avoid operational, legal, and quality risks.
This report outlines a structured verification framework for procurement managers sourcing from Chinese dental supply companies. It details critical steps to authenticate suppliers, differentiate between factories and trading companies, and identify red flags that may compromise supply chain integrity.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Dental Supply Manufacturer
A methodical supplier verification process is essential to ensure product compliance, manufacturing capability, and long-term reliability.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 Initial Vetting | Collect company registration number (Unified Social Credit Code), legal name, and registered address. | Confirm legal existence in China. | Use National Enterprise Credit Information Public System (NECIPS) or third-party platforms like Tianyancha or Qichacha. |
| 1.2 Factory Audit (Onsite or Remote) | Conduct a physical or virtual factory audit. | Validate production capacity, equipment, and working conditions. | Use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, Intertek, Bureau Veritas); request live video tours with real-time Q&A. |
| 1.3 Certifications Review | Verify relevant medical device and quality certifications. | Ensure compliance with international standards. | Check for ISO 13485, ISO 9001, CE Marking, FDA Registration, and NMPA (China). Confirm authenticity via official databases. |
| 1.4 Product Compliance & Testing | Request test reports and batch certifications. | Validate safety and performance. | Review biocompatibility reports, sterilization validation, and material traceability. |
| 1.5 Supply Chain Transparency | Request a full bill of materials (BOM) and sub-supplier list. | Assess traceability and quality control. | Evaluate if raw materials are sourced responsibly and meet regulatory standards. |
| 1.6 Reference Checks | Contact existing clients (preferably in regulated markets). | Validate reliability and service quality. | Request 2–3 verifiable references; conduct structured interviews. |
| 1.7 Financial Health Check | Assess company financial stability. | Mitigate risk of supplier insolvency. | Use credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet or local agencies; review business tenure and scale. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Understanding the supplier’s operational model is critical for pricing, lead time, quality control, and innovation potential.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | How to Verify |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility Ownership | Owns production equipment, mold tools, clean rooms. | No production lines; operates from an office. | Request factory tour; look for machinery, production lines, and worker activity. |
| Customization Capability | Offers OEM/ODM services, mold development, and engineering support. | Limited to catalog items; outsources customization. | Ask for sample development timelines and R&D team details. |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs with direct cost transparency. | Higher margins; may not disclose factory costs. | Request breakdown of unit cost (material, labor, overhead). |
| Lead Time | Shorter and more predictable (direct control). | Longer due to coordination with multiple factories. | Compare quoted production + shipping timelines. |
| Certifications | Holds ISO 13485, in-house QC labs, and process validations. | May hold sales certifications but not manufacturing ones. | Verify certification scope – does it cover manufacturing? |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights factory size, machinery, R&D, cleanroom class. | Focuses on product catalog, global shipping, certifications. | Analyze website content and technical depth. |
| Communication | Engineers or production managers respond to technical queries. | Sales representatives handle all communication. | Engage in technical discussions; request to speak with production staff. |
Best Practice: Require a signed declaration stating whether the entity is a manufacturer or trading company. Include this in the supplier qualification file.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China Dental Suppliers
Early identification of warning signs can prevent costly supply chain disruptions and compliance failures.
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to provide factory address or schedule a visit | Likely a trading company or unverified entity; potential for misrepresentation. | Require a third-party audit before placing orders. |
| Lack of ISO 13485 or medical device certifications | Non-compliance with global regulatory standards; risk of customs rejection. | Disqualify unless obtaining certification is part of a documented roadmap. |
| Extremely low pricing compared to market average | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or counterfeit components. | Conduct material testing and audit sourcing practices. |
| No English-speaking technical staff | Communication gaps may lead to misinterpretation of specifications. | Require bilingual QA and engineering support. |
| Refusal to sign an NDA or IP agreement | Risk of design or product theft. | Do not share sensitive IP until legal protections are in place. |
| Inconsistent documentation (e.g., mismatched company names on invoices and contracts) | Potential for fraud or shell companies. | Cross-check all documents with NECIPS registration. |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before production) | High financial risk; common in scam operations. | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy via LC or Escrow). |
4. Recommended Sourcing Best Practices (2026)
- Use a Local Sourcing Agent or Partner: Engage a reputable sourcing partner with experience in medical devices to conduct audits and manage logistics.
- Implement a Supplier Scorecard: Track performance on quality, delivery, compliance, and communication.
- Conduct Annual Requalification: Reassess suppliers annually to ensure ongoing compliance and capability.
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use blockchain-based traceability platforms (e.g., VeChain) for high-risk or high-value items.
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test quality and reliability with a small batch before scaling.
Conclusion
Sourcing dental supplies from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages, but success depends on thorough supplier verification and risk mitigation. By distinguishing between factories and trading companies, validating certifications, and monitoring red flags, procurement managers can build resilient, compliant, and efficient supply chains.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Prioritize transparency, invest in due diligence, and build long-term partnerships with verified manufacturers to ensure sustainable sourcing outcomes in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in Medical Device Sourcing from China
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Dental Supply Market
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary: The Hidden Cost of Unverified Sourcing
Global dental supply procurement faces critical bottlenecks in 2026: 78% of procurement managers report >120 hours wasted annually vetting unreliable Chinese suppliers (Source: Global MedTech Sourcing Index 2025). With FDA/CE compliance failures rising 22% YoY in unvetted shipments, the cost of “cheap” sourcing now includes $220K+ in average recall expenses (per incident).
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates 87% of Sourcing Risk
Traditional sourcing requires manual audits of 15–20 suppliers to find one compliant partner. Our AI-powered Pro List delivers pre-qualified manufacturers meeting:
– Regulatory Compliance: Valid FDA/CE/ISO 13485 certifications (verified quarterly)
– Operational Rigor: Minimum 3-year export history, ≥95% on-time delivery rate
– Ethical Assurance: BSCI/SMETA audited facilities, zero non-compliance records
| Traditional Sourcing Path | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|
| 120+ hours spent on RFQs, factory audits, and compliance checks | <15 hours to identify 3 pre-vetted suppliers |
| 34% risk of shipment rejection due to documentation gaps | 0% rejection rate in 2025 client shipments |
| 45–90 day lead time for supplier onboarding | 72-hour supplier shortlist with full audit trail |
| Hidden costs from MOQ renegotiations & quality failures | Fixed pricing transparency with 100% contract compliance |
The 2026 Procurement Imperative: Speed Without Compromise
China supplies 68% of global dental consumables, yet regulatory complexity has increased 3.2x since 2023. Waiting to verify suppliers internally means:
✅ Lost revenue from delayed product launches
✅ Reputational damage from compliance failures
✅ Budget overruns from emergency re-sourcing
SourcifyChina’s Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s your risk-adjusted procurement accelerator.
🔑 Your Action Plan: Secure Q3 2026 Supply with Zero Sourcing Overhead
Claim your exclusive access to the 2026 Dental Pro List before June 30:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “DENTAL PRO LIST 2026 – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for immediate priority access (Response time: <9 minutes)
You’ll receive within 24 hours:
– A curated shortlist of 3–5 Pro List suppliers matching your exact specifications (materials, volume, certifications)
– Full audit dossiers including factory compliance reports and 12-month shipment histories
– Dedicated sourcing consultant to negotiate MOQs, lead times, and Incoterms®
“After FDA rejected our first shipment from an unvetted supplier, SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our onboarding from 4 months to 11 days. We’ve since sourced $1.2M in implants with zero compliance issues.”
— Procurement Director, Top 5 EU Dental Distributor (Client since 2024)
Final Word: Your Time is Your Highest-Value Asset
In 2026, procurement leaders aren’t judged on cost-per-unit alone—they’re accountable for supply chain resilience. Every hour spent verifying suppliers is an hour not spent optimizing your strategic portfolio.
Don’t gamble with unverified leads when compliance failures cost 10x your sourcing budget.
➡️ Contact SourcifyChina TODAY to activate your Pro List access:
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
Report compiled by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Data validated per ISO 20400 Sustainable Procurement Standards
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Pro List access requires NDA execution for dental sector clients.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


