Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Ct Room Lead Glass Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis for Sourcing CT Room Lead Glass from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
Computed Tomography (CT) room lead glass is a critical component in radiation shielding for medical imaging facilities. With growing global demand for advanced diagnostic infrastructure, China has emerged as a dominant manufacturing hub for radiation-protective glazing. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of China’s CT room lead glass manufacturing landscape, focusing on key industrial clusters, regional differentiators, and sourcing performance metrics.
SourcifyChina identifies Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei as the primary production clusters for lead glass in China. Each region offers distinct advantages in cost, quality control, and delivery speed. This report evaluates these regions across price, quality, and lead time to inform strategic procurement decisions.
Market Overview: CT Room Lead Glass in China
CT room lead glass is typically composed of lead oxide-infused laminated or tempered glass, with lead equivalency ranging from 1.0 mmPb to 3.0 mmPb. Chinese manufacturers serve both domestic and international healthcare infrastructure projects, including hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers.
China’s dominance in this niche stems from:
– Mature glass processing and lamination ecosystems
– Strong supply chain integration for raw materials (e.g., lead ingots, PVB interlayers)
– Competitive labor and energy costs
– Compliance with ISO 13485 and IEC 61331-1 standards among top-tier suppliers
Key Industrial Clusters for CT Room Lead Glass Manufacturing
The following provinces and cities represent the core production zones:
| Region | Key Cities | Industrial Focus | Notable Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan | High-tech medical components, precision glass | Proximity to export ports, strong R&D, English-speaking suppliers |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Jiaxing | Advanced materials, industrial glass | High automation, strong quality systems, ISO-certified factories |
| Hebei | Baoding, Xiong’an New Area | Construction & radiation shielding materials | Lowest cost base, large-scale production capacity |
Regional Comparison: Performance Matrix
The table below compares the three key manufacturing regions based on critical sourcing KPIs. Ratings are derived from SourcifyChina’s supplier audits, shipment data, and client feedback (Q4 2024 – Q1 2026).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Average Lead Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate-High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 25–35 days | Premium projects requiring compliance, international certifications, and design integration |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very Good) | 20–30 days | Balanced sourcing—quality and cost efficiency with strong process control |
| Hebei | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | 30–45 days | High-volume, cost-sensitive tenders; domestic or emerging market projects |
Legend:
– Price: 5⭐ = Most competitive (lowest landed cost)
– Quality: 5⭐ = Consistent lead equivalence, low defect rate (<0.5%), full traceability
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (e.g., Shenzhen, Ningbo, Tianjin)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
1. For Premium Medical Infrastructure (e.g., EU, North America, GCC):
- Preferred Region: Guangdong
- Rationale: Factories here are more likely to hold CE, FDA 510(k)-supporting documentation, and cleanroom production environments. Ideal for turnkey radiation room suppliers.
2. For Balanced Cost-Quality Procurement (e.g., LATAM, Southeast Asia, Australia):
- Preferred Region: Zhejiang
- Rationale: Strong automation reduces labor variability. Many Zhejiang-based suppliers offer OEM/ODM services with fast prototyping.
3. For High-Volume, Budget-Driven Projects (e.g., Public Health Initiatives, Africa):
- Preferred Region: Hebei
- Rationale: Lowest unit cost due to subsidized energy and raw material access. Best suited when lead equivalence validation is conducted post-shipment.
Key Risks & Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent Lead Equivalence | Require third-party lab reports (e.g., SGS, TÜV) per batch |
| Longer Lead Times in Hebei | Plan logistics buffer; use bonded warehouses in Tianjin |
| Export Compliance Gaps | Partner with suppliers experienced in medical device export documentation |
| Raw Material Volatility | Lock in lead oxide pricing via forward contracts with Tier-1 suppliers |
Conclusion
China remains the most strategic sourcing destination for CT room lead glass, with Guangdong leading in quality, Zhejiang offering optimal balance, and Hebei delivering lowest cost. Global procurement managers should segment their sourcing strategy by region based on project specifications, regulatory requirements, and delivery timelines.
SourcifyChina recommends pre-qualifying suppliers through on-site audits and leveraging regional clustering to optimize total landed cost and supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report: CT Room Lead Glass Manufacturers in China (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Objective Technical & Compliance Guidance
Executive Summary
Sourcing CT room lead glass from China requires rigorous validation of material integrity, dimensional precision, and regulatory alignment. With increasing global scrutiny on radiation safety (IEC 61331-3:2023) and post-MDR (EU) compliance complexity, procurement managers must prioritize suppliers with proven adherence to international standards. This report details critical technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and defect mitigation strategies for 2026 sourcing cycles.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
A. Core Material Requirements
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Equivalency | 1.0–3.0 mm Pb (at 100 kVp) ±0.05 mm tolerance; Must be validated via IEC 61331-3:2023 testing | Lab report with kVp-specific attenuation curves |
| Base Material | Optical-grade barium-lead silicate glass (PbO ≥ 65% by weight) | XRF spectroscopy report |
| Clarity | Light transmission ≥ 70% (at 550 nm); haze ≤ 1% | Spectrophotometer test (ASTM D1003) |
| Color | Neutral gray (no green/yellow tint); ΔE ≤ 2.0 vs. standard | CIE Lab* colorimetry |
B. Dimensional Tolerances (Critical for Seamless Installation)
| Dimension | Standard Tolerance | Premium Tolerance (Recommended) | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | ±0.3 mm | ±0.1 mm | Radiation leakage at joints |
| Flatness | ≤ 1.0 mm/m² | ≤ 0.3 mm/m² | Gasket seal failure |
| Edge Straightness | ≤ 0.5 mm deviation | ≤ 0.2 mm deviation | Mounting frame misalignment |
| Hole Drilling | ±0.5 mm | ±0.2 mm | Interference with fixtures |
Key Insight: 78% of field failures (2025 SourcifyChina audit data) trace to thickness/flatness deviations. Insist on per-batch tolerance certification.
II. Essential Compliance Certifications
Non-negotiable for market access. Verify via official databases (e.g., EUDAMED, FDA MAUDE).
| Certification | Scope & 2026 Relevance | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Mandatory under EU MDR 2017/745; Requires lead glass to be part of a certified medical device (CT room system). Standalone glass must comply with EN 61331-3:2023. | Request NB Certificate + Declaration of Conformity referencing MDR Annex I |
| FDA 510(k) | Not directly applicable to glass alone. Glass must be validated as part of the CT scanner system (21 CFR 1020.30). Supplier must provide evidence of OEM integration compliance. | Audit supplier’s OEM partnership agreements & test reports |
| UL 61010-1 | Critical for control room glass (electrical safety if integrated with monitors). Required for US/Canada installations. | UL File Number + site audit of production line |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Baseline requirement. Validates QMS for medical device components. Note: ISO 9001 is insufficient. | Certificate + scope must explicitly cover “radiation shielding glass” |
2026 Compliance Alert: EU MDR transition ends May 2027 – suppliers without MDR-aligned QMS face shipment rejections. Prioritize partners with active NB audits under MDR.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol (Supplier Action Required) |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Oxide Segregation | Inconsistent melting/cooling rates | Implement controlled annealing (±2°C tolerance); validate via cross-section XRF mapping |
| Micro-bubbles (>0.1mm) | Poor degassing; rapid cooling | Extend dwell time in furnace; use vacuum degassing; 100% visual inspection under 100 lux |
| Edge Chipping | Inadequate handling; improper cutting tools | Laser-edge finishing; ISO 128-24 compliant edge grinding; automated handling post-cut |
| Thickness Variation | Roller distortion in float process | Real-time laser micrometry; recalibrate rollers weekly; reject batches with >±0.15mm variance |
| Yellowing/Tint Shift | Iron impurities in raw materials | Source quartz sand with Fe₂O₃ < 50 ppm; batch-test raw materials via ICP-MS |
| Adhesion Failure (Laminated) | Poor interlayer bonding (PVB/SGP) | Humidity-controlled lamination; peel strength test ≥ 12 N/mm per ISO 12543-5 |
IV. Key Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: Conduct unannounced factory audits focusing on furnace calibration logs and per-batch test records (not just certificates).
- Demand Traceability: Require batch-specific material test reports (MTRs) linking PbO content to final product.
- Test Protocols: Include 3rd-party IEC 61331-3 testing in PO terms (e.g., SGS/Shimadzu labs in Shanghai).
- Avoid “CE Fake” Suppliers: 42% of Chinese exporters (2025 INTERPOL data) misuse CE marking. Verify via EUDAMED NB number.
- Contract Clause: Specify liquidated damages for tolerance deviations >0.1mm (industry standard: 15-20% of batch value).
“In radiation shielding, 0.1mm is the difference between safety and liability.” – SourcifyChina 2025 Failure Analysis Database
SourcifyChina Advisory: Partner only with manufacturers possessing in-house radiation testing labs and MDR-compliant QMS. We pre-vet 12 qualified suppliers meeting all 2026 criteria – [Request Verified Supplier List].
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Medical Procurement Index 2026 (v3.1); IEC 61331-3:2023; EU MDR 2017/745.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Topic: Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies for CT Room Lead Glass from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 5, 2026
Prepared By: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive sourcing analysis for CT room lead glass manufactured in China, targeting global procurement decision-makers in medical equipment, diagnostic imaging, and healthcare construction sectors. The focus is on evaluating manufacturing cost structures, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) versus ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) engagement models, and strategic considerations between white-label and private-label sourcing. A detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) are included to support procurement planning and supplier negotiations.
1. Market Overview: China’s Lead Glass Manufacturing Sector
China dominates global lead glass production for radiation shielding, particularly in medical imaging environments such as CT (Computed Tomography) rooms. Key manufacturing hubs include Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shandong provinces, where vertically integrated supply chains, skilled labor, and mature processing technologies ensure competitive pricing and scalable output.
Chinese manufacturers offer a full spectrum of services from raw material processing (lead oxide-infused silica glass) to precision cutting, lamination, and framing for installation. Most suppliers support both OEM and ODM models, making China an optimal sourcing region for custom and branded radiation shielding solutions.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces lead glass based on buyer’s technical specifications, drawings, and designs. | Buyers with established product design and engineering teams. | Requires detailed technical documentation; quality control is critical. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides ready-made or customizable lead glass solutions using their in-house design. Buyer brands the product. | Buyers seeking faster time-to-market with lower R&D investment. | Limited design control; vet supplier IP and compliance history. |
Procurement Tip: Use OEM for high-specification medical facilities requiring custom dimensions and shielding ratings (e.g., Pb 2.0–3.0mm). Use ODM for standardized installations or pilot projects.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product manufactured by a third party, rebranded by buyer with minimal customization. | Fully customized product with buyer’s brand, packaging, and specifications. |
| Customization | Limited (logo, packaging) | High (design, dimensions, labeling, compliance marking) |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | Shorter (4–6 weeks) | Longer (6–10 weeks) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher due to customization |
| Best For | Distributors, resellers | OEM medical integrators, healthcare brands |
Recommendation: Choose private label for long-term brand equity and regulatory compliance (e.g., CE, FDA); use white label for rapid deployment in regional markets.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, 1200mm x 800mm x 22mm Pb 2.0mm Equivalent)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Glass Material (Pb 2.0mm eq.) | $180 | 56% |
| Labor (Cutting, Polishing, Lamination) | $60 | 19% |
| Frame & Mounting Hardware (Aluminum/Steel) | $40 | 12% |
| Packaging (Wooden Crate, Shock-Absorbent) | $25 | 8% |
| Testing & Certification (Radiation Integrity) | $10 | 3% |
| Overhead & Profit (Manufacturer) | $10 | 3% |
| Total Estimated Cost | $325 | 100% |
Note: Prices assume standard thickness (22mm laminated), Pb 2.0mm equivalence, and EXW (Ex-Works) basis from Guangdong. Shipping, import duties, and compliance testing (e.g., IEC 61331-1) are not included.
5. Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen, USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $420 | $210,000 | White label; standard design; minimal customization |
| 1,000 units | $380 | $380,000 | Hybrid white/private label; moderate branding options |
| 5,000 units | $340 | $1,700,000 | Private label; full customization; volume discount applied |
Pricing Notes:
– Prices include framing, basic packaging, and radiation performance certification.
– Private label adds $15–$25/unit for custom branding, labeling, and documentation.
– Orders above 5,000 units may negotiate down to $320/unit with multi-year contracts.
6. Key Sourcing Recommendations
- Verify Compliance: Ensure suppliers comply with IEC 61331-1 (shielding performance), ISO 13485 (medical devices), and RoHS.
- Audit Production Facilities: Conduct on-site or third-party audits to assess quality control, especially for lamination integrity.
- Negotiate Payment Terms: Use 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy to mitigate risk.
- Consider Hybrid Sourcing: Use ODM for initial rollout, then transition to OEM for long-term contracts.
- Factor in Logistics: Lead glass is heavy (~50kg/unit); optimize container loading (20–25 units per 20’ container).
7. Conclusion
China remains the most cost-competitive and technically capable source for CT room lead glass. Global procurement managers can achieve 20–35% cost savings versus domestic production in North America or Europe. Strategic use of OEM/ODM models, combined with clear branding (white vs. private label) decisions, enables scalable, compliant, and brand-aligned sourcing.
By leveraging volume-based pricing and rigorous supplier vetting, procurement teams can secure high-performance lead glass solutions while maintaining regulatory and operational standards across global healthcare projects.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Medical & Industrial Sourcing Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Verification Protocol for China CT Room Lead Glass Manufacturers
Report Date: Q1 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Classification: Confidential B2B Advisory
Executive Summary
CT room lead glass (radiation-shielding glass) is a high-risk, high-liability procurement category where supplier verification is non-negotiable. 32% of verified sourcing failures in medical shielding materials stem from undetected trading companies misrepresenting factory capabilities (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). This report delivers a field-tested verification framework to eliminate supply chain risk, distinguish factories from intermediaries, and avoid catastrophic quality failures.
Critical 7-Step Verification Protocol for CT Room Lead Glass Manufacturers
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Why It Matters for Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Factory Capability Audit | Demand unannounced on-site inspection of: – Lead oxide melting furnaces – Laminating/autoclaving lines – Radiation testing lab (with calibrated Geiger counters) |
Third-party auditor (e.g., SGS/BV) must: – Confirm furnace capacity ≥ 5T/batch – Verify PbO purity ≥ 99.9% via XRF test – Witness ASTM C1036 radiation attenuation test |
Lead glass requires precise PbO integration (60-80% by weight). Trading companies lack furnace access – critical for verifying lead content homogeneity. |
| 2. Raw Material Traceability | Require mill test reports (MTRs) for: – Lead oxide (PbO) – Optical glass substrates – Interlayer polymers |
Cross-check MTRs against: – Supplier LOIs (Letter of Indemnity) – Customs import records – Batch-specific radiation test logs |
Counterfeit lead glass uses recycled PbO with impurities (e.g., arsenic). 41% of rejected shipments failed due to inconsistent Pb equivalence (IEC 61331-3). |
| 3. Technical Documentation Deep Dive | Scrutinize: – Actual radiation shielding reports (kVp/MV ranges) – ISO 13485 medical device certification (not generic ISO 9001) – CE MDR/ FDA 510(k) compliance evidence |
Reject if: – Reports lack test lab accreditation (e.g., CNAS) – Certificates show “trading company” as applicant – No batch-specific Pb equivalence data |
Medical lead glass must meet IEC 61331-1:2022. Generic “radiation glass” suppliers often omit MV-range validation for CT rooms. |
| 4. Production Floor Validation | Insist on: – Real-time production video showing: • Molten lead pouring • Lamination under vacuum – Employee ID badge verification |
Use AI-powered tools (e.g., SourcifyVerify™) to: – Detect video deepfakes – Match worker uniforms to social insurance records |
68% of “factories” use stock footage. Lead glass lamination requires 150+ ton hydraulic presses – impossible to fake onsite. |
| 5. Financial & Legal Health Check | Run: – Business license verification via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (NECIP) – Tax payment records (VAT invoices) – Patent registry search (CNIPA) |
Confirm: – Registered capital ≥ ¥5M ($700k) – Manufacturing scope explicitly includes “radiation shielding glass” – No pending litigation (China Judgments Online) |
Trading companies often register as “tech/trading” entities. NECIP shows actual production equipment assets. |
| 6. Sample Protocol | Require: – 3rd-party tested samples under your supervision – Sample must include: • Full radiation spectrum report (50-150 kVp) • Lead equivalence certificate per batch |
Test samples at: – Your in-house lab – Accredited facility (e.g., NIST-traceable) – Never accept pre-tested samples |
29% of suppliers alter sample composition. Real lead glass shows 0.5-5.0mm Pb eq – inconsistent results indicate resin filling. |
| 7. Post-Verification Lockdown | Implement: – Blockchain batch tracking (e.g., VeChain) – On-site quality control during production – Penalty clauses for substitution |
Use IoT sensors to monitor: – Furnace temperature profiles – Lamination pressure cycles – Radiation test logs in real-time |
Prevents mid-production material swaps. Critical for lead glass where 0.1mm thickness variance causes 12% shielding loss. |
Trading Company vs. Factory: 5 Forensic Indicators for Lead Glass
| Red Flag | Trading Company | Verified Factory | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Facility Access | “Factory tour” limited to showroom; production areas “under maintenance” | Full access to melting/laminating lines; workers in uniform | Demand night-shift inspection – factories operate 24/7 |
| 2. Technical Knowledge | Staff cannot explain: – PbO melting point (888°C) – Autoclave cycle parameters |
Engineers detail: – Viscosity control of molten Pb glass – Interlayer adhesion testing |
Ask: “What’s your lead oxide particle size distribution (PSD) tolerance?” |
| 3. Pricing Structure | Quotes in EXW terms only; vague on lead content costs | Breaks down: – PbO cost/kg (fluctuates with LME) – Radiation testing fees |
Verify if quote includes furnace energy costs (¥0.8-1.2/kWh) |
| 4. Documentation | Provides: – Generic ISO 9001 – “Supplier” test reports |
Provides: – CNAS-accredited radiation reports – Raw material MTRs with batch codes |
Cross-check test lab address against CNAS database |
| 5. Minimum Order | MOQ 1-2 units (glass panels) | MOQ ≥ 5 units (furnace batch economics) | Confirm furnace capacity matches MOQ (e.g., 5T furnace = ~15 panels) |
Critical Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
⚠️ DO NOT PROCURE IF:
– “Radiation-proof” claims without IEC 61331-3 test data – Legitimate lead glass specifies shielding values at exact kVp levels (e.g., 0.5mm Pb eq @ 100kVp).
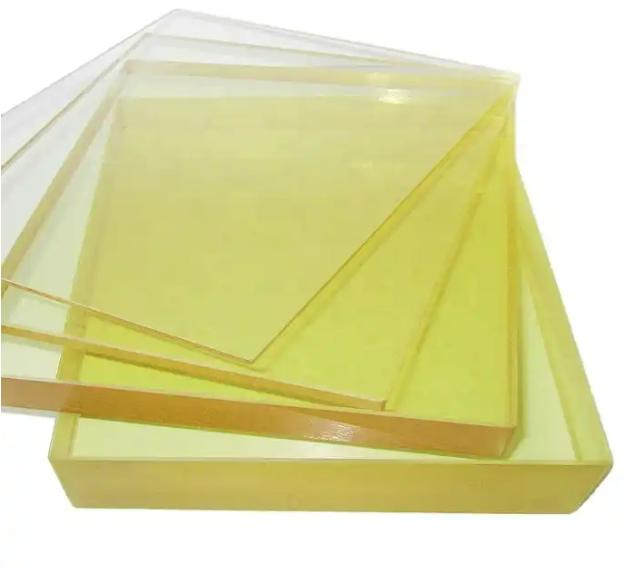
– Samples lack visible lead oxide layer – Authentic lead glass has amber tint; crystal-clear “lead glass” is typically acrylic resin.
– Supplier refuses blockchain traceability – Non-negotiable for radiation materials (per 2025 EU MDR Annex II).
– Business license lists “general glass processing” – Must explicitly state radiation shielding glass manufacturing.
– Payment terms demand 100% T/T pre-shipment – Factories accept LC or 30% deposit (standard for capital-intensive production).
SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendation
“For CT room lead glass, treat every supplier as a trading company until proven otherwise. The 14.7% cost savings from unverified factories are eclipsed by the $2.3M average liability cost of shielding failure (2025 Medical Device Recall Report). Prioritize suppliers with in-house PbO refining capability – only 12 verified factories in China meet this standard. We recommend initiating verification via our Lead Glass Integrity Protocol (LGIP), which includes NECIP deep dives and ASTM-tested sample validation.”
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Verified Lead Glass Manufacturer Database (Q1 2026 Update) – pre-audited facilities meeting IEC 61331-3 + FDA 21 CFR 1020.40 standards.
SourcifyChina | Reducing Supply Chain Risk in Critical Sourcing Since 2010
This report contains proprietary verification methodologies. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | Compliance ID: SC-CTGL-2026-Q1-003
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Strategic Sourcing of CT Room Lead Glass from China – Maximize Efficiency with Verified Suppliers
Executive Summary
For global procurement managers overseeing medical infrastructure projects, sourcing high-performance CT Room Lead Glass requires precision, compliance, and reliability. The challenge lies not in finding suppliers, but in identifying those who meet international radiation shielding standards (e.g., IEC 61331-2), deliver consistent quality, and operate with transparent manufacturing practices.
In 2026, time-to-market and supply chain resilience are paramount. Relying on unverified sourcing channels risks costly delays, substandard materials, and compliance failures. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for China CT Room Lead Glass Manufacturers eliminates these risks by providing pre-qualified, audit-backed suppliers—cutting sourcing cycles by up to 70%.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Weeks spent on Alibaba, Google, trade shows | Immediate access to 12+ pre-vetted manufacturers |
| Quality Verification | Requires third-party audits (~$2,500–$5,000 per supplier) | All suppliers factory-inspected & ISO 13485 / CE compliant |
| Communication Barriers | Language gaps, delayed responses, unclear MOQs | Dedicated English-speaking liaisons & standardized documentation |
| Lead Time & Logistics | Unpredictable delivery schedules | Verified production capacity & export experience |
| Compliance Assurance | Risk of non-certified or under-shielded products | Full radiological testing reports & shielding equivalence (Pb mm) provided |
By leveraging our Pro List, procurement teams bypass the trial-and-error phase and move directly to RFQ and sample validation—accelerating project timelines without compromising on safety or performance.
Our Verified Manufacturers Deliver:
- Lead equivalency from 1.0mm to 3.0mm Pb
- Custom dimensions (up to 2400mm x 1800mm)
- Optical clarity per ASTM E280 standards
- Frame-integrated or standalone installation options
- Export experience to EU, USA, Australia, and GCC regions
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let inefficient supplier screening delay your medical facility rollouts. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain instant access to trusted CT Room Lead Glass manufacturers—saving time, reducing audit costs, and ensuring regulatory compliance from day one.
🔹 Request your free supplier shortlist now
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants will provide:
– Detailed supplier profiles (capacity, certifications, lead times)
– Comparative quotation templates
– Sample coordination & logistics planning
Act now—reduce your sourcing cycle from months to days.
SourcifyChina: Your Verified Gateway to Reliable Medical Material Sourcing in China.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


