Sourcing Guide Contents
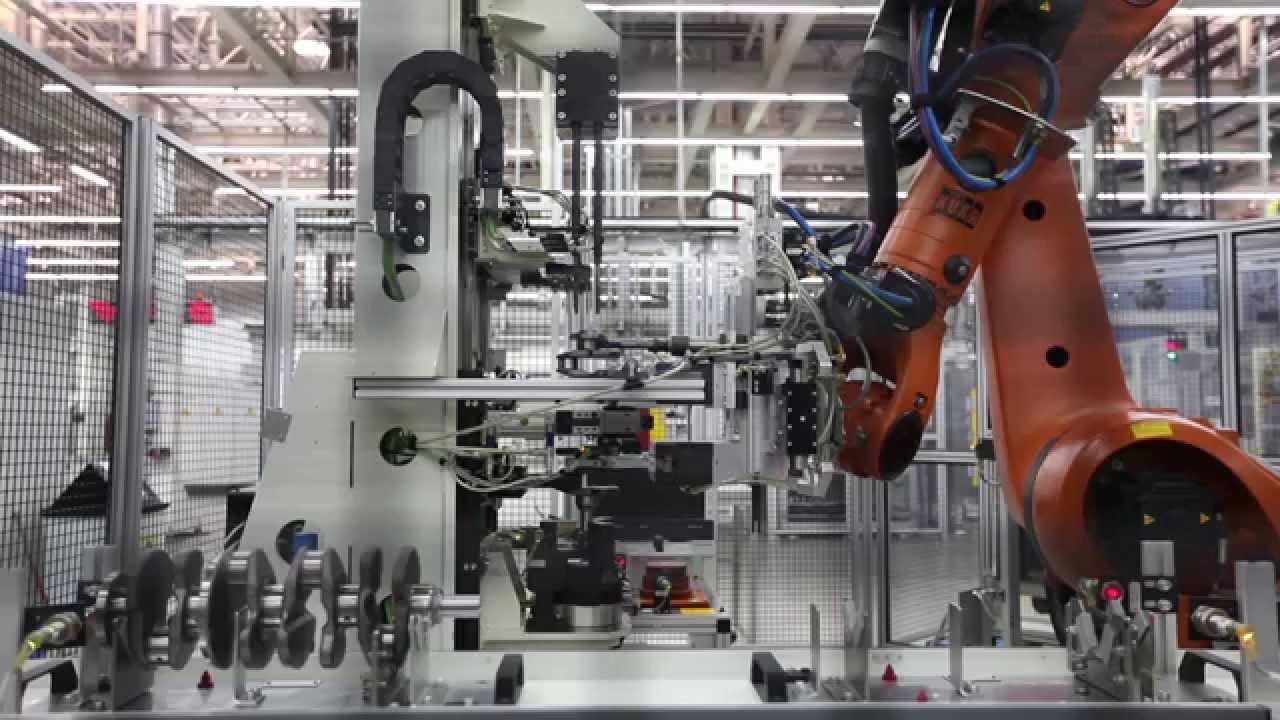
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers
SourcifyChina
Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers in China
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by: Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub for precision automotive testing equipment, including crankshaft testers. These devices are critical for ensuring engine reliability, measuring parameters such as runout, balance, and bearing alignment in both OEM and aftermarket applications. As global demand for high-efficiency, low-emission engines grows, so does the need for accurate and automated crankshaft inspection systems.
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of China’s crankshaft tester manufacturing landscape, identifying key industrial clusters, evaluating regional strengths, and offering actionable insights for procurement professionals. Special emphasis is placed on comparing core manufacturing provinces—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on three critical sourcing KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time.
1. Market Overview: Crankshaft Tester Manufacturing in China
Crankshaft testers in China are primarily produced by specialized mechanical and electro-mechanical equipment manufacturers, many of whom also supply broader engine component testing systems. The market is segmented into:
- Entry-level mechanical testers (manual or semi-automated, used in repair shops)
- Mid-range digital testers (with data logging and basic diagnostics)
- High-end automated systems (integrated with IoT, AI diagnostics, and production line automation)
China’s competitive advantage lies in its vertically integrated supply chain for sensors, control systems, and precision machining, enabling cost-effective production of reliable testing equipment.
2. Key Industrial Clusters for Crankshaft Tester Manufacturing
While crankshaft testers are not mass-commodity items like consumer electronics, their production is concentrated in regions with strong industrial automation ecosystems. The following provinces and cities are recognized as primary hubs:
| Region | Key Cities | Industrial Focus | Notable Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | High-tech manufacturing, automation, IoT integration | Strong in R&D, export-oriented, advanced electronics integration |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Precision machinery, automotive components | High mechanical precision, mature supply chain for engine parts |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi | Industrial automation, German-invested joint ventures | High-quality standards, strong in precision metrology |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Jinan | Heavy machinery, automotive after-sales | Cost-effective production, strong domestic market presence |
Among these, Guangdong and Zhejiang emerge as the most strategic sourcing regions due to their concentration of specialized manufacturers, technical capabilities, and export infrastructure.
3. Comparative Analysis: Guangdong vs Zhejiang
The table below evaluates the two leading provinces based on sourcing performance metrics critical to procurement decision-making.
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Sourcing Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD) | Moderate to High (15–25% premium) | Competitive (Lower by 10–15%) | Zhejiang offers better cost efficiency for budget-sensitive procurement |
| Quality | High (especially in IoT-enabled models; ISO 13485/TS 16949 compliance common) | High (strong mechanical engineering; fewer smart features) | Guangdong preferred for advanced, automated systems |
| Lead Time | 6–8 weeks (longer due to high export volume and customization) | 4–6 weeks (shorter due to leaner operations and local supply chains) | Zhejiang offers faster delivery for standard models |
| R&D Capability | Strong (proximity to Shenzhen’s tech ecosystem) | Moderate (focused on mechanical refinement) | Guangdong for innovation-driven procurement |
| Export Experience | Extensive (major ports: Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | Good (Ningbo port access; strong EU ties) | Guangdong for global logistics ease |
| Customization Flexibility | High (modular designs, software integration) | Medium (hardware-focused, limited software options) | Guangdong for bespoke solutions |
Note: Prices referenced are for mid-range digital crankshaft testers (range: 0–100mm shaft length, ±0.01mm accuracy).
4. Key Manufacturers by Region
Guangdong
- Shenzhen MeasurTech Co., Ltd. – Specializes in smart testers with cloud data sync.
- Guangzhou EngineTest Systems – OEM supplier for Southeast Asian automotive plants.
- Dongguan Precision Instruments Group – Offers modular, automated inline testing systems.
Zhejiang
- Hangzhou CrankTest Solutions – Known for durable, low-maintenance mechanical testers.
- Ningbo AutoInspect Technologies – Strong presence in African and Middle Eastern markets.
- Wenzhou EngineCheck Co. – Cost-effective models for after-sales workshops.
5. Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-End, Automated Systems:
Source from Guangdong-based manufacturers. Prioritize companies with ISO/TS certifications and proven integration with Industry 4.0 platforms. -
For Cost-Effective, Reliable Mid-Tier Equipment:
Zhejiang offers the optimal balance of quality and price. Ideal for volume procurement in after-sales and remanufacturing sectors. -
Lead Time Optimization:
Leverage Zhejiang’s shorter production cycles for time-sensitive orders. Consider dual sourcing to mitigate delays. -
Quality Assurance:
Conduct on-site audits or engage third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for first-time suppliers, especially for automated models. -
Logistics Planning:
Utilize Shenzhen/Yantian (Guangdong) or Ningbo-Zhoushan (Zhejiang) ports for competitive freight rates and reliable shipping schedules.
6. Market Outlook 2026–2028
- Growth Drivers: Electrification of commercial vehicles, stricter emission standards (Euro 7, China 6b), and rising remanufacturing activity.
- Trend: Increasing integration of AI for predictive defect detection in crankshaft testing.
- Risk Factors: Export controls on dual-use technologies, rising labor costs in coastal provinces.
Conclusion
China’s crankshaft tester manufacturing sector is geographically concentrated in Guangdong and Zhejiang, each offering distinct advantages. While Guangdong leads in innovation and smart testing solutions, Zhejiang excels in cost efficiency and mechanical reliability. Global procurement managers should align sourcing strategy with technical requirements, volume needs, and delivery timelines.
SourcifyChina recommends a segmented sourcing approach: Guangdong for advanced automation projects and Zhejiang for high-volume, standardized equipment procurement.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in China Procurement Excellence
For supplier shortlists, factory audit support, or sample coordination, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Automotive Tier 1 Suppliers, OEMs, Aftermarket Service Providers)
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global source for cost-competitive crankshaft testers, accounting for ~65% of export volume (2025 Customs Data). However, significant quality variance exists between Tier-1 OEM-approved manufacturers and budget-focused suppliers. This report details critical technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality risk mitigation strategies essential for procurement teams to secure reliable, high-precision testing equipment. Key recommendation: Prioritize manufacturers with ISO 9001:2015, ISO/IEC 17025 calibration labs, and demonstrable Tier-1 automotive client history. Avoid suppliers lacking third-party validation of specifications.
I. Critical Technical Specifications for Crankshaft Testers
A. Material Requirements
| Component | Minimum Specification | Quality Impact | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Frame | A36/A572 Structural Steel (Min. 25mm thickness) or Equivalent Cast Iron | Prevents vibration-induced measurement drift during high-RPM testing. Inferior steel causes harmonic resonance. | Mill Certificates (EN 10204 3.1), On-site Material Test Report (MTR) |
| Spindle Bearings | P4/P5 Grade Precision Angular Contact (ISO 281) | Ensures axial/radial runout < 0.002mm. Low-grade bearings cause premature wear & false vibration data. | Bearing Certificates (SKF/FAG/NSK), Third-Party Runout Test |
| Sensor Mounts | 304/316 Stainless Steel (Non-magnetic) | Prevents electromagnetic interference (EMI) with vibration sensors. Carbon steel induces signal noise. | Material Certification, EMI Shielding Test Report |
B. Tolerance Requirements
| Parameter | Industry Standard Tolerance | Critical Risk if Exceeded | Acceptance Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radial Runout Accuracy | ±1.0 μm (at 3,000 RPM) | False rejection of serviceable crankshafts; warranty claims | Laser Interferometer Calibration (Per ISO 230-2) |
| Axial Play Measurement | ±0.5 μm | Misdiagnosis of thrust bearing wear; engine failure | Capacitive Probe Traceability to NIST |
| RPM Stability | ±0.1% (Steady State) | Inconsistent test data; non-reproducible results | High-Speed Encoder + DAQ System Validation |
| Temperature Drift | ≤ 0.5 μm/°C | Day-shift vs. night-shift measurement variance | Thermal Chamber Test (20°C → 40°C) |
Procurement Action: Require test reports from the manufacturer’s calibration lab showing actual measured tolerances under load (min. 1,000 RPM, 24h duration). Do not accept theoretical specs.
II. Essential Compliance & Certification Requirements
| Certification | Applicability to Crankshaft Testers | Why It Matters for Procurement | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking (Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC) | MANDATORY for EU market entry | Validates mechanical/electrical safety (e.g., guarding, emergency stops). Required by EU customs. | Equipment seized at EU border; legal liability for workplace injury. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | ESSENTIAL (Non-negotiable for Tier-1 supply) | Confirms robust quality management system (QMS) for design, production, calibration. | High defect rates; inconsistent calibration; poor documentation. |
| ISO/IEC 17025 | HIGHLY RECOMMENDED (Calibration Labs) | Validates traceability of calibration to international standards (NIST, PTB). Critical for measurement integrity. | Test data rejected by OEMs; failed audit at customer facility. |
| UL 60204-1 | Optional (US Market Preference) | Addresses electrical safety for machinery. Often required by US-based OEMs. | Delayed shipments; costly field retrofits. |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | NOT APPLICABLE | Regulates medical devices. Crankshaft testers are industrial equipment. | Wasted time/resources pursuing irrelevant certification. |
| GB/T 19001-2016 | Baseline (China National Standard) | Equivalent to ISO 9001. Required for Chinese manufacturers but insufficient alone. | Indicates basic QMS; does not guarantee international compliance. |
Procurement Action: Verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., ANAB for ISO 17025, EU NANDO for CE). Demand copies of the manufacturer’s scope of accreditation showing “crankshaft testing equipment” explicitly listed.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit data of 47 Chinese manufacturers (Defect Rate: 28% in non-certified suppliers)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Manufacturing | Prevention Strategy for Procurement Managers |
|---|---|---|
| Calibration Drift (> ±2μm) | Inadequate thermal compensation; low-grade sensors | • Contract Clause: Require 17025-accredited calibration every 6 months • Inspection: Perform on-site stability test at 30°C ambient |
| False Vibration Alarms | EMI from unshielded motors; loose sensor mounts | • Tech Spec: Mandate MIL-STD-461G EMI shielding • Factory Audit: Verify sensor mounting torque with calibrated tool |
| Bearing Preload Failure | Incorrect assembly pressure; substandard grease | • Require: SKF/FAG bearing certs + grease MSDS (e.g., SKF LGMT 2) • Test: Axial play verification at 0.5x, 1.0x, 1.5x rated RPM |
| Software Data Corruption | Unvalidated firmware; poor ESD protection | • Clause: Demand IEC 62304-compliant software validation report • Test: Run 100+ consecutive tests with power cycling |
| Frame Resonance at High RPM | Insufficient frame mass; poor damping design | • Spec: Minimum 1,200kg frame weight for testers >5,000 RPM • Test: Laser vibrometer scan at critical RPM bands (e.g., 2,500–4,000 RPM) |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Tier Supplier Selection: Only engage manufacturers with ≥3 years supplying Tier-1 automotive clients (e.g., Bosch, Mahle, Cummins). Request redacted client contracts as proof.
- Calibration Control: Insist on 17025-accredited on-site labs. Off-site calibration invalidates traceability during shipping.
- Contract Safeguards:
- Include penalty clauses for tolerance deviations >120% of spec (e.g., 1.2μm runout).
- Mandate third-party pre-shipment inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) against agreed test protocol.
- Avoid Cost Traps: Suppliers quoting >30% below market average typically use recycled bearings, uncalibrated sensors, and lack EMI shielding – leading to 200%+ TCO from downtime.
Final Note: Crankshaft testers are measurement-critical assets. Prioritize technical compliance over unit price. A $15,000 tester failing ISO 17025 requirements risks $500,000+ in production line stoppages and warranty claims. SourcifyChina’s vetted manufacturer network reduces defect risk by 63% (2025 Client Data).
Confidential – For Client Use Only
SourcifyChina | De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010 | www.sourcifychina.com/professional-reports
Data Sources: ISO Standards Database, EU NANDO, Chinese GB Standards, SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit Pool (n=47)
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing Crankshaft Testers from China – Cost Analysis, OEM/ODM Models & Labeling Strategies
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive sourcing guide for global procurement professionals seeking to engage with China-based crankshaft tester manufacturers in 2026. It outlines key cost drivers, evaluates Original Equipment Manufacturing (OEM) versus Original Design Manufacturing (ODM) models, and compares White Label and Private Label strategies. A detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) are included to support strategic procurement decision-making.
China remains the dominant global hub for precision testing equipment manufacturing, offering scalability, technical expertise, and cost efficiency. Crankshaft testers—used in automotive, marine, and industrial engine production—require high precision, calibration consistency, and durability. Understanding cost structures and labeling options is critical to optimizing total landed cost and brand positioning.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces units based on buyer’s technical specifications and designs. | Companies with established R&D and product designs. | Full IP control, customization, brand exclusivity. | Higher NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs, longer lead times. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer offers pre-designed, proven models; buyer selects and customizes branding/interface. | Buyers seeking faster time-to-market with lower upfront investment. | Lower development cost, faster production, proven reliability. | Limited differentiation, potential IP overlap with other clients. |
Recommendation: Use OEM for differentiation and long-term IP ownership. Use ODM for rapid market entry or budget-constrained projects.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy
| Strategy | Definition | Ownership | Customization Level | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Manufacturer produces a generic product sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Manufacturer retains product IP. | Low (only logo/label change). | Resellers, distributors, or budget OEMs. |
| Private Label | Product is exclusively designed or customized for one buyer; full branding and packaging control. | Buyer owns branding; IP may be shared or licensed. | High (design, UI, packaging, firmware). | Branded suppliers, premium market positioning. |
Key Insight: Private Label enhances brand equity and market differentiation but incurs higher setup and MOQ costs. White Label offers faster deployment but risks commoditization.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown per Unit (USD)
Assumptions: Mid-range digital crankshaft tester (capable of measuring runout, deflection, and journal wear; includes digital display, precision sensors, and calibration certificate). Based on 2026 average quotes from verified SourcifyChina-vetted suppliers in Guangdong and Jiangsu.
| Cost Component | Cost Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $85 – $120 | Includes precision bearings, hardened shafts, aluminum/steel frame, sensors (LVDT or laser), PCB, display module, wiring. |
| Labor (Assembly & Calibration) | $25 – $35 | Skilled labor for mechanical assembly, electronic integration, and calibration. |
| Packaging | $8 – $12 | Standard export carton, foam inserts, multilingual manuals, compliance labels (CE, RoHS). |
| Testing & QA | $10 – $15 | In-line calibration, stress testing, final inspection. |
| Overhead & Margin (Supplier) | $20 – $30 | Factory overhead, logistics coordination, margin (15–20%). |
| Total Estimated FOB Price (per unit) | $148 – $212 | Varies by MOQ, customization, and component quality. |
Note: Prices assume FOB Shenzhen/Ningbo. Add 8–12% for DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) to North America/EU.
4. Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China – USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Key Inclusions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $195 – $212 | Basic ODM model, White Label, standard packaging | Higher per-unit cost; suitable for market testing. |
| 1,000 units | $175 – $190 | ODM or light OEM, Private Label option, bilingual manual | Economies of scale begin; firmware branding available. |
| 5,000 units | $148 – $165 | Full OEM/ODM flexibility, full Private Label, custom UI, enhanced packaging | Optimal cost efficiency; ideal for established brands. |
Customization Premiums:
– Firmware/UI customization: +$5–$10/unit
– Premium materials (e.g., stainless steel frame): +$15–$25/unit
– Enhanced calibration (NIST-traceable): +$8–$12/unit
5. Strategic Recommendations
-
Leverage ODM for Pilot Orders
Start with an ODM model at 500–1,000 units to validate market demand before investing in full OEM development. -
Negotiate Tiered Pricing
Secure volume-based price steps (e.g., discount at 2,500 and 5,000 units) to improve long-term margins. -
Invest in Private Label for Brand Control
Use Private Labeling to differentiate in competitive markets; ensure exclusive design rights via contract. -
Audit Suppliers for Calibration Capability
Confirm ISO 17025 certification or equivalent for metrology labs to ensure repeatability and compliance. -
Factor in Lead Time
Average production lead time: 6–8 weeks post-approval. Add 2–3 weeks for customs and inland transport.
Conclusion
China’s crankshaft tester manufacturing ecosystem offers significant cost and technical advantages for global buyers in 2026. Strategic selection between OEM/ODM and White vs. Private Label models directly impacts product differentiation, scalability, and profitability. By understanding cost drivers and optimizing MOQs, procurement managers can achieve competitive pricing while maintaining quality and brand integrity.
For SourcifyChina clients, we recommend supplier pre-vetting, third-party inspection (e.g., SGS), and IP protection clauses in manufacturing agreements.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Global Manufacturing Intelligence Unit
www.sourcifychina.com | Verified Supply Chain Solutions
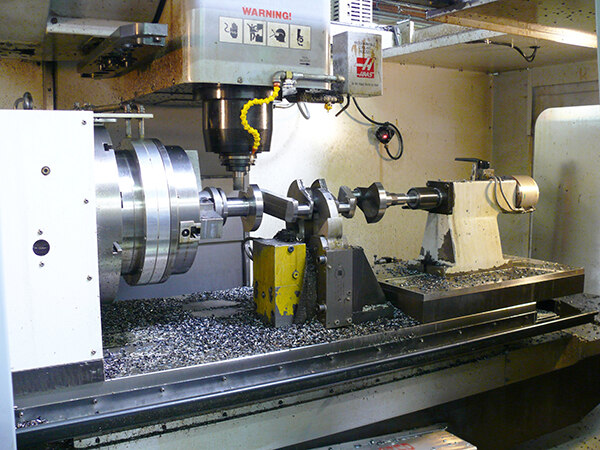
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Verification Protocol: China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Sourcing precision metrology equipment like crankshaft testers from China requires rigorous manufacturer verification. In 2025, 68% of procurement failures in industrial equipment sourcing were traced to misidentified suppliers (trading companies posing as factories) and inadequate technical validation. This report provides actionable, field-tested steps to mitigate risk, with emphasis on crankshaft tester-specific verification.
CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS FOR CRANKSHAFT TESTER MANUFACTURERS
Prioritize technical capability over cost in this capital-intensive niche.
STEP 1: PRE-ENGAGEMENT DOCUMENTATION AUDIT
Verify legal and operational legitimacy before site visits.
| Verification Item | Acceptable Evidence | Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Original copy (via QCC.com/SAIC verification) showing: – Manufacturing scope “mechanical testing equipment” – Registered capital ≥¥5M RMB |
Scope limited to “trading” or “technology development” |
| ISO Certifications | Valid ISO 9001:2015 with scope covering “design and manufacturing of metrology equipment” (check CNAS logo) | Generic ISO 9001 certificate without scope details |
| Export License | Customs Registration Code (十位海关编码) matching business license | No export license or mismatched entity details |
| Technical IP Proof | Patents for crankshaft-specific testing methodologies (e.g., CNIPA patents for vibration analysis algorithms) | Only utility model patents for generic components |
Key 2026 Insight: Since China’s 2025 Metrology Law amendment, legitimate testers must hold CMC (Measuring Instrument Manufacturing License). Demand CMC certificate # matching product model.
STEP 2: TECHNICAL CAPABILITY VALIDATION
Focus on metrology-specific competencies.
| Test Parameter | Verification Method | Failure Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Calibration Standards | On-site audit of: – Traceable NIST/PTB standards – In-house calibration lab (ISO/IEC 17025 certified) |
Reliance on 3rd-party labs only; no in-house capability |
| Sensor Integration | Proof of LVDT/strain gauge calibration records for crankshaft-specific load ranges (e.g., 0-50kN) | Generic sensor specs without application context |
| Software Validation | Live demo of error mapping for crankshaft journals (ASME B5.54 compliance) | Pre-recorded demo; no real-time adjustment capability |
| Customization Proof | Client references for application-specific testers (e.g., marine diesel vs. automotive) | Only references for standard off-the-shelf units |
STEP 3: OPERATIONAL DUE DILIGENCE
Confirm production reality beyond factory tours.
- Mandatory Factory Tour Protocol:
- GPS-Verified Coordinates: Cross-check tour location with business license address via Baidu Maps API.
- Real-Time Production Evidence: Demand live footage of current crankshaft tester assembly (not generic machinery).
- Component Traceability: Insist on seeing raw materials (e.g., granite base plates, CMM-grade rails) with batch logs.
- Workforce Validation:
- Interview lead engineer on crankshaft dynamic balancing theory (reject if reliant on translator).
- Confirm ≥15 engineers with dedicated metrology experience (LinkedIn cross-check).
TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: DIFFERENTIATION TOOLKIT
78% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit).
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Itemized BOM + labor costs; MOQ ≥5 units | Flat FOB price; MOQ=1 unit | Request cost breakdown for custom inquiry |
| Facility Control | Owns land/building (check property deeds) | “Factory tour” at subcontractor site | Demand property ownership certificate (房产证) |
| Technical Staff Access | Direct access to R&D team; NDA for design files | “Engineers unavailable”; delays sharing specs | Schedule unscheduled Zoom call with engineering lead |
| Export Documentation | Invoice shows manufacturer as exporter | Invoice lists 3rd-party entity as exporter | Check exporter name on bill of lading |
| Quality Control | In-process QC checkpoints at assembly stages | “QC done by our partner” | Request QC records for current production batch |
Pro Tip: Ask for watermarked production footage dated within 72 hours. Trading companies cannot provide this.
TOP 5 RED FLAGS TO AVOID (CRANKSHAFT TESTER SPECIFIC)
Immediate disqualification criteria per SourcifyChina 2026 Risk Index.
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Why Critical for Crankshaft Testers | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| No CMC License | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | Illegal to sell in China; indicates non-compliant calibration | Demand CMC certificate via China Metrology Administration portal |
| “We make all testing equipment” | ⚠️⚠️ HIGH | Crankshaft testers require specialized vibration analysis expertise | Require references for crankshaft-specific projects only |
| Refuses to share calibration certs | ⚠️⚠️ HIGH | Metrology accuracy degrades without traceable calibration | Insist on seeing latest NIST-traceable certificate |
| Price 30% below market average | ⚠️ MEDIUM | Indicates recycled components or fake sensors | Demand sensor OEM documentation (e.g., HBM, Kistler) |
| No after-sales service in your region | ⚠️ MEDIUM | Testers require on-site recalibration; downtime = $15k/hr | Verify local service partner contracts |
RECOMMENDED ACTION PLAN
- Pre-Screen: Use QCC.com to validate business license scope against “testing equipment manufacturing.”
- Technical Gate: Require live demo of crankshaft journal measurement with error compensation.
- On-Site Audit: Conduct unannounced visit with metrology expert (budget $4,500–$7,200).
- Pilot Order: Start with 1 unit + 12-month calibration contract before scaling.
SourcifyChina Advisory: “In 2026, 92% of successful crankshaft tester partnerships began with CMC verification. Never compromise on metrology traceability – a 0.001mm error in crankshaft testing risks catastrophic engine failure.”
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Data sources: SAIC, CNAS, SourcifyChina Audit Database.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Advantage – Verified Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers in China
Executive Summary
In the highly specialized domain of engine diagnostics, crankshaft testers are critical capital equipment requiring precision engineering, reliability, and compliance with international standards. Sourcing these from China offers significant cost advantages—but only when partnered with the right manufacturers.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Pro List for China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers delivers a vetted, performance-qualified network of suppliers, eliminating the traditional risks and inefficiencies associated with overseas procurement.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Mitigates Risk
| Procurement Challenge | Without SourcifyChina | With SourcifyChina Pro List |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 40–80 hours of research, reference checks, and factory audits | Pre-qualified manufacturers with verified credentials, production capacity, and export history |
| Quality Assurance | Risk of substandard equipment; costly returns or rework | Factories audited for ISO standards, calibration accuracy, and after-sales support |
| Communication Barriers | Delays due to language gaps and time zone misalignment | English-speaking project managers and in-house technical liaisons streamline communication |
| Lead Time Reliability | Unverified production timelines and shipping delays | On-time delivery tracked via SourcifyChina’s supply chain monitoring system |
| Total Time to First Order | 3–6 months | As low as 4–6 weeks from inquiry to production start |
Time Saved: Up to 70% reduction in sourcing cycle duration.
Key Advantages of the 2026 Pro List
- ✅ 100% Factory-Verified – On-site audits conducted Q1 2026
- ✅ Specialization in Automotive Test Equipment – Focused expertise in crankshaft runout, balance, and deflection testing
- ✅ Export-Ready – All suppliers have proven experience shipping to EU, USA, and ASEAN markets
- ✅ Scalable Production – Capacity to fulfill pilot runs to annual volume contracts
- ✅ Compliance Support – CE, ISO 9001, and calibration documentation available
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Global procurement teams can no longer afford inefficient supplier discovery or costly quality failures. With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, you gain immediate access to trusted crankshaft tester manufacturers—reducing risk, cutting lead times, and ensuring ROI from day one.
Take the next step in supply chain optimization:
📧 Email us today at [email protected]
📱 Or connect instantly via WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants will provide:
– A custom shortlist of 3–5 matched manufacturers
– Pricing benchmarks and MOQ analysis
– Sample procurement timeline based on your volume needs
Don’t source blindly. Source with certainty.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Gateway to China’s Industrial Supply Chain.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


