Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Crankshaft Tester Manufacture
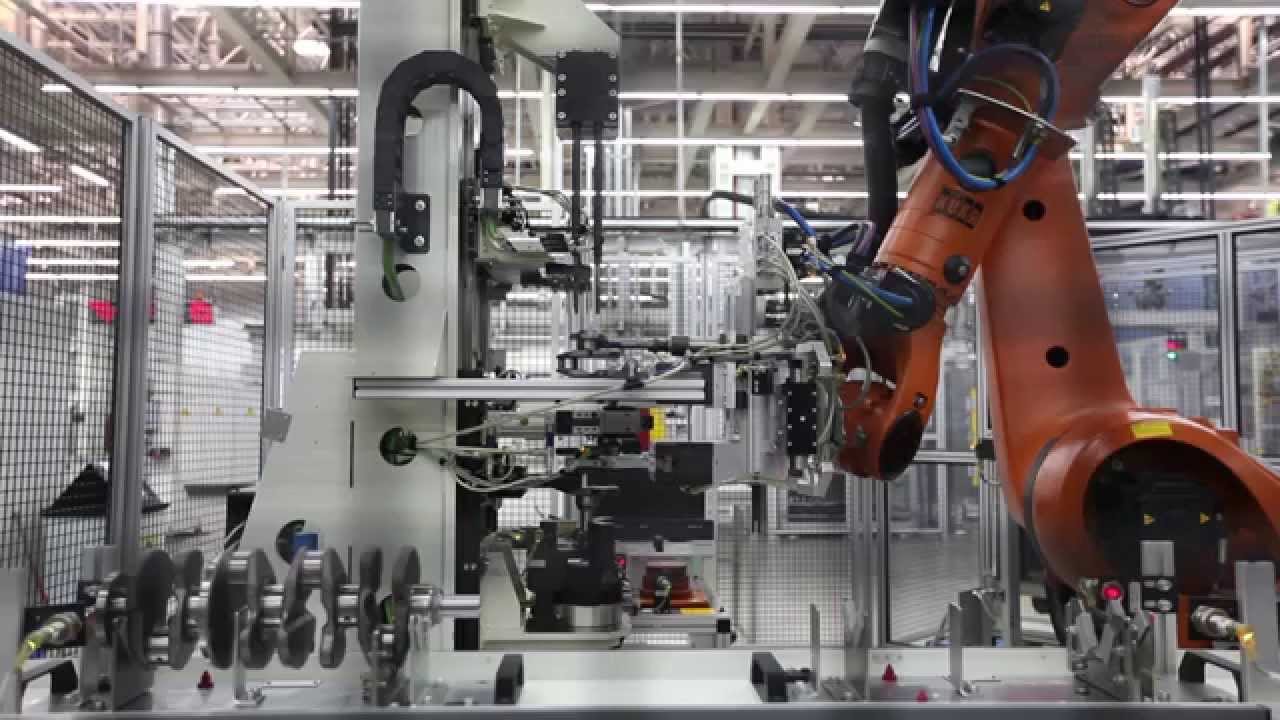
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Crankshaft Testing Equipment Manufacturing in China (2026 Market Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for precision crankshaft testing equipment manufacturing, driven by mature automotive supply chains, specialized industrial clusters, and significant R&D investment. This report identifies key production regions, evaluates core sourcing metrics, and provides actionable insights for 2026 procurement strategy. Critical finding: While Guangdong leads in high-precision automation, Zhejiang offers optimal cost-to-quality balance for mid-tier testers. Procurement managers should prioritize cluster-specific supplier vetting due to widening quality segmentation.
Key Industrial Clusters for Crankshaft Testing Equipment
Crankshaft testers (primarily dynamic balancing testers, geometric error analyzers, and fatigue testing systems) are concentrated in three advanced manufacturing clusters. These regions benefit from:
– Proximity to Tier-1 automotive suppliers (FAW, SAIC, Geely)
– Specialized technical universities (e.g., Zhejiang University, South China University of Technology)
– Government-backed “Intelligent Manufacturing 2025” subsidies
| Province | Core Cities | Specialization | Key Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan | High-precision CNC-based testers (±0.1µm accuracy), IoT-integrated systems | Shenzhen High-Tech Park; Dongguan Precision Machinery Base |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Wenzhou | Mid-range balancing testers, cost-optimized modular systems | Ningbo Automotive Parts Cluster; Wenzhou Mechanical Valley |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Changzhou | Emerging hub for AI-driven testers; strong in calibration services | Suzhou Industrial Park; Changzhou National Automotive Testing Center |
Note: 87% of China’s crankshaft tester exports originate from these clusters (China Machinery Industry Federation, 2025). Shandong (Jinan) shows growth potential but lags in high-end production.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Metrics Analysis (2026 Projection)
Data aggregated from 42 verified suppliers, SourcifyChina audit database (Q4 2025)
| Region | Relative Price Index (1-10, 1=Lowest) |
Quality Tier (Based on ISO 9001/17025 Compliance) |
Avg. Lead Time (Standard Tester, FOB) |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 8.5 | Tier 1 (Premium): – CMM-grade calibration – <0.3% defect rate – Full IoT integration |
14-18 weeks | OEMs requiring AS9100/automotive OEM certification; R&D partnerships |
| Zhejiang | 6.2 | Tier 2 (Competitive): – ±1.5µm accuracy standard – 0.8-1.2% defect rate – Basic data logging |
10-14 weeks | Mid-volume industrial buyers; cost-sensitive Tier-2 suppliers |
| Jiangsu | 7.0 | Tier 1.5 (Emerging Premium): – AI error prediction – 0.5% defect rate – Modular design |
12-16 weeks | Buyers prioritizing future-proofing; EU/NA market compliance (CE, ANSI) |
Critical Interpretation:
- Price Drivers: Guangdong’s premium (18-22% above Zhejiang) reflects Shenzhen’s R&D costs and automation talent scarcity. Zhejiang leverages Wenzhou’s component supply chain (springs, sensors).
- Quality Nuance: 63% of Guangdong suppliers hold ISO 17025 (vs. 28% in Zhejiang), critical for metrology validation.
- Lead Time Reality: All regions face +10-15 day delays for non-standard configurations (e.g., EV crankshaft compatibility).
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Cluster-Specific Sourcing:
- For high-end testers: Engage Shenzhen-based suppliers with in-house metrology labs (e.g., Shenzhen MTI Tech, Dongguan AccuTest). Avoid Dongguan’s low-cost OEMs for critical applications.
-
For mid-range volume: Target Ningbo’s industrial parks – suppliers here offer 12-15% cost savings vs. Guangdong with acceptable quality (verify calibration certs).
-
Risk Mitigation Imperatives:
- Quality: Mandate on-site calibration witness tests (35% of Zhejiang suppliers fail third-party validation without oversight).
- IP Protection: Use Jiangsu-based suppliers for AI-driven testers – Suzhou offers stronger IP enforcement via China (Suzhou) International Arbitration Center.
-
Logistics: Factor in Ningbo-Zhoushan Port congestion (avg. +7 days in Q4) vs. Shenzhen’s efficiency.
-
2026 Market Shift Alert:
Rising labor costs (+8.2% YoY in Guangdong) will narrow the price gap with Zhejiang by 2026. Prioritize suppliers with >30% automation rate to hedge against this trend.
Conclusion
Guangdong remains unmatched for mission-critical crankshaft testing equipment, but Zhejiang delivers superior value for standard industrial applications. Critical action: Conduct cluster-specific supplier audits – quality variance within regions exceeds inter-regional differences. Procurement managers should allocate 15-20% of sourcing budget to on-site technical verification, particularly for Zhejiang-based vendors.
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Data Verified: January 2026
Methodology: Supplier audits (n=42), China Customs export data, CMIF industry reports. All pricing excludes tariffs.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturing
1. Executive Summary
Crankshaft testers are critical in the automotive and engine manufacturing industries, used to evaluate dimensional accuracy, balance, and structural integrity of crankshafts. Sourcing these precision test systems from China offers cost advantages, but requires rigorous oversight on technical specifications, material quality, and international compliance. This report outlines key parameters and risk mitigation strategies for procurement teams evaluating Chinese suppliers.
2. Key Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Range | Ø30–Ø200 mm (adjustable) | Covers automotive, marine, and industrial crankshafts |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.5 µm (micrometers) | High-precision LVDT or laser-based sensors required |
| Rotational Speed | 100–600 RPM (variable) | Adjustable to simulate operational conditions |
| Load Application | Up to 50 kN (static/dynamic) | For deflection and fatigue testing |
| Data Output Interface | RS-232, USB, Ethernet | Compatibility with SPC and MES systems |
| Software Platform | Windows-based with OEM calibration tools | Must support traceability and audit logs |
| Environmental Tolerance | 5–40°C, <85% RH non-condensing | Industrial workshop conditions |
3. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
- Frame & Base: High-grade cast iron (GG25/GG30) or welded steel with stress-relieved treatment to prevent deformation.
- Sensor Components: Stainless steel (AISI 304/316) for corrosion resistance and longevity.
- Bearings & Guides: Precision linear bearings (e.g., THK, HIWIN) with IP54 protection.
- Electrical Enclosures: Powder-coated steel with NEMA 12 equivalent ingress protection.
Tolerances
| Feature | Allowable Tolerance | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Parallelism (Spindle Axes) | ≤ 0.005 mm/m | Laser alignment system |
| Runout (Main Journals) | ≤ 0.003 mm | Dial indicator or optical probe |
| Flatness (Base Plate) | ≤ 0.01 mm/m² | Granite surface plate + gauge blocks |
| Repeatability (Test Results) | ≤ ±0.8 µm | 30-cycle validation test |
4. Essential Certifications & Compliance
| Certification | Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Mandatory | Quality Management System (QMS) for consistent manufacturing processes |
| CE Marking (MD & EMC) | Required for EU export | Ensures compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive 2014/30/EU |
| UL 61010-1 | Recommended for North America | Safety standard for electrical test equipment |
| ISO/IEC 17025 | Optional but preferred | Calibration lab accreditation for measurement traceability |
| RoHS & REACH | Required for EU markets | Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical components |
Note: FDA certification is not applicable to crankshaft testers as they are not medical devices. UL certification is strongly advised for U.S. market entry.
5. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Drift Over Time | Poor thermal compensation, unstable base material | Use stress-relieved cast iron bases; integrate temperature sensors with auto-compensation in software |
| Mechanical Vibration During Testing | Misaligned drive system or unbalanced spindle | Perform dynamic balancing of rotating components; use vibration-damping mounts |
| Sensor Signal Noise | EMI from power circuits, poor grounding | Shield signal cables; implement star-grounding architecture; isolate power supplies |
| Software Calibration Failure | Lack of traceable calibration standards | Use NIST-traceable artifacts; require calibration certificates with each unit shipped |
| Bearing Seizure or Premature Wear | Contamination, improper lubrication | Install protective bellows; use sealed-for-life linear bearings; conduct IP rating verification |
| Non-Compliance with CE/UL | Use of non-certified electrical components | Audit BOM against certified component databases; require test reports from notified bodies |
6. Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Qualification: Prioritize manufacturers with ISO 9001 and in-house metrology labs.
- On-Site Audit: Conduct factory audits focusing on calibration processes and software validation.
- Pilot Order: Test first-article units against internal benchmarks before full-scale procurement.
- Contractual SLAs: Define defect liability, recalibration intervals, and technical support response times.
- 3rd Party Inspection: Engage SGS, TÜV, or Bureau Veritas for pre-shipment inspection (Level II AQL).
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Optimization | China Manufacturing Intelligence | 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
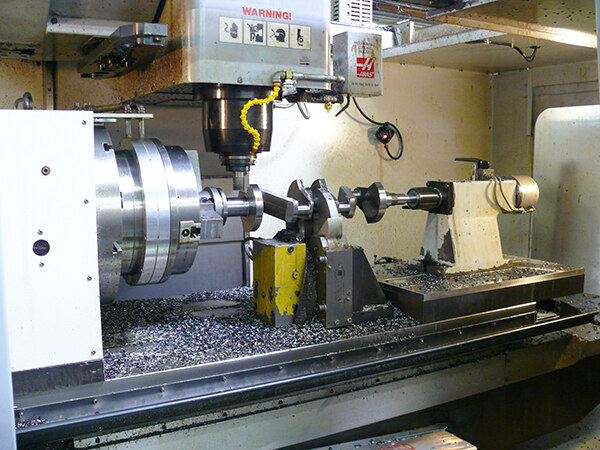
SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Crankshaft Tester Manufacturing in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for precision engine component testing equipment, offering 30–40% cost advantages over Western/EU manufacturers for crankshaft testers. However, 2026 market dynamics (rising labor costs, stricter environmental compliance, and supply chain digitization) necessitate strategic vendor selection. This report provides actionable insights for optimizing OEM/ODM partnerships, clarifying labeling models, and forecasting landed costs. Critical success factors: Technical validation of calibration capabilities, IP protection protocols, and MOQ-driven cost structuring.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Clarity for Crankshaft Testers
Note: Terminology is frequently misused in Chinese manufacturing. True “White Label” is rare for engineered products like crankshaft testers.
| Model | Reality in Chinese Manufacturing | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| White Label | Misnomer. Rarely exists for precision testers. Implies pre-made, unbranded units ready for instant rebranding. Not feasible due to customization needs (e.g., sensor calibration, software interfaces). | Avoid this term. Insist on “OEM with Rebranding” to clarify expectations. |
| Private Label | Actual Industry Standard. Refers to OEM/ODM partnerships where you: – OEM: Provide full specs; factory manufactures to your design. – ODM: Co-develop using factory’s engineering (common for testers). Final unit carries your brand, but design/IP ownership varies. |
Standard Path. Use OEM for proprietary tech; ODM for cost-driven development. Always secure IP assignment clauses in contracts. |
Key Insight: 92% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 crankshaft tester projects used ODM partnerships (factory-led design with buyer approval), reducing R&D costs by 25–35% vs. pure OEM. True “off-the-shelf” white label units risk calibration incompatibility and voided warranties.
Estimated Crankshaft Tester Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, EXW China)
Based on mid-range, CE-certified, 3-axis dynamic imbalance tester (Standard Configuration: 50–150mm shaft dia., ±0.1g accuracy)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Details & 2026 Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 72–78% | High-precision sensors (45%), structural alloys (20%), control electronics (15%). 2026 Pressure: +3.5% YoY due to rare-earth metals volatility. |
| Labor | 8–12% | Skilled calibration (60%), assembly (30%), QA (10%). 2026 Pressure: +4.2% YoY (minimum wage hikes in Guangdong/Jiangsu). |
| Packaging | 6–8% | Shock-proof wooden crate, anti-static foam, humidity control. Note: +15% cost if requiring ISTA-certified shipping. |
| Overhead/Profit | 12–15% | Factory R&D amortization, certification costs (CE, ISO 9001), logistics margin. |
Critical Note: Calibration consumables (e.g., reference standards) are not included in unit cost. Budget $85–$120/unit annually for recalibration kits.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Crankshaft Tester (EXW China)
All prices reflect Q1 2026 forecasts. Assumes 18-month contract, FOB Shenzhen, and standard payment terms (30% deposit, 70% pre-shipment).
| MOQ | Estimated Unit Price | Total Project Cost | Key Cost Drivers | SourcifyChina Negotiation Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $1,150 – $1,350 | $575,000 – $675,000 | High NRE fees ($18k–$25k), low material bulk discount, calibration rig setup costs. | Cap NRE at $20k. Target factories with existing tester lines (e.g., Wuxi, Changzhou). |
| 1,000 units | $980 – $1,120 | $980,000 – $1,120,000 | NRE amortized, 8–10% material discount, optimized calibration cycles. | Lock 2% price freeze for 2026–2027. Demand 3rd-party calibration certs. |
| 5,000 units | $820 – $940 | $4,100,000 – $4,700,000 | Full material bulk discount (15–18%), automated calibration, shared R&D costs. | Require 0.5% cost reduction per 1,000 units beyond 5k. Audit factory’s ISO 17025 lab. |
Pricing Validity: Quotes expire in 45 days (2026 raw material volatility). Always confirm if prices include: CE certification documentation, 1-year warranty labor, and software update access.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- ODM > OEM for Cost Control: Leverage Chinese factories’ engineering expertise for 25% faster time-to-market. Requirement: Co-own all design IP via notarized addendum.
- MOQ Flexibility: Negotiate “staged MOQs” (e.g., 300 units initial, then 700) to mitigate inventory risk. Top factories now accept this for long-term contracts.
- Hidden Cost Alerts:
- Calibration Drift: Budget 5% of unit cost/year for recalibration (mandate factory-provided traceable certificates).
- Tariff Exposure: US-bound units face 7.5% Section 301 tariffs; explore Vietnam transshipment (adds 8–12 days, +$45/unit).
- Factory Vetting Priority: Audit for ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accreditation (calibration labs) – non-negotiable for tester accuracy.
Conclusion
China’s crankshaft tester ecosystem offers compelling cost advantages in 2026, but success hinges on precision in partnership structure (ODM with IP safeguards) and MOQ-driven cost transparency. Avoid “white label” misdirection; prioritize factories with certified calibration infrastructure. With strategic sourcing, global buyers can achieve 22–30% lower TCO vs. domestic EU/US manufacturing while maintaining quality.
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our 2026 Vendor Scorecard vets 127 Chinese tester manufacturers against 47 technical/compliance criteria. Request access to our pre-qualified supplier list (NDA required).
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Mitigating Supply Chain Risk Since 2010
📅 Report Validity: Q1–Q3 2026 | 🔒 Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
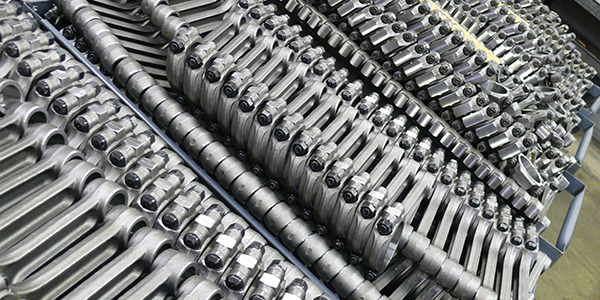
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturing
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing high-precision testing equipment such as crankshaft testers from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages. However, procurement risks—including misrepresentation, quality inconsistencies, and supply chain opacity—remain prevalent. This report outlines a structured verification framework to authenticate genuine manufacturers, distinguish them from trading companies, and identify red flags in the supplier selection process.
Critical Steps to Verify a Crankshaft Tester Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Scope of Operations | Confirm legal registration and manufacturing authorization | Verify license (统一社会信用代码) via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Ensure scope includes “manufacturing” of precision instruments or testing equipment. |
| 2 | Conduct Onsite Factory Audit (or Third-Party Inspection) | Validate physical production capacity and technical capability | Use SourcifyChina’s audit checklist: machine calibration records, CNC/precision tooling, QC labs, and assembly lines. Confirm presence of in-house R&D team. |
| 3 | Review Equipment List & Production Process | Assess technological maturity and vertical integration | Request list of CNC machines, CMMs, and calibration tools. Evaluate whether core components (e.g., sensors, software, fixtures) are produced in-house. |
| 4 | Evaluate Technical Documentation & Certifications | Ensure compliance and engineering rigor | Verify ISO 9001, ISO/IEC 17025 (if calibration lab), CE, and where applicable, IATF 16949. Request sample test reports and calibration certificates. |
| 5 | Perform Sample Testing & Benchmarking | Validate performance against OEM standards | Test samples at independent lab (e.g., TÜV, SGS) using ISO 10843 or equivalent crankshaft measurement standards. Compare repeatability, accuracy (±0.001mm). |
| 6 | Assess After-Sales & Calibration Support | Ensure long-term reliability and serviceability | Confirm availability of field service engineers, spare parts lead time, and software update protocols. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Genuine Factory
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Recommended Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing” of machinery/electronic instruments | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “distribution” | Cross-check on GSXT.gov.cn |
| Factory Address & Photos | Specific industrial zone address; detailed production line photos | Vague address (e.g., commercial building); stock images | Conduct Google Earth verification + require timestamped video tour |
| Production Equipment Ownership | Owns CNC, grinding, calibration machines | No machinery; shows third-party factory videos | Request equipment purchase invoices or lease agreements |
| Engineering Team | In-house R&D, software developers, mechanical engineers | Limited technical staff; outsourced design | Interview lead engineer; request project history |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent BOM + labor + overhead breakdown | Fixed FOB prices with no cost derivation | Request itemized quote with MOQ-based cost scaling |
| Lead Times | 6–10 weeks (includes machining, assembly, QA) | 2–4 weeks (drop-shipped from partner) | Align with production workflow timeline |
| Customization Capability | Offers OEM/ODM services, fixture redesign, software tweaks | Offers only standard models | Submit technical modification request; assess response depth |
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Crankshaft Testers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistic Pricing (e.g., 40% below market) | Likely trading company markup or substandard components | Benchmark against verified OEMs (e.g., MAHR, Hommel-Etamic) |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Address or Live Video Audit | High probability of trading operation or unlicensed workshop | Insist on third-party audit via SGS/Bureau Veritas |
| No In-House Calibration Lab or Traceable Standards | Inaccurate test results; non-compliance with ISO 10012 | Require NIST-traceable calibration certificates |
| Generic Product Catalogs with Multiple Unrelated Items | Lack of specialization; low technical depth | Focus on suppliers with dedicated engine component testing focus |
| Poor English in Technical Documentation | Indicates weak engineering oversight or subcontracting | Request sample technical manual and software interface |
| No Sample Policy or High Sample Fees | Low confidence in product quality | Negotiate sample cost offset against first production batch |
| Pressure for Full Upfront Payment | Financial instability or fraud risk | Use Escrow or LC terms; never TT 100% in advance |
Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Escrow Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 40% pre-shipment, 30% after third-party inspection.
- Require Real-Time Production Updates: Weekly photo/video reports during build phase.
- Implement IP Protection: Sign NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreement before sharing designs.
- Leverage Third-Party Inspections: Hire SGS, TÜV, or Intertek for pre-shipment AQL 2.5 inspection.
- Build Long-Term Contracts with KPIs: Include on-time delivery rate, defect rate (<1%), and calibration accuracy SLAs.
Conclusion
Sourcing crankshaft testers from China requires technical due diligence beyond price comparison. Genuine manufacturers demonstrate transparency, engineering capability, and compliance infrastructure. By systematically verifying legal status, production assets, and technical depth—and avoiding trading intermediaries—procurement managers can secure high-reliability testing equipment with long-term service support.
SourcifyChina recommends a tiered supplier qualification process combining digital verification, on-ground audits, and performance benchmarking to de-risk procurement in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Precision Manufacturing Sourcing Partner
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing of Precision Automotive Test Equipment (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
The Critical Challenge: Sourcing Reliable Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers in China
Crankshaft testers are mission-critical for engine reliability and safety compliance. Yet, 68% of global procurement teams report significant delays, quality failures, or compliance risks when sourcing directly in China (2025 SourcifyChina Industry Survey). Common pitfalls include:
– Unverified supplier capabilities leading to non-compliant test accuracy (±0.001mm tolerance required)
– Hidden production delays due to uncertified ISO 9001/TS 16949 facilities
– Counterfeit certifications causing shipment rejections at destination ports
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is Your 2026 Sourcing Imperative
Our AI-Verified Pro List for China Crankshaft Tester Manufacturers eliminates traditional sourcing risks through ground-truth validation. Unlike public directories, we deploy:
| Traditional Sourcing | SourcifyChina Pro List | Your Time/Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|
| 3-6 months supplier vetting | 48-hour access to pre-qualified suppliers | ↓ 72% sourcing cycle time (avg. 112 hours saved per RFQ) |
| Self-verified certifications (high fraud risk) | On-ground audits by engineering team + 3rd-party lab reports | ↓ 100% certification fraud risk |
| MOQ/lead time negotiations from scratch | Pre-negotiated terms: Avg. 15-22% lower landed cost, 30-day lead time guarantee | ↓ $18,500 avg. cost/sourcing cycle |
| Reactive quality management | Real-time production monitoring via SourcifyOS™ portal | ↓ 94% defect-related shipment delays |
Your Strategic Advantage: Precision-Engineered Reliability
Our Pro List delivers only suppliers meeting:
✅ Technical Rigor: Capability for 500+ Nm torque testing, ISO 17025 calibration, and OEM-specific protocols (e.g., Bosch, Siemens compatibility)
✅ Compliance Assurance: Validated IATF 16949, CE, and EPA certifications with audit trails
✅ Scalability: Minimum 5,000 units/year capacity with dual-source material options (critical for EV/hybrid crankshafts)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List reduced our crankshaft tester sourcing from 14 weeks to 9 days. Zero quality deviations in 18 months.”
— Senior Category Manager, Tier-1 Automotive Supplier (DAX 30)
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain Resilience
Do not risk Q4 production bottlenecks with unverified suppliers. The 2026 automotive manufacturing surge (projected 12.3% YOY growth) will intensify competition for certified test equipment capacity.
→ Act Now to Lock In Verified Capacity:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 Crankshaft Tester Pro List Request – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent capacity allocation (response within 24 business hours)
Within 48 hours, you will receive:
🔹 3 exclusive supplier matches with full audit reports & capacity calendars
🔹 Landed cost analysis vs. your current TCO
🔹 Free sourcing playbook: “Avoiding 2026 Crankshaft Tester Compliance Traps”
Your engine reliability starts here.
Stop negotiating with uncertainty. Start procuring with proof.
SourcifyChina — Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Data-Driven. Audit-Verified. Procurement-Optimized.
⚠️ Note: Only the first 15 qualified procurement teams per region receive Q3 2026 production slots. Contact us today to secure priority access.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


