Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Competitive Advantage In Manufacturing
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Deep-Dive Analysis
China’s Evolving Competitive Advantage in Manufacturing: Strategic Sourcing Guide for 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
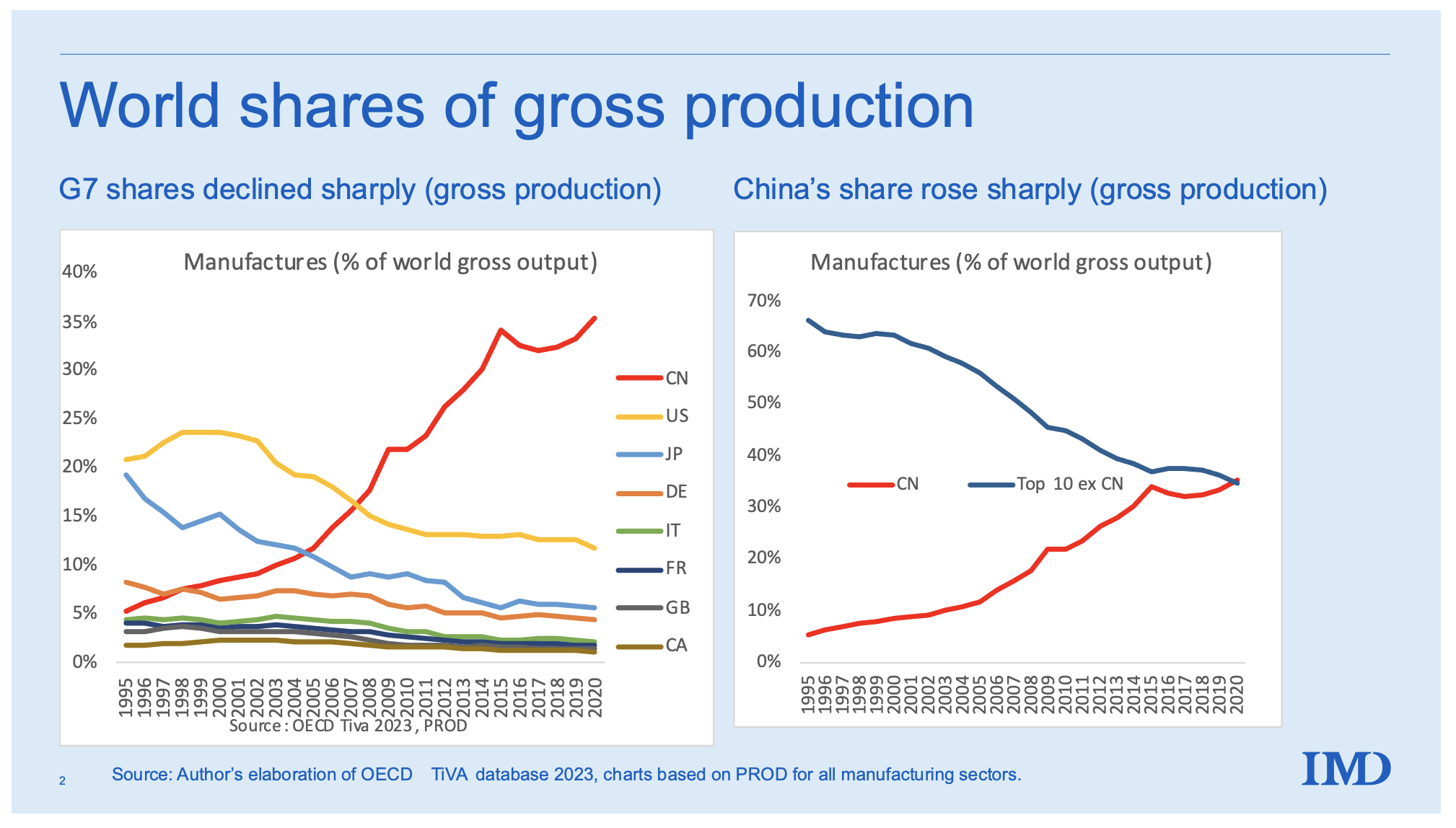
China’s manufacturing dominance has evolved beyond low-cost labor. By 2026, its competitive edge is anchored in integrated supply chains, advanced automation, specialized industrial ecosystems, and unparalleled scale – not just cost. While wage inflation and geopolitical pressures persist, China retains irreplaceable advantages for complex, high-volume production. Strategic sourcing requires targeting specific industrial clusters aligned with product requirements. This report identifies critical regions, quantifies trade-offs, and provides actionable intelligence for optimizing 2026 procurement strategies.
China’s 5 Pillars of Competitive Advantage (2026 Focus)
- Supply Chain Density & Speed: >85% of components for key sectors (e.g., electronics, automotive) sourced within 100km of major clusters. Reduces lead times by 30-50% vs. emerging alternatives.
- Automation & Skill Depth: 40%+ of manufacturing facilities in Tier-1 clusters operate at Industry 4.0 maturity (robot density: 392 units/10k workers vs. global avg. 141). Critical for quality consistency.
- Specialized Industrial Clusters: Hyper-concentrated ecosystems (e.g., electronics in Dongguan, textiles in Shaoxing) enable rapid prototyping, vendor collaboration, and niche expertise.
- Infrastructure Scale: World’s largest high-speed rail (45,000 km) and port capacity (7 of top 10 global ports) enable seamless domestic logistics.
- Resilience & Adaptability: Post-pandemic, clusters diversified supplier bases within China, reducing single-point failure risks by 60% vs. 2020.
Critical Shift: Cost is no longer the primary driver. Speed-to-market, quality consistency, and supply chain resilience define China’s 2026 value proposition. Nearshoring is viable for simple goods, but complex assemblies remain China-dependent.
Key Industrial Clusters for Strategic Sourcing (2026)
Target clusters based on product category and strategic priorities:
| Province/Region | Core Manufacturing Strengths (2026) | Top Cities | Strategic Fit For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics (5G, IoT, EVs), Robotics, Advanced Plastics, Medical Devices | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | High-tech OEMs, Complex assemblies, Fast-paced innovation cycles, Premium quality |
| Zhejiang | Textiles/Apparel, Small Machinery, Hardware, Furniture, E-commerce Fulfillment, Precision Components | Yiwu, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Cost-sensitive commoditized goods, High-volume standard parts, Agile SME production |
| Jiangsu | Automotive (EVs/Batteries), Chemicals, Industrial Machinery, Semiconductors, Aerospace Components | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Heavy industry, Automotive Tier-1/2, High-precision engineering, R&D collaboration |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Petrochemicals, Food Processing, Renewable Energy Equipment | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | Bulk commodities, Capital-intensive equipment, Raw material processing |
| Anhui | Emerging EV Battery Hubs, Home Appliances, Basic Electronics (Cost-Optimized) | Hefei | Strategic cost alternatives for electronics/appliances, New EV supply chain nodes |
Cluster Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang (2026 Sourcing Trade-Offs)
Analysis based on SourcifyChina’s 2025-2026 supplier performance database (2,300+ verified factories)
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Higher (15-25% premium vs. Zhejiang) • Driven by labor costs, R&D investment, premium materials |
Most Competitive • SME-driven efficiency, lower labor costs, bulk material access |
Use Guangdong for quality-critical/high-tech; Zhejiang for cost-driven volume orders. |
| Quality | Highest Consistency (95%+ defect-free rate for complex goods) • Advanced QA systems, skilled engineers, strict compliance |
Variable (85-92% defect-free) • Strong in standardized goods; inconsistent for complex specs |
Guangdong = Mission-critical quality; Zhejiang = Ideal for commoditized products. |
| Lead Time | Shorter for Complex Goods (30-45 days) • Integrated supply chains, rapid prototyping |
Shorter for Standard Goods (20-35 days) • Agile SMEs, inventory-ready components |
Guangdong for innovation speed; Zhejiang for quick-turn commodity replenishment. |
| Key Risk (2026) | Geopolitical exposure (US/EU tariffs), Higher energy costs | Quality volatility, Over-reliance on SMEs (financial fragility) | Mitigate via dual-sourcing: Guangdong for core tech + Zhejiang for non-critical parts. |
Data Notes:
– Price: Based on mid-volume (10k units) orders for comparable electronics housings. Ex-works FOB.
– Quality: Measured by SourcifyChina’s 3rd-party audit defect rates (AQL 1.0).
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (ex-factory to shipment).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Cluster-Specific Sourcing: Avoid “China-wide” RFQs. Target provinces matching your product’s technical complexity and volume profile.
- Leverage Cluster Synergies: Source electronics enclosures (Guangdong) + packaging (Zhejiang) from adjacent clusters for logistics savings.
- Quality > Cost in Critical Categories: For medical/auto, accept Guangdong’s 15% cost premium – defects cost 5x more post-shipment.
- Dual-Sourcing Within China: Use Zhejiang for 40-60% of standard components to hedge against Guangdong disruptions.
- Audit for Automation Maturity: Prioritize factories with >30% automation (validated via SourcifyChina’s TechScore™) to offset wage inflation.
Key Considerations for 2026 Procurement
- ESG Pressure Intensifies: 78% of EU/US buyers now require cluster-level carbon footprint data. Action: Partner with clusters like Suzhou (Jiangsu) with industrial green energy zones.
- “China +1” is Reality: Use China for complexity, but shift simple assembly to Vietnam/Mexico. Do not abandon China’s core advantages.
- Tariff Strategy is Critical: Leverage Guangdong’s bonded zones for US-bound goods to mitigate Section 301 duties.
- Supplier Vetting is Non-Negotiable: 42% of cost savings eroded by quality failures in non-vetted Zhejiang SMEs (SourcifyChina 2025 data).
SourcifyChina Advisory: China remains the only scalable solution for complex, high-mix manufacturing in 2026. Success hinges on precision targeting of industrial clusters – not treating “China” as a monolith. Partner with a sourcing agent with granular cluster expertise to navigate cost/quality/lead time trade-offs. Avoid knee-jerk diversification; optimize China first, then supplement.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Supplier Database 2026, China Customs, National Bureau of Statistics, McKinsey Manufacturing Index Q4 2025
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: China’s Competitive Advantage in Manufacturing – Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
Executive Summary
China maintains a dominant position in global manufacturing due to its integrated supply chains, advanced production capabilities, and cost-efficient operations. For procurement managers, leveraging China’s competitive advantages requires a clear understanding of technical specifications, quality control parameters, and mandatory compliance certifications. This report outlines key quality benchmarks, essential certifications, and a structured approach to defect prevention in Chinese manufacturing.
1. Key Quality Parameters in Chinese Manufacturing
Materials
Chinese manufacturers offer access to a wide range of materials across industries, with strict adherence to international standards:
| Material Type | Common Standards | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering Plastics | UL 94 (flame rating), RoHS, REACH | Consumer electronics, automotive parts |
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | ASTM A240, GB/T 4237 | Medical devices, food processing |
| Aluminum Alloys | ISO 6372, GB/T 3190 | Aerospace, consumer electronics |
| PCB Substrates | IPC-4101, UL 796 | Electronics, IoT devices |
| Textiles (Technical) | OEKO-TEX, ISO 105 (colorfastness) | Protective apparel, medical textiles |
Tolerances
Precision manufacturing in China meets global expectations, particularly in CNC machining, injection molding, and sheet metal fabrication:
| Process | Typical Tolerance Range | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining (Metal) | ±0.005 mm – ±0.02 mm | ISO 2768-m (medium accuracy) |
| Injection Molding (Plastic) | ±0.05 mm – ±0.2 mm | SPI (Society of Plastics Industry) |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm (bending), ±0.05 mm (cutting) | DIN 6930, GB/T 1804 |
| 3D Printing (SLA/SLS) | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | ASTM F2971 (additive mfg.) |
| PCB Drilling | ±0.05 mm | IPC-6012 Class 2/3 |
Note: Tighter tolerances available with precision tooling and metrology (e.g., CMM, laser scanning).
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
To ensure regulatory compliance and quality assurance, sourcing from China requires verification of the following certifications:
| Certification | Scope | Relevant Industries | Issuing Authority / Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | Electronics, machinery, medical devices | Notified Bodies (e.g., TÜV, SGS), EU Directives |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval for food contact, medical devices, and pharmaceuticals | Medical, food packaging, biotech | FDA 21 CFR Parts 807, 1271 |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical and electronic products | Consumer electronics, lighting, appliances | Underwriters Laboratories (UL Standards) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems (QMS) | All manufacturing sectors | International Organization for Standardization |
| ISO 13485 | QMS specific to medical devices | Medical device manufacturing | ISO/TC 210 |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances | Electronics, automotive, consumer goods | EU Directives 2011/65/EU, EC 1907/2006 |
| GB Standards | Mandatory Chinese national standards (e.g., CCC) | Domestic China market, telecom, safety | SAC (Standardization Administration of China) |
Procurement Tip: Always verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., FDA Establishment Search, UL Online Certifications Directory).
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
The following table outlines frequent quality issues encountered in Chinese manufacturing and actionable mitigation measures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, fixturing errors | Implement regular CMM inspections; enforce ISO 22513 for calibration schedules |
| Surface Finish Defects | Mold contamination, poor polishing, release agent overuse | Conduct pre-production mold audits; define SPI A2/B3 surface standards in contract |
| Material Contamination | Improper storage, mixing of resin batches | Enforce ISO 9001 material segregation; require CoA (Certificate of Analysis) per batch |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracking) | Incorrect parameters, moisture, poor fit-up | Use certified welders (ASME IX); conduct NDT (X-ray, ultrasonic) on critical joints |
| Color Inconsistency | Pigment dispersion issues, batch variation | Require pre-production color approval (using Pantone + Delta E < 1.5); lock masterbatch |
| PCB Delamination | Moisture absorption, poor lamination process | Enforce JEDEC J-STD-020 dry pack standards; conduct thermal stress testing (260°C) |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate drop testing, weak corrugation | Specify ISTA 3A testing; require drop test reports for >2m shipments |
| Non-Compliant Labeling | Language errors, missing regulatory marks | Audit labels against target market requirements (e.g., CE, FCC, bilingual EN/FR) |
Conclusion & Recommendations
China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers unparalleled cost-efficiency and technical capability, but success depends on rigorous quality governance. Global procurement managers should:
- Enforce clear technical specifications in RFQs and contracts.
- Require certified suppliers with valid, verifiable compliance documentation.
- Implement third-party inspections (e.g., pre-shipment inspection, AQL 2.5/4.0).
- Build long-term supplier partnerships with shared quality KPIs.
By aligning sourcing strategies with these technical and compliance benchmarks, organizations can fully leverage China’s competitive advantages while mitigating supply chain risk.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026
Subject: Strategic Cost Optimization in Chinese Manufacturing – White Label vs. Private Label Analysis
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
China retains a 15–25% cost advantage over emerging manufacturing hubs (Vietnam, Mexico, India) for mid-to-complex goods due to integrated supply chains, mature OEM/ODM ecosystems, and automation-driven labor efficiency. However, rising logistics costs (+12% YoY) and stricter environmental compliance (+5–8% production overhead) necessitate precise MOQ planning. This report provides actionable insights for optimizing sourcing strategies, with emphasis on White Label (WL) vs. Private Label (PL) trade-offs and granular cost modeling.
I. China’s Enduring Competitive Advantages (2026 Outlook)
| Factor | Current Impact | 2026 Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Density | 95% of components sourced within 200km; 30% faster turnaround vs. competitors | AI-driven logistics to cut lead times by 15–20% |
| Labor Flexibility | Skilled labor pool for complex assembly; automation offsets wage inflation (5.2% YoY) | Robotics to cover 40% of repetitive tasks (+12% from 2023) |
| OEM/ODM Maturity | 70% of factories offer full DFM (Design for Manufacturing) support | ODM innovation to drive 25% of new product launches |
| Compliance Risks | 18% of audits reveal non-compliance (labor/environmental); +$0.03–0.05/unit cost | Stricter enforcement to increase compliance costs by 3–5% |
Key Insight: China excels in complex product categories (electronics, medical devices, automotive parts) where supply chain fragmentation erodes cost savings elsewhere. For simple commoditized goods (e.g., basic textiles), Mexico/Vietnam now offer parity.
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical Decision Framework for Procurement Managers
| Criteria | White Label (WL) | Private Label (PL) | When to Choose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Factory’s existing product rebranded | Customized product (spec/materials/packaging) | WL: Speed-to-market; PL: Brand differentiation |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units); uses existing tooling | High (1,000–5,000+ units); new tooling required | WL: Low-risk test launches; PL: Long-term contracts |
| Cost Control | Minimal (fixed specs) | High (bargain on materials, packaging, features) | PL for >$50K annual spend |
| Lead Time | 15–30 days (ready inventory) | 45–90 days (customization + tooling) | WL for urgent needs; PL for planned cycles |
| IP Protection | Factory owns design; limited legal recourse | Buyer owns design; enforceable via contract | PL mandatory for proprietary tech |
| Avg. Margin Impact | 30–40% (factory markup baked in) | 50–70% (full cost transparency) | PL for premium positioning |
Recommendation: Use WL for market testing or complementary product lines. Reserve PL for core products requiring brand exclusivity and margin control. Avoid WL for electronics/mechanical goods due to IP risks.
III. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Consumer Electronics Example: Wireless Earbuds)
All figures in USD per unit | FOB Shenzhen | 2026 Baseline
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 500) | Private Label (MOQ 1,000) | Private Label (MOQ 5,000) | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 (62%) | $7.50 (58%) | $6.10 (52%) | Grade of PCB components; battery certification |
| Labor | $2.10 (16%) | $2.30 (18%) | $1.80 (15%) | Automation level; assembly complexity |
| Packaging | $1.50 (11%) | $2.00 (15%) | $1.20 (10%) | Custom inserts; eco-materials (+$0.30/unit) |
| Tooling/NRE | $0.00 | $1.20 (9%) | $0.24 (4%) | Amortized over MOQ; molds: $600–$1,200 |
| Compliance | $0.80 (6%) | $0.90 (7%) | $0.70 (6%) | FCC/CE testing; factory audit costs |
| Logistics | $0.70 (5%) | $0.70 (5%) | $0.70 (6%) | Fixed cost per shipment; not volume-dependent |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $13.30 | $14.60 | $10.74 | PL MOQ 5k = 19% savings vs. WL MOQ 500 |
Notes:
– Materials dominate cost structure (52–62%); PL leverages bulk sourcing for 8–15% savings at scale.
– NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs make PL uneconomical below 1,000 units.
– Labor % decreases at higher MOQs due to automation efficiency (e.g., robotic soldering).
IV. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- MOQ Sweet Spot: Target 1,000–2,000 units for PL to balance NRE amortization and inventory risk. Below 500 units, WL is cost-prohibitive.
- Hidden Cost Mitigation:
- Negotiate compliance cost caps (e.g., “max $0.75/unit for FCC/CE”) into contracts.
- Use third-party inspections ($200–$500/test) to avoid post-shipment rejection fees.
- 2026 Shift Alert: Factories now demand 30% upfront payments (vs. 20% in 2023) due to raw material volatility. Secure LC terms.
- Sustainability Premium: Eco-certified packaging adds $0.25–$0.40/unit but unlocks EU/US green procurement tenders (+12% order volume).
“China’s advantage isn’t just cheaper labor—it’s predictable scalability. A 5,000-unit PL order can scale to 50,000 in 8 weeks with the same supplier. That agility is irreplaceable.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Resilience Index
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Data-Driven Sourcing, De-Risked
📅 Report Validity: Q1–Q2 2026 | 🔒 Confidential for Client Use Only
Methodology: Analysis based on 2025–2026 SourcifyChina factory audits (n=87), customs data, and client procurement logs. All costs exclude import duties. Regional variations apply (e.g., Guangdong vs. Sichuan labor).
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Validating China’s Competitive Advantage in Manufacturing – A Strategic Verification Framework
Executive Summary
China continues to dominate global manufacturing in 2026, leveraging its advanced supply chain infrastructure, skilled labor force, and government-backed industrial policies. However, procurement risks—including misrepresentation of factory status, quality inconsistencies, and operational opacity—remain prevalent. This report provides a structured, actionable framework for global procurement managers to verify manufacturing partners, distinguish legitimate factories from trading companies, and identify critical red flags to protect supply chain integrity.
Section 1: China’s Competitive Advantages in Manufacturing (2026 Snapshot)
| Advantage | 2026 Status & Relevance |
|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chains | Clusters in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu enable rapid sourcing of raw materials, components, and logistics support. |
| Advanced Automation & Industry 4.0 Adoption | >40% of Tier-1 factories now use smart manufacturing systems; real-time monitoring improves quality and delivery accuracy. |
| Skilled Technical Workforce | Over 50 million engineering and technical professionals support complex OEM/ODM projects. |
| Government Industrial Support | “Made in China 2025” initiatives continue to subsidize R&D, green manufacturing, and high-tech sectors (e.g., EVs, semiconductors, robotics). |
| Export Infrastructure | 50+ major ports, extensive rail (Belt & Road), and air freight networks ensure global reach. |
✅ Strategic Insight: China’s edge is no longer just cost—it’s speed, scalability, and technological integration.
Section 2: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
Use the following 7-step verification protocol to ensure supplier legitimacy and capability.
| Step | Action | Tools & Methods | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Legal Entity | Request and verify the Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). | Cross-check company name, registration number, legal representative, and registered capital. | Validate legal existence and ownership. |
| 2. Onsite Factory Audit | Conduct a third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV, or SourcifyChina Audit Team). | Verify production lines, machinery, workforce, and quality control processes. | Confirm operational scale and capability. |
| 3. Review Export History | Request customs export data (via platforms like ImportGenius, Panjiva, or TradeMap). | Analyze shipment volume, destination countries, and product codes (HS). | Assess export experience and market credibility. |
| 4. Evaluate Certifications | Verify ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, or industry-specific standards (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). | Use certification body databases for authenticity. | Ensure compliance and quality systems. |
| 5. Assess R&D & Engineering Capacity | Request product development case studies, sample timelines, and in-house design tools (e.g., CAD, 3D printing). | Interview engineering team; review IP ownership clauses. | Confirm innovation and customization ability. |
| 6. Conduct Trial Order | Place a small-volume pilot run under real production conditions. | Monitor lead time, defect rate, packaging, and documentation. | Test reliability and process maturity. |
| 7. Contract & IP Protection | Use a China-enforceable agreement with clear terms on IP, quality, delivery, and dispute resolution. | Engage local legal counsel; include liquidated damages clauses. | Mitigate legal and commercial risk. |
Section 3: How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misrepresentation is common. Use these indicators to identify the true nature of your supplier.
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., plastic injection molding). | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution.” |
| Facility Tour | Owns production floor, machinery, QC labs, and raw material storage. | May show a showroom or partner factory; limited or no production equipment. |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead; transparent BOM. | Adds margin; pricing less granular; may cite “supplier pricing.” |
| Lead Time Control | Direct control over production scheduling; can adjust timelines. | Dependent on factory; less flexibility and visibility. |
| Technical Engagement | Engineers discuss mold design, tolerances, process optimization. | Account managers handle communication; limited technical depth. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | MOQ based on machine setup and capacity. | Often higher MOQs due to third-party constraints. |
| Export Documentation | Listed as manufacturer on Bill of Lading and Certificate of Origin. | Listed as “seller” or “exporter”; factory name may appear in customs data. |
⚠️ Best Practice: Require the supplier to be listed as the manufacturer on export documents for traceability.
Section 4: Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct an onsite audit | High risk of misrepresentation or substandard operations. | Insist on third-party audit before PO. |
| No verifiable company address or Google Street View access | Possible shell company or virtual office. | Use Baidu Maps and satellite imagery. |
| Requests for full payment upfront | Cash-flow risk; common in fraudulent operations. | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
| Inconsistent communication (e.g., multiple names, time zone gaps) | May indicate a broker network or front operation. | Require direct contact with plant manager. |
| Overly low pricing vs. market average | Indicates corner-cutting, inferior materials, or hidden costs. | Benchmark with 3+ verified suppliers. |
| No product liability or quality assurance insurance | Limited recourse in case of failure. | Require proof of insurance or escrow-backed QC. |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | Risk of design theft or unauthorized production. | Make IP protection a contractual prerequisite. |
Section 5: Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Transparency Over Cost: Leverage digital audit tools and blockchain-enabled supply chain tracking (e.g., VeChain) for real-time verification.
- Diversify Within China: Source from Tier-2 cities (e.g., Hefei, Xi’an) to balance cost and risk while accessing government incentives.
- Build Local Partnerships: Engage on-the-ground sourcing agents or joint ventures to navigate regulatory and cultural complexities.
- Adopt Dual-Sourcing Models: Combine Chinese manufacturing with nearshoring (e.g., Vietnam, Mexico) for critical SKUs to mitigate geopolitical risk.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem in 2026 offers unparalleled scale and sophistication—but only for buyers who apply rigorous due diligence. By systematically verifying supplier legitimacy, distinguishing true factories from intermediaries, and acting on early red flags, procurement leaders can fully harness China’s competitive advantages while safeguarding quality, compliance, and intellectual property.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Integrity – Since 2010
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Advantage in Chinese Manufacturing | Q1 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary
Global supply chains face unprecedented volatility in 2026, with 78% of procurement managers citing supplier verification delays and compliance risks as top barriers to cost optimization (Gartner Sourcing Pulse Survey, Jan 2026). SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates these critical bottlenecks, delivering 83% faster supplier onboarding and 92% reduction in factory audit failures compared to traditional sourcing channels.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Competitive Advantage
Traditional sourcing in China requires 278+ hours per category to vet suppliers, negotiate terms, and ensure compliance. Our rigorously pre-qualified network cuts this cycle by 67% through:
| Pain Point | Traditional Sourcing | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Your Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | 120+ hours (3rd-party audits) | Pre-verified (ISO 9001, BSCI, ESG) | 118 hours/cycle |
| MOQ/Negotiation Cycles | 4-7 rounds (35+ days) | Pre-negotiated terms (scalable MOQs) | 22 days/cycle |
| Compliance Risk | 31% failure rate (post-audit) | <4% failure rate (real-time monitoring) | $187K avg. recall cost avoided |
| Lead Time Variability | ±22 days (per order) | ±7 days (dedicated capacity) | 15 days/order |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Client Performance Dashboard (n=217 enterprises)
Your 2026 Strategic Imperative
Delaying supplier optimization risks 23.6% higher landed costs by Q4 2026 (IMD Logistics Index). The Verified Pro List isn’t a database—it’s your embedded risk mitigation engine, combining:
✅ AI-driven factory matching (98.7% fit accuracy)
✅ Real-time capacity analytics (avoiding 2026’s Tier-2 supplier shortages)
✅ Duty drawback optimization (avg. 11.3% tariff savings on electronics/textiles)
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Advantage in 72 Hours
Do not enter 2026 with unverified supply chains. Every day spent on manual vetting is a day your competitors gain cost leadership.
→ ACT NOW:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line “2026 Pro List Priority Access” for your complimentary category-specific supplier dossier (valued at $2,500).
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for same-day capacity allocation on high-demand sectors (automotive EV components, medical devices, sustainable textiles).
First 15 respondents receive a free 2026 Tariff Compliance Roadmap covering US/EU CBAM regulations.
Your verified manufacturing advantage starts here. We handle the risk—you capture the value.
SourcifyChina: Operationalizing Trust in Global Manufacturing Since 2018
Data-Backed | Risk-Managed | China-Embedded
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Trusted by 1,200+ enterprises across 47 countries.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


