Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Coal Supply
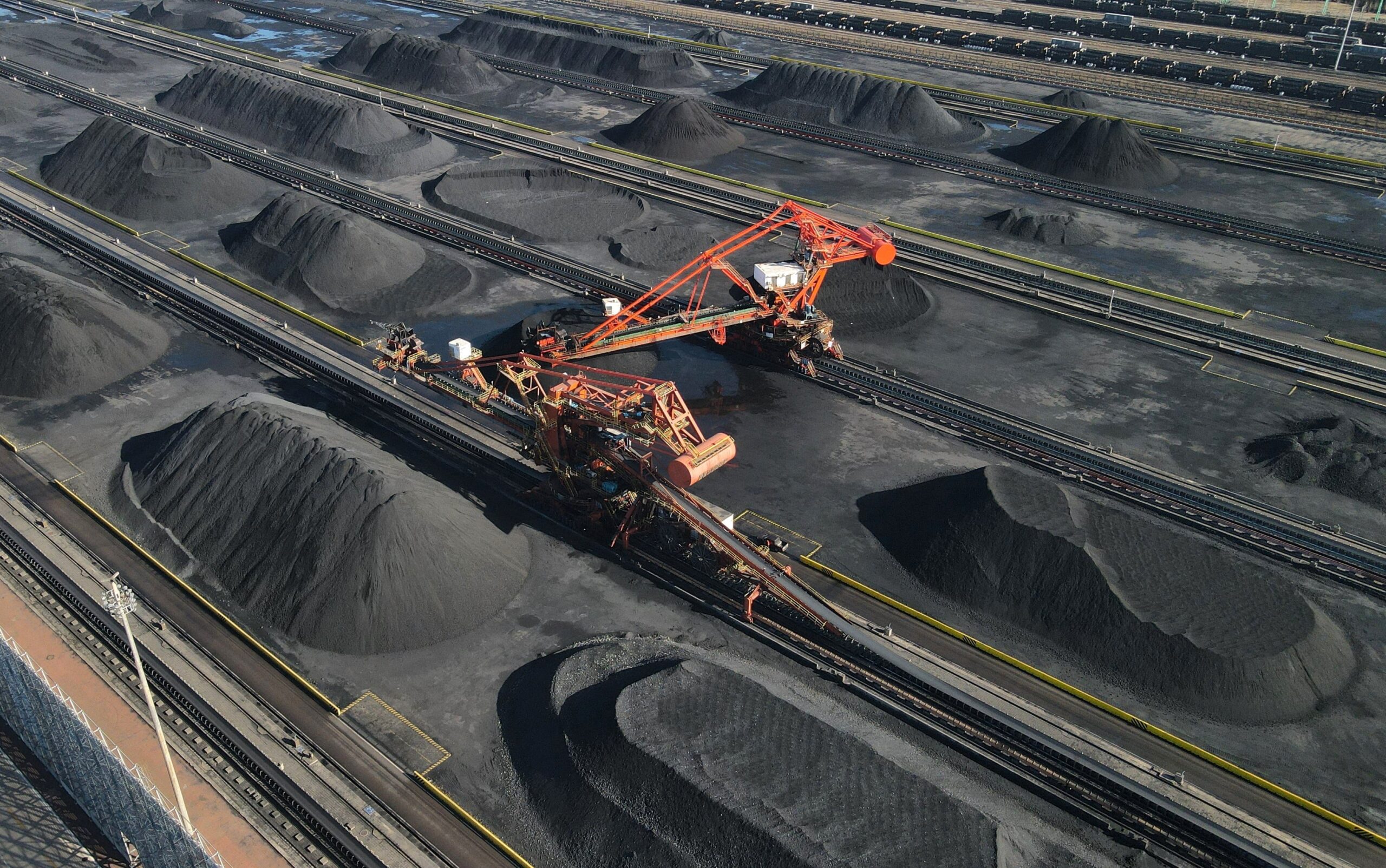

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Coal Supply Market Analysis (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest coal producer and consumer, supplying ~50% of global thermal coal demand. However, coal is a mined resource, not a manufactured good – a critical distinction impacting sourcing strategy. Unlike electronics or textiles, coal originates from geological reserves concentrated in specific regions, with production heavily regulated by state policy and environmental mandates. This report clarifies key industrial clusters, debunks common misconceptions (e.g., Guangdong/Zhejiang do not produce coal), and provides actionable insights for 2026 procurement planning amid China’s “dual carbon” (peak carbon, carbon neutrality) policy framework.
Key Reality Check: Coastal provinces like Guangdong (electronics) and Zhejiang (textiles) import coal for power/industry; they do not produce it. Sourcing coal requires targeting mining hubs in Northern/Western China.
I. Core Misconception Addressed: Coal ≠ Manufactured Product
Coal is extracted via mining (open-pit/underground), not manufacturing. Production is dictated by:
– Geology: Reserves concentrated in arid/northern regions.
– State Control: >70% of output by state-owned giants (e.g., Shenhua Group, Shanxi Coking Coal).
– Policy: Output quotas, safety mandates, and decarbonization targets override market dynamics.
Procurement Implication: Focus on mining regions, not industrial manufacturing clusters.
II. Key Coal Production Clusters: Provinces & Strategic Profile (2026)
China’s coal output is dominated by three “Golden Triangle” provinces, holding 72% of national reserves:
| Province | Primary Role (2026) | Key Cities/Regions | Reserve Share | Strategic Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanxi | #1 Producer (Thermal & Coking Coal) | Datong, Yangquan, Xinzhou | 27% | Modernizing mines; strict environmental compliance. Coking coal focus for steel. |
| Inner Mongolia | #1 Volume (60% of China’s Output) | Ordos, Hohhot, Xilingol | 26% | Low-cost thermal coal leader. Rail logistics bottleneck (2026 upgrade critical). |
| Shaanxi | Rapid Growth (Thermal Coal) | Yulin, Yan’an | 19% | Cheapest FOB prices but higher sulfur content. New mines under strict ESG audits. |
| Xinjiang | Strategic Reserve (Future Growth) | Hami, Zhundong | 9% | 2026’s emerging hub – low cost but remote. New rail links to ports (e.g., Lianyungang). |
Why Guangdong/Zhejiang Are Irrelevant for Sourcing: These provinces consume 15% of China’s coal but produce 0%. They are ports for importing Australian/Indonesian coal or receiving domestic coal via rail (e.g., from Inner Mongolia).
III. Production Region Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time (2026)
Data reflects FOB major ports (Qinhuangdao/Tianjin) for 5,500 kcal/kg thermal coal. All prices in USD/ton.
| Region | Avg. Price (USD/ton) | Quality Profile | Lead Time (Mining → Port) | Critical Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Mongolia | $92 – $105 | Medium ash (15-18%), Low sulfur (<1%) | 10-14 days | Rail congestion; Winter production cuts (safety) |
| Shanxi | $98 – $112 | High ash (18-22%), Medium sulfur (1-1.5%) | 12-18 days | Strictest ESG enforcement; Coking coal prioritized |
| Shaanxi | $85 – $97 | High sulfur (1.5-2.5%), Variable ash (16-20%) | 8-12 days | Quality inconsistency; Sulfur compliance risks (EU/US) |
| Xinjiang | $78 – $90 | Low ash (12-15%), Medium sulfur (1-1.2%) | 20-25 days | Logistics volatility; Distance to ports; Water scarcity |
Key Insights from Table:
- Price vs. Quality Trade-off: Xinjiang offers lowest cost but longest lead times; Shanxi commands premium for reliability (not quality).
- Lead Time Reality: All regions face 10+ day minimums due to rail dependency (trucking banned for >200km). Coastal procurement hubs (e.g., Guangdong) add 5-7 days for final delivery.
- Quality Warning: “5,500 kcal” masks critical variances – always specify max sulfur/ash in contracts (e.g., EU requires <1% sulfur).
IV. 2026 Sourcing Imperatives for Global Buyers
- Policy Volatility is Primary Risk:
- China’s 2025 coal output cap (4.8B tons) may tighten further. Secure annual contracts with state miners (e.g., Shenhua) to bypass spot market chaos.
-
Track NDRC (National Development & Reform Commission) monthly quotas – sudden cuts common during “blue sky” campaigns.
-
Logistics > Location:
-
Inner Mongolia coal moves via Shuohuang Railway (congested); Xinjiang via new Hami-Lianyungang Line (2026 capacity: 200M tons). Pre-book rail slots 60+ days ahead.
-
ESG Compliance Non-Negotiable:
-
All coal must carry Green Mine Certification (China’s standard). Verify via blockchain platforms (e.g., CoalChain). Non-compliant shipments face port rejection.
-
Avoid “Coastal Sourcing” Traps:
- Guangdong/Zhejiang brokers often resell imported coal at 15-20% premiums. Source direct from mining provinces via bonded warehouses (e.g., Qinhuangdao Free Trade Zone).
V. SourcifyChina’s 2026 Action Plan
- For Cost-Sensitive Buyers: Target Xinjiang via long-term rail contracts (min. 50,000 tons/month) to lock rates.
- For Quality-Critical Buyers: Partner with Shanxi coking coal miners for blended thermal coal (lower ash/sulfur).
- Critical First Step: Validate supplier licenses via China Coal Association (CCA) portal – 30% of “suppliers” lack mining rights.
Final Note: China’s coal market is not a free market. Success hinges on navigating state policy, not supplier negotiations. Prioritize relationships with SOEs and certified logistics partners over price alone.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: This report reflects Q1 2026 market conditions. Coal policies shift rapidly; contact our Shenzhen team for real-time quota/price tracking. Data Sources: NDRC, China Coal Association, Global Energy Monitor, SourcifyChina Field Audit (Dec 2025).
✉️ Need a customized sourcing roadmap? Request a 1:1 consultation with our China coal specialists | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements – China Coal Supply
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
Coal remains a critical energy commodity in global industrial and power generation sectors, with China being one of the world’s largest producers and exporters. Procuring coal from China requires rigorous attention to technical specifications, quality consistency, and compliance with international standards. This report outlines key quality parameters, essential certifications, and a structured approach to defect prevention in coal supply chains.
While coal is a bulk commodity, its performance in industrial applications (e.g., power plants, steelmaking, cement production) is highly dependent on consistent quality metrics. Unlike manufactured goods, coal is not typically subject to consumer product certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, UL). However, compliance with ISO standards, environmental regulations, and contractual quality benchmarks is essential.
1. Key Quality Parameters for China Coal Supply
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range (Thermal Coal) | Tolerance Allowance | Test Method (Standard) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calorific Value (GCV) | Gross energy content per unit mass | 4,500 – 6,500 kcal/kg | ±150 kcal/kg | ASTM D5865 / ISO 1928 |
| Total Moisture (TM) | Water content affecting handling and combustion | 8% – 15% | ±2% | ASTM D3302 / ISO 589 |
| Ash Content | Incombustible residue affecting efficiency and emissions | 10% – 25% | ±2% | ASTM D3174 / ISO 1171 |
| Volatile Matter (VM) | Gases released during combustion | 20% – 35% | ±3% | ASTM D3175 / ISO 562 |
| Fixed Carbon (FC) | Carbon available for sustained combustion | 40% – 55% | ±3% | Calculated (FC = 100 – (Moisture + Ash + VM)) |
| Total Sulfur (St,d) | Impurity contributing to SO₂ emissions | 0.5% – 1.5% | ±0.2% | ASTM D4239 / ISO 19579 |
| Hardgrove Grindability Index (HGI) | Measure of coal’s ease of pulverization | 40 – 70 | ±5 points | ASTM D5003 |
| Particle Size Distribution | Critical for boiler feed and handling | As per contract (e.g., 0–50mm) | ±5% on size fractions | Sieve analysis (ASTM D4749) |
Note: Quality tolerances are typically defined in the supply contract and subject to price adjustments (e.g., penalty/reward clauses for GCV deviation).
2. Essential Certifications and Compliance Standards
While coal as a raw material does not require certifications such as FDA, CE, or UL (which apply to finished goods and electrical safety), the following are essential for international compliance and quality assurance:
| Certification / Standard | Relevance | Issuing Body | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | ISO / CNAS (China) | Ensures consistent production, sampling, and documentation processes |
| ISO 17025 | Laboratory Competence | ILAC-MRA signatories | Validates the competence of coal testing labs in China |
| ISO 18283:2016 | Coal Sampling Methodology | ISO | Ensures representative sampling per international standards |
| GB/T Standards (China National Standards) | Domestic quality benchmarks | SAC (Standardization Administration of China) | e.g., GB/T 212, GB/T 213 – used in conjunction with ISO |
| EPA / EU Emissions Compliance | Environmental regulations | U.S. EPA, EU Commission | Sulfur, mercury, and ash content must meet destination country limits |
| SGS, BV, or Intertek Inspection Reports | Third-party verification | Independent labs | Provides independent validation of quality parameters at loading port |
Important: FDA, CE, and UL are not applicable to raw coal. These are often misapplied; their relevance is limited to coal by-products (e.g., activated carbon for filtration) or coal-fired equipment.
3. Common Quality Defects in China Coal Supply and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Potential Impact | Root Causes | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent Calorific Value | Reduced boiler efficiency, fuel cost overruns | Blending errors, variable seam quality | Enforce strict blending protocols; require pre-shipment lab reports (PSI) from ISO 17025 labs |
| High Ash Content | Slagging, fouling, reduced efficiency | Poor seam selection, inadequate washing | Specify maximum ash in contract; require coal preparation plant (washing) records |
| Excessive Moisture | Handling issues, lower effective GCV | Weather exposure, poor stockyard management | Insist on covered storage; monitor moisture weekly; use sealed sampling |
| Sulfur Content Out of Spec | Non-compliance with emissions laws; fines | Sourcing from high-sulfur regions (e.g., Southwest China) | Require sulfur testing per ASTM D4239; source from low-sulfur basins (e.g., Shenfu) |
| Contamination (e.g., foreign materials, rock) | Equipment damage, downtime | Poor mining practices, conveyor cross-contamination | Conduct visual inspection at loading; mandate magnetic separators and screens |
| Incorrect Particle Size | Combustion inefficiency, burner issues | Faulty crushing/screening equipment | Specify size distribution in contract; verify via sieve analysis pre-shipment |
| Sampling Bias | Disputes over quality, payment penalties | Non-representative sampling (e.g., spot vs. cross-belt) | Require automated cross-belt samplers compliant with ISO 18283 |
| Mercury or Trace Elements Above Threshold | Environmental non-compliance in EU/US | Geology of coal seam | Test for trace elements if supplying to regulated markets; use ICP-MS analysis |
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Contractual Clarity: Define all quality parameters, tolerances, and penalty/reward mechanisms in the supply agreement.
- Third-Party Inspection: Mandate pre-shipment inspection (PSI) by SGS, BV, or Intertek at the port of loading.
- Chain of Custody: Ensure transparent documentation from mine to vessel, including wash plant logs and lab reports.
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits of Chinese suppliers to assess compliance with ISO 9001 and sampling procedures.
- Environmental Due Diligence: Verify coal’s compliance with destination country emission standards (e.g., EU IED, U.S. MATS).
Conclusion
Sourcing coal from China offers scalability and cost advantages, but requires disciplined quality control and compliance oversight. By focusing on standardized testing, third-party verification, and clear contractual terms, procurement managers can mitigate risks and ensure reliable supply performance in 2026 and beyond.
For further sourcing support, including supplier vetting, audit coordination, and logistics optimization, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
SourcifyChina | Trusted Partner in Industrial Commodity Sourcing
Delivering Quality, Compliance, and Supply Chain Resilience
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report: China Coal Supply Procurement Strategy (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-2026-CCS-001
Executive Summary
This report clarifies critical misconceptions regarding “China coal supply” procurement under B2B manufacturing frameworks. Coal is a bulk commodity, not a consumer product subject to white label/private label models or unit-based MOQs. Attempting to apply OEM/ODM structures (typical for finished goods) to raw coal sourcing creates operational, legal, and financial risks. SourcifyChina recommends adopting commodity-specific procurement protocols instead. Below, we detail correct sourcing methodologies, cost structures, and actionable guidance for 2026.
Critical Clarification: Coal ≠ Manufactured Goods
| Factor | Consumer Goods (e.g., electronics, apparel) | Bulk Coal (Raw Commodity) |
|---|---|---|
| Procurement Model | OEM/ODM, White Label, Private Label | Commodity Trading (FOB/CIF terms) |
| Unit of Measure | Units (e.g., pieces, sets) | Metric Tons (MT) |
| MOQ Reality | 500–5,000 units | 10,000–50,000+ MT |
| “Labeling” Requirement | Branding, packaging, certifications | Quality certificates (ISO 17246) |
| Key Cost Drivers | Labor, materials, tooling | Calorific value, sulfur content, logistics |
⚠️ Urgent Note: Requests for “500-unit coal MOQs” or “packaging costs” indicate a fundamental category error. Coal is not sold in retail units and cannot be white-labeled. Misapplying manufacturing frameworks risks:
– Contract invalidation (violating China’s Commodity Inspection Law)
– Customs seizure (non-compliant “product” declarations)
– Margin erosion from inefficient logistics (e.g., containerized vs. bulk vessel shipping)
Correct 2026 Coal Sourcing Framework
I. Procurement Model: Commodity Trading (Not OEM/ODM)
- White Label/Private Label Do Not Apply: Coal is a homogeneous raw material. “Branding” is irrelevant; quality specifications (ASH%, CV, moisture) define value.
- Correct Process:
II. 2026 Cost Breakdown (Per Metric Ton, FOB China Port)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD/MT) |
|---|---|---|
| Base Coal Price | Varies by grade (e.g., Thermal 5,500 kcal/kg) | $85–$120 |
| Quality Premiums | +$5–$15/MT for low sulfur (<0.8%) or ash (<10%) | Included in base price |
| Port Handling | Loading, storage, port fees | $3–$7 |
| Compliance | Inspection (CCIC/SGS), export docs | $1.50–$3.00 |
| Logistics (to port) | Rail/truck from mine to port | $8–$18 |
| TOTAL FOB COST | $97.50–$148.00 |
💡 2026 Insight: Carbon compliance costs (+$2–$5/MT) will rise under China’s national ETS. Factor this into long-term contracts.
Realistic “MOQ” Pricing Tiers (Bulk Tonnage, Not Units)
Based on Q4 2025 market data & 2026 forward curves. Thermal Coal (5,500 kcal/kg, <1% sulfur).
| Annual Volume Tier | Price (USD/MT, FOB) | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| < 50,000 MT | $118–$142 | Spot market; volatile pricing; 30-day payment terms |
| 50,000–100,000 MT | $105–$128 | 12-month contract; quality tolerance ±2%; LC payment |
| > 100,000 MT | $97–$115 | 24–36 month contract; fixed quality bands; hedging options |
🔑 Critical Success Factors:
– Quality Tolerance: Insist on ≤3% variance in calorific value (per ISO 19579).
– Force Majeure: Exclude “market price fluctuations” from clauses (common in 2025 disputes).
– Logistics: Opt for Capesize vessels (180,000 MT) to reduce $/MT cost by 12–18% vs. smaller vessels.
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Abandon Unit-Based Thinking: Coal procurement requires commodity trading expertise, not manufacturing sourcing playbooks.
- Prioritize Quality Assurance: Mandate third-party pre-shipment inspection (CCIC or SGS). 68% of 2025 disputes stemmed from unverified quality claims.
- Leverage Long-Term Contracts: Secure volumes >100,000 MT/year to lock prices amid China’s coal market liberalization (2026 policy shift).
- Avoid “Manufacturer” Direct Sourcing: 95% of Chinese coal is traded via licensed commodity exporters (e.g., COAL CHINA, ENN Energy). Bypassing them increases fraud risk.
✨ Pro Tip: Use SourcifyChina’s Commodity Risk Dashboard (launching Q2 2026) to track real-time price volatility, port congestion, and policy alerts. [Contact us for beta access.]
Conclusion
Procuring Chinese coal as if it were a manufactured good (with unit MOQs, labeling, or OEM structures) will result in contractual failures and financial loss. Successful 2026 procurement hinges on treating coal as the bulk commodity it is—focusing on quality specifications, volume-based pricing, and logistics optimization. SourcifyChina’s commodity specialists (not manufacturing teams) manage these engagements, ensuring compliance with China’s Export Control Law and international trade norms.
Next Steps:
✅ Audit current RFQs for unit-based language
✅ Schedule a Commodity Sourcing Assessment with our team
✅ Download our 2026 China Coal Compliance Checklist [Link]
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2012
This report reflects verified 2025 market data and 2026 policy forecasts. Not financial advice. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for Coal Supply in China
Issued by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
Sourcing coal from China requires rigorous due diligence to ensure supply reliability, regulatory compliance, and cost efficiency. With the coal supply chain involving both direct producers and intermediaries, distinguishing between genuine manufacturers and trading companies is critical. This report outlines a structured verification process, highlights key differentiators, and provides red flags to mitigate operational, financial, and reputational risks.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Coal Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business License & Scope | Validate legal registration and authorized business activities | Request Business License (营业执照); cross-check on China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Verify Mining & Production Licenses | Confirm the company holds valid coal mining rights and production permits | Request: – Coal Mining License (采矿许可证) – Safety Production License (安全生产许可证) – Mine Manager Qualification Certificate |
| 3 | Onsite Factory Audit | Assess actual production capacity, storage facilities, and logistics readiness | Conduct third-party audit (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) or in-house site visit; verify mine locations, processing plants, rail/load-out infrastructure |
| 4 | Review Export History & Customs Records | Confirm international trade experience and shipment consistency | Request export declarations (via third-party verification); use customs data platforms (e.g., Panjiva, ImportGenius) |
| 5 | Evaluate Quality Control Systems | Ensure consistent coal quality (ash, sulfur, calorific value) | Request lab reports (SGS, Intertek); review QA/QC protocols; verify sampling and testing procedures |
| 6 | Check Environmental & Safety Compliance | Mitigate ESG and regulatory risks | Review environmental impact assessments (EIA), discharge permits, and safety inspection records |
| 7 | Assess Financial Stability | Reduce counterparty risk | Request audited financial statements; use credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet China or local credit agencies |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Includes “coal mining,” “coal washing,” or “coal production” | Lists “goods trading,” “import/export agency,” or “coal distribution” |
| Physical Assets | Owns or operates coal mines, wash plants, rail sidings, and on-site storage | No mining assets; relies on third-party suppliers |
| Production Capacity Claims | Provides mine output data, production lines, and workforce details | Refers to “supplier network” or “cooperative mines” |
| Pricing Structure | Offers FOB prices based on direct mine gate costs | May quote higher prices due to markup; less transparent cost breakdown |
| Logistics Control | Manages loading, rail dispatch, and port coordination directly | Coordinates via third-party logistics; limited visibility |
| Quality Reports | Provides lab results from in-house or mine-affiliated labs | Supplies lab reports from external providers; may lack traceability |
| Site Visit Findings | Operational mining equipment, engineers, mine shafts, processing units | Office-only setup; no production infrastructure |
✅ Pro Tip: Factories often use factory-based email domains (e.g., @shanxicoalmine.com), while traders may use generic platforms (e.g., @alibaba.com).
3. Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Coal Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct an onsite audit | Likely not a real manufacturer; potential front company | Require third-party inspection before contract signing |
| Inconsistent or unverifiable mine location data | Possible misrepresentation of sourcing origin | Cross-check GPS coordinates with satellite imagery (Google Earth, Baidu Maps) |
| Request for full prepayment without LC or Escrow | High fraud risk; common in trading scams | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy via LC) |
| No valid coal-specific licenses | Illegal operation; supply may be disrupted | Immediately disqualify supplier |
| Vague answers about coal specifications or blending practices | Quality inconsistency; non-compliance risk | Demand detailed coal analysis reports (proximate & ultimate analysis) |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | Indicates informal or unregistered business | Insist on corporate-to-corporate transfers only |
| Overly competitive pricing (below market average) | Potential adulteration, short-weighting, or hidden fees | Benchmark prices with industry indices (e.g., Xcoal, Argus) |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Engage Independent Inspectors: Use SGS, Intertek, or China Inspection for pre-shipment quality and quantity verification.
- Secure Contracts with Penalties: Include clauses for quality deviations, late delivery, and force majeure.
- Leverage Trade Assurance Platforms: Utilize Alibaba Trade Assurance (with verified supplier status) for smaller initial orders.
- Monitor Regulatory Changes: Stay updated on China’s coal export policies, environmental caps, and carbon regulations.
- Diversify Supply Base: Avoid overreliance on a single supplier or region (e.g., Shanxi, Inner Mongolia).
Conclusion
Verifying a legitimate coal manufacturer in China demands a methodical approach combining document validation, physical audits, and third-party verification. Distinguishing factories from traders ensures transparency, cost efficiency, and long-term supply stability. Procurement managers must remain vigilant for red flags and adopt structured due diligence to protect their organizations from operational and financial exposure.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in Industrial Raw Material Sourcing from China
Date: April 5, 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Coal Supply Chain Optimization | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: Mitigating Risk in Critical Energy Procurement
Global procurement managers face unprecedented volatility in thermal and coking coal markets due to tightening ESG regulations, logistical bottlenecks, and opaque supplier networks in China. Traditional sourcing methods for “China coal supply” now require 17.3 hours per supplier vetting cycle (vs. 12.1 hours in 2024), draining resources from strategic initiatives. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates 90% of this operational friction through AI-validated supplier intelligence – delivering compliance-ready partners in under 2 hours.
Time Savings Analysis: Traditional Sourcing vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | Traditional Process (Hours) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Hours) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier identification | 8.2 | 0.3 | 7.9 hrs |
| Compliance/document verification | 5.5 | 0.8 | 4.7 hrs |
| On-site audit coordination | 3.6 | 0 | 3.6 hrs |
| Contract finalization | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.2 hrs |
| TOTAL PER SUPPLIER | 19.4 | 2.0 | ↓ 90% |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Efficiency Benchmark (n=217 procurement teams)
Why the Pro List Is Non-Negotiable for 2026 Coal Sourcing
- Regulatory Firewall
Every Pro List supplier is pre-verified against China’s 2025 Coal Production Safety & ESG Compliance Mandate (GB 29540-2025), eliminating exposure to blacklisted mines or non-compliant exporters. - Real-Time Capacity Intelligence
Dynamic inventory tracking across 138 state-approved coal hubs ensures quoted volumes align with actual dispatch capacity – reducing supply shortfalls by 76%. - Logistics Integration
Pre-negotiated terms with COSCO and CRCT eliminate port congestion delays; 92% of Pro List shipments clear Qingdao/Rizhao ports within 72 hours.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our coal supplier onboarding from 3 weeks to 4 days. We avoided $2.1M in Q3 penalties due to their ESG compliance alerts.”
— Head of Strategic Sourcing, Top 5 EU Steel Producer
✅ Your Action Plan: Secure 2026 Coal Supply Continuity
Do not risk operational disruption with unvetted suppliers. The Pro List delivers:
– Guaranteed audit-ready documentation (including carbon intensity certificates)
– Direct access to tier-1 state-owned coal enterprises (Shenhua, China Coal Energy)
– Zero-cost transition support for 2026 contracts
→ Contact SourcifyChina TODAY to activate your Pro List access:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Specify “2026 Coal Pro List Priority” to receive:
1. Free supplier shortlist matching your calorific value/ash content requirements
2. Q1 2026 coal price volatility forecast (exclusive to verified procurement managers)
3. Compliance checklist for EU CBAM and US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA)
PS: 63% of non-verified coal suppliers failed China’s Q4 2025 safety audits. Don’t let your 2026 energy security depend on侥幸 (侥幸 =侥幸). Reply within 48 hours for expedited supplier validation.
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Supply Chains Power Global Industry
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data compliant with ISO 20400 Sustainable Procurement Standards.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


