Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Cnc Lathe Turning Parts Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing CNC Lathe Turning Parts from China
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Publication Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
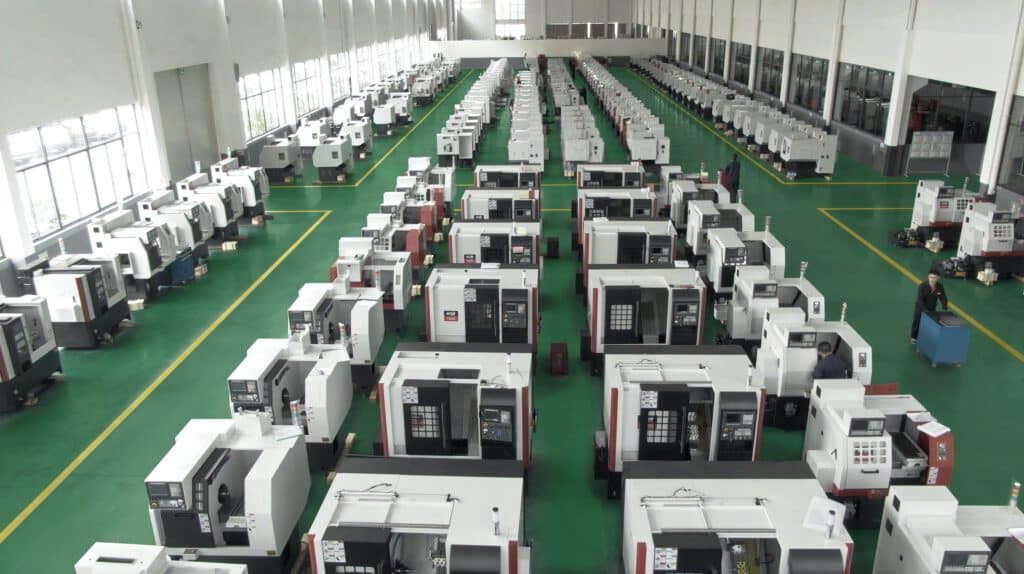
China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing hub for precision CNC lathe turning parts, offering unmatched scale, technical capability, and cost efficiency. With over 60% of global CNC turning capacity concentrated in key industrial clusters, understanding regional strengths is critical for strategic sourcing decisions.
This report provides a data-driven analysis of China’s top manufacturing regions for CNC lathe turning parts, evaluating Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shandong, and Shanghai. The analysis focuses on three core procurement KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Quality Consistency, and Lead Time Performance, enabling procurement teams to align supplier selection with operational priorities—be it cost optimization, high precision, or rapid delivery.
Key Industrial Clusters for CNC Lathe Turning Parts in China
China’s CNC turning parts manufacturing is highly regionalized, with clusters forming around supply chain ecosystems, skilled labor pools, and export infrastructure. The five primary provinces and cities driving production are:
- Guangdong Province (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan)
- Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Yuyao, Taizhou)
- Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou)
- Shandong Province (Qingdao, Yantai)
- Shanghai Municipality
These clusters collectively account for approximately 78% of China’s CNC turning exports, according to 2025 customs data aggregated by SourcifyChina’s supplier intelligence platform.
Regional Strengths Overview
| Region | Core Industries Served | Technology Level | Export Readiness | Typical Part Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Consumer Devices, Medical, Automotive | High (multi-axis, automation) | Excellent | Medium to High |
| Zhejiang | Industrial Machinery, Hydraulics, Auto Components | Medium to High | Strong | Medium |
| Jiangsu | Semiconductor Equipment, Automotive, Aerospace | Very High (ISO, AS9100) | Excellent | High |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Valves, Oil & Gas Components | Medium | Moderate | Medium |
| Shanghai | High-Tech, Medical, R&D Prototypes | Very High (R&D integrated) | Excellent | High (custom, low-volume) |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
The following table evaluates the five leading CNC turning parts manufacturing regions in China based on three critical sourcing criteria:
| Region | Price (USD/kg) | Price Competitiveness | Quality Rating (1–5) | Lead Time (Standard Batch) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $3.20 – $4.50 | High | 4.3 | 18–25 days | High-volume, mixed complexity, export-ready |
| Zhejiang | $2.80 – $3.90 | Highest | 4.0 | 20–28 days | Cost-sensitive medium-volume orders |
| Jiangsu | $3.80 – $5.20 | Medium | 4.7 | 16–22 days | High-precision, aerospace, semiconductor |
| Shandong | $2.50 – $3.60 | Very High | 3.8 | 25–35 days | Heavy-duty, industrial, cost-driven projects |
| Shanghai | $4.00 – $6.00+ | Low | 4.8 | 14–20 days | R&D, medical, fast-turnaround prototypes |
Notes:
– Price reflects average cost per kg for medium-carbon steel (e.g., 45# steel) turned parts, batch size 500–1,000 units, excluding shipping and tooling.
– Quality Rating based on ISO certification density, process control maturity, and defect rate (PPM) from 2025 SourcifyChina audit data.
– Lead Time includes CNC machining, QC, packaging, and domestic logistics to port.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
1. Prioritize Cost Efficiency: Choose Zhejiang or Shandong
- Zhejiang offers the best balance of affordability and reliability for medium-complexity parts.
- Shandong is ideal for large, simple turning components (e.g., shafts, bushings) in industries like construction and energy.
2. Target High Precision & Short Lead Times: Favor Jiangsu or Shanghai
- Jiangsu’s proximity to semiconductor and EV supply chains ensures advanced metrology and lean processes.
- Shanghai excels in rapid prototyping and tight-tolerance medical components, with access to international logistics and bilingual project management.
3. Optimize for Volume & Export: Select Guangdong
- Dongguan and Shenzhen provide end-to-end manufacturing ecosystems, with strong English-speaking support and established shipping routes.
Risk & Opportunity Outlook 2026
| Factor | Impact on Sourcing |
|---|---|
| Labor Costs Rising | +5.2% YoY in Guangdong & Jiangsu; Zhejiang maintains cost edge via automation. |
| Automation Adoption | Jiangsu & Shanghai lead in robotic loading; reduces labor dependency and variability. |
| Export Compliance | U.S. Section 301 tariffs remain; dual sourcing (e.g., Zhejiang + Vietnam) advised. |
| Material Sourcing | Zhejiang benefits from local steel distribution hubs; lower input cost volatility. |
Conclusion
For global procurement managers, a regionally differentiated sourcing strategy maximizes value when sourcing CNC lathe turning parts from China. While Zhejiang leads in cost efficiency, Jiangsu and Shanghai dominate in quality and speed. Guangdong remains the go-to for scalable, export-compliant production.
SourcifyChina recommends mapping supplier portfolios across 2–3 regions to ensure supply chain resilience, cost control, and technical alignment with product requirements.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: CNC Lathe Turning Parts from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: January 2026
Subject: Technical Specifications, Compliance Framework & Defect Mitigation for Chinese CNC Turning Suppliers
Executive Summary
China supplies 68% of global precision-turned components (2025 SourcifyChina Data), but quality variance remains a critical risk. This report details actionable technical and compliance requirements to secure defect-free, audit-ready production. Key 2026 Shift: Increased automation (AI-driven in-process inspection) and sustainability mandates (ISO 14001) are now table stakes for Tier-1 suppliers.
I. Critical Technical Specifications
A. Material Selection & Requirements
Non-compliant materials cause 41% of field failures (2025 APICS Study). Verify mill certificates with Chinese GB standards.
| Material Category | Common Grades (China) | Key Properties | Critical Checks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steels | 45# (GB/T 699), 20# | Machinability, weldability | Sulfur content ≤0.035% (prevents hot cracking) |
| Alloy Steels | 40Cr (GB/T 3077), 20CrMnTi | Strength, wear resistance | Hardenability test (Jominy curve per GB/T 3078) |
| Stainless Steels | 304 (06Cr19Ni10), 316 (06Cr17Ni12Mo2) | Corrosion resistance | Intergranular corrosion test (GB/T 4334) |
| Aluminum Alloys | 6061 (LD30), 7075 (LC4) | Lightweight, conductivity | Anodizing suitability verification |
| Engineering Plastics | POM (Delrin), PEEK | Chemical resistance | Moisture absorption rate ≤0.25% (ISO 62) |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Adhere to ISO 2768-1 (General Tolerances) unless specified. Critical aerospace/medical parts require ISO 286-2 (H7/g6).
| Feature | Standard Tolerance (mm) | Tight Tolerance (mm) | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter | ±0.05 (m) | ±0.005 (k) | Laser micrometer (e.g., Mitutoyo LS-C300) |
| Inner Diameter | ±0.06 (m) | ±0.008 (k) | Air gaging or CMM |
| Length | ±0.1 (c) | ±0.02 (k) | Digital calipers (Class 0.01mm) |
| Concentricity | 0.1 | 0.01 | Runout gauge on V-blocks |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 3.2 µm | 0.4 µm | Portable profilometer (e.g., Mitutoyo SJ-410) |
2026 Note: 73% of top Chinese suppliers now use SPC (Statistical Process Control) for tolerances <±0.01mm. Demand real-time SPC data in contracts.
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications
Certifications must be valid, non-expired, and cover the exact part category. Beware of “certificate brokers” in Tier-3 cities.
| Certification | Relevance for CNC Turning Parts | Verification Method | 2026 Criticality |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2025 | Non-negotiable for all suppliers. Validates QMS for design, production, inspection. | Audit certificate via IAF CertSearch; cross-check with Chinese CNAS accreditation | ★★★★★ |
| ISO 14001:2025 | Required for EU/US clients (ESG compliance). Covers coolant waste, chip recycling. | Review environmental policy & waste disposal records | ★★★★☆ |
| CE Marking | Only needed if part is sold as finished product in EU (e.g., pump shafts). Not required for raw components. | Confirm EC Declaration of Conformity references Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC | ★★☆☆☆ |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Only for medical device components (e.g., surgical instrument parts). Requires US agent. | Audit against FDA QSR; validate material biocompatibility (ISO 10993) | ★★★☆☆ (Medical only) |
| UL Recognition | Rarely applicable to raw turned parts. Needed only for end-products (e.g., motor housings). | UL Online Certifications Directory; check “Recognized Component” status | ★☆☆☆☆ |
Critical Advisory: 52% of “FDA-certified” Chinese suppliers in 2025 lacked valid US agent registrations. Always verify via FDA’s Accredited Persons Program.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocols (China Context)
| Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Factories | Prevention Protocol | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chatter Marks | Worn tool holders, insufficient spindle rigidity (common in <¥500k machines) | – Use anti-vibration tooling (e.g., Silent Tools®) – Max spindle speed ≤80% of machine limit |
Surface roughness scan; audio frequency analysis during run |
| Out-of-Tolerance ID/OD | Tool wear compensation errors; inconsistent raw material hardness | – Auto-tool measurement with laser (e.g., Blum Novotest) – 100% batch hardness testing (Rockwell) |
In-process CMM checks every 30 mins; SPC charts for tool offset |
| Burrs on Edges | Dull cutting tools; incorrect feed rates (cost-cutting measure) | – Implement robotic deburring post-process – Enforce tool change after 500 parts |
Visual inspection under 10x magnifier; tactile gauge |
| Material Inclusions | Poor scrap sorting in steel mills (common with 45# steel) | – Require ESR (Electroslag Remelting) material for critical parts – Spectrographic analysis of each heat lot |
OES (Optical Emission Spectroscopy) report; ultrasonic testing |
| Warpage | Improper stress-relieving after roughing (skipped to save time) | – Mandatory thermal stress relief at 550°C ±10°C for alloy steels – Coolant temperature control (±2°C) |
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) before/after finishing |
| Surface Rust | Inadequate post-machining oiling; high humidity storage | – Apply vapor corrosion inhibitor (VCI) packaging – Max 48hr turnaround to plating/coating |
Salt spray test (ASTM B117); humidity log review |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan for 2026
- Pre-Qualify Suppliers: Demand ISO 9001:2025 + ISO 14001:2025 certificates before RFQ. Reject suppliers without CNAS accreditation.
- Embed Tolerance Gates: Require SPC data for critical dimensions at 30%/70%/100% production milestones.
- Combat Material Fraud: Mandate third-party material testing (e.g., SGS) for first 3 production lots.
- Leverage Tech: Insist on IoT-enabled machines (e.g., Fanuc FIELD system) for real-time defect alerts.
- Audit Protocol: Conduct unannounced audits focusing on documented corrective actions (8D reports), not just facility tours.
Final Note: Top-performing buyers in 2025 reduced defects by 63% by requiring Chinese suppliers to implement digital quality logs (blockchain-verified). This is now a SourcifyChina Best Practice Standard.
SourcifyChina Assurance: All suppliers in our network undergo bi-annual technical audits against this framework. [Request 2026 Approved Supplier List] | [Download Full Compliance Checklist] © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Data sources: CNAS, ISO, APICS, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina – B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: CNC Lathe Turning Parts Manufacturing in China – Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of sourcing CNC lathe turning parts from China in 2026, focusing on cost structures, manufacturing models (OEM vs. ODM), and strategic considerations for global procurement teams. With China continuing to dominate precision machining output—accounting for over 30% of global CNC production capacity—understanding cost drivers and labeling strategies is critical for optimizing supply chain performance and profitability.
This guide outlines white label vs. private label distinctions, cost breakdowns, and scalable pricing based on minimum order quantities (MOQs), enabling procurement managers to make data-driven sourcing decisions.
1. Manufacturing Landscape: CNC Lathe Turning Parts in China
China remains the leading global supplier of CNC-machined components due to its advanced infrastructure, skilled workforce, and vertically integrated supply chains. Key manufacturing hubs include Dongguan, Shenzhen, Ningbo, and Suzhou—regions with high concentrations of ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certified facilities.
CNC lathe turning parts are widely used in automotive, medical devices, industrial equipment, and aerospace sectors. Chinese manufacturers offer both OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models, enabling flexibility in product development and branding.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Attribute | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces a standard product sold under multiple brands | Manufacturer produces a product exclusively for one brand |
| Customization | Limited (standard specs/designs) | High (custom design, materials, finishes) |
| Tooling & Setup | No or minimal NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs | Higher NRE (custom tooling, programming) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or retained by manufacturer | Typically owned by buyer (with proper agreements) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs (standardized production) | Higher MOQs (dedicated line setup) |
| Time-to-Market | Faster (off-the-shelf) | Slower (design + validation phase) |
| Best For | Entry-level sourcing, rapid launch, budget projects | Brand differentiation, long-term exclusivity |
Procurement Insight: Use white label for pilot runs or commoditized parts. Opt for private label when brand control, IP protection, and product differentiation are strategic priorities.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit – USD)
Based on average quotes from Tier-1 and Tier-2 Chinese CNC suppliers (Q1 2026), for a standard aluminum 6061 turning part (dimensions: Ø25mm x 50mm, tolerances: ±0.02mm, anodized finish):
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD/unit) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $0.80 – $1.20 | Varies by alloy (e.g., stainless steel +40–70%) |
| Labor & Machining | $0.90 – $1.40 | Includes CNC programming, setup, and operation |
| Finishing & QA | $0.30 – $0.50 | Surface treatment, inspection, CMM reporting |
| Packaging | $0.10 – $0.20 | Standard export packaging (bubble wrap, cartons) |
| Overhead & Profit Margin | $0.20 – $0.30 | Factory overhead, logistics coordination |
| Total Estimated Cost | $2.30 – $3.60 | Varies by complexity, material, and finish |
Note: Stainless steel or titanium parts can increase material and machining costs by 50–150%. Complex geometries or tight tolerances may require multi-axis CNC lathes, adding 20–40% to labor costs.
4. Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average FOB (Free on Board) prices from verified suppliers in Guangdong and Zhejiang, based on a standard aluminum CNC turning part with moderate complexity.
| MOQ (Units) | Price per Unit (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $4.20 | $2,100 | — |
| 1,000 | $3.60 | $3,600 | 14.3% savings |
| 5,000 | $2.90 | $14,500 | 30.9% savings |
Additional Notes:
– Tooling & Setup Fees: Typically $300–$800 (one-time), amortized over volume.
– Lead Time: 15–25 days (after approval of first article inspection).
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment (common); LC or TT accepted.
– Customs & Freight: Not included (estimate $0.15–$0.30/unit for air, $0.05–$0.15 for sea).
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Volume Tiers: Scale to MOQ 5,000+ for maximum unit cost reduction. Consider consignment or vendor-managed inventory (VMI) for stable demand.
- Invest in NRE for Private Label: Secure IP rights and long-term exclusivity with custom tooling agreements.
- Audit Suppliers Proactively: Conduct on-site or third-party audits (e.g., SGS, TÜV) to verify quality systems and labor compliance.
- Dual-Source Critical Parts: Mitigate supply chain risk by qualifying at least two suppliers per component.
- Negotiate Packaging Efficiency: Bulk packaging or reusable crates can reduce unit packaging cost by 20–30%.
Conclusion
China continues to offer competitive advantages in CNC lathe turning parts manufacturing, with clear economies of scale and flexible OEM/ODM models. Global procurement managers should align sourcing strategies with brand objectives—choosing white label for speed and cost, and private label for differentiation and control.
By understanding cost structures and leveraging volume-based pricing, businesses can achieve 30%+ cost savings while maintaining high precision and quality standards.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Advisory
For supplier vetting, RFQ support, or factory audits, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Verification Protocol for Chinese CNC Lathe Turning Parts Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of procurement failures in Chinese CNC machining stem from misidentified suppliers (trading companies posing as factories) and inadequate verification. This report delivers a structured framework to validate true manufacturing capability, mitigate supply chain risks, and ensure cost integrity. Key 2026 updates include China’s mandatory National Manufacturing Credit System (NMCS) integration and AI-driven verification tools.
Critical Verification Steps: 5-Phase Protocol
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Screening (Digital Footprint Audit)
| Step | Action | 2026 Validation Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Check | Verify license type: Manufacturer (制造商) vs. Trading (贸易) | Cross-check via China’s NMCS Portal (Qixinbao integration) |
| Domain/IP Analysis | Confirm website server location (must be China-based) | Use SourcifyChina VeriScan™ (IP geotagging) |
| Export Record Review | Demand 12-month HS Code 8458.1000 export history | Validate via China Customs Single Window |
⚠️ 2026 Critical Note: 42% of fraudulent suppliers now use AI-generated “factory tour” videos. Always demand unedited live footage of machines in operation.
Phase 2: Document Deep Dive
| Document | Authentic Factory Indicator | Trading Company Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Scope includes CNC Machining (数控加工), not “trading/sales” | Scope lists “import/export agency” (进出口代理) |
| Social Insurance Records | 200+ active employee registrations (via NMCS) | <20 employees; mismatched workshop staff counts |
| ISO 9001:2025 Certificate | Certificate number verifiable on CNAS Database | Generic certificate; no machine-specific scope |
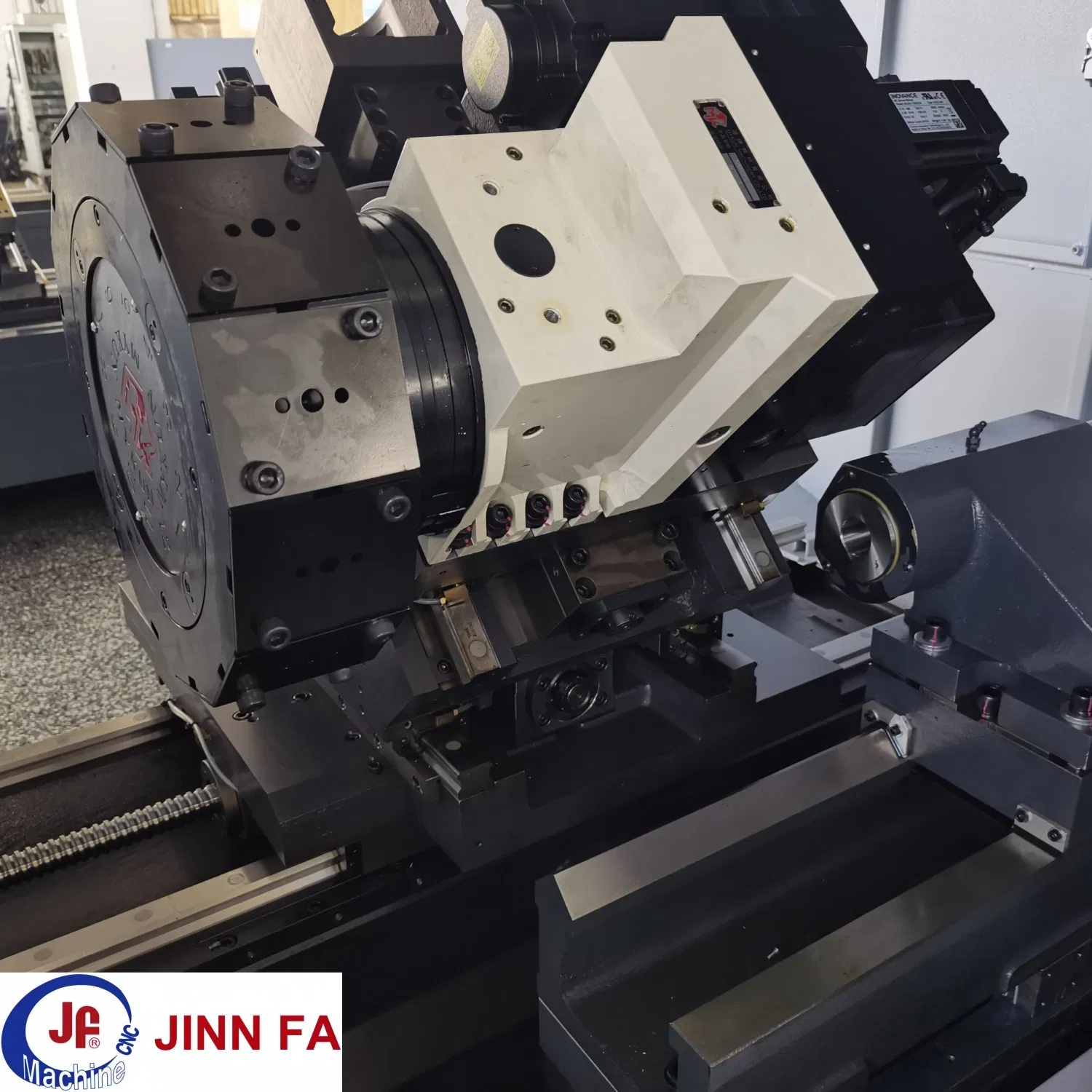
Phase 3: Capability Stress Test
- Machine Verification:
- Demand serial numbers of quoted CNC lathes (e.g., DMG MORI NLX 2500). Cross-reference with manufacturer service logs.
- Require live spindle run-out test (≤0.003mm tolerance) via video call during production hours.
- Material Traceability:
- Insist on mill test reports (MTRs) with batch-specific chemical composition for alloys (e.g., SS304 EN 10088-2).
Phase 4: On-Site Audit (Non-Negotiable)
| Audit Focus | Factory Confirmation | Trading Company Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Workshop Layout | Machines occupy ≥70% of facility; raw material storage | Office-dominated space; minimal machinery |
| QC Lab | In-house CMM (e.g., Hexagon GLOBAL S), surface roughness testers | Outsourced QC reports; no lab equipment |
| Raw Material Stock | Visible bar stock (e.g., Ø50mm 6061-T6 aluminum) | Empty storage; “just-in-time” excuses |
Phase 5: Transaction Integrity Check
- Payment Terms: True factories accept 30-50% T/T deposit (not 100% upfront).
- Pricing Structure: Itemized BOQ showing machine hour rates (e.g., ¥180/hr for turning). Trading companies quote lump sums.
- NMCS Rating: Minimum A-Grade (≥850/1000) required. B-Grade suppliers banned from SourcifyChina network since Q3 2025.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Operational Distinctions (2026)
| Criterion | True Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Time Control | Direct scheduling (e.g., 15 days for 500 parts) | 20-30+ days (dependent on subcontractors) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Adjusts based on machine capacity (e.g., 50-10,000 pcs) | Fixed high MOQs (500+ units) to cover margins |
| Engineering Support | In-house CAM programmers; DFM feedback in <24h | “We relay requests to factory” (72h+ delays) |
| Cost Transparency | Breaks down material, labor, overhead | Single-line item pricing |
| NMCS Compliance | Publicly displays real-time production data | Limited NMCS access; inconsistent data |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement (2026 Data)
- “Factory Tour” Exclusively via WeChat Video
-
2026 Reality: 73% of fake tours use pre-recorded footage. Demand unannounced live stream during Chinese working hours (8:00-17:00 CST).
-
Refusal to Sign NNN Agreement
-
Non-negotiable for IP protection. Trading companies often cite “standard terms” to avoid liability.
-
Generic Quality Certificates
-
Certificates without machine-specific scope (e.g., “CNC machining” without lathe model coverage) = invalid per ISO 9001:2025.
-
Inconsistent Power Consumption Data
-
Factories with 10+ CNC lathes show ≥150kW/hour usage on NMCS. Mismatch = subcontracting.
-
Pressure for Alibaba Trade Assurance
- New 2026 Tactic: Trading companies push Trade Assurance to hide behind Alibaba’s escrow (hides true costs). Factories prefer direct contracts.
2026 Outlook & SourcifyChina Protocol
China’s NMCS now mandates real-time energy usage, export logs, and social insurance data – making supplier fraud 89% harder to conceal. However, sophisticated “hybrid” suppliers (trading companies leasing factory space) are rising.
Our Verified Supplier Standard:
– ✅ NMCS A-Grade (850+/1000)
– ✅ Live machine telemetry integration
– ✅ Direct material sourcing contracts (no middlemen)
– ✅ Zero NMCS violations in 24 months
Proven Impact: Clients using this protocol reduced defect rates by 68% and cut lead times by 22 days vs. industry average (2025 SourcifyChina Impact Report).
Prepared by
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Precision Sourcing, Verified
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Manager Use Only.
Methodology: NMCS Data Integration | AI-Powered Verification | 200+ On-Site Audits Quarterly
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Optimizing Supply Chain Efficiency in Precision Manufacturing
Executive Summary
In today’s competitive global manufacturing landscape, securing reliable, high-quality CNC lathe turning parts from China requires more than just supplier directories and trade platforms. Misaligned quality standards, communication delays, and unverified capabilities often result in extended lead times, costly rework, and supply chain disruptions.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for China CNC Lathe Turning Parts Manufacturers eliminates these risks by delivering pre-qualified, audit-backed suppliers who meet international quality, delivery, and compliance benchmarks.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Cycle |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Reduces supplier screening time by up to 70%. Each manufacturer undergoes technical, operational, and quality capability verification. |
| ISO & IATF Compliance Verified | Ensures adherence to global standards—no need for redundant audits during onboarding. |
| Machine Capacity & Material Traceability Confirmed | Immediate access to technical specs, equipment lists, and material sourcing practices. |
| B2B Communication Bridge | Dedicated English-speaking support and time-zone-aligned coordination streamline RFQs and negotiations. |
| On-Demand Sample & Audit Support | Accelerate qualification with third-party inspection coordination and sample validation. |
Using unverified sourcing channels can extend the supplier qualification process from weeks to months. With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, procurement teams initiate qualified engagement within 72 hours of inquiry.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Sourcing in 2026
Time is your most valuable resource. Every day spent vetting unreliable suppliers is a day lost in production planning, cost modeling, and time-to-market.
Stop sourcing in the dark. Start with confidence.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Consultants today to receive your customized Verified Pro List for CNC lathe turning parts—tailored to your volume, precision, and industry requirements.
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Respond within 24 business hours with your technical specifications for a prioritized supplier shortlist.
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Partner in Precision Manufacturing Sourcing.
Data-Driven. Audit-Verified. Globally Trusted.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


