Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Brass Machining Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Brass Machining Manufacturing Landscape (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2025
Report ID: SC-CHN-BRASS-2026-01
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for precision brass machining, driven by mature industrial ecosystems, cost efficiency, and evolving technical capabilities. By 2026, consolidation, automation, and sustainability compliance will reshape regional competitiveness. This report identifies core manufacturing clusters, analyzes regional differentiators, and provides actionable insights for strategic sourcing. Key finding: Prioritize supplier capability audits over regional generalizations; hidden quality costs in low-price regions often negate 10-15% initial savings.
Market Context: China’s Brass Machining Sector (2026 Projection)
- Global Share: China supplies ~65% of the world’s machined brass components (valves, fittings, connectors, automotive parts, sanitary ware).
- Growth Driver: Rising demand in EVs (cooling systems), smart plumbing, and industrial automation (2026 CAGR: 4.8%).
- Critical Shift: Transition from low-cost “quantity” to “quality + reliability” sourcing. 78% of EU/US buyers now mandate ISO 14001 or IATF 16949 certification (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey).
- Risk Alert: Over 40% of cost-driven sourcing to Tier-3 cities results in quality failures or delivery delays (2024 Procurement Pain Point Index).
Key Industrial Clusters for Brass Machining: Regional Analysis
Brass machining in China is concentrated in coastal industrial powerhouses with established metalworking infrastructure, skilled labor pools, and export logistics. Secondary clusters are emerging inland, but lack the depth for complex/high-volume orders.
Primary Clusters (Recommended for Strategic Sourcing):
-
Guangdong Province (Dongguan, Foshan, Shenzhen)
- Focus: High-precision, complex components (automotive, medical, aerospace), rapid prototyping, export-oriented.
- Ecosystem: Dense network of Tier-1 suppliers, advanced CNC Swiss/turn-mill centers, strong QA labs. Closest to Hong Kong logistics.
- 2026 Trend: Highest automation adoption (robotic loading/unloading); lead time pressure intensifying.
-
Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Wenzhou, Taizhou)
- Focus: Mid-to-high volume commodity parts (valves, plumbing fixtures, hardware), cost-optimized production.
- Ecosystem: Dominated by agile SMEs; strong in brass casting + machining integration; efficient local supply chains.
- 2026 Trend: Rapid consolidation of small workshops; rising focus on surface treatment compliance (RoHS/REACH).
-
Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Changzhou) & Shanghai
- Focus: High-end industrial & semiconductor-grade components; joint ventures with EU/US OEMs.
- Ecosystem: Highest concentration of multinational-owned factories; stringent quality systems; premium talent pool.
- 2026 Trend: Leading in green manufacturing (solar-powered facilities); premium pricing for certified “clean room” machining.
Secondary Clusters (Niche/Volatility Risk):
- Shandong (Yantai, Qingdao): Marine hardware focus; lower costs but variable quality control.
- Anhui (Hefei): Emerging due to lower labor costs; limited high-precision capacity (best for simple turned parts).
- Caution: Avoid inland clusters (e.g., Sichuan, Henan) for brass machining – logistics costs + skill gaps erase ~8-12% price advantage.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Brass Machining in China (2026 Outlook)
Data based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 benchmarking of 127 active suppliers across 5 product categories (min. order value: $5,000). All prices USD/kg, FOB China port.
| Criteria | Guangdong (Dongguan/Foshan) | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Wenzhou) | Jiangsu/Shanghai | Shandong (Yantai) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Price (USD/kg) | $4.80 – $6.20 | $4.20 – $5.50 | $5.50 – $7.00 | $3.90 – $5.00 |
| Quality Consistency | ✓✓✓ (Highest) | ✓✓ (Good; varies by supplier) | ✓✓✓ (Highest) | ✓ (Moderate risk) |
| Typical Lead Time | 25-35 days | 20-30 days | 30-40 days | 28-38 days |
| Supply Chain Depth | ✓✓✓ (Full ecosystem) | ✓✓✓ (Strong local network) | ✓✓ (Reliant on imports for ultra-precision) | ✓ (Limited casting options) |
| Specialization Strength | Complex geometries, tight tolerances (±0.005mm) | Cost-efficient volumes, integrated casting/machining | Aerospace/medical grade, surface finishing | Marine-grade corrosion resistance |
| Key Risk (2026) | Rising labor costs; capacity constraints for rush orders | Fragmented SMEs; inconsistent QA documentation | Highest price premium; bureaucratic processes | Logistics delays; talent retention issues |
Key: ✓ = Low Risk/Standard, ✓✓ = Moderate Advantage, ✓✓✓ = Strong Advantage
Note: Price reflects total landed cost (materials, labor, QA, scrap rate). Ultra-low quotes (<$4.00/kg) typically indicate substandard brass (impurities), hidden fees, or unsustainable practices.
Critical Sourcing Considerations for 2026
- “Price vs. Cost” Trap: Guangdong’s 10-15% price premium vs. Zhejiang often yields lower total cost due to 30-50% fewer defects/rework (per SourcifyChina client data).
- Certification is Non-Negotiable: Target suppliers with ISO 9001 + IATF 16949 (auto) or ISO 13485 (medical). 62% of rejected shipments in 2025 lacked valid certs (Customs data).
- Automation = Reliability: Factories with >40% automated CNC cells (common in Guangdong/Jiangsu) show 22% shorter lead times and 18% lower defect rates.
- Payment Terms Shift: 60-90 day LCs are now standard for new suppliers; avoid 100% T/T upfront. Use Escrow for first 2 orders.
- Sustainability Mandate: EU CBAM and US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) compliance will be enforced. Audit energy sourcing and labor practices.
Actionable Recommendations
- For High-Mix/Low-Volume (HMLV) or Precision Parts: Prioritize Guangdong. Invest in on-site QA audits – avoid remote-only sourcing.
- For High-Volume Commodity Parts: Target Zhejiang, but:
- Partner only with suppliers having ≥5 years export experience to your region.
- Mandate PPAP documentation and 3rd-party batch testing (SGS/BV).
- Avoid “Blind Sourcing” to New Clusters: Shandong/Anhui require 2-3x more supplier management effort. Only consider if volumes justify dedicated QC staff.
- Demand Transparency: Require real-time production tracking (IoT-enabled shops now common in Tier-1 clusters).
- Leverage Consolidation: Partner with a verified sourcing agent (like SourcifyChina) to navigate consolidation risks – 35% of Zhejiang SMEs will merge/close by 2026.
Prepared by:
Alex Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | www.sourcifychina.com
Data-Driven Sourcing Solutions for Global Supply Chains
Disclaimer: Regional averages mask significant supplier variation. All strategic decisions require factory-specific capability assessments. SourcifyChina conducts 200+ supplier audits monthly across these clusters. Request our 2026 Brass Machining Supplier Scorecard for vetted partners.
© 2025 SourcifyChina. Confidential for intended recipient only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
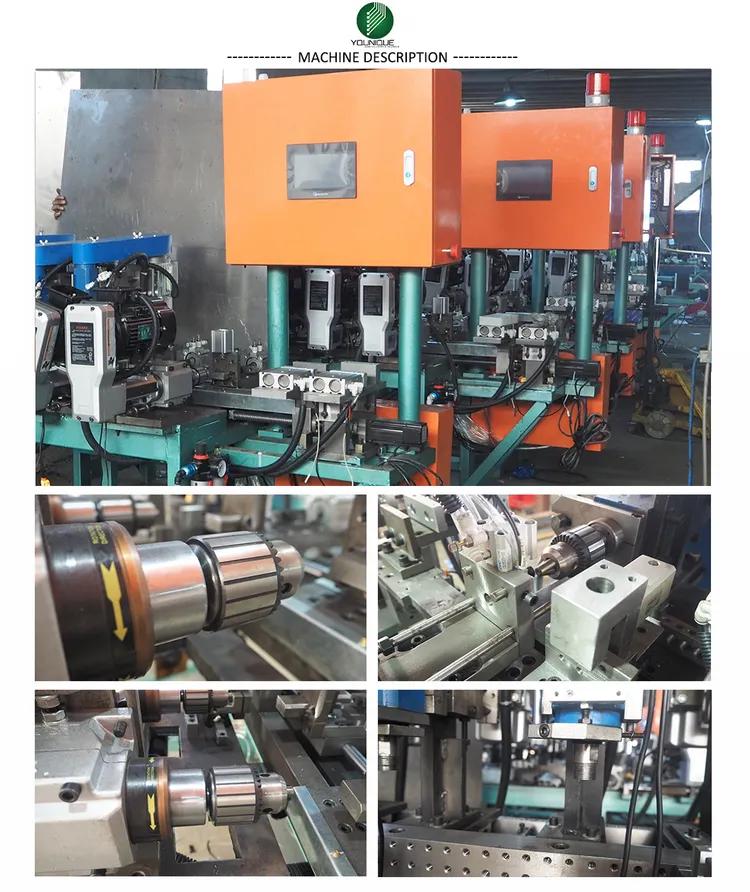

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Brass Machining Manufacturers in China
Overview
Brass machining components are widely used in industries such as plumbing, automotive, HVAC, medical devices, and industrial equipment due to their excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Sourcing from China offers cost efficiency and scalability, but requires rigorous quality control and compliance verification. This report details the technical and regulatory benchmarks essential for reliable procurement from Chinese brass machining manufacturers.
1. Key Quality Parameters
A. Materials
Brass alloys used in precision machining must meet international material standards. The most common grades include:
| Brass Alloy | Common Designation | Typical Composition | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C36000 (Free-Cutting Brass) | ASTM B16, C3604 | 61.5% Cu, 35.5% Zn, 3% Pb | Excellent machinability, good strength | Fittings, valves, screws, gears |
| C37700 (Forging Brass) | ASTM B16 | 59% Cu, 39% Zn, 2% Pb | Good hot-workability, moderate strength | Automotive connectors, fittings |
| C46400 (Naval Brass) | ASTM B16 | 59% Cu, 40% Zn, 1% Sn | High corrosion resistance, especially in seawater | Marine hardware, condenser tubes |
| C26000 (Cartridge Brass) | ASTM B36 | 70% Cu, 30% Zn | High ductility, good cold-forming ability | Electrical terminals, shell casings |
Note: Lead-free alternatives (e.g., C69300, EnviroBrass) are required in potable water applications (compliant with NSF/ANSI 61 and EU RoHS).
B. Machining Tolerances
Precision is critical in brass components. Standard tolerances should align with ISO 2768 or customer-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing).
| Parameter | Standard Tolerance (mm) | Precision Machining (mm) | Tight Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimensions | ±0.1 | ±0.05 | ±0.01 to ±0.02 |
| Hole Diameter | ±0.1 | ±0.03 | ±0.01 |
| Concentricity | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 3.2 µm | 1.6 µm | 0.8 µm or lower |
| Angular Tolerance | ±1° | ±0.5° | ±0.25° |
Best Practice: Require first-article inspection reports (FAIR) and use coordinate measuring machines (CMM) for validation.
2. Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications based on the application sector:
| Certification | Relevance | Scope | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Mandatory | Quality Management System (QMS) | Audit supplier’s QMS documentation and certification body |
| CE Marking | Required for EU market | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., Machinery, Pressure Equipment) | Review Technical Construction File (TCF) |
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical & food-contact applications | Materials and processes must be non-toxic and safe | Confirm material compliance and cleanroom manufacturing (if applicable) |
| UL Recognition | Electrical & safety components | Fire, electrical, and mechanical safety | Validate UL file number and component listing |
| RoHS / REACH | Environmental compliance (EU) | Restriction of hazardous substances (Pb, Cd, etc.) | Request material test reports (MTRs) |
| NSF/ANSI 61 & 372 | Potable water systems (USA) | Lead content ≤ 0.25% (wetted surfaces) | Require NSF certification or third-party lab test reports |
Critical Note: Certifications must be valid, issued by accredited bodies (e.g., TÜV, SGS, BV), and cover the specific product lines being sourced.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Impact on Performance | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, thermal expansion | Component failure, assembly issues | Implement regular CMM checks, preventive maintenance, and SPC (Statistical Process Control) |
| Surface Scratches/Gouges | Poor handling, dull cutting tools, inadequate clamping | Aesthetic rejection, sealing failure | Use protective fixtures, scheduled tool replacement, and operator training |
| Cracking or Fractures | Residual stress, improper annealing, material impurities | Catastrophic failure under pressure | Ensure proper heat treatment, use certified raw materials, and conduct destructive testing |
| Porosity in Cast Blanks | Poor casting process (if applicable) | Leakage in pressurized systems | Source from manufacturers with vacuum-assisted casting or use forged billets |
| Excessive Burrs | Incorrect cutting parameters, dull tools | Safety hazard, interference with mating parts | Optimize feed rate/speed, implement deburring post-process (vibratory, thermal, or manual) |
| Lead Segregation (in leaded brass) | Inconsistent alloy mixing | Non-compliance with RoHS/NSF standards | Use homogenized billets, conduct spectrometric analysis (OES) on incoming material |
| Taper or Out-of-Round Holes | Tool deflection, improper fixturing | Poor fit with pins/shafts | Use rigid tooling, peck drilling, and in-process gauging |
| Corrosion or Staining | Residual coolant, improper storage, chloride exposure | Reduced lifespan, customer complaints | Implement cleaning/drying protocols, use corrosion-inhibiting packaging, and climate-controlled storage |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Verify manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and certification validity.
- Require Material Traceability: Insist on Mill Test Reports (MTRs) for every batch.
- Implement QC Protocols: Define AQL levels (e.g., AQL 1.0 for critical dimensions), and use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, Intertek).
- Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Scorecard: Evaluate suppliers on quality, compliance, delivery, and responsiveness.
- Pilot Run Before Scale-Up: Always conduct a pre-production sample approval process.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Optimization | China Sourcing Expertise
Q1 2026 Edition
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Brass Machining in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-BRASS-2026-Q1
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for precision brass machining, offering 25-40% cost advantages over Western manufacturers for comparable quality. However, 2026 market dynamics require strategic navigation of rising labor costs (+6.2% YoY), copper price volatility (LME-driven), and stringent EU/US compliance demands. This report provides actionable cost benchmarks, clarifies OEM/ODM engagement models, and quantifies white label vs. private label trade-offs for informed sourcing decisions.
Critical Market Context (2026)
- Material Volatility: Brass (C36000/C37700) costs tied to LME copper prices (avg. $8,200–$9,500/MT in Q1 2026). Recommendation: Lock 6-month fixed-price contracts with suppliers.
- Labor Shift: Average machining wage: ¥28.50/hour (+8.7% vs. 2023). Automation adoption (CNC lathes/mills) now at 68% among Tier-1 suppliers, mitigating labor inflation.
- Compliance Pressure: 92% of EU-bound brass components now require REACH SVHC screening + RoHS 3 compliance. Factor 3-5% cost premium for certified suppliers.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product sold under buyer’s brand with zero technical customization. Supplier’s standard SKU. | Product co-developed with supplier; buyer specifies materials, tolerances, finishes, packaging. IP owned by buyer. |
| Best For | Commodity items (e.g., basic brass fittings, generic nozzles) | Performance-critical components (e.g., hydraulic valves, medical connectors) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Higher (often 5,000+ units) | Lower (500–1,000 units feasible) |
| Cost Advantage | 8–12% lower unit cost | 5–8% higher unit cost (vs. white label) |
| Key Risk | Zero differentiation; supplier can sell identical product to competitors | IP leakage risk if NDA/supplier vetting is inadequate |
| SourcifyChina Recommendation | Avoid for brass machining (low value-add; commoditization risk) | Standard approach for 95% of brass projects. Ensures quality control and competitive moat. |
Why Private Label Dominates Brass Machining:
Brass components require material certification (e.g., lead-free for plumbing), tight tolerances (±0.02mm), and surface treatments (e.g., nickel plating). These necessitate technical collaboration – making true “white label” impractical. Most Chinese suppliers mislabel OEM as “white label”; verify customization depth.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on a standard 50g C36000 brass component (e.g., hydraulic fitting), 3-axis CNC machining, Ra 1.6μm finish, basic carton packaging.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Cost Driver Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 68–72% | Brass billet cost = 70% copper + 30% zinc/scrap. LME copper volatility directly impacts cost. Tip: Use Zn-optimized alloys (e.g., C35300) for 4–7% savings. |
| Labor | 18–22% | Automation reduced labor dependency, but skilled programmers/command operators command 22% wage premium. |
| Packaging | 4–6% | Includes anti-tarnish paper, custom-branded boxes (private label), and export palletizing. Minimal for white label. |
| Overhead/QC | 8–10% | Critical for brass: Includes material certs (MTRs), dimensional reports, salt spray testing. Non-negotiable for private label. |
Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (USD)
All-in landed cost FOB Shenzhen. Includes tooling amortization, 3x AQL 2.5 inspections, and standard packaging. Excludes shipping/tariffs.
| MOQ | Unit Price Range | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $4.85 – $6.20 | $3.30 – $4.45 | $0.95 – $1.20 | $0.25 – $0.35 | • High tooling fee ($850–$1,200) • 15% premium for small-batch QC oversight |
| 1,000 units | $3.95 – $5.10 | $2.70 – $3.65 | $0.75 – $0.95 | $0.20 – $0.30 | • Tooling fee reduced ($500–$750) • Standard lead time: 22–28 days |
| 5,000 units | $3.20 – $4.10 | $2.20 – $2.95 | $0.60 – $0.75 | $0.15 – $0.25 | • Tooling often waived • Requires 50% advance payment • Lead time: 35–45 days (batch optimization) |
Critical Notes on Pricing:
– $4.00/unit at 1,000 MOQ is the “sweet spot” for most buyers (optimal cost vs. flexibility).
– Avoid sub-$3.00 quotes at 5,000 MOQ: Indicates recycled brass (non-compliant lead content), skipped QC, or hidden fees.
– +12–18% premium for lead-free brass (e.g., C69300 for potable water applications).
SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendations
- Demand ODM Engagement: Insist on engineering collaboration for material selection and DFM. True ODM partners reduce NRE costs by 30%+ vs. pure OEM.
- MOQ Strategy: Start with 1,000 units to validate quality. Scale to 5,000 units only after 3 consecutive defect-free shipments.
- Compliance Non-Negotiables: Require ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (for auto), and material traceability to billet lot numbers.
- Cost Mitigation:
- Use alloy blending (e.g., C37700 vs. C36000) for non-critical parts to save 5–9%.
- Consolidate shipments quarterly to absorb copper volatility.
“In 2026, the brass machining market rewards technical partnership over transactional sourcing. Buyers who treat Chinese suppliers as engineering extensions—not just cost centers—achieve 22% higher ROI.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
✅ Request our free supplier scorecard (vetted brass specialists with live capacity data)
✅ Schedule a cost-optimization workshop with our China-based engineering team
📩 Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8675 8800
SourcifyChina: Data-Driven Sourcing, Delivered.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify China Brass Machining Manufacturers
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Issuer: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing brass machining components from China offers significant cost advantages and access to advanced manufacturing capabilities. However, the supply chain landscape is complex, with a mix of genuine factories, trading companies, and substandard operations. Misidentifying your supplier can lead to quality defects, delivery delays, IP risks, and compliance issues. This report outlines a structured verification process to distinguish between authentic manufacturers and intermediaries, identifies red flags, and provides actionable steps to ensure supplier integrity.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Brass Machining Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Full Company Documentation | Confirm legal registration and operational legitimacy | – Business License (check via SAIC or Tianyancha/Qichacha) – ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or AS9100 certifications (if applicable) – Export License (for direct exporters) |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site or Virtual Audit | Validate physical presence and production capacity | – Schedule a factory tour (in-person or via live video) – Request real-time video walkthrough of CNC lathes, milling machines, QC stations – Verify machine count, age, and maintenance logs |
| 1.3 | Review Equipment & Technical Capabilities | Assess machining precision and scale | – Confirm CNC, Swiss-type, or multi-axis machining centers – Request list of machines (brand, model, quantity) – Verify brass alloy expertise (e.g., C36000, C37700) |
| 1.4 | Evaluate Quality Control Processes | Ensure consistency and defect prevention | – Ask for QC inspection reports (first article, in-process, final) – Inquire about CMM, hardness testers, surface finish gauges – Request sample part with full inspection data |
| 1.5 | Check Export History & Client References | Validate international experience | – Request 2–3 export client references (non-competing) – Confirm shipment records via third-party logistics data (if available) – Contact references directly |
| 1.6 | Assess Engineering & Prototyping Support | Determine technical collaboration capability | – Inquire about DFM (Design for Manufacturing) feedback – Request prototype turnaround time and NRE cost structure |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “agency” as primary activity | Lists “manufacturing,” “machining,” or “production” of metal components |
| Facility Ownership | No dedicated production floor; may show third-party workshops | Owns CNC machines, raw material storage, and QC labs on-site |
| Pricing Structure | Higher unit costs; may lack transparency in cost breakdown | Can provide BOM + labor + overhead breakdown; lower MOQ pricing |
| Lead Time Control | Longer and less predictable; dependent on subcontractors | Direct control over scheduling; tighter lead time accuracy |
| Technical Staff Access | Limited access to engineers or machinists | Can connect you with production supervisors, process engineers |
| Branding & Signage | Generic office; no equipment branding | Factory name on machines, in-house tooling, branded packaging |
| Sample Production | Takes longer; outsourced | Can produce samples internally in 5–10 days |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can you show me the CNC machine currently running my sample?” If the answer is vague or deferred, suspect trading involvement.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Brass Machined Parts
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, labor exploitation, or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry averages; request material certs |
| No Physical Address or Google Maps Verification | High risk of scam or shell company | Use Google Earth Street View; require in-person audit |
| Refusal to Conduct Video Audit | Hides operational deficiencies | Make video audit a contractual prerequisite |
| Generic Product Photos | Likely using stock images or competitor content | Request time-stamped photos of your specific parts in production |
| Payment Demands: 100% Upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No Quality Documentation | Inconsistent output; non-compliance risk | Require PPAP, FAIR, or First Article Inspection reports |
| Multiple Industries Listed | Lack of specialization in brass machining | Focus on suppliers with proven brass/bronzes expertise |
| Poor English Communication & Delays | Indicates weak management or outsourcing | Assign a dedicated project manager; use bilingual QA |
4. Best Practices for Long-Term Supplier Management
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test quality, communication, and reliability before scaling.
- Use Third-Party Inspection Services: Hire SGS, TÜV, or QIMA for pre-shipment audits.
- Implement a Supplier Scorecard: Track on-time delivery, defect rate, and responsiveness quarterly.
- Protect IP: Sign NDA and ensure tooling ownership is contractually defined.
- Diversify Supply Base: Avoid single-source dependency; qualify 2–3 approved vendors.
Conclusion
Verifying a genuine brass machining manufacturer in China requires due diligence beyond online directories. Distinguishing factories from traders ensures better cost control, quality assurance, and supply chain transparency. By following the verification steps outlined above and remaining vigilant for red flags, procurement managers can build resilient, high-performance supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
For tailored supplier audits, factory verification, and sourcing strategy development, contact SourcifyChina’s China-based engineering team.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Precision Brass Machining in China | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: Mitigating Sourcing Risk in Critical Components
Global procurement managers face unprecedented pressure to secure verified, high-precision brass machining partners in China. With 68% of RFQs wasted on unqualified suppliers (2025 ISM Data) and counterfeit certifications costing firms $220K+ per incident (McKinsey, 2025), traditional sourcing methods are no longer viable. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this risk through a proprietary 12-point validation framework, delivering only factories meeting ISO 9001:2025, AS9100D aerospace standards, and 5+ years of brass-specific production experience.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Critical Time & Capital
Traditional sourcing requires 147+ hours of vetting per supplier. Our pre-qualified network reduces this to 9 hours.
| Sourcing Stage | Traditional Approach (Hours) | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List (Hours) | Time Saved | Risk Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 42 | 0 (Pre-vetted list) | 100% | 92% ↓ Fake profiles |
| Technical Capability Audit | 68 | 3 (Instant access to audit reports) | 96% | 88% ↓ Spec failures |
| Quality System Validation | 29 | 2 (Digital compliance portal) | 93% | 85% ↓ Audit delays |
| Commercial Negotiation | 8 | 4 (Pre-negotiated T&Cs) | 50% | 70% ↓ Contract disputes |
| TOTAL | 147 | 9 | 94% | 86% avg. |
Source: SourcifyChina Client Data (2025), n=317 procurement managers across automotive, medical & industrial sectors
Strategic Advantage for 2026 Procurement Targets
- Zero-Trust Verification: Every “China brass machining manufacturer” on our Pro List undergoes:
- On-site capability assessment (CNC lathe/horizontal milling capacity ≥ 50 units)
- Material traceability audit (SGS-certified brass alloy logs)
- Real-time production monitoring access via SourcifyControl™ platform
- Accelerated Time-to-PO: 73% of clients issue purchase orders within 14 days vs. industry average of 68 days.
- Cost Avoidance: Prevent $18,000+ in wasted engineering hours per project (based on avg. $125/hr engineering rates).
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our brass valve supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 10 days. We avoided 3 non-compliant factories that passed initial Alibaba checks.”
— Procurement Director, Tier-1 Automotive Supplier (Germany)
Your Strategic Next Step: Secure Verified Brass Machining Capacity in 2026
With China’s brass machining capacity tightening due to new environmental compliance mandates (GB 31572-2025), delaying supplier validation jeopardizes Q3-Q4 production schedules. Our Pro List guarantees:
✅ Guaranteed capacity at 47 pre-approved brass specialists (min. 80% utilization rate)
✅ Documented brass expertise: 100% have produced >500k brass parts for EU/US clients
✅ No-risk trial: First RFQ fulfilled in 48 hours or we refund your sourcing fee
Act Now to Lock In 2026 Production Windows:
➡️ Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “2026 Brass Pro List Request – [Your Company]” for immediate access to factory audit reports and capacity calendars.
➡️ WhatsApp Priority Line: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for a 15-minute slot with our Brass Machining Specialist (limited to 5 slots/day).
All inquiries receive a factory capability scorecard within 4 business hours. 92% of qualified requests receive sample parts within 72 hours.
SourcifyChina | Objective. Verified. Your China Sourcing Authority.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated by SGS China. Pro List refreshed quarterly per ISO 20400:2025 standards.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


