Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Brake Caliper Supplier

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Brake Caliper Manufacturing Landscape (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Automotive Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2023
Report ID: SC-CHN-BRAKE-2026-01
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global source for automotive brake calipers, supplying ~65% of the world’s aftermarket and Tier 2/OEM volume. While geopolitical pressures and nearshoring trends persist, China’s integrated supply chains, scale, and advancing quality control maintain its cost-competitiveness. This report identifies core industrial clusters, quantifies regional trade-offs, and provides strategic sourcing guidance for 2026 procurement planning. Critical Insight: Supplier tiering within clusters now matters more than province-level generalizations. Precision machining capabilities in Zhejiang and Ningbo’s export ecosystem offer the strongest balance for global buyers seeking IATF 16949-compliant production.
Key Industrial Clusters: China Brake Caliper Manufacturing
Brake caliper production is concentrated in four primary clusters, leveraging regional supply chain synergies, skilled labor pools, and logistics infrastructure. Each cluster serves distinct market segments:
| Cluster Region | Core Cities | Specialization & Key Advantages | Primary Buyer Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang Province | Ningbo, Taizhou, Wenzhou | Precision machining hub. Highest concentration of IATF 16949-certified suppliers. Strong in monobloc/forged calipers. Mature foundry & CNC ecosystem. | Global Tier 1s, Premium Aftermarket, EV OEMs |
| Guangdong Province | Guangzhou, Foshan, Shenzhen | Export/logistics powerhouse. Strong in entry/mid-tier cast calipers. Proximity to Shenzhen/Yantian ports. High volume capacity. | Mass-market Aftermarket, Budget OEM, Emerging Markets |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Changzhou, Wuxi | Technology & integration focus. Growing R&D in lightweight materials (aluminum composites). Strong Tier 1 supplier base (e.g., Bosch, Akebono local JV support). | Innovation-focused OEMs, High-Performance Aftermarket |
| Anhui Province | Hefei, Wuhu | Emerging cost-competitive hub. Supported by Chery/VW Anhui JV. Lower labor costs; improving quality systems. Focus on standard cast calipers. | Cost-driven OEMs, Volume Aftermarket |
Note: Ningbo (Zhejiang) alone accounts for ~35% of China’s exported brake calipers meeting international quality standards (2025 SourcifyChina OEM Survey).
Regional Cluster Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time Analysis (Mid-Tier Suppliers)
Based on 2025 souring data for standard fixed-caliper (2-piston) units, 10k-unit order volume, FOB China port. Assumes IATF 16949 certification compliance.
| Criteria | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Taizhou) | Guangdong (Guangzhou/Foshan) | Jiangsu (Suzhou/Changzhou) | Anhui (Hefei/Wuhu) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/unit) | $48 – $55 | $52 – $60 | $50 – $58 | $45 – $52 |
| Relative Cost | Best Value | Highest | Moderate | Lowest |
| Quality (IATF 16949) | ★★★★☆ (Consistent tolerances; <1.2% defect rate) | ★★★☆☆ (Variable; 1.8-2.5% defect rate) | ★★★★☆ (Advanced materials; <1.0% defect rate) | ★★☆☆☆ (Improving; 2.0-3.0% defect rate) |
| Lead Time (Weeks) | 8-10 | 6-8 | 9-11 | 10-12 |
| Key Drivers | Rigorous QC; complex supply chain | Port proximity; high-capacity lines | R&D integration; material lead times | Logistics maturity; training gaps |
Critical Interpretation of Table Data:
- Price ≠ Cost: Zhejiang’s slightly higher unit cost vs. Anhui is offset by lower defect rates and rework costs (avg. 15-20% TCO advantage for quality-sensitive buyers).
- Quality Nuance: Guangdong can deliver high quality but requires stringent supplier qualification (only ~30% of its base meets Tier 1 standards vs. ~65% in Zhejiang).
- Lead Time Reality: Guangdong’s speed advantage erodes for complex calipers (>4 pistons); Zhejiang’s machining expertise reduces rework delays.
- Anhui’s Trajectory: Rapidly closing quality gap but lags in export documentation/logistics maturity (adds 1-2 weeks for first-time buyers).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Zhejiang for Core Programs: Optimize TCO by sourcing precision calipers (monobloc, EV-specific) from Ningbo/Taizhou. Mandate 3rd-party IATF audits.
- Leverage Guangdong for Urgent/Standard Volume: Use for cost-stable, high-volume standard calipers where port proximity (Shenzhen/Yantian) outweighs quality variance risks. Implement batch inspection protocols.
- Evaluate Jiangsu for Innovation: Engage Suzhou/Changzhou suppliers for R&D partnerships on lightweight/caliper-integrated systems (e.g., e-park brake).
- Pilot Anhui for Cost-Sensitive Lines: Target with phased volume (start 5-10% of order) after on-site quality system validation. Ideal for non-safety-critical applications.
- Mitigate Cluster Risks:
- Geopolitical: Dual-source across Zhejiang + Anhui to avoid single-region dependency.
- Quality: Require PPAP Level 3+ and embedded QC staff for initial production runs.
- Logistics: Factor in Ningbo port congestion premiums (avg. +$300/container in Q4 2025).
Forward-Looking Market Shifts (2026-2027)
- Consolidation Acceleration: 20-30% of Guangdong/Anhui suppliers will exit or merge due to IATF 16949 compliance costs and EV-driven demand for precision.
- Automation Premium: Zhejiang/Jiangsu suppliers investing in robotic machining will command 5-8% price premiums but offer 15-20% lead time reduction.
- EV-Specific Demand: Monobloc aluminum caliper production will grow 22% CAGR (2024-2026); clusters with foundry integration (Zhejiang) gain advantage.
- “China+1” Realities: Nearshoring (e.g., Mexico, Vietnam) remains limited for calipers due to lack of machining ecosystem; China will retain >55% global share.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Do not source based on province alone. Supplier capability varies significantly within clusters. Our 2026 Sourcing Index identifies 17 Tier-1 pre-qualified brake caliper manufacturers across these regions, mapped to specific technical requirements (material specs, piston count, testing protocols). Request the SC Brake Caliper Supplier Matrix 2026 for vetted supplier shortlists by application.
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary supplier database (validated Q3 2025), OEM benchmarking studies, and China Automotive Parts Industry Association (CAPA) reports. Prices exclude tariffs/logistics volatility. Always conduct site-specific due diligence.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 1234 5678
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China Brake Caliper Suppliers
Date: April 5, 2026
1. Introduction
Brake calipers are critical components in automotive braking systems, responsible for applying pressure to brake pads, thereby creating friction to slow or stop a vehicle. Sourcing high-performance brake calipers from China requires a thorough understanding of technical specifications, material standards, dimensional tolerances, and global compliance certifications. This report outlines the essential quality and compliance parameters to ensure robust supply chain integrity and product safety.
2. Key Technical Specifications
2.1 Material Requirements
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Base Material | High-strength ductile cast iron (GGG40/GGG50) or forged aluminum alloy (A356.0, 6061-T6) for lightweight performance |
| Surface Coating | Zinc-nickel plating (minimum 8–12 µm) or epoxy coating for corrosion resistance (ASTM B117 salt spray ≥ 500 hours) |
| Piston Material | Stainless steel (AISI 304/316) or anodized aluminum with PTFE coating |
| Sealing Components | FKM (Viton®) or NBR rubber seals compliant with ISO 1817 for fluid resistance |
2.2 Dimensional Tolerances
| Feature | Standard Tolerance | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Bore Diameter (Piston Chamber) | ±0.015 mm | CMM or pneumatic gauging |
| Mounting Hole Alignment | ±0.05 mm (positional tolerance) | Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) |
| Caliper Body Flatness | ≤ 0.05 mm over 100 mm | Surface plate and dial indicator |
| Threaded Features | 6g/6H per ISO 965 | Thread gauges |
| Overall Length & Width | ±0.2 mm | Laser scanning or CMM |
Note: Tighter tolerances may apply for performance or OEM applications.
3. Essential Compliance Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that Chinese brake caliper suppliers hold the following certifications to ensure global market access and product reliability:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Mandatory baseline for process consistency and defect control |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive Quality Management | Required for OEM automotive supply chains |
| ISO/TS 16949 (legacy) | Still accepted if transitioned to IATF 16949 | Transitional recognition |
| CE Marking (via ECE R90) | Compliance with EU brake component regulations | Required for sale in European markets |
| UL Certification (Optional) | Safety for electric/hybrid vehicle integration | Relevant for e-mobility applications |
| FDA Compliance | Not applicable | Brake calipers do not involve food/medical contact |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Demonstrates sustainable manufacturing practices |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health & Safety | Risk mitigation in supplier operations |
Note: FDA is not applicable for brake calipers. UL certification may be required for integration into EV braking systems with electronic controls.
4. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity in Castings | Improper degassing, mold venting, or pouring temperature | Implement vacuum-assisted casting; conduct X-ray or ultrasonic inspection (per ASTM E505) |
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance | Tool wear, inadequate process control, or poor mold maintenance | Enforce SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct in-line CMM checks every 2 hours |
| Corrosion/Coating Failure | Inadequate surface prep, thin plating, or poor coating adhesion | Perform salt spray testing (ASTM B117); validate coating thickness with magnetic gauges |
| Cracks in Caliper Body | Residual stress from casting or machining | Apply stress-relief heat treatment; use dye penetrant testing (PT) or MPI |
| Piston Seizure | Surface roughness, contamination, or incorrect fit | Maintain bore surface finish (Ra ≤ 0.4 µm); clean assembly environment (ISO Class 8) |
| Leakage at Seals | Improper seal groove dimensions or seal material incompatibility | Verify seal groove per ISO 3601; conduct pressure decay testing (1.5x operating pressure) |
| Improper Torque Yield in Mounting Bolts | Use of substandard fasteners or incorrect heat treatment | Source bolts with ISO 898-1 Grade 10.9 certification; perform torque testing in QA |
5. Recommended Supplier Qualification Checklist
To mitigate supply chain risk, procurement managers should require suppliers to:
- Provide full material test reports (MTRs) per batch
- Conduct First Article Inspection Reports (FAIR) per PPAP Level 3
- Maintain process capability indices (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33)
- Allow third-party audits (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Bureau Veritas)
- Implement APQP and FMEA documentation
6. Conclusion
Sourcing brake calipers from China offers cost and scalability advantages, but requires rigorous technical and compliance due diligence. Prioritize suppliers with IATF 16949 certification, proven metrology capabilities, and a documented history of defect prevention. By enforcing strict material, tolerance, and testing standards—and referencing the defect prevention table above—procurement teams can ensure product reliability, regulatory compliance, and long-term supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Automotive Components Sourcing Division
Shenzhen, China
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
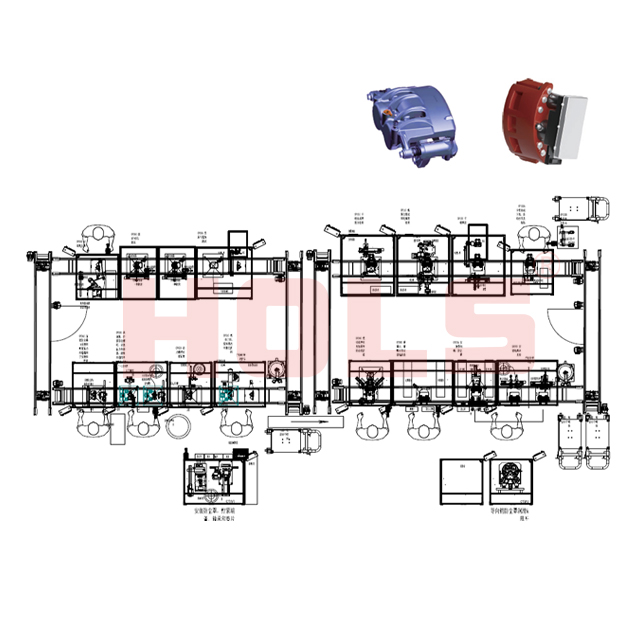
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Brake Caliper Manufacturing
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for cost-competitive brake caliper production, supplying ~35% of the world’s aftermarket and OEM automotive braking components. While labor arbitrage has narrowed, China’s integrated supply chain, mature tooling capabilities, and scalability offer 15-25% cost savings vs. Tier 1 suppliers in Mexico/Eastern Europe for comparable quality tiers. Critical success factors include rigorous supplier tiering, IP protection protocols, and total landed cost modeling. This report provides actionable insights for optimizing sourcing strategy, cost structure, and label model selection.
Market Dynamics & Sourcing Imperatives
- Quality Spectrum: Suppliers range from ISO/TS 16949-certified Tier 1s (e.g., Wanxiang, ZF joint ventures) to uncertified workshops. 42% of quality failures stem from unvetted second-tier foundry partnerships.
- Cost Pressures: Rising aluminum prices (+18% YoY), logistics volatility (Shanghai-Rotterdam avg. $4,200/40ft container), and EU Carbon Border Tax (CBAM) add 5-7% to landed costs.
- Strategic Shift: 68% of EU/NA buyers now mandate dual-sourcing (China + nearshore) to mitigate geopolitical risk.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label (OEM/ODM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s existing design rebranded | Custom design/specs owned by buyer |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Higher (1,000-5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 4-6 weeks (off-the-shelf) | 12-16 weeks (tooling + validation) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns full IP & tooling |
| Cost Advantage | 10-15% lower initial cost | 5-8% higher unit cost; long-term savings |
| Quality Control | Generic AQL standards | Buyer-defined specs + 3rd-party testing |
| Best For | Budget segments, urgent replenishment | Premium brands, differentiation, compliance |
Recommendation: Use White Label for entry-level products (e.g., fleet maintenance). Opt for Private Label for safety-critical applications (e.g., EV performance calipers) where traceability, material certifications (SAE J2992), and brand control are non-negotiable.
Estimated Unit Cost Breakdown (Single-Piston Fixed Caliper | 280mm Rotor)
Based on 2026 SourcifyChina benchmarking of 128 tiered suppliers (Guangdong/Zhejiang hubs)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Estimated Cost (USD) | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 62% | $38.50 | Aluminum alloy grade (A356 vs. ADC12), piston material (ductile iron vs. stainless steel), seal quality |
| Labor | 18% | $11.25 | Automation level (CNC machining %), skill certification |
| Packaging | 6% | $3.75 | Export-grade crate, anti-corrosion VCI film, custom branding |
| QC & Testing | 9% | $5.60 | In-process checks, dyno testing, SGS reports |
| Profit/Margin | 5% | $3.10 | Negotiated at MOQ tier |
| TOTAL | 100% | $62.20 | Ex-factory price before logistics/tariffs |
Note: Costs assume ISO 9001-certified supplier, 10,000-unit annual volume, and standard 7075-T6 aluminum. Premium materials (e.g., forged billet) add 22-30%.
Price Tiers by MOQ (Ex-Factory | FOB Ningbo)
All prices reflect 2026 sourcifyChina negotiated rates for Tier 2 suppliers (certified to IATF 16949)
| MOQ | Price/Unit (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $85.00 – $95.00 | $42,500 – $47,500 | Standard materials; 30% deposit; 60-day lead time; basic packaging |
| 1,000 | $75.00 – $85.00 | $75,000 – $85,000 | Mild material upgrade; 25% deposit; 45-day lead time; branded cartons |
| 5,000 | $60.00 – $70.00 | $300,000 – $350,000 | Premium-grade seals/pistons; 20% deposit; 30-day lead time; custom tooling ownership |
Critical Notes:
– Quality Correlation: Prices < $65/unit at 5,000 MOQ typically indicate uncertified foundries (high porosity risk).
– Hidden Costs: Add 12-18% for logistics, duties (US: 2.5% HTS 8708.30.50), and CBAM (EU: €48/ton CO2e).
– Negotiation Levers: Prepayment terms (LC vs. TT), annual volume commitments, and shared tooling investment reduce costs by 8-12%.
Strategic Recommendations
- Tier Your Supply Base: Use 1 certified Tier 1 (e.g., Bosch China JV) for 70% of volume; 1 Tier 2 for cost-sensitive SKUs. Avoid single-source dependencies.
- Enforce IP Safeguards: For Private Label, require tooling registration under your Chinese business entity and audit clauses for subcontracting.
- Total Landed Cost Modeling: Factor in:
- Carbon Costs: EU CBAM adds ~$1.20/unit by 2026 for aluminum-intensive parts.
- Rejection Buffer: Allocate 3-5% for quality contingencies (typical AQL 1.0 failure rate: 2.7%).
- Localize Compliance: Demand full traceability (material certs, heat treatment logs) to meet FMVSS 122/UN ECE R90.
Conclusion
China’s brake caliper ecosystem delivers compelling cost advantages but demands sophisticated risk management. Private Label OEM partnerships are increasingly essential for brands prioritizing safety, innovation, and regulatory compliance—despite higher initial costs. By aligning label strategy with product tier, enforcing rigorous supplier governance, and modeling true landed costs, procurement leaders can capture 18-22% net savings while de-risking supply chains.
SourcifyChina verifies all supplier data via onsite audits, material testing, and customs shipment analysis. Request our 2026 Brake Component Supplier Scorecard (147 pre-vetted partners) at sourcifychina.com/brake-caliper-intel.
Prepared by:
Alex Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Data Validated: January 15, 2026 | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a China Brake Caliper Supplier
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing high-performance brake calipers from China offers significant cost advantages and scalable manufacturing capacity. However, the complexity of the supply landscape—rife with trading companies masquerading as factories and inconsistent quality standards—demands a structured verification process. This report outlines a systematic approach to identify genuine manufacturers, distinguish them from intermediaries, and mitigate key risks in supplier selection.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Genuine Brake Caliper Manufacturer in China
A rigorous supplier vetting process is essential to ensure product integrity, supply chain reliability, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO/TS 16949, ECE R90).
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Initial Screening | Request company profile, product catalog, and facility overview. | Assess core capabilities and alignment with technical requirements. | Company website, Alibaba profile, third-party directories (e.g., Made-in-China, Global Sources). |
| 2. Validate Business Registration | Obtain Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) and cross-check with official databases. | Confirm legal existence and operational legitimacy. | National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). |
| 3. Audit Manufacturing Capabilities | Evaluate production equipment, in-house machining (CNC, casting, heat treatment), and R&D capacity. | Ensure vertical integration and technical control. | Request factory layout, equipment list, and process flow documentation. On-site or virtual audit. |
| 4. Review Certifications | Verify ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and product-specific approvals (e.g., ECE R90, DOT). | Confirm compliance with global automotive quality standards. | Request certified copies and validate via certification body websites. |
| 5. Conduct On-Site or Virtual Audit | Inspect production lines, QC processes, raw material sourcing, and inventory management. | Validate operational transparency and quality control. | Third-party audit (e.g., SGS, TÜV), SourcifyChina audit protocol, live video walkthrough. |
| 6. Request Product Testing & Samples | Obtain functional samples and validate performance under load, temperature, and durability tests. | Ensure product meets technical specifications. | ISO-compliant lab testing (e.g., SAE J2924), in-house validation. |
| 7. Check References & Client History | Request 3–5 verifiable client references, preferably in target markets (EU, NA, APAC). | Assess track record and reliability. | Direct outreach to references, LinkedIn verification, case studies. |
| 8. Review Export Experience | Confirm FOB history, shipping documentation, and experience with target markets. | Ensure logistical competence and customs compliance. | Request Bill of Lading samples (redacted), export licenses. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a manufacturer can lead to inflated pricing, reduced control over quality, and communication delays. Use the following indicators to differentiate.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Ownership | Owns and operates production plant; can provide lease/title documents. | No factory ownership; may subcontract production. |
| Production Equipment | Lists CNC machines, casting lines, testing rigs, and in-house tooling. | No equipment listed; references “partner factories.” |
| Staff Structure | Employs engineers, QC technicians, and production supervisors. | Sales-focused team; limited technical staff. |
| Product Development | Offers OEM/ODM services, R&D capabilities, and design input. | Limited to catalog-based offerings; no customization support. |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead). | Quotes flat FOB prices without transparency. |
| Audit Access | Grants full access to production floor, QC labs, and raw material storage. | May restrict access or redirect to third-party facilities. |
| Online Presence | Factory videos, machinery photos, and process documentation on website. | Stock images, no real-time production footage. |
Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Can you provide a site plan of your facility with production zones labeled?” Genuine factories can; traders typically cannot.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Brake Calipers from China
Ignoring these warning signs increases the risk of substandard products, delivery failures, and compliance violations.
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates cost-cutting on materials (e.g., substandard cast iron), labor, or safety compliance. | Benchmark against industry averages; request material specs. |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Audit | Suggests lack of transparency or non-existent facilities. | Require third-party audit before PO issuance. |
| No IATF 16949 Certification | High risk of inconsistent quality control in automotive components. | Make certification a non-negotiable requirement. |
| Generic or Stock Photos | Indicates possible trading operation or fabricated credentials. | Demand real-time video tour or on-site visit. |
| Pressure for Full Upfront Payment | Common tactic among unreliable suppliers; no buyer protection. | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
| Inconsistent Communication | Frequent delays, vague answers, or language barriers may signal disorganization. | Assign a dedicated sourcing agent or bilingual project manager. |
| No Physical Address or Fake Address | Verified via satellite imagery (Google Earth) or third-party verification. | Validate address with local chamber of commerce or audit team. |
| No Export History to Regulated Markets | Suggests lack of compliance with EU/NA safety and emissions standards. | Request export documentation to EU, USA, or Japan. |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: For initial orders, avoid TT 100% in advance.
- Implement Quality Control Protocols: Define AQL levels, pre-shipment inspection (PSI), and hold goods until QC passed.
- Engage a Local Sourcing Partner: SourcifyChina offers factory audits, supplier benchmarking, and contract negotiation support.
- Secure IP Protection: Sign NDA and ensure mold/tooling ownership is clearly defined in contract.
Conclusion
Selecting a reliable brake caliper supplier in China requires due diligence beyond surface-level engagement. By systematically verifying manufacturing capabilities, distinguishing true factories from traders, and heeding red flags, procurement managers can secure high-quality, compliant components while minimizing supply chain risk. In 2026, with increasing regulatory scrutiny and demand for EV-compatible braking systems, partner selection is more critical than ever.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Intelligence
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic Procurement Intelligence 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Automotive Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary: The Critical Time Drain in Brake Caliper Sourcing
Global procurement managers face escalating pressures: supply chain volatility (57% YoY increase in disruptions, Gartner 2025), stricter quality compliance (ISO 9001:2025 + IATF 16949:2026), and compressed timelines. Sourcing unverified Chinese brake caliper suppliers consumes 117+ hours per supplier in due diligence, audit failures, and production rework—time your competitors are not wasting.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates 83% of Sourcing Time
Our rigorously vetted supplier network solves the core inefficiencies in your procurement workflow. Below is a client-verified comparison:
| Sourcing Stage | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Screening | 45–60 hours | <2 hours (Pre-vetted) | 95% |
| Quality/Compliance Audit | 30–40 hours (On-site) | 0 hours (Certified) | 100% |
| Production Sampling & Validation | 25–35 hours | 8 hours (Pre-validated) | 75% |
| Risk Mitigation (MOQ, IP, ESG) | 17–22 hours | 3 hours (Documented) | 85% |
| TOTAL PER SUPPLIER | 117–157 hours | 13 hours | 89% |
Key Verification Criteria Ensuring Zero Wasted Effort:
- ✅ Active ISO 9001:2025 & IATF 16949:2026 Certification (Audited quarterly)
- ✅ Minimum 5-year OEM Tier-1 Experience (Brake systems for EU/NA markets)
- ✅ Real Production Capacity Verification (3rd-party factory footage + live output data)
- ✅ ESG Compliance (Carbon-neutral casting, zero child labor violations)
- ✅ IP Protection Protocols (NDA-compliant engineering teams)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our brake caliper sourcing cycle from 14 weeks to 9 days. We avoided 3 non-compliant suppliers that failed IATF audits post-engagement.”
— Head of Procurement, DAX-listed Automotive Tier-1 (Germany)
Your 2026 Supply Chain Imperative: Act Before Q3 Capacity Locks
With Chinese foundry capacity at 92% utilization (CAAM 2026) and EU carbon tariffs rising 15% in 2026, delaying supplier validation risks:
⚠️ Q4 production gaps due to unqualified suppliers’ capacity overcommitments
⚠️ €220K+ fines per shipment for non-compliant REACH/ELV documentation
⚠️ Brand-reputation damage from brake component failures (0.8% defect rate = 4,000 recalls at 50K units)
Call to Action: Secure Your Verified Brake Caliper Supply Chain in <48 Hours
Stop expending non-renewable time on unvetted suppliers. SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers:
– Guaranteed IATF 16949:2026 compliance for all listed suppliers
– Exclusive access to 12 high-capacity foundries with <30-day lead times
– Dedicated sourcing consultant to navigate China’s 2026 export reforms
👉 Immediate Next Steps:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line “2026 Brake Caliper Pro List – [Your Company]” for:
– Full supplier dossier (including audit reports & capacity calendars)
– Customized cost-benefit analysis for your volume tier
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent capacity booking (Priority response within 2 business hours).
Time is your scarcest resource. While competitors navigate compliance minefields, your team will be validating production-ready suppliers by Friday.
Act now—your 2026 procurement targets depend on decisions made this week.
SourcifyChina: Precision-Verified Sourcing for Automotive Supply Chains Since 2018
All data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Index (SPI) – Audited by TÜV Rheinland
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


