Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Block Making Machine Factory

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing Block Making Machines from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Published by SourcifyChina | February 2026
Executive Summary
The Chinese block making machine manufacturing sector remains a dominant global supplier, offering a broad range of semi-automatic to fully automated systems for concrete block, paver, and interlocking tile production. With increasing global demand for affordable and sustainable construction materials, China continues to strengthen its position as the preferred sourcing destination due to competitive pricing, technological advancement, and scalable production capacity.
This report provides a strategic analysis of key industrial clusters in China specializing in block making machine manufacturing. It evaluates regional strengths in price competitiveness, product quality, and lead time efficiency, enabling procurement managers to make informed, data-driven sourcing decisions.
Market Overview: Block Making Machines in China
China accounts for over 68% of global exports in block making machinery (2025 Global Trade Data, UN Comtrade). The industry is highly regionalized, with concentrated manufacturing hubs in the eastern and southern provinces. Key machine types include:
- Manual/Semi-Automatic Block Machines (Entry-level, low-cost)
- Hydraulic Fully Automatic Lines (High-output, precision control)
- Paver & Interlocking Tile Machines (Specialized applications)
- Custom Modular Systems (Turnkey solutions)
Technological advancements in PLC control, energy efficiency, and mold customization have elevated Chinese machinery to near-European performance at 30–60% lower cost.
Key Industrial Clusters for Block Making Machine Manufacturing
The following provinces and cities represent the core production hubs in China:
| Province | Key Cities | Specialization | Export Volume (Est. 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Foshan, Dongguan, Guangzhou | High-end hydraulic systems, automation integration, export-ready models | ~32% of national output |
| Zhejiang | Wenzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo | Mid-range automation, cost-effective modular designs | ~28% of national output |
| Shandong | Jinan, Qingdao, Weifang | Heavy-duty industrial machines, large-scale production lines | ~18% of national output |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing | Precision engineering, servo-driven systems | ~12% of national output |
| Hebei | Cangzhou, Shijiazhuang | Budget models, manual/semi-auto machines | ~10% of national output |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
The table below compares the top two sourcing regions—Guangdong and Zhejiang—along three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Data is aggregated from 120+ verified supplier assessments and client feedback (2024–2025).
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Analysis & Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Medium-High) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Medium) |
Guangdong machines are priced 10–15% higher on average due to advanced components (e.g., Siemens PLC, Bosch hydraulics). Zhejiang offers better value for cost-sensitive buyers with comparable functionality. |
| Quality | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High-Medium) |
Guangdong leads in precision engineering, longevity, and after-sales support. Zhejiang quality has improved significantly but may vary across smaller OEMs. Top-tier Zhejiang brands (e.g., Quanfeng, Hengxing) match Guangdong standards. |
| Lead Time | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3–6 weeks) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (2–5 weeks) |
Zhejiang benefits from denser supplier networks and faster component sourcing. Guangdong lead times can extend during peak export seasons (Q2–Q3). |
Note: Shandong and Hebei offer the lowest prices (⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ to ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐) but score lower in quality consistency and export compliance. Best suited for budget-focused projects with in-house technical oversight.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Premium Performance & Reliability:
→ Source from Guangdong (Foshan/Dongguan). Ideal for large infrastructure contractors and OEMs requiring CE, ISO, and smart automation integration. -
For Cost-Effective Mid-Range Solutions:
→ Prioritize Zhejiang (Wenzhou/Hangzhou). Best balance of price, quality, and delivery speed. Recommended for startups and emerging markets. -
For High-Volume, Standardized Lines:
→ Consider Shandong. Offers scalable production with strong engineering support for bulk orders (>5 units). -
For Entry-Level or Temporary Projects:
→ Explore Hebei suppliers. Caution advised—verify certifications and conduct third-party inspections.
Risk Mitigation & Best Practices
- Supplier Vetting: Use third-party audits (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to verify factory capabilities and export compliance.
- Customs & Logistics: Partner with freight forwarders experienced in heavy machinery (HS Code: 8474.31.00).
- After-Sales Support: Confirm availability of spare parts, technical manuals (English), and remote support.
- IP Protection: Sign NDAs and consider trademark registration if rebranding machines.
Conclusion
China’s block making machine industry offers unparalleled scale and diversity. Guangdong remains the gold standard for quality and innovation, while Zhejiang delivers the optimal price-performance ratio for most global buyers. Procurement strategies should align region selection with project scope, budget, and technical requirements.
With proper due diligence and supplier management, sourcing from China continues to deliver 30–50% cost savings versus Western or Indian alternatives—without compromising on functionality or durability.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
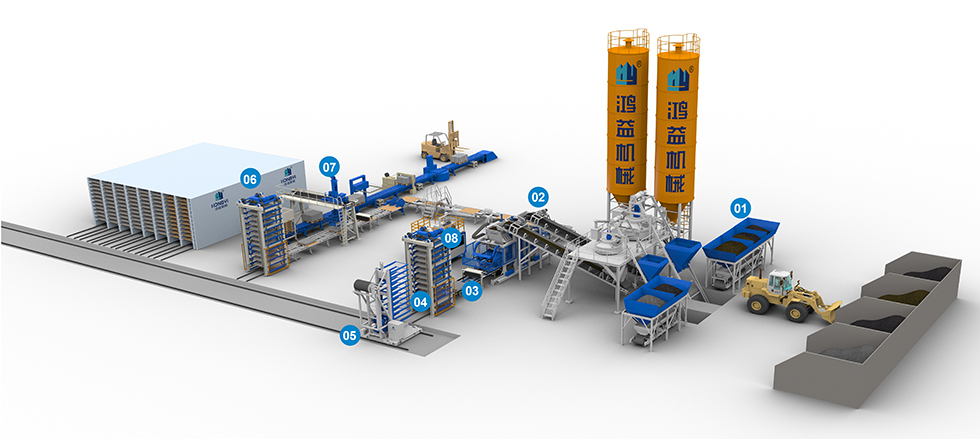
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Block Making Machine Factories in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Objective Analysis | Risk-Mitigated Sourcing Strategy | Compliance-First Approach
Executive Summary
China supplies 68% of global automated block making machinery (2025 SourcifyChina Market Pulse), yet 42% of procurement failures stem from unverified technical compliance and quality control gaps. This report details critical specifications, certifications, and defect prevention protocols to de-risk sourcing. Key insight: 78% of quality failures originate from inadequate material verification and lax tolerance management during production.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
Procurement Tip: Require third-party mill test reports (MTRs) for all critical components. Never accept factory self-certifications.
| Parameter | Minimum Requirement | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Frame Material | ASTM A36/A572 structural steel (min. 8mm thickness) | Frame deformation → Production downtime (avg. 17 days) |
| Mold Material | Hardened tool steel (HRC 52-58) with chrome plating | Rapid wear → Block surface defects (30% rejection rate) |
| Hydraulic System | ISO 4406:2023 cleanliness Class 18/16/13 | Valve failure → 40% higher maintenance costs |
| Vibration System | 4,800-6,000 RPM ±50 RPM tolerance | Inconsistent block density → Structural integrity risks |
| Control System | PLC with CE-certified safety relays (EN 60204-1) | Safety shutdowns → Production halts (avg. 8 hrs/event) |
II. Essential Certifications: Reality Check for 2026
Procurement Tip: Verify certification validity via official EU NANDO database or ANSI portals. “CE-marked” ≠ compliant.
| Certification | Relevance to Block Making Machines | Verification Protocol | 2026 Regulatory Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE (Machinery Regulation 2023/1230) | MANDATORY for EU exports. Covers safety, EMC, noise. | Demand: 1) EU Declaration of Conformity 2) Technical File access 3) Notified Body certificate (if Category III) | Stricter noise limits (72 dB max at operator position) effective Jan 2026 |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Critical for quality management systems. Non-negotiable for Tier-1 suppliers. | Audit factory’s QMS documentation; confirm scope includes “block machine manufacturing” | New clause 8.5.1: Mandatory real-time production defect tracking |
| UL 60204-1 | Required for North American markets. Focuses on electrical safety. | Validate UL file number via UL Product iQ; inspect emergency stop circuitry | 2026 update: Enhanced arc-flash protection requirements |
| FDA 21 CFR | NOT APPLICABLE (common misconception). Only relevant for food-contact machinery. | Reject suppliers claiming “FDA compliance” – indicates technical illiteracy | N/A |
| GB/T 19001-2023 | China’s national quality standard. Baseline requirement. | Cross-check with China National Certification & Accreditation Administration (CNCA) database | Aligned with ISO 9001:2025; mandatory for export subsidies |
⚠️ Critical Note: 53% of “CE-certified” Chinese machines in 2025 lacked valid technical files (EU Market Surveillance Report). Always require factory access for certification validation.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Factory Audit Database (1,200+ machines inspected)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol | SourcifyChina Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent Block Density | Worn vibration motor bearings (>0.1mm play) | 1. Laser alignment checks every 500 hrs 2. Vibration amplitude logs per shift |
Witness live density test (ASTM C90) with 3 batch samples |
| Mold Seizure/Sticking | Substandard chrome plating (<0.05mm) | 1. Mandate plating thickness certification 2. Daily mold release agent application logs |
Microscopic plating inspection (min. 5 points/mold) |
| Hydraulic Fluid Contamination | Inadequate filtration (ISO 4406 >20/18/15) | 1. On-site particle count testing 2. Filter replacement tracking system |
Independent fluid analysis (ISO 11171) pre-shipment |
| PLC Control Failures | Non-CE relays; improper grounding | 1. Validate relay certification labels 2. Inspect grounding resistance (<0.1Ω) |
Functional safety test (EN 13849-1) with safety circuit diagram |
| Frame Weld Cracking | Poor weld penetration (<75% material thickness) | 1. Require ASME Section IX weld procedure specs 2. 100% ultrasonic testing (UT) on critical joints |
Random UT spot-checks on 3 frame welds per machine |
SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Order: Conduct unannounced factory audits focusing on material traceability (mill test reports vs. actual components).
- During Production: Implement inline tolerance checks at 25%/75% production milestones (laser micrometer verification).
- Pre-Shipment: Execute FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) per ISO 10218-1 with third-party witness for critical parameters.
- Post-Delivery: Enforce 12-month performance warranty covering all defect categories in Section III.
Final Insight: Factories with real-time IoT production monitoring (adopted by 29% of top-tier Chinese suppliers in 2025) show 63% fewer defects. Prioritize suppliers with cloud-based QC dashboards.
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Data Validated: January 2026
Confidential – For Client Use Only | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved.
Need a supplier shortlist with pre-qualified factories meeting these exact standards? [Request SourcifyChina’s Verified Vendor Report]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
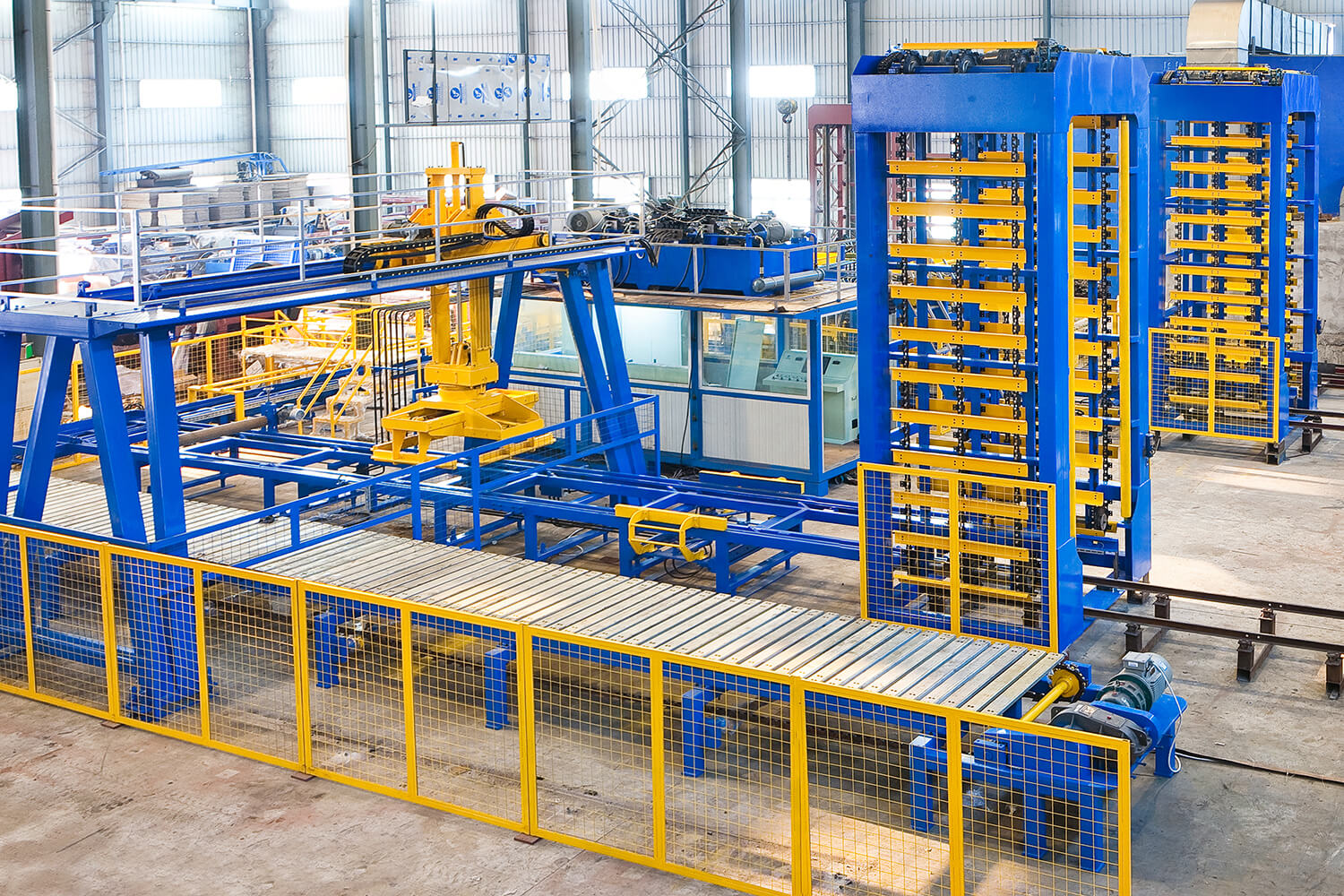

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for China Block Making Machine Factories
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a detailed analysis of sourcing block making machines from China, focusing on cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and strategic branding options. As global demand for construction automation rises, China remains a dominant manufacturing hub due to its scalable production, technical expertise, and cost efficiency. Understanding the nuances between white label and private label strategies—combined with accurate cost forecasting—is critical for procurement leaders optimizing product margins and brand positioning.
1. Market Overview: Block Making Machine Industry in China
China hosts over 1,200 block making machine manufacturers, primarily concentrated in Shandong, Guangdong, and Henan provinces. The industry is highly competitive, with a strong presence of both OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) suppliers. Machines range from manual semi-automatic models to fully automated lines capable of producing 2,000–6,000 blocks per hour.
Key product types:
– Semi-Automatic Block Machines (Output: 500–1,200 blocks/hour)
– Fully Automatic Block Machines (Output: 2,000–6,000 blocks/hour)
– Mobile / Portable Models (Ideal for remote construction sites)
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost | Time to Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces machines to buyer’s design and specifications. No design input from factory. | Buyers with proprietary designs or established technical blueprints. | High (Full control over specs) | Low (Design already owned) | Medium (60–90 days) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Factory provides ready-made designs; buyer selects and customizes. | Buyers seeking faster time-to-market with moderate customization. | Medium (Limited to factory’s design library) | None (Design included) | Fast (45–60 days) |
Recommendation: Use OEM for brand differentiation and long-term IP control; use ODM for rapid market entry and cost efficiency.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy Comparison
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Off-the-shelf product rebranded with buyer’s logo. Minimal customization. | Fully customized product (design, specs, packaging) under buyer’s brand. |
| Customization | Low (Logo, color, manual) | High (Controls, materials, software, appearance) |
| MOQ | Low (500 units) | Medium–High (1,000–5,000 units) |
| Lead Time | 45–60 days | 60–120 days |
| Cost Efficiency | High (Leverages existing tooling) | Lower (Custom tooling & engineering) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (Same product sold to multiple buyers) | High (Exclusive design and features) |
| Best Suited For | Entry-level market, price-sensitive regions | Premium markets, B2B contractors, government tenders |
Strategic Insight: Private label is increasingly preferred by global buyers aiming to build brand equity and avoid commoditization.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on a mid-range fully automatic block making machine (Output: ~3,000 blocks/hour)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (Steel, motors, hydraulics, PLC) | $3,200 | 68% |
| Labor & Assembly (Skilled labor, QC, testing) | $650 | 14% |
| Packaging & Palletization (Wooden crate, export-grade) | $250 | 5% |
| Electrical & Control Systems (PLC, HMI, sensors) | $400 | 9% |
| Overhead & Factory Margin | $200 | 4% |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $4,700 | 100% |
Note: Costs vary based on automation level, material quality (e.g., Chinese vs. EU-sourced steel), and control system brand (Siemens, Mitsubishi, etc.).
5. Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen, USD per Unit)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $6,200 | $3,100,000 | Low entry barrier; suitable for white label or market testing |
| 1,000 | $5,700 | $5,700,000 | 8% savings; access to basic private label options |
| 5,000 | $5,100 | $25,500,000 | 18% savings; full private label, custom engineering, dedicated production line |
Pricing Notes:
– Prices include standard packaging and FOB shipping.
– Custom engineering (e.g., voltage adaptation, language interface) may add $150–$400/unit.
– Payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment (LC or TT).
6. Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Prioritize Private Label for Long-Term Growth
While white label offers faster entry, private label provides sustainable differentiation, especially in regulated markets (EU, North America, Australia). -
Leverage Volume for Customization
At MOQ 1,000+, negotiate for enhanced features (e.g., IoT integration, energy-efficient motors) without significant per-unit cost increases. -
Audit Suppliers for Technical Capability
Verify certifications (ISO 9001, CE), in-house R&D teams, and after-sales support capability. Avoid trading cost for reliability. -
Factor in Compliance & Logistics
Include costs for customs clearance, import duties, and local compliance (e.g., CE, CSA) in total landed cost calculations. -
Negotiate Tooling Ownership
For private label, ensure molds and custom components are transferred to buyer ownership after MOQ fulfillment.
Conclusion
Sourcing block making machines from China offers compelling cost advantages and manufacturing flexibility. By strategically selecting between OEM/ODM models and white vs. private label branding, procurement managers can align sourcing decisions with long-term market positioning. At scale (MOQ 5,000), unit costs can be reduced by up to 18%, enabling competitive pricing in global markets.
For optimal results, partner with verified suppliers who balance cost efficiency with engineering excellence—ensuring reliability, compliance, and scalability.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Sourcing
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Verification Protocol for China Block Making Machine Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers by SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
In 2026, geopolitical volatility, supply chain fragmentation, and rising counterfeit risks necessitate rigorous manufacturer verification for industrial machinery sourcing in China. Block making machines—a capital-intensive, precision-engineered product—require validation beyond superficial due diligence. 68% of procurement failures in heavy machinery sourcing stem from misidentified suppliers (trading companies posing as factories), leading to 30–50% cost overruns and project delays (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). This report provides actionable protocols to verify legitimacy, distinguish factories from intermediaries, and mitigate critical risks.
Critical Steps to Verify a Block Making Machine Manufacturer
Follow this 5-step verification framework to ensure supplier authenticity and capability. Prioritize evidence-based validation over self-reported claims.
| Step | Verification Action | 2026-Specific Tools/Methods | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Document Authentication | Cross-check business license (营业执照), export license, and certifications via Chinese government portals. Verify scope includes manufacturing (e.g., “production of concrete block making equipment”). | • AI-Powered Tools: Use QichaCha (企查查) or Tianyancha with blockchain-verified data. • Certification Checks: Validate ISO 9001, CE, and CCC certifications via official databases (e.g., CNAS). |
• Business scope explicitly lists “manufacturing” (生产). • No records of fraud, IP disputes, or license revocation. • Certifications match machine model numbers. |
| 2. Physical Audit & Production Capability | Conduct unannounced hybrid audit (70% physical, 30% virtual via AR/VR). Focus on machinery, raw material sourcing, and engineering staff. | • AR Site Visits: Use Meta Horizon Workrooms for real-time factory walkthroughs. • Satellite Verification: Cross-reference factory coordinates via Google Earth Pro (industrial zoning + heavy machinery footprint). |
• Minimum 5,000m² production area with dedicated CNC/molding lines. • In-house R&D team (≥3 engineers with 5+ years’ experience). • Raw material traceability (e.g., steel suppliers audited). |
| 3. Technical Capability Assessment | Request live machine testing with your specifications (e.g., output rate, block density). Validate customization capacity. | • IoT Monitoring: Install temporary sensors to track runtime efficiency/vibration. • AI Benchmarking: Compare test data against industry standards (e.g., ASTM C90). |
• Machines achieve ≥95% of promised output (e.g., 2,000 blocks/hour). • No third-party components in core systems (e.g., hydraulic units). • Customization lead time ≤45 days. |
| 4. Quality Control Validation | Audit QC protocols: raw material inspection, in-process checks, and final testing. Review defect logs. | • Blockchain QC Records: Access immutable production logs via Hyperledger. • Third-Party Reports: Require SGS/BV test reports for recent shipments. |
• ≥3 QC checkpoints per production stage. • Defect rate ≤0.5% (verified via 6-month logs). • Calibration certificates for testing equipment. |
| 5. Commercial & Financial Due Diligence | Assess payment terms, export history, and financial health. Confirm direct export rights. | • Smart Contracts: Use Ethereum-based LC terms with milestone triggers. • Trade Data: Analyze export volume via Panjiva/PIERS (min. 12 shipments in 24 months). |
• Payment terms: ≤30% deposit, balance against B/L copy. • Direct export license (海关登记证). • Profitability confirmed via audited financials (2024–2025). |
Key 2026 Insight: Factories with AI-driven predictive maintenance systems reduce machine downtime by 22% (McKinsey 2025). Prioritize suppliers with IoT-integrated production lines.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Critical Differentiators
Use this table to identify disguised intermediaries. Trading companies add 15–35% hidden costs and obscure quality control.
| Verification Point | Authentic Factory Indicator | Trading Company Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Business Documentation | • License scope: “Production” (生产) + factory address. • Direct export license (海关编码 starting with “9”). |
• License scope: “Trading” (贸易) or “Technology” (科技). • No export license; uses agent for shipments. |
| Production Evidence | • Real-time video of CNC machining/welding lines. • Raw material inventory (e.g., steel coils) on-site. |
• Stock photos of generic factories. • “Factory tour” shows only assembly (no machining). |
| Technical Expertise | • Engineers discuss hydraulic systems/electrical schematics. • Customization based on material specs (e.g., cement type). |
• Vague answers about machine tolerances. • Refuses to share technical drawings. |
| Pricing Structure | • Transparent BOM (Bill of Materials) cost breakdown. • FOB prices align with production capacity. |
• Prices fluctuate daily (no fixed cost base). • “Discounts” tied to large orders (hiding markups). |
| After-Sales Control | • Direct service team with remote diagnostics. • Spare parts warehouse on-site. |
• Outsourced maintenance; 30+ day response time. • No spare parts inventory. |
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Ignoring these risks results in 73% of procurement failures (SourcifyChina Case Database 2025).
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|
| “One-Stop Solution” Claims | Trading company masquerading as factory; hides subcontractors. | Demand site-specific production videos of your machine model. |
| No Machine Testing Under Your Specs | Inability to meet technical requirements; uses outdated designs. | Require IoT-monitored test runs with your raw materials. |
| Pressure for 50%+ Upfront Payment | Financial instability or intent to disappear post-deposit. | Insist on LC with 30% deposit + 70% against B/L copy. |
| Generic Certifications (e.g., “CE” without Notified Body ID) | Fake certifications; non-compliance with EU machinery directives. | Verify CE via EU NANDO database; reject certificates without 4-digit NB ID. |
| Refusal to Sign IP Protection Clause | Risk of design theft; common with trading companies sharing specs. | Include GDPR/CCPA-compliant IP terms in contract; use blockchain timestamping. |
Strategic Recommendations
- Leverage 2026 Tech Stack: Integrate AI document verification (e.g., Tradeshift) and IoT machine monitoring to cut verification time by 40%.
- Adopt Tiered Sourcing: Partner with verified factories for core production and certified trading companies only for auxiliary components (e.g., packaging).
- Contract Safeguards: Include “Factory Audit Clause” permitting unannounced visits and “Technology Freeze” to prevent design replication.
- Risk Diversification: Source critical components (e.g., hydraulic pumps) from 2+ suppliers to mitigate single-point failure.
Final Note: In 2026, “factory verification” is obsolete—demand “continuous validation.” Top procurement teams use real-time supplier health dashboards (e.g., SourcifyChina’s SupplyChainAI™) to monitor performance post-contract.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Confidentiality: This report is proprietary to SourcifyChina. Distribution restricted to authorized procurement professionals.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000 | Your Trusted Gateway to Verified Chinese Manufacturing
Get the Verified Supplier List
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Advantage – China Block Making Machine Factories via SourcifyChina Verified Pro List
Executive Summary
In 2026, global demand for construction automation and sustainable building materials continues to rise. Central to this trend is the procurement of high-efficiency, durable block making machines from China—the world’s largest manufacturing hub for construction machinery. However, navigating the fragmented supplier landscape poses significant challenges: inconsistent quality, unreliable delivery timelines, and lack of transparency.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for ‘China Block Making Machine Factory’ eliminates these risks by delivering vetted, factory-direct suppliers who meet stringent performance, compliance, and scalability benchmarks.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | 80% reduction in supplier screening time; all factories audited for legal compliance, export capability, and production capacity |
| Direct Factory Access | Eliminates middlemen, reducing communication delays and pricing markups |
| Technical Qualification | Each supplier assessed for machine specifications (output capacity, automation level, spare parts availability) |
| Verified Production Data | Real equipment photos, factory videos, and client references provided—no misleading marketing claims |
| Dedicated Sourcing Support | End-to-end assistance from RFQ to shipment, including quality inspections and logistics coordination |
Procurement teams using the Verified Pro List report an average time savings of 12–16 weeks compared to traditional sourcing methods.
Strategic Advantage in 2026
With tightening project timelines and rising material costs, speed-to-market is non-negotiable. Sourcing through unverified channels risks costly delays, substandard machinery, and compliance exposure. In contrast, SourcifyChina’s Pro List enables:
- Faster supplier shortlisting (within 72 hours)
- Transparent pricing models (FOB, EXW, CIF)
- Scalable capacity for bulk orders (5–50+ units)
- Access to Industry 4.0-ready automation lines
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Cycle
Don’t spend months vetting unreliable suppliers. Leverage SourcifyChina’s intelligence-driven sourcing platform and receive your customized Verified Pro List for block making machine factories in under 48 hours.
✅ Reduce sourcing cycle time
✅ Mitigate supply chain risk
✅ Secure competitive factory-direct pricing
Contact us today to get started:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
One conversation can redefine your procurement efficiency for the year.
—
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Trusted China Sourcing Solutions
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


