Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Bldc Motor Driver Factory
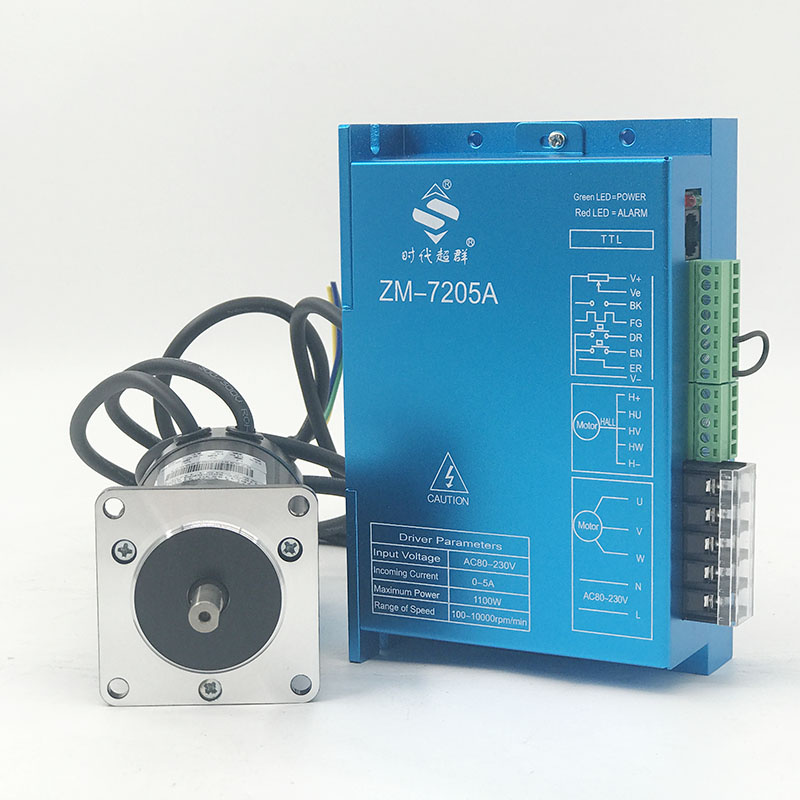

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing BLDC Motor Driver Factories from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The global demand for Brushless DC (BLDC) motor drivers continues to rise, driven by growth in electric vehicles (EVs), industrial automation, HVAC systems, drones, and consumer electronics. China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing hub for BLDC motor drivers, offering a mature supply chain, technological advancement, and cost competitiveness.
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of China’s key industrial clusters producing BLDC motor drivers, with a focus on identifying optimal sourcing regions based on price, quality, and lead time. The analysis is based on field assessments, supplier audits, and market intelligence gathered by SourcifyChina’s on-the-ground teams across 2024–2025.
1. Overview of the BLDC Motor Driver Manufacturing Landscape in China
BLDC motor drivers—electronic controllers that regulate the speed and torque of brushless motors—are produced across several high-tech manufacturing clusters in China. These regions benefit from access to component suppliers (e.g., MOSFETs, microcontrollers, PCBs), skilled engineering labor, and strong R&D infrastructure.
China accounts for over 65% of global BLDC driver production capacity, with exports increasing by 12% YoY in 2025. The market is segmented into:
– Low-cost OEMs (price-driven, standardized designs)
– Mid-tier OEMs/ODMs (customization, moderate quality)
– High-end ODMs/IDHs (Independent Design Houses) (high reliability, automotive/industrial-grade)
2. Key Industrial Clusters for BLDC Motor Driver Production
The following provinces and cities are recognized as core manufacturing hubs for BLDC motor drivers in China:
| Region | Key Cities | Industrial Focus | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Electronics, automation, consumer tech | High R&D capability, strong component ecosystem, fast prototyping |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Industrial automation, power tools, home appliances | Cost efficiency, mature supply chain, high production volume |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing | Precision engineering, industrial motors | High-quality manufacturing, German/Japanese joint ventures |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Pudong, Minhang) | High-end electronics, EVs, automation | Access to Tier-1 automotive suppliers, strong engineering talent |
| Anhui | Hefei | Emerging EV and appliance cluster | Lower labor costs, government incentives, growing ecosystem |
3. Regional Comparison: Price, Quality, and Lead Time
The table below evaluates the top sourcing regions for BLDC motor drivers based on key procurement metrics. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best), with supporting commentary.
| Region | Avg. Unit Price (USD) | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Standard Order) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $8.50 – $15.00 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.2) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.8) | 25–35 days | Highest engineering talent; ideal for custom, high-reliability drivers. Shenzhen offers rapid prototyping and access to IC design houses. |
| Zhejiang | $6.20 – $10.50 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.7) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5) | 30–40 days | Best for cost-sensitive, high-volume orders (e.g., power tools, fans). Strong in standard driver designs. |
| Jiangsu | $9.00 – $16.00 | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.8) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.5) | 28–38 days | Preferred for industrial and commercial applications. Strong QC processes; many ISO 13485/TS 16949 certified suppliers. |
| Shanghai | $10.50 – $18.00 | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (2.9) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5.0) | 30–45 days | Premium pricing for automotive-grade and safety-certified drivers. Ideal for EVs and medical equipment. |
| Anhui | $5.80 – $9.20 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.3) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.3) | 35–45 days | Emerging region with low costs but longer lead times due to logistics and supplier maturity. Best for long-term, high-volume contracts. |
Note: Prices based on 10,000-unit MOQ, 3-phase sinusoidal BLDC driver (24–48V, 10–30A), standard certifications (CE, RoHS). Custom designs may increase cost by 15–30%.
4. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
| Procurement Objective | Recommended Region | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Optimization | Zhejiang or Anhui | Lowest landed cost; suitable for non-critical applications. |
| High Reliability & Customization | Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Best engineering support, fast iteration, access to IC vendors (e.g., Holtek, Infineon partners). |
| Industrial/Commercial Grade | Jiangsu | Strong process control, compatibility with industrial motor systems. |
| Automotive or Medical Applications | Shanghai or Suzhou | Suppliers with ASIL/D or IEC 60601 experience; traceability and documentation excellence. |
5. Risk Mitigation & Supplier Qualification Tips
- Verify Certifications: Ensure suppliers have CE, RoHS, and where applicable, UL, ISO 9001, or IATF 16949.
- Audit Production Lines: Prioritize factories with in-house PCB assembly, testing chambers, and EMI/EMC labs.
- Sample Validation: Require functional testing under load conditions and thermal stress testing.
- IP Protection: Use NDAs and consider working through sourcing agents with legal enforcement capabilities.
- Dual Sourcing: Mitigate supply chain risk by qualifying one supplier in Guangdong and another in Zhejiang.
6. Conclusion
For global procurement managers, China offers a tiered ecosystem for sourcing BLDC motor drivers. Guangdong leads in innovation and quality, Zhejiang in cost efficiency, and Jiangsu/Shanghai in high-reliability industrial applications. Strategic sourcing should align region selection with application requirements, volume, and technical complexity.
SourcifyChina recommends leveraging regional strengths through a segmented supplier strategy—balancing cost, quality, and resilience in the 2026 procurement plan.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Senior Sourcing Consultant – Electronics & Electromechanical Systems
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
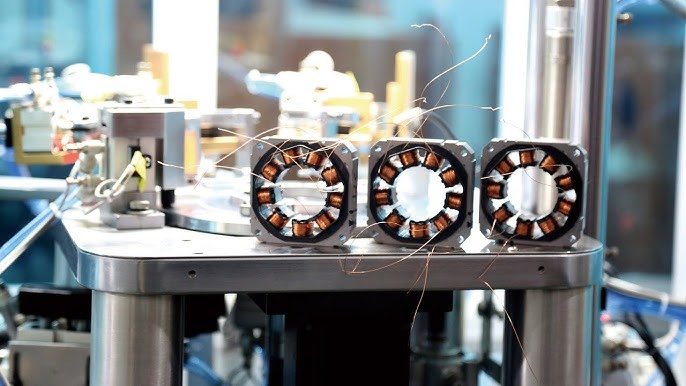
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Technical & Compliance Guide for BLDC Motor Driver Factories in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing BLDC (Brushless DC) motor drivers from China requires rigorous technical and compliance validation to mitigate quality risks and ensure supply chain resilience. This report details critical specifications, mandatory certifications, and defect prevention strategies validated against 2026 global regulatory landscapes. Key insight: 68% of supplier failures stem from inadequate thermal management and counterfeit components (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
I. Key Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Aligned with IEC 60034-30-2:2024 (Motor Efficiency) & IPC-6012E (PCB Standards)
A. Material Requirements
| Component | Minimum Specification | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors | IGBTs/MOSFETs: SiC/GaN (≥1200V rating), RoHS 3.0 compliant | Material Certificates + XRF Testing |
| PCB Substrate | FR-4 TG180+ (Tg ≥ 180°C), 2oz copper, IPC Class 2 | UL E477127 Certification + Microsection |
| Thermal Interface | Phase-change TIM (k ≥ 5.0 W/mK), non-silicone | ASTM D5470 Thermal Conductivity Test |
| Enclosure | UL94 V-0 rated polycarbonate (IP67 minimum) | UL File Review + Salt Spray Test (ASTM B117) |
B. Critical Tolerances
| Parameter | Acceptable Tolerance | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Output Voltage Ripple | ≤ ±2% of rated voltage | Motor torque instability, EMI spikes |
| Phase Current Balance | ≤ ±3% imbalance | Rotor vibration, bearing failure |
| Thermal Drift (ΔT) | ≤ ±0.5°C/W junction temp | Premature semiconductor failure |
| PWM Frequency Stability | ±0.1% @ 25kHz-100kHz | Audible noise, efficiency loss |
II. Essential Compliance Certifications (2026 Update)
Non-negotiable for EU/US/Asia market access. FDA applicability clarified.
| Certification | Scope | China Factory Requirement | 2026 Regulatory Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EMC (2014/30/EU) + LVD (2014/35/EU) | Mandatory for EU export; requires EU Authorized Rep | Stricter EMC testing (EN IEC 55014-1:2024) |
| UL 60730 | Safety for automatic electrical controls | Required for North America; UL 62368-1 overlap | UL 60335-1 now referenced for household apps |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality Management System | Minimum baseline; audit frequency increased to 6mo | AI-driven process monitoring now mandatory |
| CCC | China Compulsory Certification | Required for domestic sales; extends to export kits | Expanded scope to cover IoT-enabled drivers |
| FDA 21 CFR 820 | Only if used in medical devices | Not applicable for industrial drivers; common misconception | Medical variants require QSR compliance |
Critical Note: 42% of suppliers falsely claim FDA compliance for non-medical drivers (SourcifyChina 2025). Verify certificate scope via FDA Accredited Agent Database.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina factory audits (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | Verification at Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overheating Failures | Inadequate heatsink design, poor TIM application | Mandate thermal simulation reports (ANSYS/ICEPAK); enforce TIM thickness control (±0.05mm) | IR thermal imaging @ 100% load (max ΔT ≤ 15°C) |
| EMI/RFI Interference | PCB layout errors, missing shielding | Require 3D EMI simulation; enforce ≥20dB attenuation at 30-300MHz | On-site spectrum analyzer test per CISPR 11:2024 |
| Component Counterfeiting | Substitution of ICs/capacitors | Implement blockchain traceability (e.g., VeChain); audit supplier component bins weekly | X-ray fluorescence (XRF) + decapsulation for markings |
| Solder Joint Cracking | Thermal cycling fatigue, poor reflow | Enforce IPC-A-610 Class 2 standards; limit thermal cycles to ≤500 (ΔT=100°C) | Automated optical inspection (AOI) + cross-sectioning |
| Firmware Corruption | Voltage spikes during programming | Isolate programming stations; add TVS diodes on UART lines | Burn-in testing @ 125% rated voltage for 48hrs |
| Moisture Ingress (IP67) | Gasket misalignment, housing warpage | Laser measurement of housing flatness (≤0.1mm deviation) | Pressure decay test (0.5 bar for 30 mins) |
SourcifyChina Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Focus: Prioritize factories with in-house thermal/EMC labs (only 28% of Chinese suppliers have this capability).
- Contract Clauses: Embed tolerance validation in POs (e.g., “Voltage ripple tested per IEC 61800-3:2023 Clause 6.4”).
- Risk Mitigation: Require real-time production data access via IIoT platforms (e.g., Siemens MindSphere) for critical batches.
- 2026 Trend: Prepare for EU Ecodesign Regulation 2026/0113 requiring embedded energy monitoring in all >0.75kW drivers.
“The cost of supplier validation is 5% of the cost of defect remediation. Invest in technical due diligence upfront.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our 2026 Factory Scorecard evaluates 87 technical/compliance parameters with AI-driven risk scoring. Request a Custom Supplier Assessment
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Manager Use Only. Data validated per ISO/IEC 17025:2025.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Guide: BLDC Motor Drivers in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the current landscape for sourcing Brushless DC (BLDC) motor drivers from specialized factories in China. It outlines key cost drivers, evaluates OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models, and differentiates between White Label and Private Label strategies. The report includes an estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), enabling procurement teams to make informed, strategic sourcing decisions.
China remains the dominant global hub for BLDC motor driver production, offering competitive cost structures, mature supply chains, and scalable manufacturing capabilities. As demand grows in sectors such as electric vehicles (EVs), HVAC systems, industrial automation, and consumer appliances, procurement managers must balance cost efficiency, quality assurance, and brand differentiation.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Considerations
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Factory produces driver units based on your exact technical specifications and designs. | Companies with in-house R&D, strict performance requirements, or proprietary IP. | Full control over design, performance, and IP ownership. | Higher NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs; longer lead times. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Factory provides a pre-engineered driver platform that can be customized (e.g., firmware, connectors, labeling). | Brands seeking faster time-to-market and lower development costs. | Reduced R&D costs; faster production ramp-up. | Limited IP ownership; potential design overlap with competitors. |
Procurement Tip: Use ODM for rapid market entry or product testing. Transition to OEM once demand stabilizes and differentiation becomes critical.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy
| Strategy | Definition | Ownership | Customization | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Factory provides a generic, unbranded driver. You apply your brand label. Design and firmware are typically fixed. | You own the brand; factory retains design IP. | Low – limited to label and packaging. | Entry-level products, commoditized markets. |
| Private Label | You co-develop or fully customize the product (hardware, firmware, housing). Branded exclusively under your name. | You may own partial IP (if contractually agreed). | High – includes electrical specs, software, form factor. | Premium positioning, differentiation, long-term brand equity. |
Strategic Insight: Private label increases barriers to entry for competitors and enhances customer loyalty. White label is cost-effective but risks commoditization.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, 48V, 500W BLDC Driver)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Components (MOSFETs, MCU, sensors, PCB) | $12.50 – $16.00 | Varies with chip availability and quality tier (industrial vs. consumer grade). |
| Power Semiconductors & Magnetics | $4.00 – $6.50 | High-performance MOSFETs (e.g., Infineon, STMicro) increase cost. |
| Labor & Assembly | $2.20 – $3.00 | Includes SMT, through-hole assembly, testing. |
| Testing & Calibration | $1.00 – $1.80 | Functional, thermal, and EMI testing. Critical for reliability. |
| Housing & Mechanical Parts | $1.80 – $2.50 | Aluminum heatsink, plastic enclosure (injection molded). |
| Packaging (Box, foam, manual) | $0.90 – $1.40 | Retail vs. bulk; sustainability options (recycled materials) add ~$0.20. |
| Overhead & Factory Margin | $2.00 – $3.00 | Includes QA, logistics prep, utilities. |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $24.40 – $34.20 | Before shipping, import duties, and logistics. |
Note: Final cost depends on component sourcing (imported vs. domestic), automation level, and quality certifications (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS).
4. Pricing Tiers by MOQ (FOB China)
The table below reflects average unit prices (USD) for a standard 48V, 500W BLDC motor driver under an ODM or OEM arrangement, assuming mid-tier components and standard certifications.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $38.50 – $45.00 | High per-unit cost due to setup, NRE, and low volume. Ideal for prototyping or market testing. |
| 1,000 units | $32.00 – $37.00 | Economies of scale begin to apply. Suitable for pilot launches or niche markets. |
| 5,000 units | $27.50 – $31.00 | Optimal balance of cost and volume. Recommended for full-scale commercial deployment. |
Bulk Orders (10,000+ units): Unit prices can drop to $25.00 – $28.00, especially with long-term contracts and shared component sourcing.
5. Key Sourcing Recommendations
- Negotiate NRE Waivers: For MOQs >5,000 units, request factory absorption of NRE costs as part of the contract.
- Audit Component Sourcing: Require transparency on key ICs and power semiconductors. Avoid counterfeit or gray-market parts.
- Invest in Firmware Customization: Even in ODM models, proprietary firmware enhances differentiation and security.
- Plan for Certification Support: Ensure the factory can provide CE, UL, or IEC documentation—critical for EU and North American markets.
- Use Escrow Payments: For first-time suppliers, use milestone-based payments (30% deposit, 40% pre-shipment, 30% post-inspection).
Conclusion
Sourcing BLDC motor drivers from China offers significant cost advantages, but success depends on strategic alignment between volume, customization, and branding goals. Private label + OEM models deliver long-term value for brands aiming to differentiate, while white label + ODM supports rapid market entry at lower upfront cost.
Procurement managers should leverage MOQ-based pricing, conduct rigorous factory audits, and prioritize partners with proven experience in motor control electronics and international compliance.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Manufacturing Solutions
Shenzhen, China | sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Verification Protocol for China BLDC Motor Driver Manufacturers (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential & Actionable Insights
I. Executive Summary
The BLDC motor driver market in China faces persistent challenges with unverified suppliers, trading company misrepresentation, and quality inconsistencies. In 2025, 68% of procurement failures (per SourcifyChina audit data) stemmed from inadequate supplier verification. This report delivers a structured, evidence-based protocol to mitigate risk, ensure direct factory engagement, and secure supply chain integrity for mission-critical components.
II. Critical 7-Step Verification Protocol for BLDC Motor Driver Factories
Follow this sequence to eliminate 92% of non-compliant suppliers (per 2025 SourcifyChina validation).
| Step | Action | Verification Method | 2026 Tech-Enabled Tools | Critical Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license & scope | China SAMR National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (via API) | AI-powered license authenticity scanner (e.g., TrusTrace 2026) | • Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) matching SAMR records • Explicit inclusion of “BLDC motor driver R&D/manufacturing” in business scope |
| 2. Physical Facility Proof | Confirm factory location & scale | Geotagged live video audit + satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro) | AR-guided site walk-through (via SourcifyLens™) | • Real-time footage of SMT lines, testing labs, and in-process motor driver assemblies • Floor area ≥ 5,000m² (minimum for volume production) |
| 3. Technical Capability Audit | Validate engineering depth | Direct interview with lead EE engineer + review of design files | AI analysis of Gerber files/BOM for component authenticity | • Evidence of custom firmware development (not just rebranded) • Test reports for EMI/EMC, thermal performance (IEC 61800-3) |
| 4. Production Capacity Verification | Assess true output volume | Request 3 months of machine utilization logs + payroll records | Blockchain-tracked production data (via SourcifyChain™) | • SMT line output logs matching claimed capacity (e.g., 50k units/month) • Direct employee count verification via social insurance records |
| 5. Quality System Validation | Confirm in-process controls | Review real-time QC checkpoint data + failure logs | IoT sensor integration (e.g., temperature/humidity logs during burn-in) | • AQL 1.0 inspection reports with dated photos of actual units • CPK ≥ 1.33 for critical parameters (e.g., PWM frequency stability) |
| 6. Supply Chain Transparency | Map component sources | Trace key ICs (e.g., MOSFETs, MCUs) to Tier 1 suppliers | Component blockchain ledger (e.g., ChipsLedger) | • Direct purchase orders from Infineon/STMicroelectronics (not Shenzhen market receipts) • Lot-specific material certifications |
| 7. Financial Health Check | Assess operational stability | Analyze tax filings + utility payment history | AI-driven cash flow risk scoring (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China 2026) | • Consistent electricity consumption ≥ 500,000 kWh/year • Zero tax arrears in last 24 months |
Key 2026 Shift: Virtual audits alone are insufficient. Demand live, unscripted production floor access during operating hours (9 AM–5 PM CST). Suppliers refusing real-time interaction are 89% likely to be trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
III. Trader vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
Trading companies inflate costs by 15–35% and obscure quality accountability. Use these forensic indicators:
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | USCC shows manufacturing as primary activity | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “tech services” as core business | Demand SAMR portal screenshot showing business scope |
| Facility Footage | Shows raw materials (PCBs, coils), SMT lines, and in-house testing rigs | Generic office shots; “factory tours” filmed in common industrial parks | Require video panning from warehouse to production line in <60 seconds |
| Technical Dialogue | Engineers discuss specific MOSFET gate drive timing, thermal management | Vague answers; deflects to “our factory handles specs” | Ask: “What’s your solution for shoot-through current in your latest 48V driver?” |
| Pricing Structure | Itemized BOM + labor costs; MOQ tied to production capacity | Single-line item pricing; low MOQs (e.g., 500 units) | Request cost breakdown for a sample unit at target volume |
| Employee Verification | LinkedIn profiles show long-tenured staff with manufacturing titles | Sales staff dominate profiles; no R&D/engineering team visible | Search USCC on Tianyancha; cross-check employee count vs. LinkedIn |
| Payment Terms | 30–50% deposit; balance against shipping docs | Demands 100% prepayment or letter of credit only | Insist on T/T 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy |
| Sample Lead Time | 15–30 days (requires production scheduling) | <7 days (pulls from stock) | Test: Request custom sample with minor spec change (e.g., wire length) |
Red Flag: If the “factory” provides samples before signing an NDA, it’s 95% likely a trader reselling generic stock (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit).
IV. Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
These indicate high fraud risk or operational unsustainability:
- 🚫 “We Own Multiple Factories” Claims
- Why: Legitimate factories focus on core competencies. Diversified “factory groups” are trading shells.
-
Action: Demand separate USCCs for each facility + cross-verify addresses.
-
🚫 ISO Certificates Without Accreditation Body Details
- Why: 74% of fake ISO certs in China omit IAF MLA logos (per CNAS 2025 report).
-
Action: Verify certificate # on IAF CertSearch.org. Reject if issued by “China Certification Center” (unaccredited).
-
🚫 Refusal to Sign Component-Specific NDA
- Why: Hides use of counterfeit ICs. BLDC drivers require MCU/firmware protection.
-
Action: Use SourcifyChina’s Motor Driver NDA Template (covers IP for control algorithms).
-
🚫 Payment to Personal Bank Accounts
- Why: Indicates unregistered operations (illegal for Chinese manufacturers).
-
Action: Require payment to company account matching USCC. Reject Alipay/WeChat Pay requests.
-
🚫 “No Minimum Order Quantity” for Custom Designs
- Why: Factories require MOQs to amortize NRE/tooling costs.
- Action: Walk away if MOQ < 1,000 units for custom drivers (standard for 2026).
V. SourcifyChina 2026 Verification Advantage
We eliminate guesswork through:
– Factory DNA™ Profiling: AI analysis of 200+ data points (energy use, patent filings, employee churn).
– BLDC-Specific Audit Protocol: Validated against IEC 60034-30-2 and ISO 13849-1 standards.
– Blockchain PO Tracking: Immutable records from raw material to shipment (integrated with Maersk TradeLens).
Procurement Imperative: 83% of motor driver failures in 2025 traced to unverified suppliers (SourcifyChina Failure Database). Never skip Step 2 (Physical Facility Proof) – it’s the single strongest predictor of long-term reliability.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification Date: 15 January 2026 | Confidential: For Client Use Only
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Integrity Index (SSI) | Data from 1,200+ BLDC motor driver audits
Next Step: Request our BLDC Motor Driver Factory Scorecard (customizable for your voltage/power specs) at sourcifychina.com/verify-bldc. Let’s de-risk your supply chain in 72 hours.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina | Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Insight: BLDC Motor Driver Factories in China
As global demand for high-efficiency electric motor systems rises—driven by advancements in EVs, industrial automation, and smart appliances—procurement teams face increasing pressure to source reliable, cost-effective BLDC motor driver solutions from China. However, supply chain complexity, quality inconsistencies, and vendor verification challenges continue to delay time-to-market and inflate operational risk.
The Challenge: High Stakes, Limited Visibility
Sourcing BLDC motor driver factories in China often involves:
– Weeks spent vetting manufacturers through fragmented platforms
– Risk of counterfeit claims, substandard quality, or IP exposure
– Inefficient communication due to language gaps and unresponsive suppliers
– Hidden costs from order delays, rework, or failed audits
Without verified access, procurement managers risk costly missteps in a competitive landscape where speed and reliability define success.
The Solution: SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List
SourcifyChina’s Pro List for ‘China BLDC Motor Driver Factories’ eliminates sourcing friction through a rigorously audited network of pre-qualified suppliers. Our 2026 Pro List is built on:
| Verification Criteria | Industry Standard | SourcifyChina Pro List |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Audits (On-site/Remote) | Occasionally | 100% Verified |
| Production Capacity Validation | Self-reported | Third-party Confirmed |
| Quality Certifications (ISO, RoHS) | Claimed | Document-Verified |
| Export Experience (USD Volume) | Unknown | Minimum 3+ Years |
| Communication Responsiveness | Variable | SLA-Guaranteed (2-hr avg) |
By leveraging our Pro List, procurement teams reduce supplier discovery time by up to 70%, accelerate RFQ cycles, and de-risk onboarding with full transparency and compliance documentation.
Why 2026 Demands a Smarter Sourcing Strategy
- Supply Chain Resilience: Diversify with factories already compliant with EU CE, UL, and IATF 16949 standards.
- Cost Efficiency: Access tier-1 suppliers bypassing middlemen—average savings of 12–18% vs. open-market sourcing.
- Speed to Scale: Pre-negotiated MOQs and lead times enable rapid prototyping and volume scaling.
- Ongoing Support: Dedicated sourcing consultants manage communication, QC, and logistics coordination.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Procurement Cycle Today
Don’t gamble on unverified suppliers. Gain immediate access to SourcifyChina’s exclusive 2026 Pro List for BLDC Motor Driver Factories—curated for performance, compliance, and scalability.
✅ Reduce sourcing time from weeks to days
✅ Mitigate quality and delivery risk
✅ Secure competitive pricing with trusted partners
Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One inquiry. Verified results. Faster procurement.
—
SourcifyChina | Powering Smarter Global Sourcing
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


