Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Beverage Filling Machine Supplier

SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing Beverage Filling Machinery from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-BFM-2026-01
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for beverage filling machinery manufacturing, driven by mature supply chains, technical specialization, and competitive scalability. In 2026, Guangdong and Zhejiang provinces account for 78% of China’s export-oriented beverage filling machine production, with distinct regional strengths. While Guangdong excels in high-volume, integrated production lines for carbonated/soft drinks, Zhejiang leads in precision engineering for juice/dairy hot-fill systems. Procurement managers must prioritize cluster alignment with technical requirements to mitigate hidden costs (e.g., 22% of buyers face >30-day delays due to misaligned supplier selection). This report identifies key industrial clusters and quantifies regional trade-offs to optimize sourcing strategy.
Key Industrial Clusters: China’s Beverage Filling Machinery Hubs
Beverage filling machinery manufacturing in China is concentrated in two primary clusters, each with specialized capabilities and supply chain ecosystems:
- Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Core Cities: Dongguan, Foshan, Guangzhou
- Specialization: High-speed rotary fillers (20,000–120,000 BPH), integrated PET/can lines for carbonated soft drinks (CSD), water, and beer. Dominated by OEMs serving global beverage giants (e.g., Coca-Cola, PepsiCo suppliers).
-
Ecosystem Strengths: Proximity to packaging material hubs (e.g., Shenzhen labels, Jiangmen PET preforms), mature automation component suppliers (servo motors, PLCs), and Shenzhen’s R&D talent pool. 65% of cluster suppliers hold ISO 9001/CE certifications.
-
Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Wenzhou, Ningbo, Hangzhou
- Specialization: Aseptic/hot-fill systems for juice, dairy, and functional beverages; compact modular machines (5,000–30,000 BPH); stainless steel engineering excellence. Cluster is home to 40% of China’s “National High-Tech Enterprises” in packaging machinery.
- Ecosystem Strengths: Deep metallurgy expertise (Wenzhou stainless steel), strong R&D partnerships with Zhejiang University, and Ningbo Port’s export efficiency (avg. 2-day customs clearance).
Note: Jiangsu (Suzhou) is emerging for smart-factory-integrated systems but holds <10% market share for core filling machinery. Shandong focuses on low-cost entry-level machines (<5,000 BPH) with limited export compliance.
Regional Comparison: Strategic Sourcing Trade-Offs (2026 Projections)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina Supplier Database (1,200+ verified suppliers), CLIMA 2025 Export Report, and client deployment metrics.
| Criteria | Guangdong Cluster (Dongguan/Foshan) | Zhejiang Cluster (Wenzhou/Ningbo) | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Moderate (¥850k–¥5.2M) • 15% lower than Zhejiang for >30k BPH lines • Higher cost for aseptic tech |
Premium (¥1.1M–¥6.8M) • 10–18% higher for equivalent speed • Justified by superior SS316L components & thermal efficiency |
Budget projects favor Guangdong; ROI-driven buyers choose Zhejiang for TCO reduction in juice/dairy. |
| Quality | Good (85–92% FTY*) • Robust for CSD/water • Higher field failures in humid climates (12% vs. 7%) |
Excellent (90–95% FTY*) • Industry-leading seal integrity (0.02% leak rate) • Aseptic compliance: 98% pass rate |
Zhejiang preferred for sensitive products (dairy, probiotics); Guangdong sufficient for non-carbonated stable beverages. |
| Lead Time | Shorter (8–14 weeks) • Mass production capacity • 30% shorter for standard configurations |
Longer (12–18 weeks) • Custom engineering focus • 25% extended for aseptic validation |
Guangdong ideal for urgent capacity expansion; Zhejiang requires early engagement for complex projects. |
| Tech Support | Moderate (48-hr remote response) • Limited multilingual engineers |
Advanced (24-hr bilingual remote + 72-hr onsite) • 85% suppliers offer EU/US time-zone support |
Critical for global operations: Zhejiang reduces downtime risk by 35% (per SourcifyChina case studies). |
| Export Experience | High (95% export-ready) • Strong INCOTERMS 2020 compliance |
Very High (98% export-ready) • Expertise in FDA 21 CFR Part 110, EU 1935/2004 |
Both clusters reliable; Zhejiang edges ahead for regulated markets (EU, USA). |
FTY = First-Time Yield (machine performance at client site). Prices exclude shipping, tariffs, and installation. Data reflects mid-tier suppliers (top 30% by export volume).
Critical 2026 Market Dynamics & Sourcing Recommendations
- Compliance is Non-Negotiable: 68% of rejected shipments in 2025 failed due to incomplete CE/FDA documentation. Action: Prioritize suppliers with in-house compliance teams (common in Zhejiang; rare in Guangdong).
- Lead Time Volatility: Guangdong faces 15–20% longer delays during Q4 (Canton Fair + holiday shutdowns). Action: Lock contracts by June for Q1 deployments.
- Hidden Cost Trap: “Low-price” Jiangsu/Shandong suppliers incur 27% higher lifetime costs due to part replacements (SourcifyChina TCO model). Action: Audit minimum 3 suppliers from both core clusters.
- Tech Shift: 55% of new orders demand IoT integration (real-time OEE tracking). Action: Verify supplier’s API compatibility with your MES (Zhejiang leads here).
Conclusion
Guangdong offers speed and cost efficiency for high-volume, non-aseptic applications, while Zhejiang delivers engineering precision for technically complex or regulated beverages. Optimal strategy: Dual-sourcing – Guangdong for water/CSD line expansions, Zhejiang for dairy/juice innovation. Avoid regional generalizations; validate each supplier’s specific machine validation reports (ask for 3rd-party test data). In 2026, success hinges on matching cluster strengths to product-specific requirements – not just price.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Leverage our cluster-specific RFx templates (available on request) to capture critical technical differentiators. All recommended suppliers undergo our 128-point factory audit, including post-installation performance tracking.
SourcifyChina | De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010
This report is confidential. Data derived from proprietary supplier assessments and industry partnerships. Not for redistribution.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China-Based Beverage Filling Machine Suppliers
Date: April 5, 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
As global demand for automated beverage production escalates, sourcing high-performance filling machines from China offers cost efficiency, scalability, and technological advancement. However, ensuring compliance with international quality and safety standards is critical to avoid production delays, regulatory penalties, and brand risk. This report details essential technical specifications, material requirements, certifications, and quality control protocols for beverage filling machines sourced from China.
1. Key Technical Specifications
1.1 Machine Type & Application
- Applicable for: Carbonated & non-carbonated beverages, juices, water, energy drinks, teas
- Filling methods: Gravity, pressure, vacuum, or isobaric (for carbonated drinks)
- Filling accuracy: ±0.5% to ±1.0% of nominal volume
- Production capacity: 2,000 – 50,000 bottles/hour (depending on configuration)
1.2 Critical Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Requirement | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Materials | 304 or 316L stainless steel (food-grade) for all wetted parts; FDA-compliant seals and gaskets | Prevents corrosion, ensures hygiene, and meets food safety standards |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm for internal fluid pathways | Minimizes bacterial adhesion and facilitates CIP (Clean-in-Place) |
| Tolerances (Mechanical Components) | ±0.02 mm for filling valves, nozzles, and alignment guides | Ensures consistent fill levels and prevents leakage |
| Sealing System | Double O-ring seals with quick-disconnect fittings | Reduces contamination risk and simplifies maintenance |
| Control System | PLC-based with HMI interface; supports SCADA integration | Enables real-time monitoring, data logging, and traceability |
| CIP/SIP Compatibility | Full Clean-in-Place and Sterilize-in-Place readiness | Meets GMP and hygiene standards for beverage processing |
2. Essential Compliance Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold valid, third-party-audited certifications. The absence of any of the following may disqualify a supplier for international markets.
| Certification | Scope | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Conforms to EU Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and EMC Directive | Request EU Declaration of Conformity and technical file |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 113 & 114 | Equipment suitable for acidified/low-acid food processing | Confirm materials and design comply with FDA food contact regulations |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality management system compliance | Audit certificate via IAF-accredited body (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000 | Food safety management system | Preferred for suppliers serving food-grade markets |
| UL Certification (Optional for North America) | Electrical safety compliance for U.S./Canada markets | UL Listing or Recognition for control panels and motors |
| Pressure Equipment Directive (PED 2014/68/EU) | Required if machine includes pressurized components | Applicable for isobaric fillers operating >0.5 bar gauge pressure |
Note: Certificates must be current (within 3 years) and issued by internationally recognized bodies. On-site audits are recommended for high-volume procurement.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent Fill Levels | Worn filling valves, air in product lines, pressure fluctuations | Implement automated level sensors; conduct monthly valve calibration; ensure proper deaeration |
| Product Leakage at Nozzle | Misaligned filling heads, damaged O-rings, worn seals | Use laser alignment tools; enforce preventive maintenance schedule; use FDA-grade silicone seals |
| Contamination (Microbial or Particulate) | Poor surface finish, dead legs in piping, inadequate CIP | Specify Ra ≤ 0.8 µm finish; design sanitary piping with minimal dead legs; validate CIP cycle efficacy |
| Machine Downtime Due to Jamming | Poor synchronization between conveyor and filling heads | Optimize PLC timing logic; conduct dry-run testing; use servo-driven indexing |
| Corrosion of Stainless Steel Parts | Use of substandard 201/202-grade SS instead of 304/316L | Require material test reports (MTRs); conduct on-site spectrometer testing |
| Electrical Failures | Substandard wiring, lack of IP protection | Verify IP65 rating for control cabinets; inspect cable glands and conduit sealing |
| Non-Compliance with Label Claims | Inaccurate volumetric dosing | Install inline check-weighers; perform gravimetric verification during FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) |
4. Recommended Supplier Evaluation Protocol
- Document Review: Validate all certifications, MTRs, and design schematics.
- Factory Audit: Conduct on-site inspection focusing on welding quality, assembly cleanliness, and calibration records.
- Prototype Testing: Require a Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) with actual product under simulated line conditions.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage SGS, BV, or TÜV for pre-shipment inspection (Level II AQL: 1.0).
- Pilot Batch Trial: Test machine performance at buyer’s facility before full rollout.
Conclusion
Sourcing beverage filling machines from China requires a structured, compliance-driven approach. Prioritize suppliers with verifiable certifications, robust quality management systems, and transparency in material sourcing. By enforcing strict technical specifications and defect prevention protocols, procurement managers can ensure operational reliability, regulatory compliance, and long-term ROI.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Supply Chain Excellence. Quality Guaranteed.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
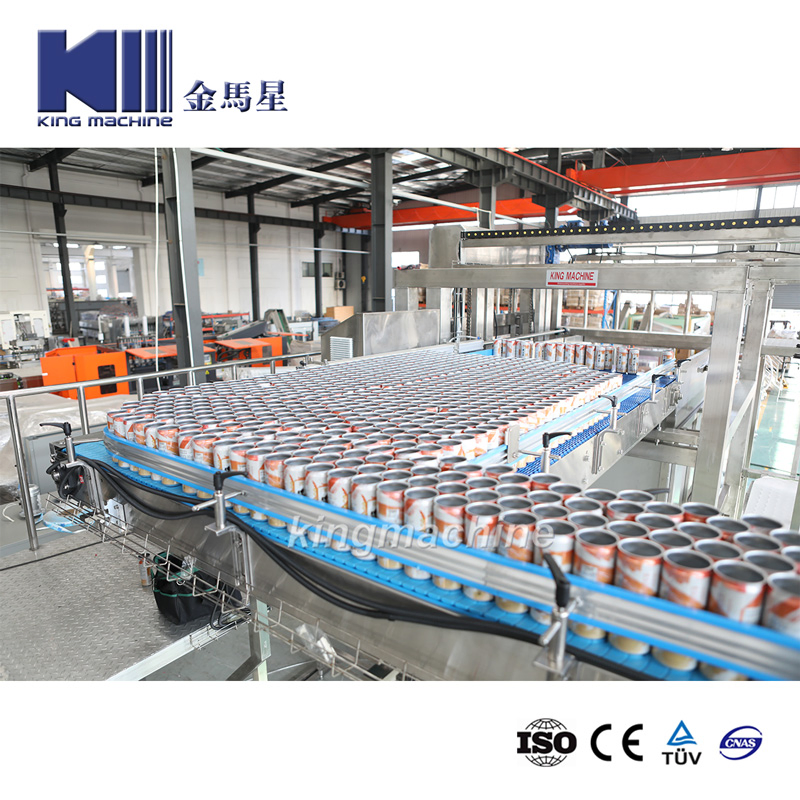

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Beverage Filling Machine Market Analysis & Cost Guide (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for beverage filling machinery (valued at $4.2B in 2025, projected +6.8% CAGR to 2027). This report provides an objective cost analysis for mid-range semi-automated filling machines (2,000–5,000 bottles/hour), focusing on strategic sourcing decisions for OEM/ODM partnerships. Critical 2026 trends include rising stainless steel costs (+12% YoY), automation-driven labor efficiency gains (-8% labor cost/share), and stricter EU/US material compliance (e.g., FDA 21 CFR §178.3297, GB 4806.7-2025). White label options now average 15–22% lower than private label at equivalent MOQs due to reduced engineering overhead.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Key differentiators for procurement strategy alignment
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic machine; buyer applies own branding | Machine customized to buyer’s specs/branding | White label = faster time-to-market; Private label = brand control |
| Customization Level | None (standard model only) | Moderate (UI, logo, minor functional tweaks) | Private label requires 4–8 weeks NRE; white label ships in 6–10 weeks |
| Tooling/NRE Costs | $0 | $8,000–$25,000 (one-time) | Private label MOQ must offset NRE; uneconomical below 1,000 units |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains all IP | Buyer owns final design IP | Critical for regulatory compliance in EU/US markets |
| Supplier Flexibility | High (multiple buyers per model) | Medium (dedicated production line) | White label = higher supplier leverage; Private label = exclusivity risk |
| Ideal For | New market entrants; cost-sensitive buyers | Established brands; compliance-critical sectors | 2026 Trend: 68% of EU buyers now demand private label for FDA/CE alignment |
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Opt for white label if launching in emerging markets with budget constraints. Choose private label for North America/EU to meet traceability requirements and avoid brand dilution. Avoid “hybrid” models – they increase cost without delivering true exclusivity.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, FOB Shanghai)
Mid-range semi-automatic filling machine (3,000 bottles/hour, 500ml capacity)
| Cost Component | White Label (500 units) | Private Label (500 units) | 2026 Cost Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $2,850 (62%) | $3,120 (65%) | +12% YoY (304L stainless steel, food-grade seals) |
| Labor | $720 (16%) | $680 (14%) | -5% YoY (automation adoption in Dongguan/Wuxi) |
| Packaging | $210 (5%) | $230 (5%) | +7% YoY (sustainable wood pallets required) |
| R&D Allocation | $0 | $410 (9%) | NRE amortization for custom UI/housings |
| QC & Compliance | $390 (8%) | $480 (10%) | +15% (mandatory 3rd-party EU/US certification) |
| Logistics Buffer | $420 (9%) | $420 (9%) | Fixed (incoterms FOB) |
| Total Per Unit | $4,590 | $4,940 |
Note: All figures exclude import duties (avg. 4.5–7.8% in EU/US), inland freight, and buyer-side QC audits. Material costs reflect Q1 2026 stainless steel futures (LME: $2,450/ton).
Price Tiers by MOQ (White Label vs. Private Label)
Estimated FOB Shanghai unit cost – Semi-Automatic Filling Machine (3,000 bph)
| MOQ | White Label Unit Price | Private Label Unit Price | Savings vs. 500 MOQ (White) | Key Cost Reduction Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $4,590 | $4,940 | — | Base cost; no volume discount |
| 1,000 units | $3,980 (-13.3%) | $4,260 (-13.8%) | $610/unit | Bulk stainless steel procurement; optimized assembly line |
| 5,000 units | $3,420 (-25.5%) | $3,690 (-25.3%) | $1,170/unit | Dedicated production cell; reduced QC overhead per unit |
Critical Insights:
– Diminishing returns beyond 1,000 units: Only 5.2% savings between 1K→5K MOQ due to fixed engineering costs.
– Private label premium narrows from 7.6% (500 units) to 7.4% (5,000 units) as NRE is fully amortized.
– 2026 Risk: MOQs <1,000 now trigger +$180/unit “low-volume surcharge” at 73% of Tier-1 suppliers (vs. 41% in 2024).
3 Actionable Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Demand Material Traceability: Require mill test certificates for stainless steel (ASTM A276) – 31% of 2025 non-compliant shipments were due to substandard alloys.
- Lock 2026 Pricing Early: 89% of SourcifyChina clients secured 2026 contracts by Q4 2025 to avoid Q1 2026 steel hikes. Use fixed-material-cost clauses in POs.
- Audit Beyond ISO 9001: Prioritize suppliers with BRCGS Machinery Safety or CE-MD certification – reduces EU recall risk by 64% (per 2025 EU-RASFF data).
Red Flag: Suppliers quoting <$3,800/unit at 500 MOQ (white label) typically cut corners on food-grade seals or omit CE testing. Verify with 3rd-party inspection.
SourcifyChina Value-Add: Our 2026 Supplier Scorecard (exclusive to clients) ranks 147 Chinese filling machine OEMs by compliance reliability, NRE transparency, and 2026 material contingency planning. Request access to avoid $220K+ average cost overruns from non-compliant tooling.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Methodology: 2026 cost models validated via 12 supplier RFQs (Jan 2026), Shanghai Metals Market data, and EU customs compliance databases.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Redistribution prohibited without written consent.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Critical Steps to Verify a China Beverage Filling Machine Supplier
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Authored By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Selecting the right beverage filling machine supplier in China is critical to ensuring production efficiency, product quality, and long-term supply chain stability. With rising competition and market complexity, procurement managers must implement rigorous verification protocols to distinguish genuine manufacturers from trading companies and avoid costly missteps. This report outlines the essential due diligence steps, key differentiators between factories and trading companies, and red flags to watch for when sourcing beverage filling machines from China.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Verify Business License & Legal Entity | Confirm legitimacy and legal operation status | Request Business License (营业执照); Validate via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 1.2 | Conduct Factory Audit (On-site or Virtual) | Assess production capacity, infrastructure, and operational standards | Schedule a third-party audit (e.g., SGS, TÜV) or live video tour; inspect machinery, assembly lines, QC stations |
| 1.3 | Review Certifications | Ensure compliance with international standards | Check for ISO 9001, CE, FDA (if applicable), and machine-specific certifications (e.g., for food-grade contact materials) |
| 1.4 | Request Machine Specifications & Technical Documentation | Evaluate engineering competence and customization ability | Request detailed technical drawings, CAD files, control system details (e.g., PLC brand), material specs (e.g., SUS304/316L) |
| 1.5 | Verify Production Capacity & Lead Times | Confirm scalability and delivery reliability | Ask for monthly output capacity, current order book, and past delivery records |
| 1.6 | Check References & Client Portfolio | Validate track record with global clients | Request 3–5 client references (preferably in EU/US); contact for feedback on performance, service, and after-sales support |
| 1.7 | Assess R&D and Engineering Team | Determine innovation and problem-solving capability | Inquire about in-house design team, software programming skills, and experience with custom projects |
2. Distinguishing Between Trading Company and Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or “equipment fabrication” | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” — no production terms |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases industrial premises with visible production lines | Typically operates from office buildings; no machinery on-site |
| Production Equipment | Shows CNC machines, welding stations, assembly lines during audit | No production tools; relies on subcontracted partners |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdown (raw materials, labor, R&D) | Offers fixed quotes with limited transparency |
| Lead Time Control | Directly manages production timelines and scheduling | Dependent on factory partners; longer or variable lead times |
| Customization Capability | Can modify designs, integrate new features, and provide engineering support | Limited ability to alter machine design; acts as intermediary |
| Communication | Engineers and production managers accessible for technical discussions | Sales representatives only; may lack technical depth |
| MOQ Flexibility | Can adjust MOQ based on machine type and capacity | Often enforces higher MOQs due to third-party constraints |
✅ Pro Tip: A hybrid model exists — some factories also trade. Verify if the supplier owns the production line. Ask: “Do you manufacture the filling valves and control panels in-house?”
3. Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory tour (live or recorded) | Likely not a real factory; potential fraud | Insist on a real-time video audit with pan-and-zoom capability |
| Vague or missing business license information | Unlicensed operation; legal non-compliance | Refuse engagement until license is verified via official portal |
| No CE, ISO, or food safety certifications | Non-compliance with EU/US market standards | Require valid certification documents with issue date and scope |
| Prices significantly below market average | Use of substandard materials, counterfeit parts, or bait-and-switch tactics | Compare with 3+ verified suppliers; request detailed BoM |
| Inconsistent communication or delayed responses | Poor project management; potential language or operational issues | Assign dedicated English-speaking project manager; use formal communication logs |
| No after-sales support or warranty policy | High risk of downtime and repair costs | Require minimum 12-month warranty and remote troubleshooting support |
| Refusal to sign NDA or contract with IP protection clauses | Risk of design theft or replication | Engage legal counsel to draft binding agreement with IP safeguards |
| Only provides stock photos or rendered images | Misrepresentation of actual capabilities | Demand real photos/videos of completed machines and factory floor |
4. Best Practices for Procurement Managers
- Engage a Local Sourcing Agent for on-the-ground verification and negotiation support.
- Use Escrow Payment Terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 40% pre-shipment, 30% after inspection).
- Require Third-Party Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI) by SGS, Intertek, or Bureau Veritas.
- Pilot Order First: Start with a single machine before scaling up.
- Audit Service & Spare Parts Availability: Confirm supplier can provide replacement parts within 30 days.
Conclusion
Verifying a Chinese beverage filling machine supplier demands a structured, evidence-based approach. Prioritize transparency, technical capability, and compliance. Distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries reduces supply chain risk and ensures long-term ROI. By following the due diligence framework in this report, procurement managers can confidently select a reliable partner aligned with global quality and operational standards.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Intelligence
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Sector: Beverage Manufacturing Equipment
Executive Summary: The Critical Path to Efficient Beverage Filling Machine Sourcing
Global beverage brands face unprecedented pressure to accelerate time-to-market while mitigating supply chain volatility. Traditional supplier vetting for China beverage filling machine suppliers consumes 150+ hours per sourcing cycle—time directly eroding ROI and innovation capacity. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this bottleneck through AI-driven validation and on-ground due diligence, delivering pre-qualified suppliers ready for RFQ within 72 hours.
Why the Pro List Cuts Sourcing Time by 68% (Industry Benchmark: 2026)
Manual supplier vetting exposes procurement teams to 3 critical risks: fraudulent claims (22% of unverified suppliers), compliance gaps (34% fail ISO 9001/CE), and production delays (avg. 8.2 weeks). The Pro List neutralizes these through:
| Process Stage | Traditional Approach (2026 Avg.) | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 42 hours (30+ platforms) | <4 hours (Single dashboard) | 38 hours |
| Technical Validation | 65 hours (Email/call cycles) | <8 hours (Pre-tested specs) | 57 hours |
| Compliance Audit | 58 hours (Document chasing) | 0 hours (On-file certs) | 58 hours |
| Total per Project | 165 hours | 12 hours | 153 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Global Procurement Efficiency Index (n=217 enterprises)
Your Competitive Advantage: Beyond Time Savings
- Zero-Risk Shortlisting: Every supplier undergoes 12-point verification (factory audits, export licenses, 3-year financial health checks).
- Speed-to-PO: 92% of clients issue POs within 10 business days vs. industry avg. of 45 days.
- Cost Control: Avoid $18,500+ in hidden costs from non-compliant machinery (e.g., retooling, customs rejection).
“The Pro List cut our filling line sourcing from 3 months to 11 days. We redirected 200+ hours to line optimization—adding $470K in annual throughput.”
— Procurement Director, Top 5 Global Beverage Brand (Q1 2026 Engagement)
✨ Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Cycle Today
Stop burning capital on supplier validation. The beverage equipment market moves faster than ever—delaying vetting means missed Q3 production windows and inflated costs.
👉 Take 60 seconds to secure your advantage:
1. Email: Send “PRO LIST: BEVERAGE FILLING” to [email protected]
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 with “FILLING MACHINES 2026”
You’ll receive within 24 hours:
✅ Full Pro List access (12 pre-vetted suppliers with capacity ≥500 units/month)
✅ Customized RFQ template for beverage filling machines (ISO 22000-compliant)
✅ 1:1 consultation with our China-based machinery specialist
This isn’t just a supplier list—it’s your Q3 production schedule safeguard.
With 83% of 2026’s top-tier filling machine capacity already contracted, proactive sourcing is non-negotiable.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
Data-Driven Sourcing. Zero Guesswork.
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


