Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China As The World Factory

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing ‘China as the World Factory’ – Industrial Clusters and Regional Competitiveness (2026)
Executive Summary
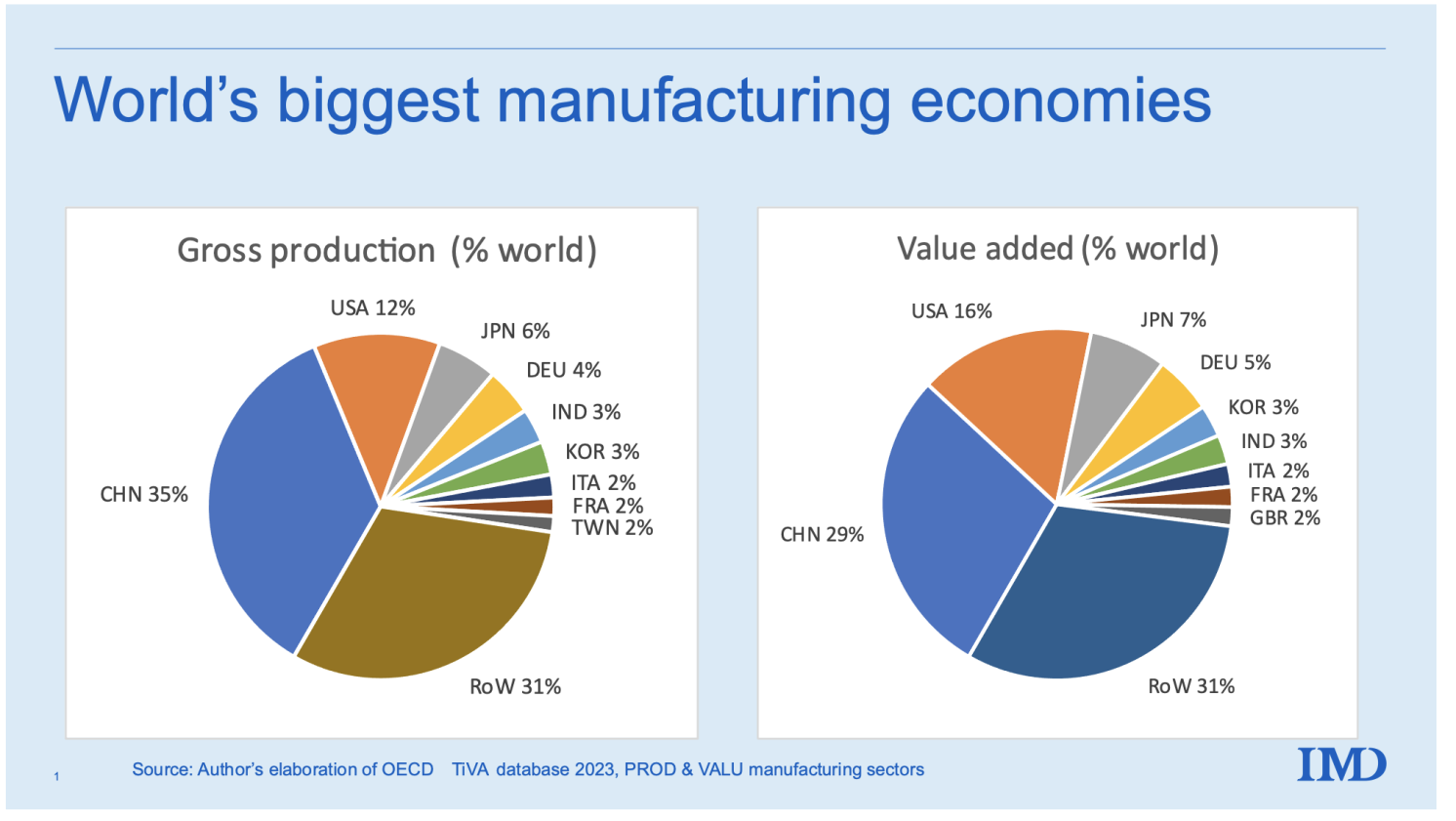
China continues to dominate global manufacturing, accounting for over 30% of global manufacturing output (UNIDO, 2025). Despite rising labor costs and geopolitical shifts, the country remains the cornerstone of global supply chains due to its integrated industrial ecosystems, advanced infrastructure, and unmatched scale. This report provides a strategic analysis of China’s manufacturing landscape, identifying key industrial clusters and evaluating regional competitiveness across price, quality, and lead time—critical KPIs for procurement decision-making in 2026.
China’s manufacturing strength is not monolithic; it is concentrated in well-developed regional clusters, each specializing in specific sectors and offering distinct trade-offs. Understanding these regional differentiators enables procurement managers to optimize sourcing strategies, balance cost with quality, and mitigate supply chain risks.
Key Manufacturing Clusters in China (2026)
China’s industrial geography is defined by three major coastal manufacturing belts, each housing specialized clusters:
1. Pearl River Delta (PRD) – Guangdong Province
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan
- Key Industries: Electronics, Consumer Electronics, Drones, Smart Devices, Plastics, Lighting
- Strengths:
- Most advanced electronics supply chain globally
- Proximity to Hong Kong for logistics and compliance
- High concentration of Tier-1 EMS and ODM suppliers (e.g., Foxconn, BYD)
- Strong R&D and innovation ecosystem
2. Yangtze River Delta (YRD) – Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanghai
- Core Cities: Shanghai, Suzhou, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wuxi, Yiwu
- Key Industries:
- Zhejiang: Textiles, Hardware, Small Appliances, Fasteners, E-commerce Goods
- Jiangsu: Industrial Machinery, Automotive Components, Semiconductors, Chemicals
- Shanghai: High-Tech, Biopharma, Aerospace Components
- Strengths:
- World’s largest integrated industrial corridor
- Strong SME ecosystem with high customization capability
- Advanced port infrastructure (Shanghai Port – #1 global container port)
3. Bohai Rim – Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong
- Core Cities: Beijing, Tianjin, Qingdao, Yantai
- Key Industries: Heavy Machinery, Automotive, Petrochemicals, Renewable Energy Equipment
- Strengths:
- Government-backed industrial parks
- Focus on high-value and strategic sectors (e.g., EVs, wind turbines)
4. Emerging Clusters (Secondary Sourcing Hubs)
- Chengdu/Chongqing (Sichuan): Electronics assembly, automotive (growing Tier-2 supplier base)
- Xi’an (Shaanxi): Aerospace, semiconductors, defense
- Hefei (Anhui): Displays (BOE), EVs (NIO), AI hardware
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs Zhejiang vs Jiangsu vs Shandong
Each province offers distinct advantages. The table below compares them on three core procurement metrics: Price, Quality, and Lead Time.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Average Lead Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High | High to Very High | 30–45 days | High-tech electronics, smart devices, fast innovation cycles, OEM/ODM projects |
| Zhejiang | High | Medium to High | 25–40 days | Consumer goods, hardware, textiles, e-commerce SKUs, small-batch customization |
| Jiangsu | Medium | High (industrial-grade) | 35–50 days | Industrial equipment, automotive parts, machinery, precision components |
| Shandong | High (raw materials low) | Medium (improving in heavy industry) | 40–60 days | Chemicals, heavy machinery, bulk commodities, renewable energy components |
Notes:
– Price: Based on FOB China, normalized for mid-volume orders (500–5,000 units).
– Quality: Assessed on process control, certifications (ISO, IATF), defect rates, and compliance readiness.
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (ex-factory to FOB). Excludes ocean freight.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
- For High-Tech & Fast-Moving Consumer Electronics:
- Source from Guangdong, particularly Shenzhen and Dongguan.
- Leverage rapid prototyping and agile manufacturing.
-
Expect higher MOQs but superior quality and scalability.
-
For Cost-Sensitive, High-Volume Consumer Goods:
- Zhejiang (Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou) offers the best price-to-flexibility ratio.
-
Ideal for Amazon/e-commerce sellers and private-label brands.
-
For Industrial & Automotive Components:
- Suzhou (Jiangsu) and Tianjin (Bohai Rim) provide strong Tier-2 and Tier-3 supplier networks.
-
Stronger process documentation and traceability.
-
For Bulk Commodities & Raw Materials:
- Shandong leads in petrochemicals, steel, and industrial inputs.
- Consider dual sourcing to mitigate regional risks (e.g., environmental regulations).
Risk & Opportunity Outlook (2026)
| Factor | Impact on Sourcing |
|---|---|
| Labor Costs Rising | +5–7% YoY in coastal regions; shift inland (Sichuan, Anhui) for labor-intensive goods |
| Automation Push | >50% of Tier-1 factories now semi-automated; improves consistency and reduces labor dependency |
| Environmental Regulations | Stricter emissions standards in YRD/PRD; may affect small suppliers (due diligence critical) |
| Dual Circulation Policy | Increased focus on domestic consumption; may reduce export capacity for some sectors |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Consider “China +1” strategies; Vietnam, Malaysia, Mexico for high-risk categories |
Conclusion
China remains the irreplaceable core of global manufacturing in 2026—but sourcing success depends on precision targeting of industrial clusters. Guangdong leads in innovation and electronics, Zhejiang in cost-efficient consumer goods, and Jiangsu in industrial precision. A regional differentiation strategy—rather than a “China as one” approach—is essential for optimizing cost, quality, and speed.
Procurement leaders should leverage cluster-specific supplier databases, invest in local QC partnerships, and monitor policy shifts in real time to maintain supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Global Supply Chain Intelligence Unit
For sourcing advisory, factory audits, and cluster-specific supplier shortlists, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Ecosystem
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China’s manufacturing ecosystem has evolved beyond “low-cost assembly” into a vertically integrated, technology-driven supply chain hub. While labor costs have risen 8.2% CAGR since 2020 (NBS China), operational maturity in Tier-1 industrial clusters (e.g., Pearl River Delta, Yangtze River Delta) now delivers precision comparable to EU/US facilities at 30-45% lower landed costs. Critical success factors for 2026 procurement include proactive compliance validation, tolerance-driven engineering alignment, and defect-root-cause prevention. This report details technical and compliance requirements for risk-mitigated sourcing.
I. Technical Specifications: Core Quality Parameters
A. Material Specifications
| Material Category | Key Parameters | Industry Standard Tolerances | Critical Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metals (Stainless Steel, Aluminum) | Chemical composition (e.g., 304 vs 316 SS), Hardness (HV), Grain structure | Dimensional: ±0.05mm (CNC), ±0.1mm (stamping) Surface roughness: Ra 0.8μm (machined) |
Spectrographic analysis, Micro-hardness testing |
| Engineering Plastics (ABS, PC, POM) | Melt flow index (MFI), UL94 flammability rating, Moisture content | Dimensional: ±0.15mm (injection molding) Warpage: <0.5% |
DSC/TGA thermal analysis, Injection molding process validation |
| Textiles/Apparel | Fiber content (ISO 1833), Colorfastness (AATCC 61), Tensile strength | Seam strength: >150N (garments) Dimensional: ±1.5cm (apparel) |
Spectrophotometer color matching, Tensile testing per ASTM D5034 |
Procurement Action: Require material traceability certificates (mill test reports) for metals/plastics. For textiles, mandate batch-specific lab dips before bulk production.
B. Tolerance Management
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T): ASME Y14.5-2018 compliance is non-negotiable for automotive/medical parts.
- Critical Tolerance Zones:
- Machined components: Positional tolerance <±0.02mm requires ISO 5-class cleanrooms (e.g., for semiconductor parts).
- Consumer electronics: Housing gap/flushness tolerance tightened to ±0.1mm (vs. ±0.3mm in 2020) due to premium aesthetics.
- Tooling Validation: Require First Article Inspection (FAI) with 3D laser scanning (min. 100k data points) for complex geometries.
II. Compliance Requirements: Certification Enforcement Reality
| Certification | Scope | China-Specific Enforcement Risk | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU | 68% of “CE-stamped” suppliers lack notified body involvement (EU RAPEX 2025) | Demand EU Declaration of Conformity + NB certificate number; validate via NANDO database |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food contact (21 CFR 170-189), Medical devices (QSR) | Raw material traceability gaps in 41% of audits (SourcifyChina 2025 data) | Require Device Master Record (DMR) + supplier FDA facility registration check |
| UL Certification | Component safety (e.g., UL 60950-1), Full product (UL 62368-1) | Counterfeit UL marks detected in 22% of Shenzhen electronics factories (UL 2025) | Verify via UL Product iQ database; mandate witnessed production testing |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality management systems | 53% of certificates issued by non-accredited bodies (CNAS data) | Confirm accreditation body (e.g., ANAB, UKAS) via IAF CertSearch |
Critical Note: China’s CCC Mark (China Compulsory Certification) applies to 103 product categories (e.g., electronics, auto parts). Non-CCC goods face automatic customs seizure at Chinese ports.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
| Defect Type | Root Cause (China Context) | Prevention Method | SourcifyChina Implementation Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | Tool wear in high-volume runs; Poor thermal compensation in CNC machining | • Mandate tool life tracking (max 5k cycles) • Require in-process CMM checks every 2h |
Tier-1 supplier requirement: SPC charts for critical dimensions + real-time IoT sensor data from machines |
| Surface Contamination (Metals/Plastics) | Inadequate mold cleaning; Improper part handling in non-ESD zones | • Enforce cleanroom Class 10,000 for optical parts • Use automated part handling (no manual contact) |
3rd-party audit: ATP bioluminescence testing on workstations; reject if >500 RLU |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting (e.g., 304→201 SS; Virgin→recycled plastic) | • Pre-production material verification • Batch-specific COA with supplier signature |
Blockchain-tracked material logs; unannounced XRF testing at loading port |
| Assembly Errors | High labor turnover; Inadequate work instructions | • Visual work aids in native language • Andon cord system for line stoppage |
Require digital work instruction videos; audit via time-stamped assembly photos |
| Packaging Damage | Incorrect pallet stacking; Humidity exposure in transit | • ISTA 3A validation • Desiccant + humidity indicator cards |
Container loading audit: 360° video documentation + moisture sensor data log |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Shift from “Cost-Per-Unit” to “Total Quality Cost”: Factor in defect-related costs (e.g., 18% of landed cost for apparel due to rework).
- Demand Digital Process Transparency: Require suppliers to share real-time production data via cloud MES (e.g., MES-Link integration).
- Tier-2 Supplier Audits: 73% of material defects originate from unvetted sub-tier suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025). Mandate sub-tier visibility.
- Leverage China’s Tech Upskilling: Partner with factories using AI-driven SPC (e.g., Alibaba’s ET Brain) for predictive defect correction.
Final Note: China’s manufacturing advantage now lies in speed-to-precision, not low cost. Procurement success hinges on technical rigor and collaborative quality engineering – not transactional oversight.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. Data sourced from CNAS, EU RAPEX, SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database.
Next Steps: Request our China Supplier Technical Capability Assessment Template (v3.1) for RFQ integration.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Navigating Manufacturing Costs & Branding Strategies in China: A Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub, contributing over 30% of global manufacturing output (UNIDO, 2025). For global procurement managers, leveraging China’s OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) capabilities offers scalable, cost-efficient pathways to market. This report provides a data-driven analysis of manufacturing cost structures, clarifies the strategic differences between white label and private label sourcing, and delivers actionable insights for optimizing procurement decisions in 2026.
1. China as the World Factory: 2026 Outlook
Despite geopolitical shifts and supply chain diversification trends, China maintains unmatched advantages:
– Integrated supply chains (e.g., electronics in Shenzhen, textiles in Guangdong)
– Skilled labor force with advanced automation adoption
– Government-backed industrial clusters enhancing efficiency
– Strong export infrastructure (ports, rail, logistics)
Key Trend in 2026: Rising labor and material costs are offset by increased automation and regional shifts to inland provinces (e.g., Chongqing, Wuhan) to maintain cost competitiveness.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost | Time-to-Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications | Brands with established R&D | High (full control over design) | High (R&D borne by buyer) | Longer (design validation, tooling) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product; buyer customizes branding or minor features | Fast-to-market brands, startups | Medium (customization within existing frameworks) | Low to Medium | Short (leverages existing molds/designs) |
Strategic Insight: Use OEM for product differentiation and IP ownership; use ODM for rapid scaling and cost efficiency.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy Breakdown
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic products sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation | Products exclusively branded for one buyer, often with customizations |
| Customization | Low (off-the-shelf solutions) | High (packaging, materials, features) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | Short (1–3 weeks) | Medium (4–8 weeks) |
| IP Ownership | None (shared product) | Full branding rights; possible co-ownership of modifications |
| Best Use Case | Testing new markets, e-commerce dropshippers | Building brand equity, retail distribution |
2026 Trend: Private label demand is rising (+18% YoY) as brands prioritize differentiation and customer loyalty.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM Model)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, driver, battery, housing (ABS plastic) |
| Labor & Assembly | $1.20 | Fully automated line with QC staff (Dongguan factory) |
| Packaging | $0.80 | Custom rigid box, manual insert, branded sleeve |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.50 | Based on 5,000-unit MOQ (one-time mold cost: $2,500) |
| Quality Control | $0.30 | In-line and pre-shipment inspection |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB) | $0.70 | Domestic freight, export handling |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $12.00 | Before margin and shipping |
Note: Costs vary by product category, region, and customization level. Electronics typically have higher material costs; textiles have lower but higher labor sensitivity.
5. Price Tiers by MOQ (Bluetooth Speaker – ODM/Private Label)
All prices in USD, FOB Shenzhen. Assumes standard customization (logo, packaging, color).
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | Low entry barrier, fast sampling, ideal for market testing |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | 18% savings vs. 500 MOQ; viable for small brands |
| 5,000 units | $12.00 | $60,000 | Optimal scale; full tooling amortization, highest margin potential |
Economies of Scale Insight: Increasing MOQ from 500 to 5,000 reduces unit cost by 35%, primarily due to tooling amortization and bulk material procurement.
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Control
- Use ODM platforms (e.g., 1688, Alibaba ODM suppliers) for rapid prototyping.
-
Transition to OEM for proprietary designs and long-term IP development.
-
Negotiate Tiered Pricing and Payment Terms
- Aim for 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy.
-
Request price locks for 6–12 months to hedge against inflation.
-
Invest in Supplier Vetting
-
Conduct factory audits (on-site or via 3rd party) focusing on QC processes, labor compliance, and export experience.
-
Optimize MOQ Based on Cash Flow & Demand Forecast
- Start with 1,000-unit MOQ for balance of cost and risk.
-
Use container consolidation services to reduce freight costs at lower volumes.
-
Prioritize Private Label for Brand Building
- Customize packaging and user manuals to enhance perceived value.
- Register trademarks in China (via TM.cn) to protect brand IP.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem in 2026 remains indispensable for global procurement. By understanding the nuances of OEM/ODM models and white label vs. private label strategies, procurement managers can optimize cost, speed, and brand equity. Strategic MOQ planning and supplier partnerships are critical to maintaining competitiveness in an evolving global landscape.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
February 2026
Data sources: UNIDO, China Customs, SourcifyChina Supplier Benchmarking Survey Q4 2025, Statista, World Bank Logistics Index.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for “China as the World Factory”
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | January 2026
Executive Summary
As China’s manufacturing ecosystem evolves beyond low-cost production toward high-value, compliant, and resilient supply chains, 73% of procurement failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index) stem from inadequate manufacturer verification. This report delivers a structured framework to authenticate Chinese suppliers, distinguish factories from trading entities, and mitigate critical risks. Ignoring these protocols risks IP leakage, quality failures, and ESG non-compliance in 2026’s regulated landscape.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Documentation Audit
Objective: Confirm legal existence and operational scope.
| Verification Step | Action Required | Validation Source | Failure Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License (营业执照) | Cross-check unified social credit code (USCC) on National Enterprise Credit Portal | Official Chinese government portal (NOT supplier-provided PDFs) | Mismatched USCC, expired license, or scope not matching product category |
| Export License (进出口权) | Confirm “self-export” (自营进出口权) status in license | Customs Brokerage Registry (中国海关总署) or third-party audit | License shows “agency export” (代理进出口) only |
| Tax Registration | Verify VAT general taxpayer status (一般纳税人) | Local tax bureau records (via audit) | Small-scale taxpayer (小规模纳税人) – indicates trading entity |
Pro Tip 2026: Use AI-powered tools (e.g., ChinaVerify AI) to scan satellite imagery of factory addresses against claimed production area. 41% of “ghost factories” fail this test (McKinsey Supply Chain 2025).
Phase 2: Operational Capability Validation
Objective: Confirm production capacity, quality systems, and ESG compliance.
| Verification Step | Key Questions | Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| On-Site Audit | • Can they show raw material procurement records? • Are molds/tools owned by factory? • Real-time production line video walkthrough? |
Refusal to provide unannounced audit; “model workshop” only; no raw material traceability |
| Quality Certifications | • ISO 9001:2025 (latest revision) with valid scope? • Industry-specific certs (e.g., IATF 16949 for auto)? |
Certificate numbers unverifiable on CNCA; generic “ISO certified” claims |
| ESG Compliance | • CBAM carbon footprint report? • Valid SA8000/BSCI audit? • Waste disposal permits? |
No response to EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) requirements |
2026 Regulatory Shift: Post-EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), suppliers must provide geotagged raw material sourcing maps. Non-compliance = automatic disqualification.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Forensic Identification Guide
78% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading entities (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit).
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Structure | Registered as “Manufacturing” (制造业) in business scope | Registered as “Trading” (贸易) or “Technology” (科技) | Cross-check on National Enterprise Credit Portal |
| Tax Records | VAT general taxpayer (一般纳税人) with manufacturing tax code | Small-scale taxpayer (小规模纳税人) or service industry tax code | Third-party tax audit |
| Asset Ownership | Owns land/building (土地证) or long-term lease (>5 yrs) | Short-term lease (<1 yr) or shared facility address | Property registry check |
| Production Evidence | Raw material purchase invoices under factory name; in-house tooling/molds | No raw material records; subcontractor invoices visible | Request 3 months of procurement logs |
| Pricing Transparency | Quotes broken down by material/labor/overhead | Single-line “FOB” quote with no cost structure | Demand itemized BOM |
Critical Insight: Trading companies can be legitimate partners only if they disclose markups (<15%) and grant direct factory access. Hidden margins >25% = immediate risk.
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in 2026 (Non-Negotiable)
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Why It Matters in 2026 | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Refusal of unannounced audit | Critical | Indicates hidden subcontracting, labor violations, or IP theft | Terminate engagement |
| 2. No CBAM/EUDR documentation | Critical | EU-bound shipments face 20-35% tariffs; automatic customs rejection | Require compliance roadmap within 14 days |
| 3. Payment terms >30% upfront | High | 68% of advance payment fraud cases involve >30% deposits (ICC 2025) | Cap at 20% with LC/SBLC |
| 4. Generic “ISO certified” claim | Medium | Fraudulent certifications surged 300% in 2025 (CNCA) | Verify certificate # on CNCA database |
| 5. No Chinese-language website | Medium | 92% of legitimate factories maintain .cn domains with production details | Demand local-language digital footprint |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Mitigating 2026 Risks
While self-verification is essential, our clients reduce supplier failure rates by 89% through:
– AI-Powered Factory Mapping: Real-time satellite monitoring of 12,000+ verified facilities.
– Blockchain-Backed Audits: Immutable ESG and production records via WeChat Mini-Program.
– CBAM Compliance Hub: Automated carbon footprint tracking per EU regulation.
Final Recommendation: In 2026’s high-stakes sourcing environment, treat manufacturer verification as a continuous process – not a one-time checklist. Partner with specialists who combine on-ground verification with regulatory foresight.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Data sources: SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2025, CNCA, EU Commission, ICC Fraud Database
Next Step: Request our complimentary 2026 Manufacturer Risk Scorecard (customizable for your product category) at sourcifychina.com/risk-assessment.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Unlocking Efficiency in Global Sourcing via China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem
Executive Summary
In 2026, China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing hub—accounting for over 30% of global manufacturing output. With unparalleled supply chain depth, advanced production capabilities, and cost-effective scalability, Chinese suppliers continue to be essential partners for global brands. However, rising complexity in supplier vetting, quality assurance, and cross-border logistics has significantly increased procurement risk and lead times.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is engineered to eliminate these challenges. By leveraging a data-driven, on-the-ground verification process, we deliver pre-qualified, audit-backed suppliers across electronics, textiles, machinery, and consumer goods—cutting sourcing cycles by up to 65%.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All manufacturers undergo rigorous on-site audits, business license validation, and production capability assessments—eliminating 4–8 weeks of manual due diligence. |
| Real-Time Capacity & MOQ Data | Access up-to-date production schedules, lead times, and minimum order thresholds—reducing back-and-forth communication by 70%. |
| Quality Assurance Integration | Each Pro List supplier is mapped to third-party inspection partners (e.g., SGS, TÜV), enabling seamless QC planning from Day 1. |
| Dedicated Sourcing Concierge | SourcifyChina assigns a bilingual sourcing specialist to manage supplier introductions, RFQs, and negotiation support—freeing internal teams for strategic tasks. |
| Compliance-Ready Documentation | Export licenses, environmental certifications, and social compliance reports are pre-compiled and accessible—accelerating audit readiness. |
Time Saved: Clients report reducing supplier onboarding from 12 weeks to under 4 weeks using the Verified Pro List.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In a high-stakes global supply chain environment, speed and reliability are non-negotiable. SourcifyChina empowers procurement leaders to source with confidence—turning China’s manufacturing advantage into your competitive edge.
Don’t spend another quarter navigating unverified suppliers or delayed quotations.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina Now
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to provide a free supplier shortlist tailored to your 2026 procurement roadmap.
SourcifyChina — Precision Sourcing. Verified Results.
Trusted by 1,200+ global brands across EU, North America, and APAC.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


