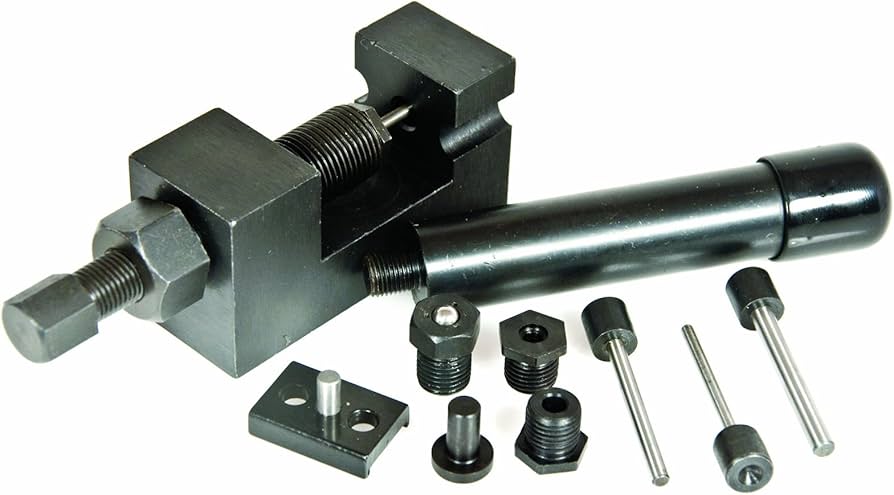
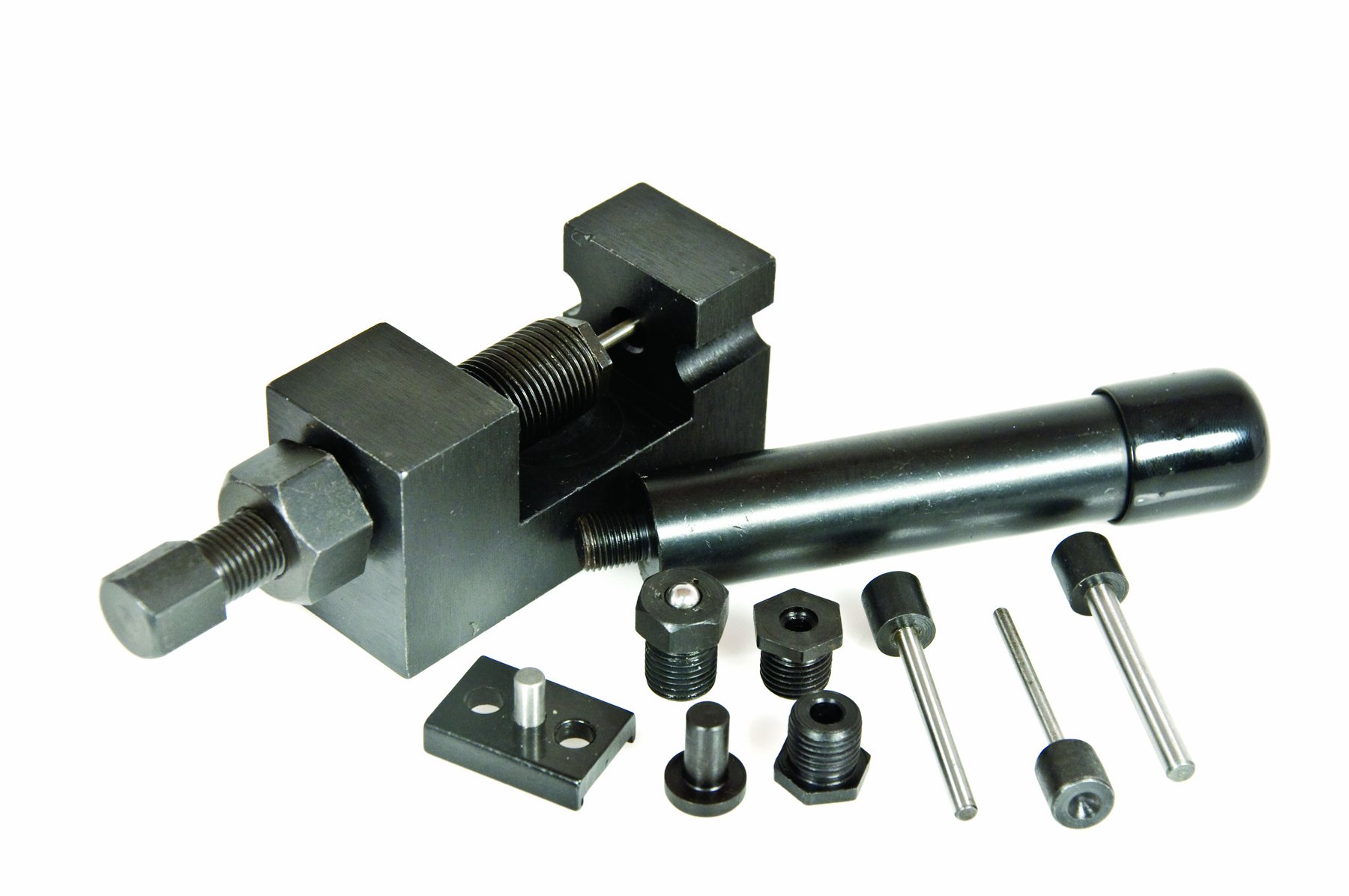
The global demand for industrial maintenance tools, particularly chain breaker tools used extensively in automotive, manufacturing, and heavy machinery sectors, has seen steady growth in recent years. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global hand tools market—which includes chain breakers—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing mechanization and rising infrastructure development. This growth is further supported by expanding applications in the electric vehicle (EV) and railway maintenance industries, where chain tension adjustment and sprocket maintenance are critical. As reliability and precision become key differentiators, manufacturers are investing in high-strength materials and ergonomic designs to meet evolving user demands. In this competitive landscape, nine leading companies have emerged as pioneers in innovation, quality, and global market reach—setting the standard for performance in chain breaker tool manufacturing.
Top 9 Chain Breaker Tool Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Chain Breakers Tools On U.S. Tsubaki Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: chains.ustsubaki.com
Key Highlights: US Tsubaki Power Transmission, LLC. produces high-quality products for a wide range of industries and applications including roller chains, conveyor chains, ……
#2 BCI Chain Breaker
Domain Est. 2018
Website: bciks.com
Key Highlights: The BCI Chain Breaker is a heavy-duty, field-proven tool engineered to make the assembly and disassembly of welded steel chains fast, safe, and hassle-free….
#3 Chain & Chain Breakers
Domain Est. 1995
#4 Chain Repair Tools
Domain Est. 1997
Website: granberg.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsExplore Granberg’s chain repair tools for bars and chains. Durable and efficient solutions for repairing and maintaining your tools….
#5 Professional Tools for Chain Assembly and Maintenance
Domain Est. 1997
Website: iwis.com
Key Highlights: iwis offers high-quality chain tools for assembly, disassembly, and maintenance of chains. Efficient and precise tools for durable and reliable drive ……
#6 EC #40 Chain Breaker Tool – Heavy
Domain Est. 1998
Website: eccarburetors.com
Key Highlights: In stockThe EC #40 Chain Breaker Tool is a professional-grade chain rivet extractor and installer, designed to make cutting and reassembling #40 roller chain fast, ……
#7 Engineered Chain breaker and Assembly Tool
Domain Est. 2002
Website: renoldjeffrey.com
Key Highlights: The Engineered Chain Assembly and Disassembly Tool from Renold is a quick and easy way to assemble and disassemble engineered chains….
#8 Leaf chain cutting tool from FB Leaf Chain. Products
Domain Est. 2005
Website: leafchain.com
Key Highlights: The leaf chain cutting tool or chain breaker is a hand tool designed to be used by service technicians and maintenance engineers….
#9 Double Pitch Chain Breakers
Domain Est. 2010
Expert Sourcing Insights for Chain Breaker Tool
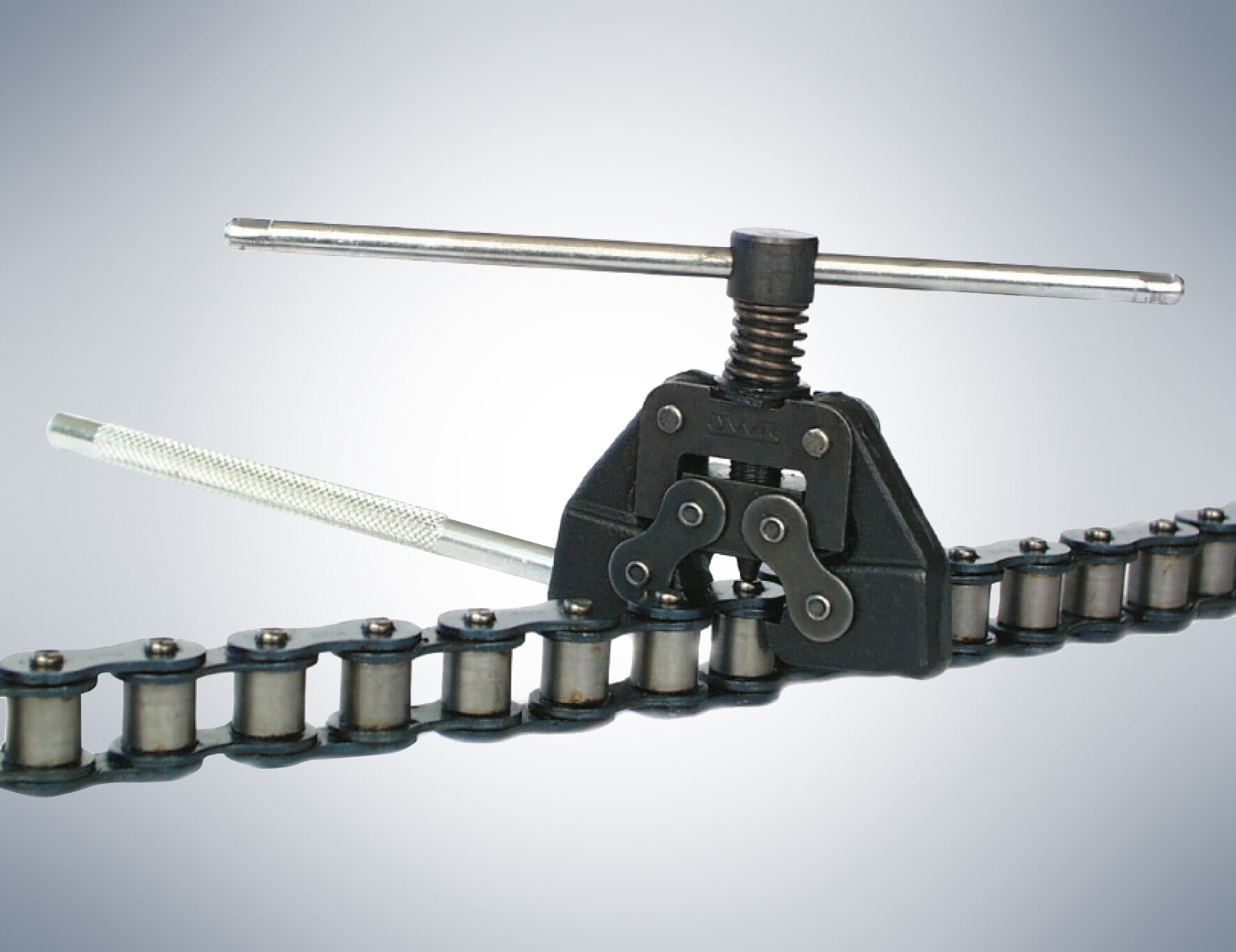
2026 Market Trends for Chain Breaker Tool
The global market for chain breaker tools is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by advancements in technology, shifts in manufacturing practices, and growing demand across key industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, and cycling. As maintenance efficiency and equipment longevity become central priorities, chain breaker tools—essential for disassembling and maintaining roller chains—are experiencing increased innovation and market expansion. This analysis explores the key trends shaping the chain breaker tool market in 2026.
Rising Demand in the Automotive and Industrial Sectors
The automotive and industrial manufacturing sectors remain primary drivers of growth for chain breaker tools. With the continued reliance on conveyor systems, assembly lines, and power transmission mechanisms that use roller chains, maintenance tools like chain breakers are critical. By 2026, increasing automation in factories and the push for predictive maintenance are expected to elevate demand for high-precision, durable chain breakers capable of withstanding heavy usage. OEMs and maintenance teams are prioritizing tools that reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency, fueling investments in robust and ergonomic designs.
Expansion in the Cycling and E-Bike Market
The global surge in cycling, particularly the rapid adoption of electric bicycles (e-bikes), is creating new opportunities for chain breaker tools. As e-bikes become more prevalent in urban transportation, the need for reliable maintenance tools grows. Cyclists and repair shops alike require compact, user-friendly chain breakers compatible with modern derailleur and internal gear systems. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to focus on lightweight, portable models with compatibility across multiple chain standards (e.g., Shimano, SRAM, Campagnolo), supporting both consumer and professional use.
Innovation in Tool Design and Materials
Technological advancements are transforming chain breaker tool design. By 2026, expect to see increased use of high-strength alloys, corrosion-resistant coatings, and ergonomic enhancements to improve durability and user comfort. Integration with digital maintenance platforms—such as QR code-based tool tracking or mobile app compatibility for usage logs—is emerging in professional-grade models. Additionally, modular and multi-functional tools that combine chain breaking with other drivetrain maintenance tasks (e.g., chain rivet pressing, master link installation) are gaining popularity, offering greater value to end users.
Regional Market Growth and Manufacturing Shifts
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region for chain breaker tool demand in 2026, led by industrial expansion in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Local manufacturing hubs are increasingly adopting international maintenance standards, boosting the need for reliable maintenance tools. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are seeing growth driven by aftermarket automotive services and the cycling boom. Sustainability concerns are also influencing production, with more manufacturers adopting eco-friendly materials and packaging to meet regulatory and consumer expectations.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The chain breaker tool market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established brands (e.g., Park Tool, X-Tools, Rohloff) and new entrants innovating to capture market share. By 2026, consolidation is expected as larger tool manufacturers acquire niche brands specializing in bicycle or industrial maintenance tools. Online retail platforms are also playing a pivotal role, enabling direct access to global consumers and accelerating product feedback cycles, which in turn drives faster innovation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the chain breaker tool market will be defined by technological sophistication, sector-specific customization, and global accessibility. Driven by industrial automation, the e-bike revolution, and a growing emphasis on maintenance efficiency, the demand for reliable, versatile, and innovative chain breaking solutions will continue to rise. Stakeholders who invest in product differentiation, user-centric design, and sustainable manufacturing will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
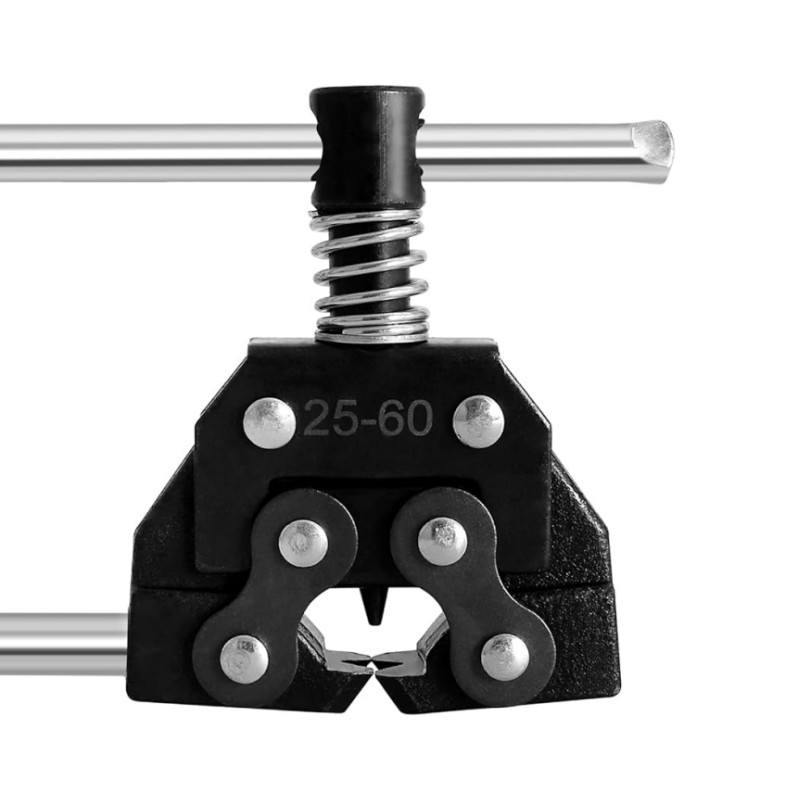

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Chain Breaker Tool (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a chain breaker tool—especially from overseas suppliers or lesser-known brands—can expose businesses to significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to avoid costly delays, safety issues, and legal complications.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Material Defects
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing chain breaker tools is inconsistent or substandard manufacturing quality. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior steel alloys or cut corners in heat treatment processes, resulting in tools that deform, crack, or fail under normal use. This not only damages your brand’s reputation but may also pose safety risks to end users.
Lack of Precision in Critical Components
Chain breaker tools require high precision in components such as the screw mechanism, anvil, and alignment guides. Poor machining tolerances can lead to misalignment, making the tool ineffective or damaging the chain during removal. Sourcing from manufacturers without strict quality control systems increases the risk of receiving inconsistent batches.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Reputable tools often undergo fatigue and load testing to ensure durability. Many generic or unbranded chain breaker tools lack proper testing documentation or certifications (such as ISO or CE, where applicable). Without these, it’s difficult to verify performance claims or ensure compliance with safety standards.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate designs from well-known brands—such as Park Tool, Shimano, or Pedro’s—can expose your business to IP infringement claims. Even if the supplier offers an identical-looking tool at a lower price, using patented designs without authorization may result in legal action, product seizures, or costly recalls.
Misrepresentation of OEM/Authorized Production
Some suppliers falsely claim to be original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or authorized producers of branded tools. Always verify the supplier’s credentials and request proof of licensing agreements if they claim affiliation with a known brand. Failure to do so can result in unknowingly distributing counterfeit products.
Inconsistent Quality Across Production Batches
Even if an initial sample meets expectations, mass production may vary significantly in quality due to loose manufacturing standards or supply chain changes. Without ongoing quality audits or third-party inspections, subsequent shipments may not meet the required specifications.
Lack of Technical Documentation and Support
Low-cost suppliers may not provide detailed technical drawings, material specifications, or user instructions. This absence complicates quality verification, after-sales support, and compliance with regulatory requirements in your target market.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: audit potential suppliers, request material certifications, perform independent product testing, and consult legal experts to verify IP compliance. Using third-party inspection services and clear contractual agreements can further protect your business.
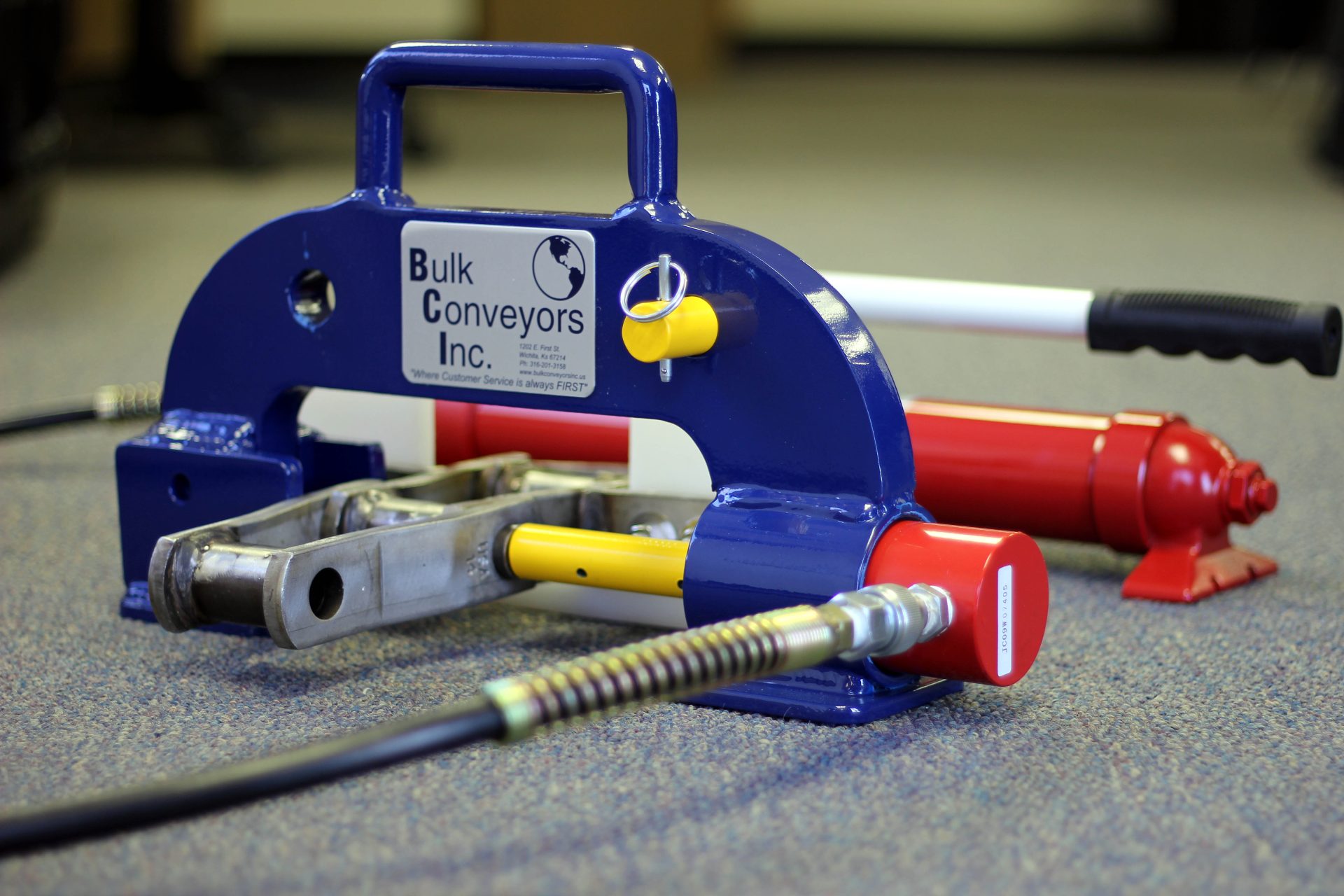

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Chain Breaker Tool
Product Classification & Regulatory Compliance
Chain breaker tools are typically categorized as hand tools used in mechanical maintenance, especially for bicycles and industrial equipment. Depending on the design and materials, they may fall under HS Code 8205.40 (hand tools n.e.c.) for international trade. Ensure compliance with relevant safety standards such as ISO 539:1985 (for bicycle chain tools) or applicable regional standards (e.g., CE marking in the EU, ANSI/ASME standards in the U.S.). Confirm that manufacturing adheres to quality control protocols and that materials used meet RoHS or REACH requirements, particularly if exporting to Europe.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Package chain breaker tools in durable, protective materials to prevent damage during transit. Use standard retail blister packs or bulk industrial packaging depending on distribution channels. Labels must include:
– Product name and model number
– Manufacturer or brand information
– Country of origin
– Safety warnings (e.g., eye protection recommended)
– Compliance marks (e.g., CE, UKCA)
– Barcode for inventory tracking
Ensure multilingual labeling if shipping internationally, particularly in regions like the EU, Canada, or Japan.
Shipping & Transportation
Chain breaker tools are non-hazardous and can be shipped via standard ground, air, or sea freight. Use appropriate packaging to meet carrier requirements (e.g., UPS, FedEx, DHL) and prevent shifting in transit. For bulk shipments, palletize securely and wrap with stretch film. Include proper shipping documentation such as:
– Commercial invoice
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or air waybill
– Certificate of origin (if required for customs duty reduction)
Mark packages with orientation arrows and “Fragile” tags as needed.
Import/Export Documentation
For international shipments, prepare the following:
– Harmonized System (HS) code (typically 8205.40.30 or similar)
– Export declaration (e.g., AES filing in the U.S.)
– Import permits, if required by destination country
– Customs valuation documentation
Verify tariff rates and potential trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU–Canada CETA) that may reduce duties.
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Store chain breaker tools in dry, secure warehouse environments to prevent corrosion or damage. Use barcode or RFID systems for inventory tracking. Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) practices to manage stock rotation, especially for models with multiple versions. Maintain safety stock levels based on demand forecasts and lead times.
Returns & Warranty Handling
Establish a clear return policy for defective or incorrect items. Warranty periods typically range from 6 months to 1 year, covering manufacturing defects. Provide return authorization (RMA) numbers and pre-labeled return packaging when applicable. Inspect returned items for compliance with warranty terms before processing refunds or replacements.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
Ensure production waste is managed in accordance with local environmental regulations. If the tool contains metal components or coatings, comply with WEEE directives (in Europe) for end-of-life product handling. Provide end-user guidance on proper disposal or recycling through authorized channels.
Training & Documentation for Distributors
Supply distributors with product specification sheets, user manuals, safety guidelines, and compliance certificates. Offer training on proper usage and troubleshooting. Maintain up-to-date technical documentation to support customer service and regulatory audits.
Audit & Recordkeeping
Maintain records of compliance certifications, shipment logs, quality control checks, and customer complaints for a minimum of 5 years (or as required by jurisdiction). Conduct periodic internal audits to ensure adherence to logistics and compliance protocols.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Chain Breaker Tool:
Sourcing the right chain breaker tool is essential for ensuring efficiency, durability, and precision in bicycle maintenance, motorcycle repair, or industrial applications. After evaluating key factors such as compatibility with chain types (e.g., single-speed, multi-speed, or narrow-wide chains), build quality, ease of use, and user reviews, it becomes clear that selecting a reliable and well-constructed tool significantly impacts long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. Opting for reputable brands or suppliers that offer durability, ergonomic design, and compatibility with current and future chain standards ensures a worthwhile investment. Additionally, considering tools with additional features—such as integrated rivet storage or combination functionality—can enhance convenience and value. Ultimately, sourcing a high-quality chain breaker tool not only improves maintenance accuracy but also saves time and reduces the risk of component damage, making it a critical addition to any professional or enthusiast’s toolkit.