The global cervical dilator balloon market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising cesarean delivery rates, increasing maternal health complications, and advancements in obstetric medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global obstetric devices market—of which cervical dilator balloons are a key component—was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence reports that the increasing prevalence of preterm labor and the growing emphasis on minimizing surgical intervention during labor induction are accelerating demand for non-invasive cervical ripening methods, including balloon catheters. As healthcare providers prioritize patient safety and procedural efficacy, cervical dilator balloons have become a preferred mechanical method for cervical dilation, particularly in settings where pharmacological induction carries higher risks. This data-backed market momentum underscores the importance of reliable, innovative manufacturers in meeting clinical demands. Below are the top four cervical dilator balloon manufacturers shaping the landscape through product innovation, regulatory compliance, and global reach.
Top 4 Cervical Dilator Balloon Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Resources
Domain Est. 2003
Website: cookmedical.com
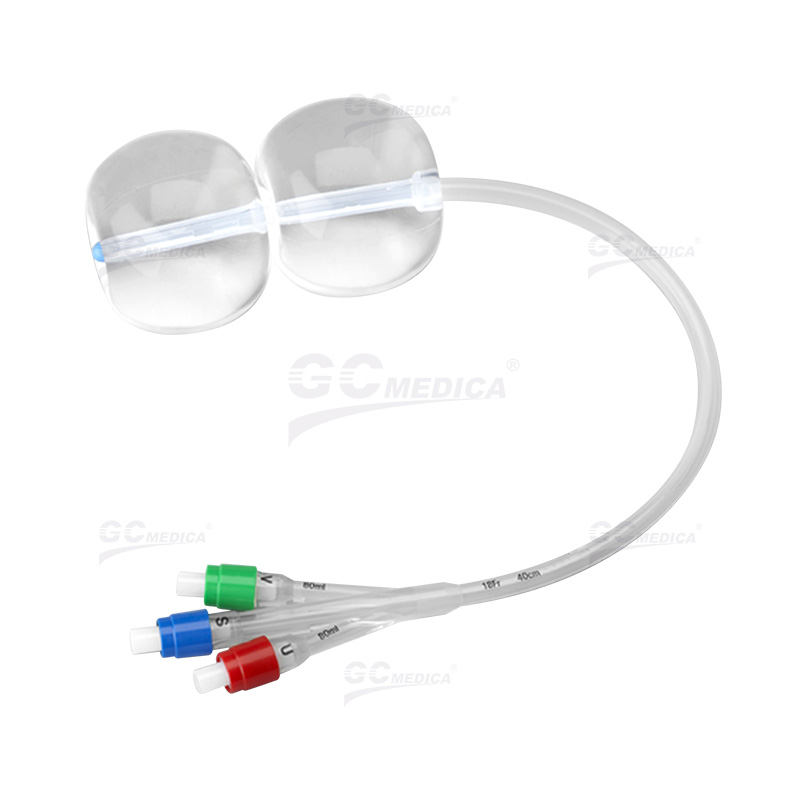
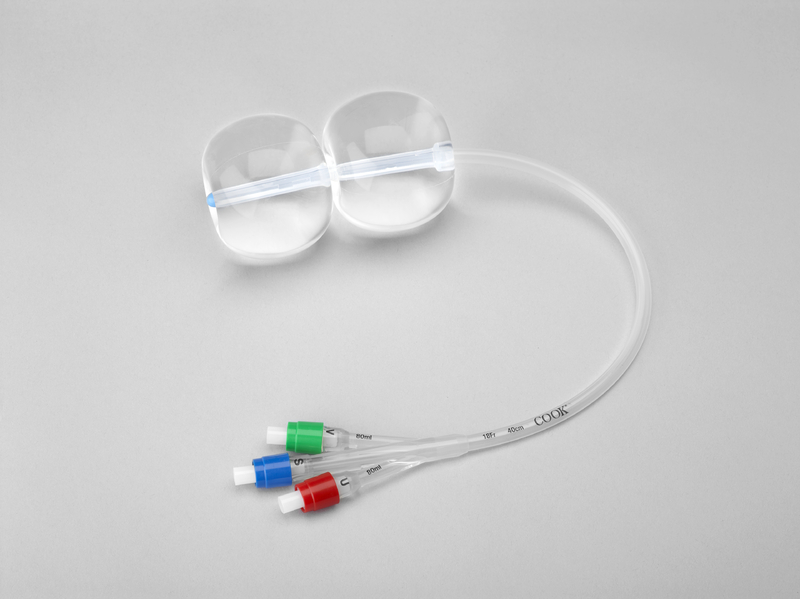
Key Highlights: The Cook® Cervical Ripening Balloon with Stylet (CRBS) is used for mechanical dilation of the cervical canal prior to labor induction….
#2 Gynedil
Domain Est. 2009
Website: gynedil.com
Key Highlights: Its flexible balloon dilator allows penetration in the cervical canal with minimal resistance and adaptation to curvature of the patient’s anatomy. This ……
#3 Dilapan-S®
Domain Est. 2020
Website: dilapans.com
Key Highlights: Dilapan-S is an FDA-cleared, mechanical cervical dilator designed for gentle and predictable cervical ripening in the induction of labor….
#4 Cook® Cervical Ripening Balloon with Stylet
Website: cookmedical.eu
Key Highlights: Used for mechanical dilation of the cervical canal prior to labour induction at term when the cervix is unfavourable for induction….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cervical Dilator Balloon

H2: Market Trends for Cervical Dilator Balloons in 2026
The global cervical dilator balloon market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in medical technology, increasing emphasis on minimally invasive gynecological procedures, and growing maternal healthcare awareness. This analysis outlines key trends shaping the market landscape in 2026.
-
Rising Demand for Labor Induction and Cervical Ripening
With increasing rates of medically indicated labor inductions due to conditions such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and post-term pregnancies, cervical dilator balloons are becoming a preferred mechanical method for cervical ripening. Their non-pharmacological nature offers a safer alternative to prostaglandins, especially in women with contraindications to hormonal induction. This trend is bolstered by clinical guidelines from obstetric organizations advocating mechanical methods as first-line options, fueling adoption in both developed and emerging markets. -
Technological Innovation and Product Differentiation
Manufacturers are focusing on enhancing device design to improve efficacy, comfort, and ease of use. Key innovations include dual-balloon systems with optimized inflation mechanisms, radiopaque markers for better visualization, and materials that reduce tissue trauma. Additionally, smart balloons integrated with pressure sensors and telemetry systems are entering clinical trials, aiming to provide real-time feedback on cervical dilation progress—potentially improving outcomes and reducing intervention time. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing rapid growth in maternal healthcare infrastructure and obstetric service accessibility. Government initiatives to reduce maternal mortality and improve birth outcomes are increasing the adoption of evidence-based tools like cervical dilator balloons. Local manufacturing partnerships and cost-effective product variants are enabling wider penetration in public health systems, contributing to market expansion. -
Regulatory and Reimbursement Support
In North America and Europe, favorable reimbursement policies for labor induction procedures and streamlined regulatory pathways for obstetric devices are supporting market growth. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are placing greater emphasis on device safety and clinical efficacy, prompting manufacturers to invest in robust clinical trials and post-market surveillance—ultimately enhancing trust and uptake. -
Shift Toward Outpatient and Ambulatory Care Settings
A growing trend in 2026 is the use of cervical dilator balloons in outpatient settings for pre-induction cervical ripening. This shift reduces hospital stay duration, lowers healthcare costs, and improves patient satisfaction. Devices designed for secure placement and patient mobility are gaining traction, supported by telehealth monitoring solutions that allow clinicians to remotely assess progress. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Collaborations
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with key players such as CooperSurgical, BD (Becton, Dickinson), and MedGyn leading through product innovation and geographic expansion. Strategic collaborations with hospitals, academic institutions, and digital health companies are accelerating R&D and enabling data-driven improvements in device performance.
In summary, the cervical dilator balloon market in 2026 reflects a convergence of clinical best practices, technological advancement, and healthcare system evolution. As maternal care continues to prioritize safety, efficiency, and patient-centered approaches, cervical dilator balloons are expected to maintain a central role in labor management strategies worldwide.
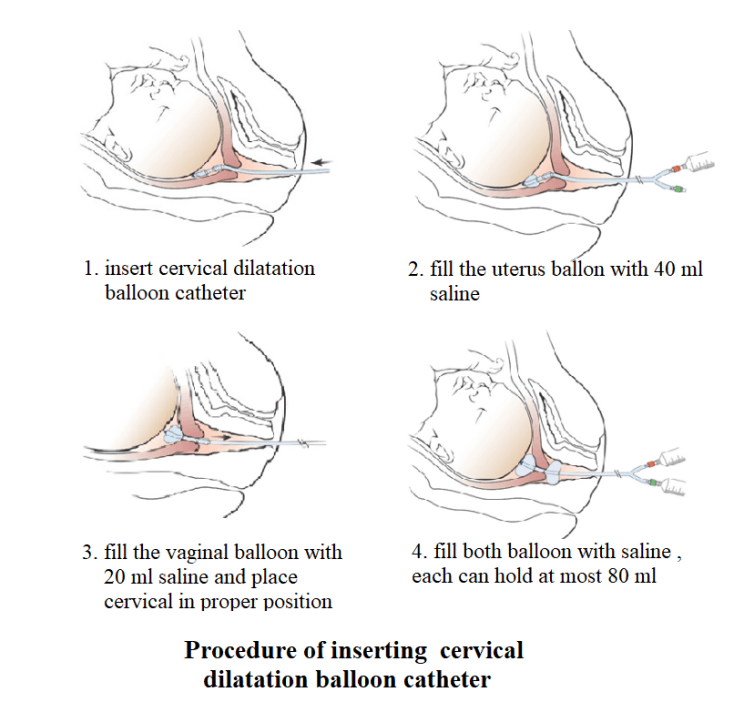
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cervical Dilator Balloons (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing cervical dilator balloons, especially from overseas manufacturers, involves navigating significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these risks can lead to regulatory non-compliance, patient safety concerns, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Not all manufacturers adhere to stringent quality management systems such as ISO 13485 or comply with FDA QSR (Quality System Regulation). Sourcing from facilities without proper certifications increases the risk of inconsistent product quality, material defects, or non-sterile packaging—potentially leading to clinical complications.
Use of Substandard Materials
Low-cost suppliers may use inferior-grade silicone or latex materials that lack biocompatibility or mechanical reliability. This can result in balloon rupture during use, allergic reactions, or inadequate dilation performance, jeopardizing patient outcomes.
Inadequate Sterilization and Packaging Controls
Improper sterilization (e.g., incorrect EO or gamma radiation doses) or compromised packaging integrity can introduce contamination risks. Suppliers without validated sterilization processes or environmental monitoring may deliver non-sterile devices, violating regulatory requirements.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor batch traceability and incomplete device history records (DHR) make it difficult to investigate field failures or conduct effective recalls. Suppliers that do not maintain detailed manufacturing logs or certificates of conformance (CoC) introduce significant compliance and liability risks.
Insufficient Regulatory Compliance
Some manufacturers may claim regulatory approval without providing verifiable evidence. Always confirm that the device is listed with the FDA (if intended for the U.S. market), holds CE marking under MDR (for EU), or meets other relevant local regulatory requirements. Beware of falsified documentation.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Designs or Technologies
Many cervical dilator balloons incorporate proprietary features such as dual-balloon configurations, specialized inflation mechanisms, or unique catheter materials. Sourcing from manufacturers producing devices that mimic patented designs—even unintentionally—can expose your company to infringement lawsuits and costly litigation.
Lack of Clear IP Ownership in Contracts
Failing to define IP ownership in supplier agreements can result in disputes over tooling, design modifications, or custom developments. Without explicit clauses, the manufacturer may claim rights to improvements or reuse designs for other clients, undermining your competitive advantage.
Counterfeit or Copycat Products
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “equivalent” versions of branded devices, which may be exact replicas infringing on existing IP. These products often lack proper testing and regulatory validation, increasing legal and clinical risks.
Weak Enforcement in Sourcing Regions
In certain jurisdictions, IP enforcement is limited or inconsistent. Even if your IP is protected in your home market, manufacturing in regions with weak IP oversight increases the risk of unauthorized production, reverse engineering, or leakage of sensitive design information.
Failure to Conduct IP Due Diligence
Skipping freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses or patent landscaping before finalizing a supplier can result in unknowingly adopting infringing technologies. Proactively vetting product designs against existing patents is essential to mitigate legal exposure.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Audit suppliers on-site to assess quality systems and manufacturing conditions.
- Require full regulatory documentation and verify claims independently.
- Conduct material biocompatibility testing (e.g., ISO 10993).
- Include robust IP clauses in contracts, specifying ownership and confidentiality.
- Perform FTO searches and work with IP counsel before finalizing designs.
- Use trusted legal and regulatory consultants in target markets.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure safer, compliant, and legally sound sourcing of cervical dilator balloons.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cervical Dilator Balloon
This guide outlines the critical logistics and regulatory compliance considerations for the distribution, storage, and use of Cervical Dilator Balloon devices. These medical devices are subject to stringent regulations due to their direct impact on patient safety in obstetric and gynecological procedures.
Regulatory Classification and Approval
Cervical Dilator Balloons are classified as medical devices and are typically regulated as Class II devices by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under 21 CFR 884.5310. They require 510(k) premarket notification to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device. In the European Union, they fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745 and generally require conformity assessment under Class IIb. Manufacturers must maintain technical documentation, obtain CE marking, and appoint an Authorized Representative within the EU if based outside the region. Compliance with ISO 13485 (quality management systems) and ISO 14971 (risk management) is essential for global market access.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
All packaging and labeling must comply with FDA’s Unique Device Identification (UDI) requirements, including a UDI on the label and in submissions to the Global Unique Device Identification Database (GUDID). Labels must include the device name, manufacturer details, lot number, expiration date, sterile indication, single-use statement, and any specific handling instructions. In the EU, labeling must also include the CE mark, UDI, Authorized Representative information, and comply with MDR Annex I general safety and performance requirements. Packaging must ensure sterility is maintained during shipping and storage, using validated sterile barrier systems (e.g., peelable pouches or rigid trays).
Storage and Handling Conditions
Cervical Dilator Balloons must be stored in a clean, dry environment at controlled room temperature (typically 15°C to 30°C / 59°F to 86°F) unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer. Devices should be protected from direct sunlight, moisture, and physical damage. Storage areas must be monitored and documented for temperature and humidity to ensure compliance with shelf-life specifications. Devices should be stored off the floor and rotated using a first-expired, first-out (FEFO) inventory system to prevent use of expired products.
Transportation and Distribution
Transportation must maintain product integrity and sterility throughout the supply chain. Shipments should use validated packaging methods suitable for ambient or controlled conditions, depending on device specifications. Temperature excursions during transit must be monitored using data loggers when required. Carriers must be qualified and compliant with Good Distribution Practices (GDP) for medical devices. International shipments require adherence to customs regulations, import licenses, and proper documentation such as Certificates of Free Sale, Certificates of Conformity, and import permits where necessary.
Import and Export Compliance
Export of Cervical Dilator Balloons from the United States requires compliance with FDA export regulations (21 CFR Part 801 and 807), including submission of Form FDA 2877 for devices not approved in the U.S. Import into foreign countries may require local regulatory approvals, registration with national health authorities (e.g., Health Canada, TGA in Australia, NMPA in China), and adherence to local language labeling requirements. Exporters must ensure compliance with international trade controls, including ITAR and EAR, although most cervical dilator balloons are not subject to these.
Post-Market Surveillance and Adverse Event Reporting
Manufacturers and distributors are responsible for maintaining a post-market surveillance system to monitor device performance and patient safety. Any adverse events, product defects, or malfunctions must be reported per FDA’s Medical Device Reporting (MDR) regulation (21 CFR Part 803) and EU MDR’s incident reporting requirements (Articles 87–89). Field safety corrective actions (FSCAs), including recalls, must be initiated promptly and reported to relevant authorities. Complaint handling procedures must be documented and auditable.
Training and Healthcare Provider Support
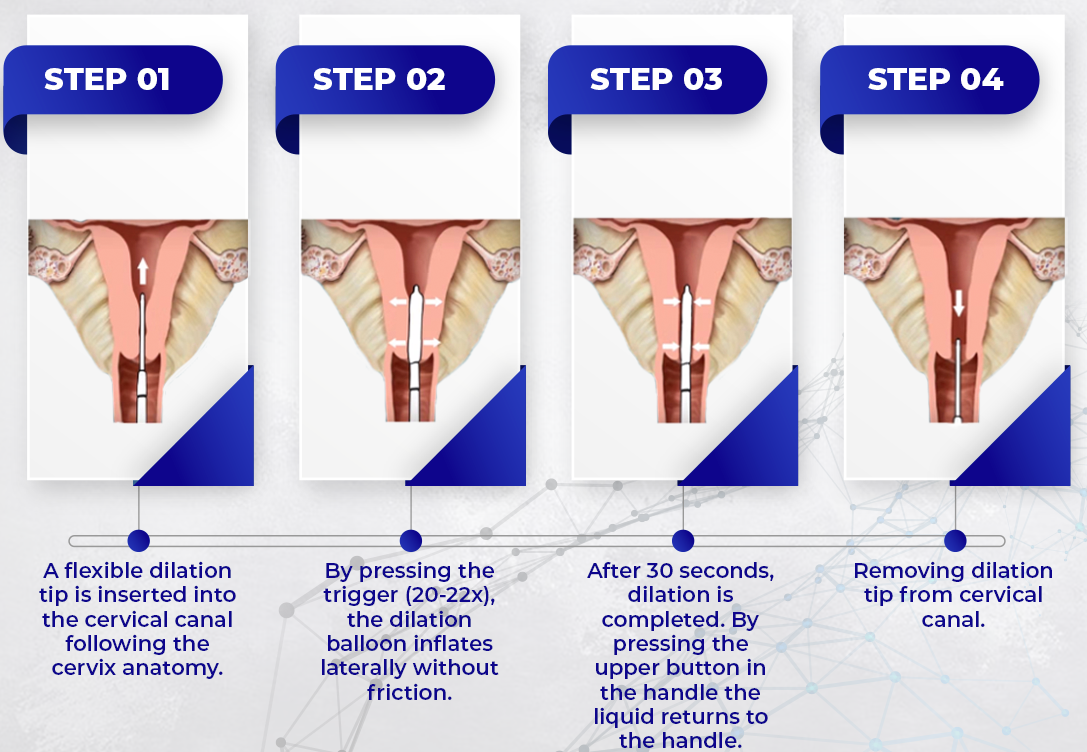
End-users (e.g., obstetricians, midwives) must receive appropriate training on the correct insertion, inflation, monitoring, and removal of the cervical dilator balloon. Manufacturers should provide comprehensive instructions for use (IFU), including contraindications, warnings, and precautions. Training materials should be available in local languages for international markets. Technical support must be accessible to address clinical or logistical queries.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Cervical Dilator Balloons are single-use devices and must be disposed of as medical waste in accordance with local biohazard and environmental regulations. Facilities should follow protocols for segregation, containment, and treatment (e.g., autoclaving or incineration) of contaminated devices. Manufacturers should provide disposal guidance in IFUs and ensure packaging materials comply with environmental directives such as the EU’s Directive 94/62/EC on packaging waste.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cervical Dilator Balloons
In conclusion, sourcing cervical dilator balloons requires a comprehensive approach that balances clinical efficacy, patient safety, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness. These devices play a critical role in cervical ripening and labor induction, offering a minimally invasive alternative to pharmacological methods. When selecting a supplier, healthcare facilities must prioritize products that meet stringent quality standards, such as CE marking, FDA approval, or other relevant regulatory certifications, to ensure safety and reliability.
Key considerations include the design and material of the balloon (e.g., single vs. double balloon, silicone composition), ease of insertion and monitoring, and compatibility with standard clinical protocols. Establishing relationships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who provide consistent product quality, technical support, and training is essential. Additionally, bulk purchasing agreements, supply chain reliability, and responsiveness to demand fluctuations should be evaluated to avoid clinical disruptions.
Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy for cervical dilator balloons not only supports improved maternal outcomes but also enhances operational efficiency within obstetric departments. Continuous evaluation of new technologies and feedback from clinical teams will further ensure that sourcing decisions remain aligned with best practices and evolving healthcare needs.