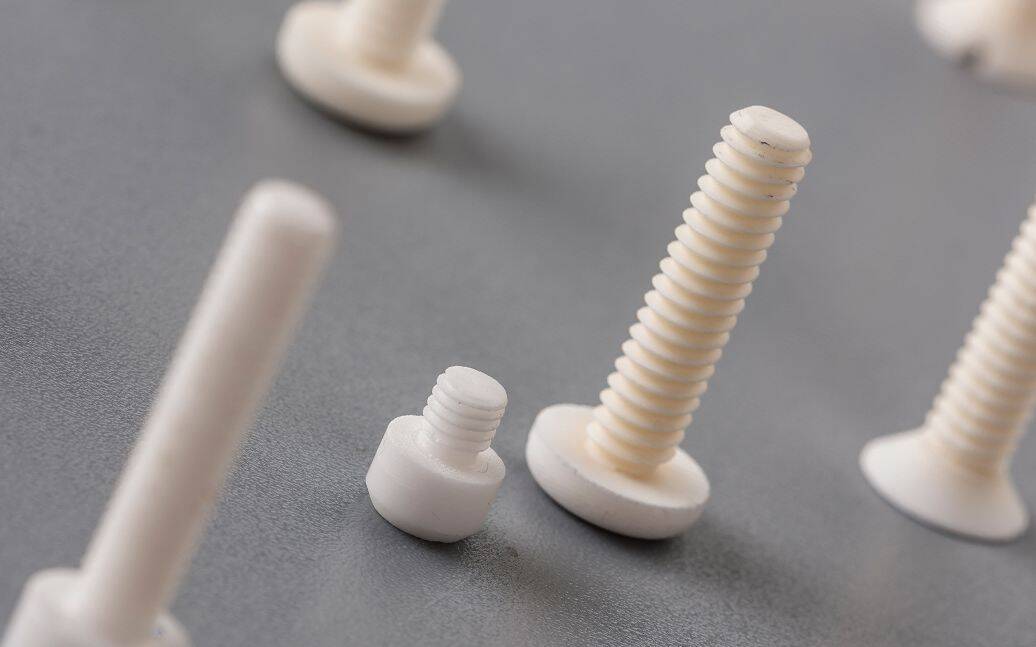
The global ceramic screws market is gaining momentum as industries increasingly prioritize high-performance, corrosion-resistant, and electrically insulating fasteners. According to Mordor Intelligence, the ceramic components market—which includes ceramic screws—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.2% from 2023 to 2028, driven by rising demand in aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, medical devices, and automotive sectors. Ceramic screws, made from advanced materials like zirconia and alumina, offer superior thermal stability and non-magnetic properties, making them ideal for extreme environments where traditional metal fasteners fail. Grand View Research further supports this trend, noting that innovations in material science and expanding applications in clean energy technologies are accelerating adoption across high-tech industries. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in precision engineering and scalable production of ceramic screws—setting new standards for quality and reliability in the advanced materials space.
Top 9 Ceramic Screws Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
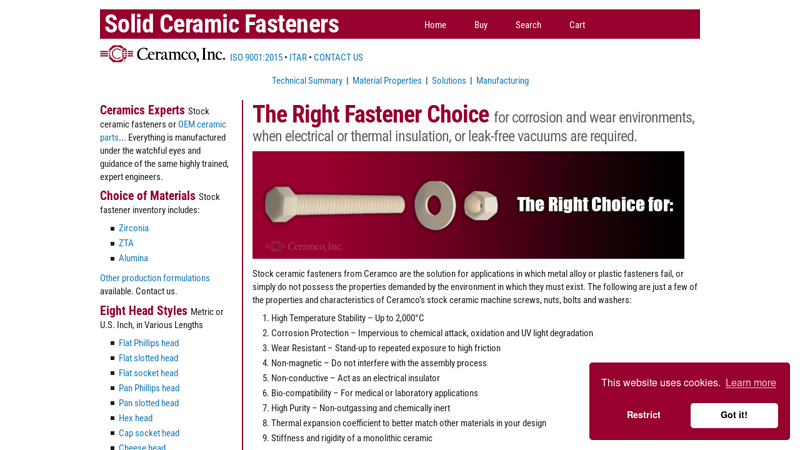
#1 Stock Ceramic Fasteners
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ceramcoceramics.com
Key Highlights: Stock ceramic fasteners from Ceramco are the solution for applications in which metal alloy or plastic fasteners fail….
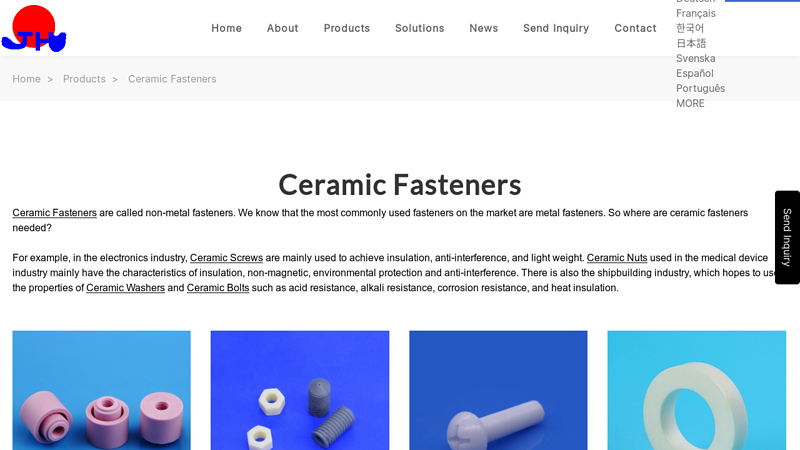
#2 Ceramic Screws – Fasteners
Website: usa.kida.co.jp
Key Highlights: We are manufactures of a great variety of standard ceramic machine screws. There are nearly 1000 items with (1) 6 head types and every length, (2) 2 types of ……
#3 Kimura Tec Inc.|Ceramic Screws
Website: kimuratec.co.jp
Key Highlights: We provide a wide variety including ceramic metric threads, unified threads, free sized threads, etc. Free options are available for the head shape….
#4 Alumina and Zirconia Hex Head Screws
Domain Est. 1998
Website: intlceramics.com
Key Highlights: International Ceramic Engineering manufactures 99.8% Alumina and Zirconia Hex Head Screws. Call Us: 800-779-3321…
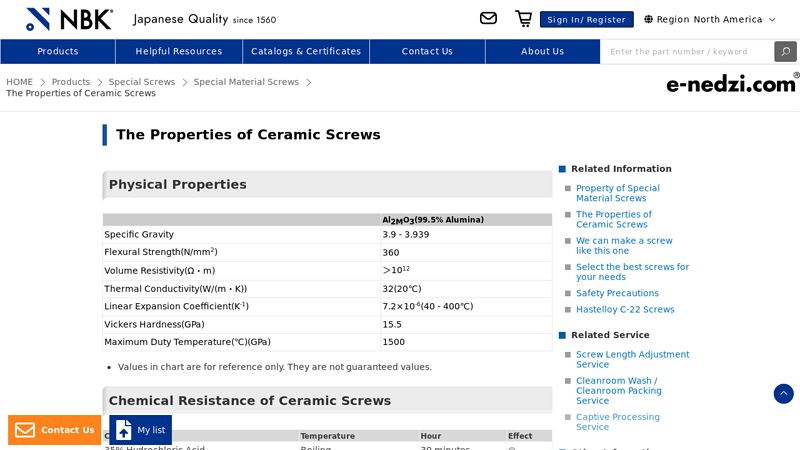
#5 The Properties of Ceramic Screws
Domain Est. 2000
Website: nbk1560.com
Key Highlights: This page describes the properties of ceramic screws. It contains tables listing numerical value tables of physical properties and chemical resistance, ……
#6 Alumina Screws
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ortechceramics.com
Key Highlights: In stock $12 deliveryOrtech supplies ceramic screws, In stock we have Alumina and Zirconia ceramic screws which have matching ceramic washers and ceramic nuts….
#7 Extreme Bolt
Domain Est. 2012
Website: extreme-bolt.com
Key Highlights: We focus solely on ENGINEERED POLYMER, ADVANCED CERAMIC and SPECIALTY METAL fasteners for the most challenging applications….
#8 ceramicfasteners.com
Domain Est. 2014
#9 Technical Solid Ceramic Fasteners in Alumina and Zirconia
Domain Est. 2017
Website: ceramictek.com
Key Highlights: Technical Ceramic Fasteners exhibit versatile advantages,including super wear resistance, corrosion resistance,electrical or thermal insulation….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ceramic Screws

H2: Projected Market Trends for Ceramic Screws in 2026
The global ceramic screws market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in material science, rising demand from high-performance industries, and the growing need for corrosion- and heat-resistant fastening solutions. As industries increasingly prioritize durability, electrical insulation, and lightweight components, ceramic screws—made primarily from materials such as zirconia, alumina, and silicon nitride—are gaining traction across aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and industrial automation sectors.
Rising Demand in High-Tech Industries
By 2026, the aerospace and defense sector is expected to be a major growth driver for ceramic screws. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist oxidation makes them ideal for use in jet engines, satellite systems, and hypersonic vehicles. Additionally, their non-magnetic and non-conductive properties support applications in sensitive electronic environments, where metal fasteners could cause interference.
In the medical technology field, biocompatible ceramic screws—especially those composed of zirconia—are anticipated to see increased adoption in orthopedic and dental implants. As global healthcare systems focus on long-term implant durability and reduced revision surgeries, ceramic fasteners offer a compelling alternative to traditional titanium or stainless steel screws.
Technological Advancements and Manufacturing Innovations
Ongoing improvements in precision manufacturing, including additive manufacturing (3D printing) of ceramics and advanced sintering techniques, are expected to reduce production costs and expand design flexibility by 2026. These innovations will enable complex screw geometries and tighter tolerances, making ceramic screws viable for miniaturized electronics and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Furthermore, hybrid ceramic-metal fastening systems are emerging, combining the best properties of both materials. These hybrid solutions may dominate niche markets where mechanical strength and thermal resilience are both critical.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to lead the ceramic screws market by 2026, fueled by robust growth in electronics manufacturing (particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea) and increasing investments in advanced medical devices. North America and Europe will follow, supported by strong aerospace R&D, stringent regulatory standards for implantable devices, and a focus on sustainable materials.
Sustainability and Regulatory Factors
Environmental regulations favoring non-toxic, recyclable, and long-lasting materials will further boost the appeal of ceramic screws. Unlike metal fasteners, ceramics do not corrode or leach harmful ions, reducing lifecycle environmental impact. Regulatory bodies are also showing increased interest in non-metallic implant materials, which may accelerate approval pathways for ceramic-based medical fasteners.
Challenges and Outlook
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain. Ceramic screws are inherently brittle compared to metals, limiting their use in high-tensile applications. Additionally, high production costs and limited standardization may hinder widespread adoption. However, with continued investment in material engineering and industrial partnerships, these barriers are expected to diminish by 2026.
In conclusion, the ceramic screws market in 2026 will be shaped by technological innovation, expanding applications in critical industries, and a growing emphasis on performance and sustainability. Companies that invest in R&D and strategic market positioning are likely to capture significant value in this evolving niche.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ceramic Screws: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing ceramic screws presents unique challenges compared to standard metal fasteners. Buyers must be vigilant about both quality inconsistencies and potential intellectual property (IP) issues to avoid costly failures, safety hazards, and legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Ceramic materials, while offering advantages like high-temperature resistance, electrical insulation, and corrosion resistance, are inherently brittle and sensitive to processing variables. Poor quality control during manufacturing can lead to critical failures.
Inconsistent Material Composition and Purity
One of the most common quality pitfalls is variability in the base ceramic material—typically alumina (Al₂O₃), zirconia (ZrO₂), or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄). Suppliers may use lower-grade powders or inconsistent sintering processes, resulting in reduced mechanical strength, poor thermal shock resistance, or compromised electrical insulation. Without proper certification (e.g., ISO 9001, material test reports), buyers risk receiving screws with inadequate performance characteristics.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish
Ceramic screws require precise machining and grinding post-sintering, which is costly and technically demanding. Low-cost suppliers may skip or shortcut these steps, leading to out-of-tolerance thread dimensions, uneven surfaces, or micro-cracks. Such defects can cause thread stripping during installation or premature failure under load.
Lack of Reliability Testing and Traceability
Reputable suppliers conduct rigorous batch testing for fracture toughness, tensile strength, and dielectric properties. However, many suppliers—especially in less regulated regions—offer minimal or falsified test data. Without traceability to raw materials and production batches, identifying the root cause of a failure becomes nearly impossible.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Ceramic fastener designs, especially those engineered for specialized applications (e.g., aerospace, medical devices), often involve patented technologies. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers can expose buyers to significant IP infringement risks.
Unauthorized Replication of Patented Designs
Some suppliers may reverse-engineer high-performance ceramic screws protected by patents and offer “compatible” versions at lower prices. While these may appear identical, using them can result in legal action from the patent holder. Buyers may face injunctions, fines, or be forced to recall end products.
Lack of Design Freedom and Certification
Using generic or copied screws without proper design validation can void certifications (e.g., UL, CE, AS9100) for the end product. If the ceramic screw design is integral to a certified assembly, substituting it with a non-licensed equivalent—even if functionally similar—can invalidate compliance and expose the OEM to liability.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Many suppliers outsource production or source components from third parties without disclosing the origin. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to verify whether the screws are manufactured under license or whether the supplier has the right to sell the design. Conducting supplier audits and requesting IP indemnification clauses in contracts is essential.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Specify material grades and performance standards clearly in procurement documents.
– Require third-party test reports and material certifications.
– Vet suppliers through on-site audits and request design IP documentation.
– Include contractual clauses for IP indemnification and quality warranties.
– Work with established manufacturers or authorized distributors whenever possible.
Ignoring these quality and IP considerations can lead to product failures, regulatory non-compliance, and costly litigation—outweighing any initial cost savings from low-priced suppliers.
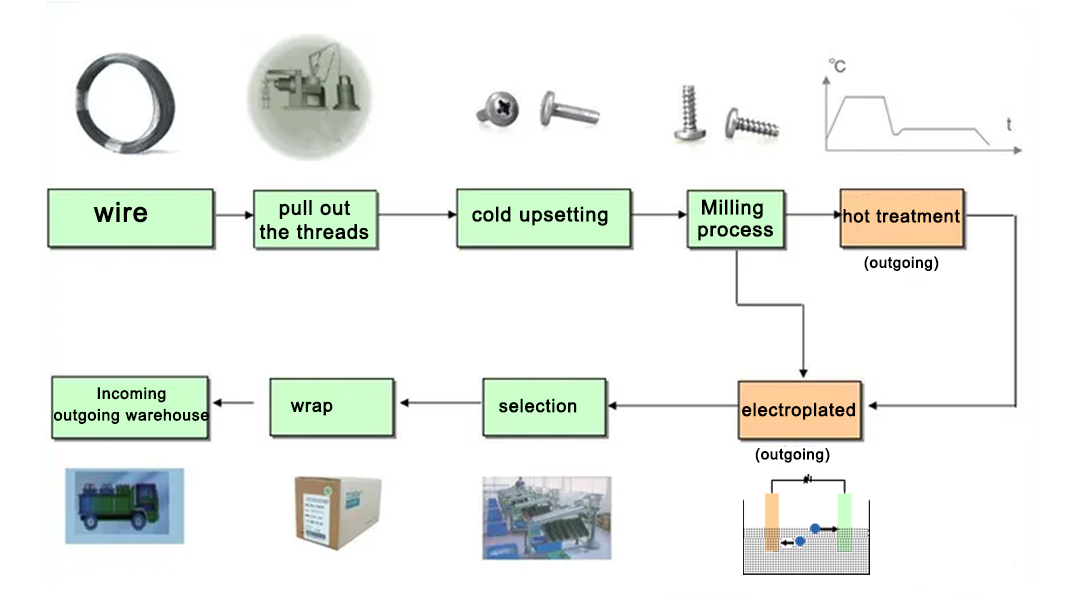
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ceramic Screws
Overview
Ceramic screws, typically made from materials such as zirconia (zirconium dioxide) or alumina (aluminum oxide), are used in high-performance applications requiring electrical insulation, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. Due to their specialized nature and material composition, shipping and handling require careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance.
Material Classification & HS Code
Ceramic screws are generally classified under the following Harmonized System (HS) code:
HS Code: 8481.80 – Other taps, cocks, valves, and similar appliances for pipes, boiler shells, tanks, vats, or the like, including fittings (e.g., joints, elbows, flanges), of ceramics.
Note: Confirm with local customs authorities; some jurisdictions may classify ceramic fasteners under 6909.19 (Ceramic goods for technical uses).
Packaging & Handling
- Fragility: Ceramic screws are brittle. Use anti-static, shock-absorbent packaging (e.g., foam inserts, bubble wrap) to prevent breakage.
- Moisture Protection: Include desiccants in sealed packaging to prevent moisture damage during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “Handle with Care.” Include product name, material type, quantity, lot number, and manufacturer details.
- Static Control: Use anti-static bags or containers, especially for applications in electronics or cleanroom environments.
Shipping & Transportation
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, or ground freight. Air freight is recommended for time-sensitive or high-value shipments.
- Temperature & Humidity: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or high humidity during storage and transit. Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and material safety data sheet (MSDS) where applicable.
Regulatory & Compliance Requirements
- REACH & RoHS Compliance (EU): Confirm that ceramic screws are free from restricted substances. While inherently compliant due to material composition, verify with supplier documentation.
- FDA & USP (USA): Required only if used in medical or pharmaceutical applications. Ensure compliance with 21 CFR for biocompatibility if applicable.
- Customs Documentation: Provide accurate product descriptions, value declaration, and end-use information to avoid delays.
- Export Controls: Ceramic components may be subject to export regulations if used in aerospace, defense, or semiconductor industries. Check EAR (Export Administration Regulations) for potential licensing requirements.
Import Considerations
- Tariffs & Duties: Vary by country. Verify duty rates under the appropriate HS code in the destination country.
- Import Restrictions: Some countries may require conformity assessments or certifications for industrial components.
- Local Standards: Ensure compliance with regional standards (e.g., DIN in Germany, JIS in Japan) if specified by the customer.
Storage & Shelf Life
- Storage Conditions: Store in a clean, dry environment at room temperature (15–25°C), away from direct sunlight and corrosive chemicals.
- Shelf Life: Ceramic screws have an indefinite shelf life if protected from physical damage and contamination.
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Non-Toxic: Ceramic screws are generally inert and non-toxic. However, fine dust from machining may require respiratory protection (use MSDS as a guide).
- Disposal: Dispose of damaged or excess parts according to local waste regulations. Ceramic waste is typically non-hazardous.
Supplier & Quality Assurance
- Certifications: Require ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) from suppliers.
- Traceability: Maintain lot traceability for quality control and compliance audits.
- Testing Reports: Request material composition, mechanical strength, and electrical resistance test reports as needed.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance for ceramic screws involve attention to packaging, accurate classification, adherence to international regulations, and coordination with customs authorities. Always verify requirements with local agencies and maintain detailed documentation to ensure smooth global distribution.
In conclusion, sourcing ceramic screws requires careful evaluation of material properties, supplier reliability, application requirements, and cost considerations. Due to their exceptional electrical insulation, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and non-magnetic characteristics, ceramic screws are ideal for specialized applications in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and high-temperature engineering. However, their brittleness and higher cost compared to metallic fasteners necessitate a strategic sourcing approach.
Key success factors include identifying reputable suppliers with proven expertise in advanced ceramics, verifying material certifications and quality control processes, and ensuring precise dimensional tolerances and performance consistency. Engaging in early collaboration with suppliers can aid in customizing solutions and optimizing lead times. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—factoring in longevity, maintenance, and performance benefits—can justify the initial investment.
Ultimately, effective sourcing of ceramic screws hinges on balancing technical requirements with supply chain reliability, ensuring that the selected components meet both performance standards and project timelines. With due diligence and a focus on quality, ceramic screws can deliver superior performance in demanding environments where traditional fasteners fall short.