The global ceramic mold manufacturing industry is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the ceramic molds market was valued at USD 11.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by the increasing adoption of advanced ceramics in high-temperature and high-wear applications, where precision and durability are critical. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that innovations in additive manufacturing and near-net-shape molding technologies are further accelerating market development, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific, where industrial production and R&D investments are on the rise. As demand for high-performance, complex-geometry components grows, so does the need for reliable ceramic mold manufacturers capable of delivering consistency and technical excellence. In this evolving landscape, the following eight companies have emerged as leaders, combining scale, innovation, and a strong track record in ceramic mold production.
Top 8 Ceramic Mold Companies Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Shinko Ceramics Co., Ltd. Ceramic mold maker for rubber gloves
Domain Est. 2000
Website: shinko-cera.com
Key Highlights: We handle approximately 2,500 types of ceramic glove formers. All our products are made to order to meet the needs of our customers. Our ……
#2 Starlite Molds Price Lists
Domain Est. 2000
Website: evansceramics.com
Key Highlights: We are the largest manufacturer of molds for the fired arts industry. We produce the finest quality molds using USG #1 grade pottery plaster….
#3 Petro Mold Company
Domain Est. 2001
Website: petromolds.com
Key Highlights: Custom Ceramic Mold Design. Creating the finest quality molds for ceramics, pottery, public sculpture, bronze, industrial refractories, and much more….
#4 Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: glaserceramics.com
Key Highlights: Glaser Ceramics is a proud distributor for the following mold lines. Refine Search. Alberta · Arnel’s · Atlantic · Boothe · Byron Molds · Ceramic Emporium….
#5 Clay Magic
Domain Est. 1998
Website: claymagicinc.com
Key Highlights: Home · New Releases · Search for Molds · Mold Order Cart · Order Clay Magic Molds · Order TL Designs Molds · Order Mayco Molds; Catalogs; Clay Magic Molds ……
#6 Holland Mold
Domain Est. 2000
Website: hollandmolds.com
Key Highlights: Holland Molds manufactures quality ceramic molds including: Gare Molds, Kentucky Molds, Norwood Molds, Ocean State Molds, Reward Molds and Custom Designs….
#7 Mudshark Studios
Domain Est. 2010
Website: mudsharkstudios.com
Key Highlights: Whether you’re looking for custom molds or ceramic production services, our dedicated and experienced team is ready for action. … Website: BlueCollar Studio….
#8 Gare
Domain Est. 2019
Website: gareceramics.com
Key Highlights: Gare Ceramics designs and manufactures ceramic bisque, glazes, fired color, pottery glazes, and acrylic paints for the Paint Your Own Pottery and DIY ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ceramic Mold Companies
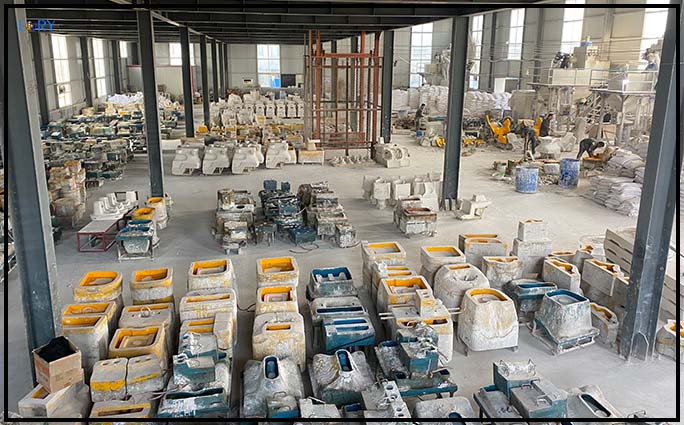

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ceramic Mold Companies
The global ceramic mold industry is poised for transformative growth and innovation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials science, expanding industrial applications, and rising demand in high-tech sectors. Below are key market trends shaping the future of ceramic mold companies:
-
Increased Demand from Advanced Manufacturing Sectors
By 2026, industries such as aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, and electric vehicles (EVs) are expected to significantly boost demand for precision ceramic molds. These sectors require molds with high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional accuracy—qualities inherent in advanced ceramics like zirconia and alumina. Investment in additive manufacturing (3D printing) of ceramic molds is accelerating to meet these complex specifications. -
Growth in Additive Manufacturing and Digital Design Integration
Ceramic mold companies are increasingly adopting 3D printing technologies to produce intricate mold geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. The integration of AI-driven design software and digital twin technologies enables faster prototyping, improved mold performance, and reduced time-to-market. By 2026, over 35% of high-end ceramic mold production is expected to involve some form of additive manufacturing. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Production Practices
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing ceramic mold manufacturers to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Innovations in low-temperature sintering and the use of recycled ceramic materials are gaining traction. Companies investing in green manufacturing processes will likely gain a competitive edge and meet stricter regulatory standards in North America and Europe. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, will continue to be major growth drivers due to rapid industrialization and government support for advanced manufacturing. Local ceramic mold producers are upgrading their capabilities to serve domestic and export markets, contributing to a more competitive global landscape. -
Rising Adoption in Medical and Dental Applications
The medical device and dental industries are increasingly relying on ceramic molds for producing biocompatible implants and prosthetics. With aging populations and rising healthcare expenditures globally, the demand for high-precision, customizable ceramic molds in these sectors is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8% through 2026. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Following disruptions from global events in prior years, ceramic mold companies are re-evaluating supply chains. There is a growing trend toward regionalizing production and securing raw material sources to mitigate risks. Strategic partnerships and vertical integration are becoming more common to ensure supply continuity and cost efficiency. -
Material Innovation and Hybrid Solutions
Research into nano-ceramics and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) is leading to molds with enhanced mechanical properties and longer lifespans. Hybrid molds combining ceramics with metals or polymers are also emerging, offering tailored solutions for specific industrial applications.
In summary, by 2026, ceramic mold companies that embrace digitalization, sustainability, and material innovation will be best positioned to capitalize on expanding opportunities across high-growth industries. Strategic investments in R&D and global market diversification will be critical to maintaining a competitive advantage in an evolving marketplace.
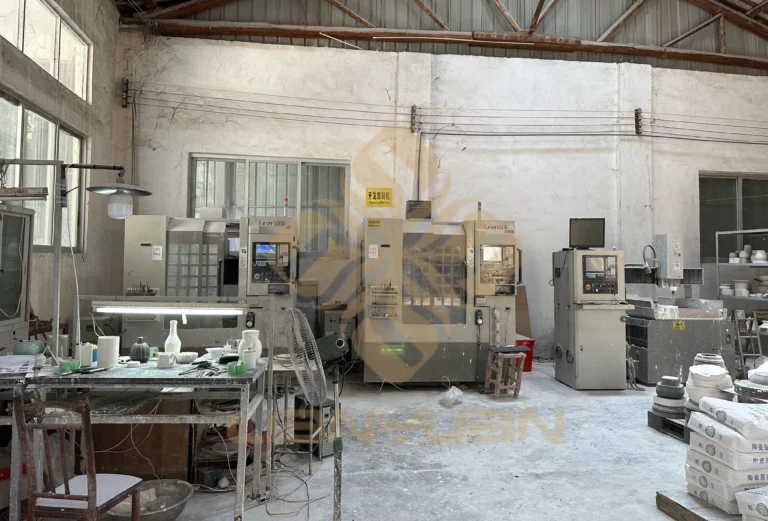

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ceramic Mold Companies (Quality, IP)
Sourcing ceramic mold manufacturers, especially overseas, can introduce significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these common pitfalls is crucial for safeguarding your business interests.
Quality Inconsistencies and Defects
One of the most frequent challenges is receiving molds that do not meet the required precision, durability, or surface finish standards. Ceramic molds demand tight tolerances and consistent material properties, and minor deviations can lead to production failures or subpar end products. Inexperienced or under-resourced suppliers may lack the proper equipment, skilled technicians, or quality control processes—such as dimensional inspection, thermal shock testing, or porosity analysis—needed to ensure reliability. Without on-site audits or third-party inspections, defects may go undetected until the molds are already in use.
Lack of Process Transparency and Traceability
Many ceramic mold suppliers, particularly smaller or less established ones, do not maintain transparent documentation of their manufacturing processes, material sourcing, or quality testing procedures. This lack of traceability makes it difficult to diagnose issues when mold failures occur and complicates root cause analysis. Without clear records, you cannot verify whether the supplier adheres to best practices in sintering, machining, or assembly—critical stages that influence mold performance and longevity.
Inadequate Intellectual Property Protection
Sharing technical drawings, CAD files, and proprietary mold designs with external manufacturers exposes your IP to potential misuse or unauthorized replication. In some regions, enforcement of IP laws is weak, and suppliers may reverse-engineer your designs to produce competing products or sell copies to other clients. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are often poorly enforced or absent altogether, and there may be no legal recourse if your designs are compromised. Additionally, joint ownership ambiguities can arise if design improvements are made during tooling development.
Misalignment in Technical Capabilities and Communication
Ceramic molding involves specialized knowledge in materials science, thermal processing, and precision engineering. Some suppliers may overstate their capabilities or lack experience with your specific application—such as high-temperature resistance, biocompatibility, or complex geometries. Poor communication, language barriers, or time zone differences can exacerbate misunderstandings about technical specifications, lead times, or design modifications, resulting in costly delays or rework.
Supply Chain and Long-Term Reliability Risks
Relying on a single or unproven supplier can create vulnerabilities in your supply chain. Ceramic mold production often involves long lead times and customized tooling, so disruptions—whether from financial instability, production capacity issues, or geopolitical factors—can severely impact your operations. Without contingency plans or verified alternate sources, you may face extended downtime or be forced into unfavorable renegotiations.
Mitigating these risks requires thorough due diligence, including supplier audits, sample testing, robust legal agreements, and ongoing quality monitoring throughout the partnership.
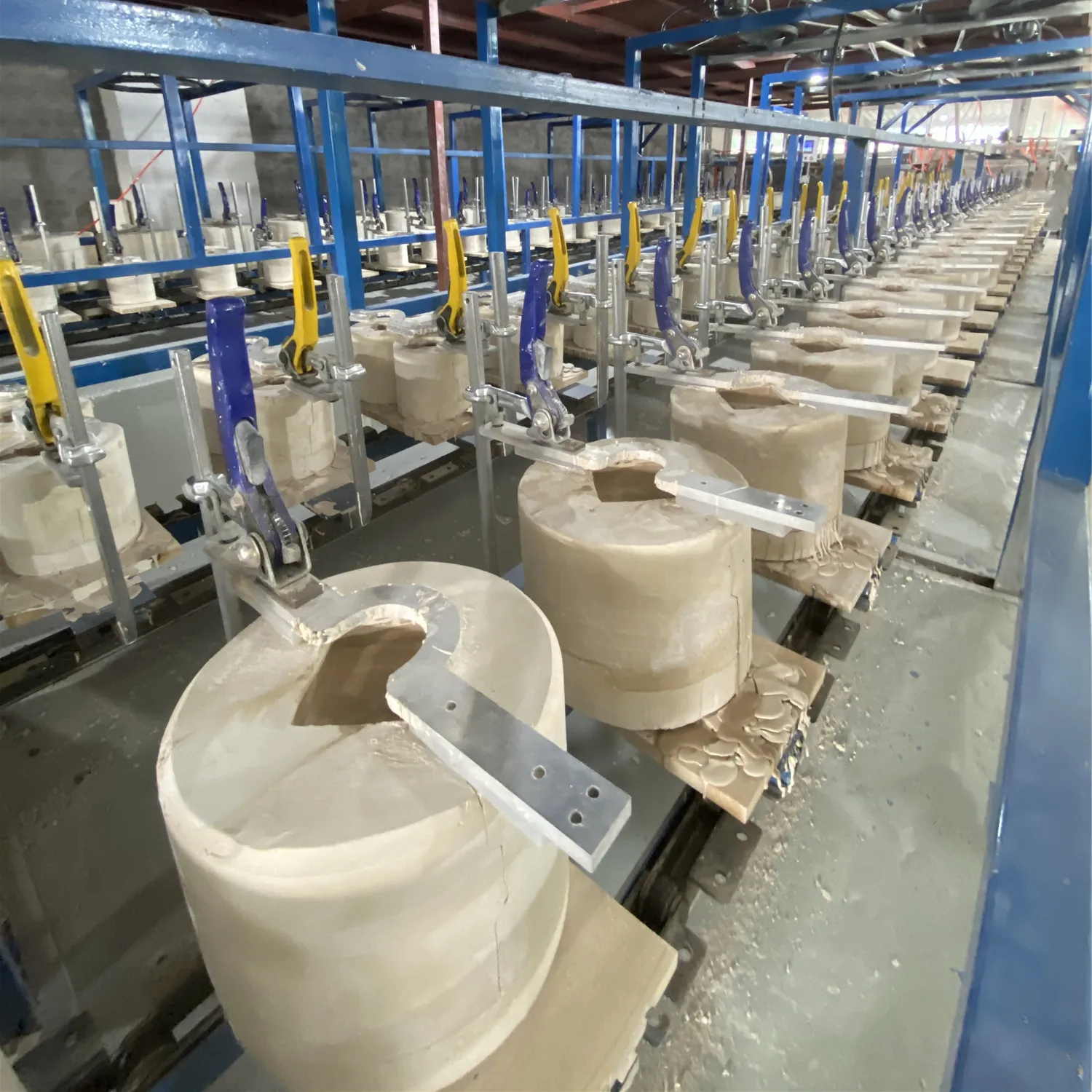

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ceramic Mold Companies
Overview of Ceramic Mold Industry Logistics
Ceramic mold manufacturing involves intricate processes from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. Efficient logistics ensures timely production, cost control, and customer satisfaction. Key logistical considerations include handling fragile molds, managing high-temperature materials, and coordinating with suppliers and customers across global markets.
Supply Chain Management
Establish reliable relationships with suppliers of raw materials such as alumina, silica, and binders. Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices where feasible to reduce storage costs and minimize material degradation. Use supplier performance metrics to ensure consistency in material quality and delivery timelines.
Raw Material Handling and Storage
Store raw materials in climate-controlled environments to prevent moisture absorption or contamination. Clearly label all materials by type, batch number, and date of receipt. Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory rotation to maintain material integrity and comply with quality standards.
Production and Work-in-Process Logistics
Optimize internal material flow between mixing, molding, drying, and firing stages. Design production layouts to minimize handling and reduce the risk of mold damage. Track work-in-process (WIP) items using barcodes or RFID tags to enhance traceability and production planning.
Packaging Requirements for Ceramic Molds
Use custom-designed packaging with cushioning materials such as foam inserts or corrugated dividers to protect molds during transit. Clearly mark packages as “Fragile” and “This Side Up.” Include moisture barriers if shipping to humid environments. Label packages with product specifications, handling instructions, and safety warnings.
Transportation and Shipping
Partner with freight carriers experienced in handling industrial ceramics. Choose transportation modes (road, rail, air, or sea) based on delivery urgency, destination, and mold fragility. For international shipments, use ISO-standard containers and ensure proper securing to prevent movement during transit.
International Trade Compliance
Ensure compliance with export and import regulations in all target markets. Obtain necessary licenses and certifications (e.g., ECCN classification under the U.S. Export Administration Regulations). Accurately complete commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Use Harmonized System (HS) codes specific to ceramic molds (e.g., 6909.19 or 6909.90, depending on composition and use).
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Adhere to relevant international standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and IATF 16949 (if supplying automotive sectors). Comply with regional regulations like REACH (EU) for chemical substances and RoHS if applicable. Maintain documentation for audits and customer requests.
Product Safety and Hazard Communication
Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for raw materials and any treated ceramic products. Train employees on handling hazardous substances and emergency procedures. Clearly label products with required safety symbols and disposal instructions.
Customs Clearance Procedures
Prepare accurate documentation for customs, including a detailed description of goods, value, origin, and end-use. Work with licensed customs brokers for complex international shipments. Anticipate inspections and maintain records for at least five years for audit purposes.
Reverse Logistics and Returns Management
Establish a clear process for handling damaged or defective molds returned by customers. Inspect returned items promptly, document the condition, and determine whether to repair, recycle, or scrap. Update inventory and quality control systems accordingly.
Environmental and Sustainability Practices
Minimize waste by reprocessing scrap ceramic material where technically feasible. Implement recycling programs for packaging and non-hazardous waste. Monitor energy consumption in kilns and dryers to reduce carbon footprint and comply with environmental regulations.
Digital Tools and Logistics Software
Utilize Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to integrate logistics, production, and compliance data. Leverage Transportation Management Systems (TMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to improve efficiency. Employ track-and-trace technologies for real-time shipment monitoring.
Training and Compliance Audits
Conduct regular training for staff on logistics procedures, compliance requirements, and safety protocols. Schedule internal audits to verify adherence to regulatory standards and identify areas for improvement. Maintain audit logs and corrective action records.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Identify potential risks such as supplier delays, transportation disruptions, or regulatory changes. Develop contingency plans, including alternative suppliers and shipping routes. Maintain insurance coverage for cargo, liability, and business interruption.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management are critical to the success of ceramic mold companies. By integrating robust supply chain practices, adhering to international regulations, and leveraging technology, companies can ensure reliable delivery, maintain high-quality standards, and remain competitive in the global marketplace.
In conclusion, sourcing ceramic mold companies requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, technical capability, and reliability. It is essential to conduct thorough due diligence by evaluating suppliers based on their material expertise, manufacturing processes, customization abilities, production capacity, and quality control measures. Establishing strong communication, visiting facilities when possible, and reviewing samples can significantly mitigate risks and ensure that the chosen partner aligns with your project requirements.
Additionally, considering factors such as lead times, scalability, and logistics will contribute to long-term success and supply chain stability. Whether sourcing domestically or internationally, building trusted relationships with reputable ceramic mold manufacturers enables innovation, consistency, and efficiency in end-product development. Ultimately, selecting the right supplier is a critical step in achieving high-performance results across industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods.