Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
Selecting the right centrifugal monoblock pump for your industrial operations directly impacts operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and long-term ROI. For procurement managers and engineers across the USA and Europe, navigating this market presents distinct challenges—from evaluating integrated motor-pump configurations to ensuring compliance with regional standards.
The Challenge
Centrifugal monoblock pumps combine the motor and pump into a single compact unit, eliminating separate assembly requirements and reducing installation complexity. However, this integrated design means buyers must evaluate multiple technical factors simultaneously:
- Performance specifications matching your flow rate and pressure requirements
- Space constraints in existing facilities
- Maintenance accessibility for long-term operational costs
- Supplier reliability across international supply chains
- Regulatory compliance (ATEX in Europe, UL/CSA in North America)
What This Guide Covers
This comprehensive B2B guide provides actionable insights for making informed purchasing decisions:
| Section | Focus Area |
|———|————|
| Technical Specifications | Key performance parameters and selection criteria |
| Application Matching | Industry-specific requirements and use cases |
| Supplier Evaluation | Vetting manufacturers and distributors |
| Cost Analysis | TCO considerations beyond purchase price |
| Compliance | Regional certification requirements |
Whether you’re sourcing pumps for agricultural irrigation, HVAC systems, manufacturing fluid transfer, or wastewater management, this guide equips you with the knowledge to evaluate options confidently and negotiate effectively with suppliers.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for centrifugal monoblock pump
- Understanding centrifugal monoblock pump Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of centrifugal monoblock pump
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘centrifugal monoblock pump’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for centrifugal monoblock pump
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for centrifugal monoblock pump
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘centrifugal monoblock pump’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for centrifugal monoblock pump Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing centrifugal monoblock pump With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for centrifugal monoblock pump
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the centrifugal monoblock pump Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of centrifugal monoblock pump
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for centrifugal monoblock pump
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 10 top pump manufacturers of the world
Domain: jeepumps.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Top pump manufacturers include Grundfos (Denmark), Xylem (New York), KSB (Germany), and JEE Pumps (India)….
2. Top 12 Centrifugal Pump Companies in the World – IMARC Group
Domain: imarcgroup.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Top centrifugal pump companies include Baker Hughes, Circor, Ebara, Flowserve, Grundfos, ITT, Pentair, Someflu, Tsurumi, Weir, Wilo, and Xylem….
3. Top 10 Centrifugal Pump Manufacturer in World 2025 – Liancheng
Domain: liancheng-pump.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: The top 10 centrifugal pump manufacturers are: Grundfos, Flowserve, ITT, KSB, Sulzer, EBARA, Liancheng, DXPE, FPI, and CORNELL….
4. Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Manufacturer – Lubi Pumps
Domain: lubipumps.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Centrifugal monoblock pumps offered by Lubi pumps. All pumps are developed by our experts using premium quality material & leading techniques of industry….
5. ANSI & API Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers | PumpWorks | Houston …
Domain: pumpworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: PumpWorks is an industrial pump manufacturer of API and ANSI Centrifugal Process Pumps. We offer a full range of centrifugal pumps to meet the demands of a wide ……
6. agriculture monoblock pump
Domain: veerpump.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Veer Pumps a leading and popular household name in the Indian Pump Industry offers / introduces newly developed VMB Series Centrifugal MonoBlock Pump….
7. Monoblock Centrifugal Pump – Tapflo UK, Leading Manufacturer
Domain: tapflopumps.co.uk
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Our Monoblock Centrifugal Pump is available in horizontal and vertical configurations and is well suited to Water Supply, Irrigation & HVAC Systems….
Understanding centrifugal monoblock pump Types and Variations
Understanding Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Types and Variations
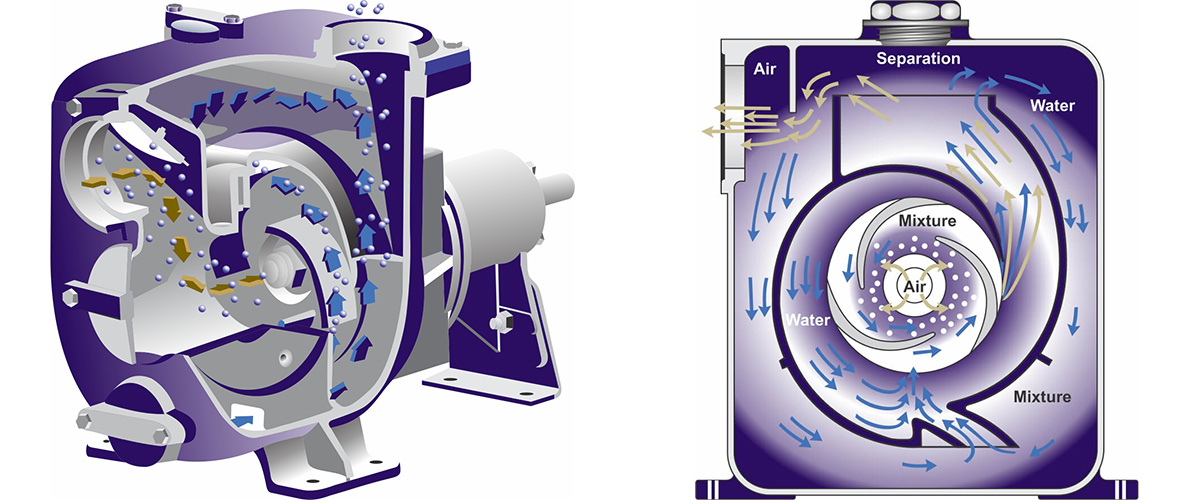
Centrifugal monoblock pumps combine the fluid-moving efficiency of centrifugal pump technology with an integrated motor-pump design housed in a single casing. This configuration eliminates the need for separate motor assembly and coupling alignment, resulting in compact, installation-ready units. Understanding the distinct types available enables procurement teams to match specifications with operational requirements precisely.
Overview of Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Types
| Type | Key Features | Primary Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Priming Monoblock | Built-in priming chamber; handles air-entrained fluids | Drainage, dewatering, agricultural irrigation | No external priming needed; handles intermittent supply | Lower efficiency than non-self-priming variants |
| End-Suction Monoblock | Horizontal configuration; single-stage impeller; direct motor coupling | HVAC systems, water supply, industrial fluid transfer | Simple maintenance; cost-effective; high flow rates | Limited to low-to-medium pressure applications |
| Submersible Monoblock | Fully sealed motor-pump unit; operates underwater | Borewell extraction, sewage handling, flood control | No cavitation issues; quiet operation; space-efficient | Complex repairs; higher upfront cost |
| Regenerative (Peripheral) Monoblock | Multi-vane impeller; generates high head at low flow | Boiler feed, pressure boosting, small-scale industrial processes | High pressure from compact unit; handles low NPSH | Not suitable for solids; lower flow capacity |
| Multi-Stage Monoblock | Multiple impellers in series; progressive pressure buildup | High-rise water supply, reverse osmosis systems, firefighting | Achieves high discharge pressure; energy-efficient at high heads | Higher complexity; increased maintenance requirements |
Detailed Type Specifications
Self-Priming Monoblock Pumps
Self-priming monoblock pumps incorporate a recirculation chamber that allows the unit to evacuate air from the suction line and establish prime without manual intervention. The integrated design houses both the priming mechanism and centrifugal impeller within a single compact casing.
Technical Characteristics:
– Suction lift capability: typically 6–8 meters
– Handles fluids with up to 10% air content
– Requires initial priming fluid charge only at first startup
Optimal Use Cases:
– Agricultural irrigation from open wells or tanks
– Construction site dewatering
– Transfer applications with inconsistent fluid supply
End-Suction Monoblock Pumps
The most widely deployed configuration, end-suction monoblock pumps feature a horizontal shaft arrangement with the suction inlet positioned perpendicular to the discharge outlet. The motor mounts directly to the pump casing, eliminating alignment concerns associated with coupled pump-motor assemblies.
Technical Characteristics:
– Flow rates: 5–500 m³/h (varies by model)
– Head range: 10–80 meters
– Single-stage impeller design
Optimal Use Cases:
– Building water circulation and HVAC systems
– Industrial process water transfer
– Municipal water distribution networks
Submersible Monoblock Pumps
Submersible variants position the entire motor-pump assembly below the fluid surface. The motor is hermetically sealed and often oil-filled or water-cooled, enabling continuous underwater operation without overheating concerns.
Technical Characteristics:
– Operating depths: up to 300+ meters for borewell applications
– Corrosion-resistant construction (stainless steel, bronze, or engineered polymers)
– Integrated thermal overload protection
Optimal Use Cases:
– Deep borewell and groundwater extraction
– Sewage and wastewater pumping stations
– Marine and offshore installations
Regenerative (Peripheral) Monoblock Pumps
Regenerative monoblock pumps utilize a unique impeller design with multiple peripheral vanes that impart energy to the fluid through repeated acceleration cycles. This enables high-pressure output from a single-stage unit operating at relatively low flow volumes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Technical Characteristics:
– Discharge pressure: up to 10 bar from single stage
– Best efficiency at flows below 10 m³/h
– Requires clean fluid free of solids
Optimal Use Cases:
– Boiler feed water systems
– Pressure boosting for domestic and light commercial installations
– Chemical dosing and transfer of clean process fluids
Multi-Stage Monoblock Pumps
Multi-stage configurations stack multiple impellers on a common shaft within an elongated casing. Each stage adds incremental pressure, enabling these units to achieve discharge heads unattainable with single-stage designs while maintaining the installation simplicity of monoblock construction.
Technical Characteristics:
– Stage count: typically 2–8 stages
– Head capability: up to 200+ meters
– Horizontal or vertical mounting options

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal Use Cases:
– High-rise building water supply
– Reverse osmosis and desalination feed pumps
– Industrial pressure washing and firefighting systems
Selection Considerations
When evaluating centrifugal monoblock pump types, procurement and engineering teams should assess:
- System head requirements — Match pump type to required discharge pressure
- Flow rate specifications — Ensure pump capacity aligns with process demands
- Fluid characteristics — Consider viscosity, solids content, and chemical compatibility
- Installation constraints — Evaluate available space, mounting orientation, and accessibility for maintenance
- Total cost of ownership — Balance upfront investment against energy efficiency and maintenance frequency
Key Industrial Applications of centrifugal monoblock pump
Key Industrial Applications of Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
Centrifugal monoblock pumps combine the hydraulic efficiency of centrifugal pump technology with an integrated motor-pump design, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable fluid transfer with minimal installation complexity. Below are the primary industrial sectors leveraging these pumps.
Industry Application Overview
| Industry | Primary Applications | Typical Fluids Handled |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Irrigation | Field irrigation, greenhouse systems, livestock watering, fertigation | Water, liquid fertilizers |
| Manufacturing | Process fluid transfer, cooling systems, machine tool operations | Coolants, process water, light chemicals |
| Water & Wastewater | Municipal supply, treatment plant operations, effluent transfer | Raw water, treated water, light slurries |
| HVAC & Building Services | Chilled water circulation, heating systems, pressure boosting | Conditioned water, glycol mixtures |
| Oil & Gas | Transfer operations, cooling circuits, utility services | Light hydrocarbons, cooling water |
| Food & Beverage | CIP systems, ingredient transfer, wash-down operations | Potable water, low-viscosity liquids |
| Pharmaceutical & Chemical | Process transfer, solvent handling, utility applications | Purified water, mild chemicals |
Detailed Benefits by Application
Agriculture & Irrigation
- Reduced footprint allows installation in pump houses with limited space
- Simplified maintenance minimizes downtime during critical growing seasons
- Self-priming variants handle applications with fluctuating water levels
- Energy efficiency reduces operational costs across large-scale irrigation networks
Manufacturing & Process Industries
- Compact design integrates easily into existing production lines
- Consistent flow rates support process stability and product quality
- Lower vibration due to integrated motor-pump alignment extends equipment lifespan
- Quick installation reduces commissioning time for new facilities
Water & Wastewater Management
- Reliable continuous operation meets 24/7 municipal supply demands
- Corrosion-resistant materials (stainless steel, cast iron) handle varying water quality
- Standardized designs simplify spare parts inventory and replacement
HVAC & Building Services
- Quiet operation suits commercial and residential building installations
- Space efficiency critical for mechanical rooms with multiple systems
- Variable speed compatibility enables energy optimization in modern BMS-controlled environments
Oil & Gas Operations
- Robust construction withstands demanding industrial environments
- Sealed configurations prevent leakage in hydrocarbon-adjacent applications
- High availability supports continuous refinery and processing operations
Selection Considerations
When specifying centrifugal monoblock pumps for industrial applications, evaluate:
- Flow rate and head requirements — Match pump curves to system demands
- Fluid characteristics — Temperature, viscosity, solids content, chemical compatibility
- Operating environment — Ambient conditions, hazardous area classifications
- Duty cycle — Continuous vs. intermittent operation requirements
- Efficiency standards — IE3/IE4 motor compliance for energy cost reduction
The integrated design of centrifugal monoblock pumps delivers measurable advantages in installation speed, maintenance simplicity, and space utilization—making them a practical choice across diverse industrial fluid handling applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘centrifugal monoblock pump’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Unexpected Downtime Due to Motor-Pump Alignment Issues
Scenario: A manufacturing facility experiences frequent unplanned shutdowns because their traditional centrifugal pump systems require regular realignment between the motor and pump components. Maintenance teams spend excessive hours troubleshooting vibration issues and coupling failures.
Problem: Separate motor-pump assemblies demand precise shaft alignment. Misalignment causes premature bearing wear, seal failures, and increased energy consumption—leading to costly production interruptions and maintenance overhead.
Solution: Transition to centrifugal monoblock pumps with integrated motor-pump design. The single-casing construction eliminates alignment requirements entirely, reducing vibration-related failures and cutting maintenance frequency by up to 40%. This translates to improved uptime and lower total cost of ownership.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 2: Space Constraints in Facility Layouts
Scenario: A European food processing plant needs to expand pumping capacity but faces limited floor space. Installing additional conventional pump-motor assemblies would require costly facility modifications.
Problem: Traditional centrifugal pump setups require separate motor mounting, coupling guards, and alignment clearances—consuming significant footprint per installation.
Solution: Deploy centrifugal monoblock pumps that combine motor and pump in a compact, space-saving unit. Benefits include:
| Factor | Traditional Setup | Monoblock Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Footprint | 100% baseline | 30-50% reduction |
| Installation time | 4-6 hours | 1-2 hours |
| Components to manage | Multiple | Single unit |
Pain Point 3: Complex Installation and Skilled Labor Requirements
Scenario: A U.S. agricultural operation needs to install multiple irrigation pumps across remote locations but struggles to source qualified technicians for proper motor-pump assembly and coupling installation.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem: Conventional centrifugal pumps require specialized expertise for assembly, alignment, and commissioning—increasing project timelines and labor costs.
Solution: Specify centrifugal monoblock pumps for simplified plug-and-play installation. The integrated design requires no coupling assembly or alignment procedures, enabling faster deployment with general maintenance personnel. This reduces installation costs and accelerates time-to-operation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for centrifugal monoblock pump
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
Selecting the appropriate construction materials for centrifugal monoblock pumps directly impacts operational longevity, maintenance costs, and overall system reliability. This guide provides a systematic framework for material selection based on application requirements, fluid characteristics, and environmental conditions.
Critical Components Requiring Material Consideration
The integrated design of monoblock pumps means material decisions affect three primary assemblies:
Impeller Assembly
The impeller operates under continuous rotational stress while directly contacting the pumped fluid. Material selection must account for:
– Erosion resistance from suspended solids
– Corrosion compatibility with fluid chemistry
– Fatigue strength under cyclic loading
– Cavitation resistance at high-speed operation
Pump Casing
The casing contains fluid pressure and guides flow through specifically formed channels. Requirements include:
– Pressure containment capability
– Dimensional stability under thermal cycling
– Resistance to external environmental factors
– Compatibility with sealing systems
Shaft and Coupling Components
In monoblock configurations, the shaft transmits rotational energy directly from the integrated motor to the impeller. Material must provide:
– High torsional strength
– Minimal deflection under load
– Compatibility with bearing and seal interfaces
– Resistance to fatigue failure
Material Options by Application Category
Cast Iron (Gray Iron / Ductile Iron)
Cast iron remains the standard choice for general-purpose water handling applications. Gray iron offers excellent machinability and vibration damping, while ductile iron provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance.
Optimal Applications:
– Municipal water distribution
– HVAC circulation systems
– General industrial water transfer
– Irrigation systems with clean water
Limitations:
– Unsuitable for acidic fluids (pH below 6.5)
– Susceptible to corrosion in chloride-rich environments
– Not recommended for food-grade applications
Stainless Steel (304 / 316 / 316L)
Stainless steel variants offer enhanced corrosion resistance for demanding applications. Grade 316/316L provides molybdenum content for improved chloride resistance.
Optimal Applications:
– Chemical processing (mild chemicals)
– Food and beverage production
– Pharmaceutical manufacturing
– Seawater and brackish water handling (316L)
– High-temperature applications

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Limitations:
– Higher material cost (2-3x cast iron)
– Potential for galling in close-tolerance fits
– Susceptible to stress corrosion cracking in specific chloride/temperature combinations
Bronze and Brass Alloys
Bronze impellers paired with cast iron casings represent a cost-effective upgrade for improved corrosion resistance. Common alloys include gunmetal bronze (C83600) and aluminum bronze (C95400).
Optimal Applications:
– Marine and shipboard systems
– Potable water systems requiring lead-free construction
– Moderate chemical exposure
– Applications requiring superior wear resistance
Limitations:
– Dezincification risk with certain brass alloys
– Not suitable for ammonia-containing fluids
– Higher cost than cast iron alternatives

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Engineered Polymers and Composites
Polypropylene (PP), PVDF, and fiber-reinforced composites serve specialized corrosive applications where metals prove inadequate.
Optimal Applications:
– Aggressive acid handling
– Electroplating operations
– Semiconductor manufacturing
– Ultra-pure water systems
Limitations:
– Lower pressure ratings than metallic construction
– Temperature restrictions (typically below 90°C)
– Reduced mechanical strength
– Limited availability in larger pump sizes
High-Alloy Materials (Hastelloy, Duplex Stainless, Titanium)
Premium alloys address severe service conditions where standard materials fail prematurely.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal Applications:
– Concentrated acid handling
– High-chloride environments at elevated temperatures
– Offshore oil and gas processing
– Desalination systems
Limitations:
– Significant cost premium (5-10x standard materials)
– Extended lead times for procurement
– Specialized welding and machining requirements
Fluid Compatibility Assessment
Material selection begins with comprehensive fluid analysis:
Chemical Composition
– pH level and buffering capacity
– Chloride and sulfate concentrations
– Presence of oxidizing or reducing agents
– Dissolved gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide)

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Physical Properties
– Operating temperature range
– Specific gravity and viscosity
– Suspended solids content and particle hardness
– Abrasive characteristics
Process Conditions
– Continuous vs. intermittent operation
– Temperature cycling frequency
– Potential for fluid stagnation
– Cleaning and sanitization requirements
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
USA Market Requirements:
– NSF/ANSI 61 certification for potable water contact materials
– FDA compliance for food-contact applications
– OSHA considerations for hazardous fluid handling
– State-specific lead-free requirements (California Proposition 65)
European Market Requirements:
– EN 12502 standards for metallic materials in contact with water
– WRAS approval for UK potable water applications
– EC 1935/2004 for food-contact materials
– REACH compliance for chemical substances

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Material selection decisions should incorporate lifecycle costs beyond initial purchase price:
Maintenance Frequency
Higher-grade materials typically reduce maintenance intervals, offsetting initial cost premiums in demanding applications.
Spare Parts Inventory
Standardizing on common material grades across multiple pumps reduces inventory complexity and carrying costs.
Downtime Costs
Critical process applications justify premium materials when unplanned failures create significant production losses.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Energy Efficiency
Surface finish quality affects hydraulic efficiency; corrosion-resistant materials maintain performance over extended periods.
Material Selection Comparison Table
| Material | Typical Applications | pH Range | Max Temp (°C) | Relative Cost | Chloride Resistance | Abrasion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray Cast Iron | General water service, HVAC | 6.5-12 | 120 | 1.0x (baseline) | Poor | Moderate |
| Ductile Cast Iron | Higher pressure water applications | 6.5-12 | 150 | 1.2x | Poor | Good |
| 304 Stainless Steel | Mild chemicals, food processing | 4-10 | 200 | 2.5x | Moderate | Moderate |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Marine, brackish water, chemicals | 3-10 | 200 | 3.0x | Good | Moderate |
| 316L Stainless Steel | Welded applications, pharmaceuticals | 3-10 | 200 | 3.2x | Good | Moderate |
| Gunmetal Bronze | Marine, potable water | 5-9 | 150 | 2.0x | Good | Excellent |
| Aluminum Bronze | High-wear applications | 5-9 | 200 | 2.2x | Good | Excellent |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Aggressive acids, ultra-pure water | 1-14 | 80 | 1.5x | Excellent | Poor |
| PVDF | Concentrated acids, solvents | 1-14 | 90 | 2.5x | Excellent | Moderate |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | High chloride, elevated temperature | 2-10 | 250 | 5.0x | Excellent | Good |
| Hastelloy C-276 | Severe chemical service | 1-14 | 300 | 8.0x | Excellent | Moderate |
| Titanium Grade 2 | Seawater, chlorine dioxide | 1-12 | 250 | 10.0x | Excellent | Moderate |
Seal and Gasket Material Compatibility
Material selection extends to sealing components, which must maintain compatibility with both the pumped fluid and the pump housing materials:
| Seal Material | Compatible Fluids | Temperature Range (°C) | Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Buna-N) | Petroleum products, water | -30 to +100 | Moderate |
| EPDM | Water, steam, mild chemicals | -40 to +150 | Good (non-petroleum) |
| Viton (FKM) | Chemicals, fuels, acids | -20 to +200 | Excellent |
| PTFE | Universal chemical compatibility | -200 to +260 | Excellent |
| Silicon Carbide | Abrasive slurries, high-temperature | -40 to +400 | Excellent |
Decision Framework Summary
- Define fluid characteristics – Complete chemical and physical analysis
- Establish operating parameters – Temperature, pressure, flow requirements
- Identify regulatory requirements – Certifications needed for target markets
- Calculate lifecycle costs – Initial investment plus maintenance and downtime
- Verify material availability – Lead times and spare parts accessibility
- Confirm compatibility – All wetted components including seals and gaskets
Proper material selection for centrifugal monoblock pumps requires balancing technical requirements against economic constraints. Consultation with pump manufacturers during the specification phase ensures optimal material combinations for specific application demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for centrifugal monoblock pump
Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
The integrated design of centrifugal monoblock pumps—where motor and pump share a single casing—demands precision manufacturing and rigorous quality control. Understanding these processes helps procurement teams evaluate supplier capabilities and product reliability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Process Overview
Stage 1: Material Preparation
| Component | Common Materials | Preparation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Impeller | Stainless steel, bronze, cast iron | Raw material inspection, chemical composition verification |
| Casing | Cast iron, stainless steel | Material certification review, dimensional stock verification |
| Shaft | Hardened steel, stainless steel | Ultrasonic testing for internal defects |
| Seals | Ceramic, carbon, elastomers | Batch testing for material consistency |
Material selection directly impacts pump performance, corrosion resistance, and operational lifespan. Suppliers typically source certified materials with traceable mill certificates.
Stage 2: Component Forming
Casting and Machining:
– Impeller production: Investment casting or sand casting followed by CNC machining to achieve precise blade geometry
– Casing manufacture: Pattern-based casting with subsequent boring and facing operations
– Shaft fabrication: Precision turning, grinding, and surface finishing to achieve required tolerances (typically ±0.01mm)
Critical Tolerances:
– Impeller-to-casing clearance: 0.2–0.5mm (application-dependent)
– Shaft runout: <0.025mm
– Surface finish on wetted parts: Ra 1.6–3.2 μm
Stage 3: Assembly
The monoblock configuration requires precise alignment since the motor and pump share a common shaft or direct coupling:
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Motor integration: Direct mounting of motor to pump housing
- Impeller installation: Secure fitting with appropriate torque specifications
- Seal assembly: Mechanical seal installation with proper seating verification
- Final housing closure: Gasket placement and fastener torquing to specification
Quality Control Checkpoints
| Stage | Test/Inspection | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming materials | Spectroscopy, hardness testing | Material certification compliance |
| Post-machining | CMM dimensional inspection | Drawing tolerance adherence |
| Pre-assembly | Visual inspection, surface finish measurement | No defects, Ra within spec |
| Post-assembly | Hydrostatic pressure test | No leakage at 1.5× rated pressure |
| Final testing | Performance curve verification | Flow/head within ±5% of rated values |
Applicable Quality Standards
ISO Certifications:
– ISO 9001:2015: Quality management system requirements
– ISO 5199: Technical specifications for centrifugal pumps (Class II)
– ISO 9906: Hydraulic performance acceptance tests
Regional Compliance:
– CE Marking (Europe): Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
– UL/CSA Certification (North America): Electrical safety standards
– ATEX (Europe): For pumps in explosive atmospheres
Supplier Evaluation Criteria
When assessing manufacturers, verify:
- Third-party certification audits (ISO registrar documentation)
- In-house testing capabilities (test rigs, calibrated instrumentation)
- Traceability systems (lot tracking from raw material to finished product)
- Non-conformance handling procedures
- Warranty terms tied to documented QC processes
Manufacturers with vertically integrated operations—controlling casting, machining, and assembly in-house—typically deliver more consistent quality than those relying heavily on outsourced components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘centrifugal monoblock pump’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
Sourcing centrifugal monoblock pumps requires systematic evaluation of technical specifications, supplier credentials, and total cost of ownership. Use this checklist to streamline your procurement process and minimize risk.
Step 1: Define Application Requirements
Before contacting suppliers, document your operational parameters:
| Parameter | Details to Specify |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Required GPM/m³/h (minimum, maximum, typical) |
| Head Pressure | Total dynamic head (TDH) in feet/meters |
| Fluid Type | Water, chemicals, slurries, temperature, viscosity |
| Operating Environment | Indoor/outdoor, ambient temperature, humidity |
| Duty Cycle | Continuous, intermittent, hours per day |
| Power Supply | Voltage, frequency, single/three-phase availability |
Step 2: Establish Technical Specifications
- [ ] Determine pump material requirements (cast iron, stainless steel, bronze) based on fluid compatibility
- [ ] Specify motor power rating (HP/kW) and efficiency class (IE2, IE3, IE4)
- [ ] Identify required certifications (CE, UL, ATEX for hazardous environments)
- [ ] Define inlet/outlet connection sizes and flange standards (ANSI, DIN, ISO)
- [ ] Confirm IP rating requirements for motor protection
- [ ] Specify seal type (mechanical seal, gland packing) based on application
Step 3: Identify and Qualify Suppliers
Supplier Evaluation Criteria:
- [ ] Verify manufacturing certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 14001)
- [ ] Confirm production capacity meets your volume requirements
- [ ] Review supplier’s industry experience and reference clients
- [ ] Assess geographic proximity for logistics and support
- [ ] Evaluate after-sales service network in your region (USA/Europe)
- [ ] Check warranty terms and conditions
Documentation to Request:
- Product datasheets and performance curves
- Material certifications and test reports
- Quality control procedures
- Customer references in similar applications
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotations
RFQ Essentials:
- [ ] Submit detailed technical specifications to minimum 3 qualified suppliers
- [ ] Request itemized pricing (unit cost, spare parts, shipping, installation support)
- [ ] Clarify lead times and production schedules
- [ ] Confirm payment terms and Incoterms
- [ ] Request sample units or factory visit for large orders
Comparison Matrix:
| Evaluation Criteria | Weight | Supplier A | Supplier B | Supplier C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical compliance | 25% | |||
| Price competitiveness | 20% | |||
| Lead time | 15% | |||
| Warranty coverage | 15% | |||
| Service/support network | 15% | |||
| References/track record | 10% |
Step 5: Conduct Due Diligence
- [ ] Verify supplier financial stability
- [ ] Review product certifications against regional compliance requirements
- [ ] Confirm spare parts availability and pricing
- [ ] Validate delivery logistics and customs documentation
- [ ] Assess supplier’s communication responsiveness
Step 6: Negotiate and Finalize Contract
Contract Checklist:
- [ ] Lock in unit pricing and volume discount tiers
- [ ] Define delivery schedule with penalties for delays
- [ ] Specify warranty period (minimum 12-24 months recommended)
- [ ] Include performance guarantee clauses
- [ ] Establish spare parts supply agreement
- [ ] Define acceptance testing procedures
- [ ] Clarify dispute resolution mechanisms
Step 7: Post-Purchase Verification
- [ ] Conduct incoming inspection against specifications
- [ ] Perform acceptance testing per agreed protocols
- [ ] Document serial numbers and warranty registration
- [ ] Establish preventive maintenance schedule
- [ ] Archive supplier contact information for ongoing support
Key Considerations for Monoblock Pump Sourcing
Advantages to leverage:
– Integrated motor-pump design simplifies installation
– Compact footprint reduces space requirements
– Fewer components mean lower maintenance complexity
Risk factors to address:
– Motor failure requires complete unit service
– Ensure local service capability for integrated units
– Verify motor specifications match your power infrastructure
Download this checklist and customize it for your specific procurement requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for centrifugal monoblock pump Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Sourcing
Understanding the complete cost structure of centrifugal monoblock pumps enables procurement teams to make informed purchasing decisions and negotiate effectively with suppliers. This analysis breaks down all cost components and provides actionable strategies to optimize your sourcing budget.
Total Cost of Ownership Framework
When evaluating centrifugal monoblock pump costs, consider the complete lifecycle rather than just the purchase price. The integrated motor-pump design of monoblock units affects costs differently than traditional centrifugal pumps with separate components.
Material Cost Breakdown
Material selection significantly impacts both upfront costs and long-term performance. Here’s a comparative analysis:
| Component | Standard Materials | Premium Materials | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pump Casing | Cast Iron | Stainless Steel 316 | +40-60% |
| Impeller | Bronze/Cast Iron | Stainless Steel/Duplex | +30-50% |
| Shaft | Carbon Steel | Stainless Steel 304/316 | +25-40% |
| Seals | Rubber/PTFE | Mechanical Seals (Silicon Carbide) | +50-80% |
| Motor Housing | Aluminum | Cast Iron | +15-25% |
Key Material Cost Drivers:
- Fluid compatibility requirements: Corrosive or abrasive fluids demand premium materials
- Operating temperature range: High-temperature applications require specialized alloys
- Regulatory compliance: Food-grade, pharmaceutical, or hazardous environment certifications increase material costs by 20-35%
- Motor efficiency class: IE3/IE4 premium efficiency motors add 15-25% to base costs but reduce operational expenses
Labor Cost Analysis
The integrated design of monoblock pumps offers distinct labor cost advantages:
Manufacturing Labor
| Cost Category | Centrifugal Pump (Separate Motor) | Monoblock Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Assembly Time | 4-6 hours | 2-3 hours |
| Alignment Requirements | Critical (adds 1-2 hours) | Eliminated |
| Quality Testing | Extended coupling tests | Simplified single-unit testing |
| Estimated Labor Cost | $150-300 per unit | $80-150 per unit |
Installation Labor
- Monoblock advantage: No motor-pump alignment required, reducing installation time by 40-60%
- Typical installation costs:
- Monoblock pumps: $200-500 (USA/Europe)
- Separate motor-pump assemblies: $400-900
- Foundation requirements: Monoblock units require simpler mounting, reducing civil work costs
Maintenance Labor
| Maintenance Task | Annual Labor Cost (Monoblock) | Annual Labor Cost (Traditional) |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Inspection | $100-200 | $150-300 |
| Seal Replacement | $150-300 | $200-400 |
| Bearing Service | $200-350 | $300-500 |
| Complete Overhaul | $500-800 | $800-1,200 |
Logistics and Shipping Costs
Domestic Shipping (USA/Europe)
| Pump Capacity | Typical Weight | LTL Freight Cost | Full Truckload Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5-2 HP | 15-40 kg | $75-150 | 20+ units |
| 3-7.5 HP | 45-100 kg | $150-300 | 12-15 units |
| 10-25 HP | 120-300 kg | $300-600 | 6-10 units |
| 30+ HP | 350+ kg | $500-1,200 | 4-6 units |
International Sourcing Costs
| Origin | FOB Price Advantage | Freight (per unit, 5HP) | Import Duties (USA) | Import Duties (EU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| India | 30-45% lower | $80-150 | 0-2.5% | 1.7-2.5% |
| China | 25-40% lower | $70-130 | 25%* | 1.7-2.5% |
| Italy/Germany | Baseline | $30-80 (intra-EU) | 0-2.5% | 0% (intra-EU) |
| USA (domestic) | Baseline | $50-150 | N/A | N/A |
*Note: Tariff rates subject to trade policy changes; verify current rates before procurement decisions.
Hidden Logistics Costs to Account For
- Customs clearance fees: $150-400 per shipment
- Documentation and compliance: $50-200
- Insurance: 0.3-0.8% of cargo value
- Port handling and drayage: $200-500
- Warehousing (if required): $50-150 per pallet/month
Pricing Tiers by Application and Specification
Standard Industrial Monoblock Pumps
| Power Rating | Flow Rate | Head | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 HP | 50-100 LPM | 10-15m | $180-350 |
| 1 HP | 100-200 LPM | 15-25m | $250-500 |
| 2 HP | 200-400 LPM | 20-35m | $400-750 |
| 5 HP | 400-800 LPM | 30-50m | $700-1,400 |
| 10 HP | 800-1,500 LPM | 40-70m | $1,200-2,500 |
| 25 HP | 1,500-3,000 LPM | 50-100m | $3,000-6,000 |
Premium/Specialized Applications
| Application | Price Premium | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage (3A certified) | +40-60% | Sanitary design, polished surfaces, FDA-compliant materials |
| Chemical Processing | +50-80% | Corrosion-resistant alloys, specialized seals |
| High-Temperature (>150°C) | +35-55% | Heat-resistant materials, special lubricants |
| Explosion-Proof (ATEX/UL) | +60-100% | Certified motors, specialized construction |
| Variable Speed (VFD-ready) | +20-35% | Inverter-duty motors, enhanced insulation |
Cost-Saving Strategies for Procurement Teams
1. Optimize Specifications
- Right-size your pumps: Over-specification increases costs by 20-40%. Conduct accurate system curve analysis.
- Standardize across facilities: Reducing SKU variety by 30% can decrease spare parts inventory costs by 25-40%.
- Evaluate material requirements: Specify premium materials only where fluid compatibility demands it.
2. Strategic Sourcing Approaches
| Strategy | Potential Savings | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Volume consolidation | 10-25% | Low |
| Multi-year contracts | 8-15% | Medium |
| Supplier diversification | 5-12% | Medium |
| Regional sourcing optimization | 15-30% | High |
| Consortium buying | 12-20% | High |
3. Negotiate Total Package Pricing
Request bundled pricing that includes:
– Base pump unit
– Spare parts kit (seals, bearings, impeller)
– Extended warranty (2-3 years vs. standard 1 year)
– Technical documentation and training
– First-year maintenance support
Typical bundle discount: 12-18% vs. purchasing components separately
4. Leverage Monoblock Design Advantages
The integrated motor-pump construction provides inherent cost benefits:
- Reduced installation costs: No coupling alignment required
- Smaller footprint: Lower foundation and space costs
- Simplified maintenance: Fewer components to service
- Lower spare parts inventory: Single-unit replacement simplifies stocking
5. Consider Total Cost of Ownership
| Cost Category | % of 10-Year TCO | Optimization Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Energy consumption | 40-60% | Specify IE3/IE4 motors; ROI typically 18-36 months |
| Initial purchase | 15-25% | Volume negotiations, specification optimization |
| Maintenance | 15-25% | Preventive maintenance programs, quality seals |
| Downtime | 5-15% | Reliability-focused supplier selection, spare parts availability |
6. Timing and Market Considerations
- Order during Q4: Many manufacturers offer 5-10% discounts to meet annual targets
- Avoid peak seasons: Agricultural irrigation seasons (spring) see price increases of 8-15%
- Monitor raw material indices: Steel and copper prices directly impact pump costs
- Consider lead times: Rush orders typically incur 15-25% premiums
Supplier Evaluation Cost Factors
When comparing suppliers, request detailed breakdowns including:
| Evaluation Criteria | Weight | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Unit price | 30% | Direct |
| Warranty terms | 15% | Indirect (future repair costs) |
| Delivery reliability | 15% | Indirect (production delays) |
| Technical support quality | 10% | Indirect (troubleshooting costs) |
| Spare parts availability | 15% | Indirect (downtime, inventory) |
| Certification compliance | 15% | Direct (regulatory requirements) |
Regional Pricing Considerations
United States Market
- Domestic manufacturers command 15-25% premium but offer faster delivery and local support
- “Buy American” requirements for government contracts limit sourcing options
- Strong aftermarket support network reduces long-term service costs
European Market
- CE marking mandatory; factor certification costs into non-EU sourcing
- ATEX compliance for hazardous environments adds significant cost
- Intra-EU sourcing eliminates customs complexity and reduces lead times
- Energy efficiency regulations (ErP Directive) require IE3 minimum for most applications
Summary: Cost Optimization Checklist
- [ ] Conduct accurate hydraulic calculations to right-size specifications
- [ ] Standardize pump models across facilities where possible
- [ ] Request itemized quotes separating materials, labor, and logistics
- [ ] Negotiate volume-based pricing with 2-3 qualified suppliers
- [ ] Include spare parts and warranty in initial negotiations
- [ ] Factor in total cost of ownership, not just purchase price
- [ ] Verify compliance certifications are included in quoted price
- [ ] Plan procurement timing to avoid seasonal premiums
- [ ] Evaluate monoblock vs. traditional centrifugal based on installation and maintenance requirements
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing centrifugal monoblock pump With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps With Other Solutions
Selecting the right pumping solution requires evaluating operational requirements, installation constraints, and total cost of ownership. This analysis compares centrifugal monoblock pumps against two primary alternatives: traditional coupled centrifugal pumps and positive displacement pumps.
Comparison Overview
| Factor | Centrifugal Monoblock Pump | Coupled Centrifugal Pump | Positive Displacement Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Integrated motor-pump unit in single casing | Separate motor and pump connected via coupling | Enclosed cavities move fixed fluid volumes |
| Installation Complexity | Low — minimal assembly required | Moderate — requires alignment and coupling | Moderate to High — depends on type |
| Footprint | Compact, space-saving | Larger installation area | Varies by configuration |
| Maintenance | Simplified — fewer components | Higher — coupling wear, alignment checks | Higher — seals, rotors, valves |
| Flow Characteristics | Variable flow, pressure-dependent | Variable flow, pressure-dependent | Constant flow, independent of pressure |
| Viscosity Handling | Low to medium viscosity fluids | Low to medium viscosity fluids | High viscosity fluids |
| Efficiency at Variable Loads | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Moderate | Higher |
| Best Applications | Water transfer, irrigation, HVAC, general fluid handling | Heavy industrial, high-power applications | Metering, chemical dosing, viscous fluids |
Detailed Analysis
Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps vs. Coupled Centrifugal Pumps
Coupled centrifugal pumps offer flexibility in motor selection and can handle higher power requirements. However, the separate motor-pump configuration demands precise shaft alignment during installation and ongoing monitoring to prevent premature bearing and coupling wear. Centrifugal monoblock pumps eliminate alignment concerns entirely, reducing both installation time and long-term maintenance burden. For applications under 50 HP where space is constrained, monoblock designs typically deliver superior value.
Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps vs. Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps excel in applications requiring precise flow control or handling of viscous, shear-sensitive, or abrasive fluids. They maintain consistent output regardless of discharge pressure variations. However, centrifugal monoblock pumps offer significant advantages for high-volume, low-viscosity fluid transfer: lower acquisition costs, simpler operation, and reduced maintenance complexity. For standard water handling, irrigation, and HVAC applications, centrifugal monoblock pumps remain the cost-effective choice.
Selection Criteria
Choose centrifugal monoblock pumps when:
– Handling clean, low-viscosity fluids
– Space constraints exist
– Minimizing installation and maintenance costs is priority
– High flow rates at moderate pressures are required
Choose alternatives when:
– Power requirements exceed monoblock capacity limits
– Handling highly viscous or abrasive media
– Precise volumetric dosing is essential
– Operating conditions require motor serviceability independent of pump
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for centrifugal monoblock pump
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
Understanding the critical technical specifications and industry-standard trade terminology is essential for effective B2B procurement of centrifugal monoblock pumps. This section provides procurement professionals and engineers with the foundational knowledge required for specification, sourcing, and supplier negotiations.
Key Technical Properties
Performance Parameters
| Parameter | Definition | Typical Units | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate (Q) | Volume of fluid delivered per unit time | m³/h, GPM, L/min | Determines pump capacity for application requirements |
| Head (H) | Energy imparted to fluid, expressed as height | meters, feet | Indicates pressure capability and vertical lift potential |
| Efficiency (η) | Ratio of hydraulic power output to electrical input | % | Impacts operational costs and energy consumption |
| NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head) | Minimum pressure required at pump inlet to prevent cavitation | meters, feet | Critical for installation design and pump longevity |
| Power Rating | Motor power consumption | kW, HP | Determines electrical infrastructure requirements |
Mechanical Specifications
| Specification | Description | Common Options |
|---|---|---|
| Impeller Type | Blade configuration affecting flow characteristics | Closed, semi-open, open |
| Impeller Material | Construction material for corrosion/wear resistance | Cast iron, stainless steel (SS304/SS316), bronze, plastic |
| Casing Material | Pump body construction | Cast iron (CI), ductile iron, stainless steel |
| Shaft Seal Type | Mechanism preventing fluid leakage | Mechanical seal, gland packing |
| Motor Frame Size | Standardized motor dimensions | IEC (56-315), NEMA (42-449) |
Electrical Specifications
- Voltage/Frequency: 220-240V/50Hz (Europe), 110-120V/60Hz (USA), 380-440V/3-phase
- Insulation Class: F or H (determines thermal tolerance)
- Protection Rating (IP): IP44, IP55, IP65 (ingress protection against dust/water)
- Motor Efficiency Class: IE1, IE2, IE3, IE4 (per IEC 60034-30-1)
Operating Conditions
| Parameter | Specification Range |
|---|---|
| Fluid Temperature | -10°C to +120°C (application-dependent) |
| Ambient Temperature | -15°C to +50°C |
| Maximum Viscosity | Typically ≤20 cSt for standard designs |
| Solid Handling | Clean water to 3% solids (application-specific) |
Critical Design Characteristics
Integrated Motor-Pump Assembly
The defining feature of monoblock pumps is the direct coupling of motor and pump within a single housing:
- Close-coupled design: Eliminates alignment issues common in coupled pump-motor assemblies
- Compact footprint: Reduces installation space requirements by 30-40% versus conventional configurations
- Reduced maintenance: Fewer components and connection points minimize failure modes
Impeller Configuration
| Type | Application | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Closed Impeller | Clean water, high efficiency | Highest efficiency, limited solids handling |
| Semi-Open Impeller | Slightly contaminated fluids | Moderate efficiency, improved solids passage |
| Open Impeller | Slurries, viscous fluids | Lower efficiency, maximum solids handling |
B2B Trade Terminology
Procurement Terms
| Term | Definition | Business Implication |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Smallest order a supplier will accept | Affects inventory strategy; typical range: 1-50 units |
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer producing pumps for rebranding | Enables private labeling and custom specifications |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Supplier providing design and manufacturing | Offers turnkey product development |
| SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) | Unique product identifier | Essential for inventory management and reordering |
| Lead Time | Duration from order to delivery | Standard: 2-8 weeks; affects project scheduling |
Commercial Terms
| Term | Definition | Application |
|---|---|---|
| FOB (Free On Board) | Seller’s responsibility ends at shipping point | Common for international transactions |
| CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) | Seller covers shipping and insurance to destination | Simplifies landed cost calculation |
| EXW (Ex Works) | Buyer assumes all costs from seller’s facility | Lowest seller obligation |
| DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) | Seller handles all costs including import duties | Maximum seller obligation |
Quality and Compliance Terms
| Term | Definition | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system certification | Indicates consistent manufacturing processes |
| CE Marking | European conformity certification | Mandatory for EU market entry |
| UL Listing | US safety certification | Required/preferred for North American markets |
| ATEX | Explosive atmosphere certification | Required for hazardous environment applications |
| API 610 | American Petroleum Institute pump standard | Specifies requirements for oil/gas applications |
| ISO 2858 | Dimensional standard for centrifugal pumps | Ensures interchangeability between manufacturers |
Warranty and Service Terms
| Term | Definition | Standard Practice |
|---|---|---|
| MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) | Average operational time before failure | Indicates reliability; higher = better |
| Warranty Period | Manufacturer’s defect coverage duration | Typically 12-24 months from commissioning |
| Spare Parts Availability | Commitment to component supply | Critical for long-term maintenance planning |
| Technical Data Sheet (TDS) | Comprehensive product specification document | Essential for engineering review |
Specification Checklist for Procurement
When requesting quotations, ensure suppliers provide:
Performance Data:
– [ ] Pump curve (H-Q characteristic)
– [ ] Efficiency curve
– [ ] NPSH required curve
– [ ] Power consumption curve
Documentation:
– [ ] General arrangement drawing (GA)
– [ ] Sectional drawing
– [ ] Bill of materials (BOM)
– [ ] Installation and operation manual (IOM)
– [ ] Test certificates
Compliance:
– [ ] Material certificates (EN 10204 3.1)
– [ ] Motor test certificate
– [ ] Hydrostatic test certificate
– [ ] Performance test certificate
Standard Classifications
By Application
| Classification | Head Range | Flow Range | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic/Residential | 10-40 m | 1-10 m³/h | Water supply, pressure boosting |
| Agricultural | 15-60 m | 5-50 m³/h | Irrigation, livestock |
| Industrial | 20-150 m | 10-500 m³/h | Process water, cooling systems |
By Construction Standard
- EN 733: European standard for end-suction centrifugal pumps
- ISO 5199: Technical specifications for centrifugal pumps
- ANSI/HI 1.3: American hydraulic institute standards
Mastery of these technical properties and trade terms enables efficient communication with suppliers, accurate specification development, and informed procurement decisions across international markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the centrifugal monoblock pump Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Centrifugal Monoblock Pump Sector
The centrifugal monoblock pump market continues to evolve as industrial buyers across the USA and Europe face shifting priorities around efficiency, sustainability, and supply chain resilience. Understanding these dynamics is essential for procurement professionals and engineers making strategic sourcing decisions.
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
The centrifugal monoblock pump sector benefits from the integrated design advantages these units offer—combining motor and pump in a single casing eliminates separate assembly requirements and reduces installation complexity. This compact configuration has driven adoption across multiple industries:
| Industry Sector | Primary Applications | Growth Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems | Water scarcity management, precision farming |
| Manufacturing | Fluid transfer, process systems | Automation, operational efficiency |
| HVAC | Building systems, chilled water | Green building standards, retrofits |
| Wastewater | Treatment facilities | Infrastructure modernization |
| Oil & Gas | Processing operations | Upstream/downstream optimization |
Key Sourcing Trends
1. Energy Efficiency Standards
European ErP (Energy-related Products) directives and US DOE regulations are pushing manufacturers toward higher-efficiency motor designs. Buyers should prioritize IE3/IE4-rated motors to ensure regulatory compliance and reduce total cost of ownership.
2. Supply Chain Diversification
Post-pandemic sourcing strategies now emphasize:
– Regional manufacturing partnerships
– Dual-supplier arrangements for critical components (impellers, shafts, casings)
– Inventory buffer strategies for high-turnover SKUs
3. Material Innovation
Corrosion-resistant alloys and advanced polymer composites are gaining traction for applications involving aggressive fluids, extending service life and reducing maintenance cycles.
Sustainability Considerations
Procurement teams increasingly evaluate suppliers against environmental criteria:
- Lifecycle assessment data for pump systems
- Recyclability of pump components at end-of-life
- Manufacturing carbon footprint transparency
- Variable frequency drive (VFD) compatibility for demand-based operation
Historical Context
The monoblock pump design emerged as a response to industrial demands for simplified installation and reduced footprint. The integration of motor and pump into a single unit eliminated coupling alignment issues inherent in traditional centrifugal pump configurations, making these systems particularly valuable where space constraints and maintenance accessibility are priorities.
Procurement Recommendations
| Priority | Action Item |
|---|---|
| Compliance | Verify motor efficiency ratings meet regional standards |
| TCO Analysis | Calculate energy costs over 10-year operational horizon |
| Supplier Vetting | Assess manufacturing locations and lead time reliability |
| Sustainability | Request environmental product declarations (EPDs) |
Understanding these market dynamics positions B2B buyers to negotiate effectively and select centrifugal monoblock pump solutions aligned with both operational requirements and organizational sustainability objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of centrifugal monoblock pump
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
1. What is a centrifugal monoblock pump, and how does it differ from a standard centrifugal pump?
A centrifugal monoblock pump integrates the motor and pump into a single compact unit within one casing. Unlike standard centrifugal pumps that require separate motor and pump assembly with coupling alignment, monoblock pumps eliminate this complexity. The motor connects directly to the pump impeller, reducing footprint, simplifying installation, and minimizing potential points of failure.
| Feature | Standard Centrifugal Pump | Centrifugal Monoblock Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Separate motor and pump | Integrated single unit |
| Installation | Requires alignment | Plug-and-play |
| Footprint | Larger | Compact |
| Maintenance | More complex | Simplified |
2. What industries and applications are centrifugal monoblock pumps best suited for?
Centrifugal monoblock pumps serve diverse B2B applications:
- Agriculture: Irrigation systems and water transfer
- Manufacturing: Process fluid handling and coolant circulation
- HVAC Systems: Chilled water and heating circulation
- Water Treatment: Municipal and industrial wastewater management
- Commercial Buildings: Pressure boosting and water supply
- Oil & Gas: Non-critical fluid transfer operations
3. What are the key specifications B2B buyers should evaluate before procurement?
Critical specifications to assess include:
- Flow rate (m³/h or GPM): Match to your system’s demand
- Head pressure (meters or feet): Ensure adequate lift for your application
- Motor power (kW or HP): Verify electrical compatibility
- Inlet/outlet size: Confirm piping compatibility
- Material of construction: Stainless steel, cast iron, or engineered polymers based on fluid characteristics
- Voltage and frequency: 50Hz/60Hz, single-phase or three-phase requirements
- IP rating: Environmental protection level for your installation conditions
4. What are the primary advantages of monoblock pumps for commercial and industrial operations?
Operational Benefits:
– Reduced installation time and labor costs
– Lower maintenance requirements due to fewer components
– Space efficiency for constrained installations
– No coupling alignment issues, reducing downtime risk
– Simplified spare parts inventory management
Cost Benefits:
– Lower total cost of ownership
– Reduced energy losses from direct motor-pump connection
– Decreased maintenance frequency and associated costs
5. What maintenance considerations should procurement teams factor into TCO calculations?
Key maintenance factors affecting total cost of ownership:
| Maintenance Item | Typical Frequency | Impact on TCO |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical seal inspection | Every 6-12 months | Medium |
| Bearing lubrication | Per manufacturer specs | Low |
| Impeller wear assessment | Annually | Medium-High |
| Motor winding inspection | Every 2-3 years | Medium |
| Complete overhaul | 5-7 years | High |
Monoblock designs typically reduce maintenance labor by 20-30% compared to coupled pump systems due to integrated construction.
6. How do we determine the correct pump sizing for our application?
Proper sizing requires these data points:
- Required flow rate at peak and normal operating conditions
- Total dynamic head (TDH): Static lift + friction losses + discharge pressure
- Fluid properties: Viscosity, temperature, specific gravity, solids content
- Suction conditions: NPSH available vs. NPSH required
- Duty cycle: Continuous, intermittent, or variable operation
Request pump curves from suppliers and verify the best efficiency point (BEP) aligns with your operating conditions. Operating within 80-110% of BEP optimizes efficiency and longevity.
7. What certifications and compliance standards should B2B buyers verify?
Ensure suppliers provide documentation for applicable standards:
- CE Marking: Required for European market compliance
- UL/CSA Certification: North American electrical safety
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems
- ISO 2858/5199: Dimensional and performance standards for centrifugal pumps
- ATEX/IECEx: For hazardous environment installations
- NSF/ANSI 61: Potable water applications
- API 610: For oil and gas sector specifications
8. What warranty terms and after-sales support should buyers negotiate?
Standard B2B procurement should secure:
- Warranty period: Minimum 12-24 months from commissioning
- Coverage scope: Manufacturing defects, material failures, performance guarantees
- Spare parts availability: Confirmed stock for critical components (seals, bearings, impellers)
- Technical support: Response time SLAs for troubleshooting
- On-site service: Commissioning support and emergency repair availability
- Training: Operator and maintenance personnel training programs
- Documentation: Complete technical manuals, installation guides, and maintenance schedules
Request references from existing customers in similar applications to validate supplier reliability and support quality.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for centrifugal monoblock pump
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion: Centrifugal Monoblock Pumps
Centrifugal monoblock pumps represent a strategic investment for organizations prioritizing operational efficiency, space optimization, and reduced total cost of ownership. Their integrated motor-pump design delivers measurable advantages:
Key Value Drivers:
– Simplified procurement — Single-unit sourcing eliminates component matching complexity
– Reduced installation costs — No separate motor-pump assembly required
– Lower maintenance burden — Fewer components mean streamlined service protocols
– Space efficiency — Compact footprint suits constrained industrial environments
Market Outlook
The centrifugal monoblock pump sector continues evolving with:
– Enhanced energy-efficient motor integrations meeting IE3/IE4 standards
– Smart monitoring capabilities for predictive maintenance
– Expanded material options addressing corrosive and high-temperature applications
Sourcing Recommendations
| Priority | Action |
|---|---|
| Short-term | Audit current pump inventory for consolidation opportunities |
| Mid-term | Establish supplier partnerships with technical support capabilities |
| Long-term | Integrate IoT-enabled units into asset management systems |
For procurement teams across agriculture, manufacturing, HVAC, and water management sectors, centrifugal monoblock pumps offer a proven, cost-effective solution. Prioritize suppliers demonstrating application expertise, comprehensive warranty coverage, and regional service networks to maximize return on investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.