The global laser market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand across industrial, construction, and electronics applications. According to Grand View Research, the global laser market size was valued at USD 13.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% from 2023 to 2030. A key contributor to this growth is the rising adoption of precision tools in construction and surveying, where ceiling level lasers play a critical role in ensuring accuracy and efficiency. Mordor Intelligence projects a similar upward trajectory, highlighting the construction sector’s digital transformation and automation as major growth catalysts. As demand for high-accuracy alignment tools intensifies, manufacturers of ceiling level lasers are innovating rapidly to meet evolving industry standards. In this competitive landscape, the top six ceiling level laser manufacturers stand out for their technological advancements, product reliability, and global market reach.
Top 6 Ceiling Level Laser Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
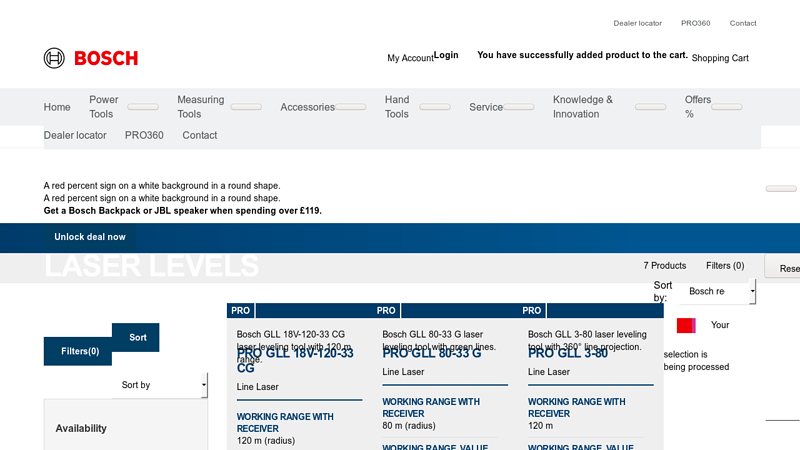
#1 Laser levels Measuring technology
Domain Est. 2008
Website: bosch-professional.com
Key Highlights: Laser levels | Precise lines with high visibility for the professional user. Fast horizontal and vertical alignment of lines: Effortless and highly precise ……
#2 PM 40
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hilti.com
Key Highlights: $31 delivery 28-day returnsMulti-line laser with 3 green lines for plumbing, leveling, aligning and squaring. Accuracy: ±0.08 in at 33 ft; Max. operating distance (diameter): 131 f…
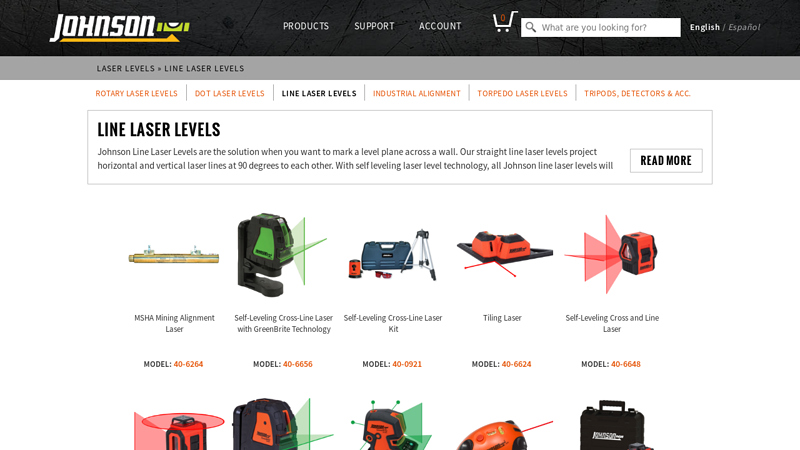
#3 Line Laser Levels
Domain Est. 1997
Website: johnsonlevel.com
Key Highlights: Johnson Line Laser Levels are the solution when you want to mark a level plane across a wall. Our straight line laser levels project horizontal and vertical ……
#4 PLS 180R Laser Level
Domain Est. 1999
Website: plslaser.com
Key Highlights: The PLS 180 R is a professional self-leveling cross line laser level equipped for multiple applications including wall construction, acoustic ceiling ……
#5 CHAUVET Professional
Domain Est. 2010
Website: chauvetprofessional.com
Key Highlights: CHAUVET Professional ; Featured Story Color Strike M Sets Mood For Ilario Alicante, at Unique Milanese Venue ; Product Spotlight STRIKE Saber 10 ; Featured Video ……
#6 Ceiling Laser Level
Domain Est. 2014
Website: dovoh.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery Free 30-day returnsCeiling Laser Level ; Floor Laser Level 4×360°- Dovoh K4-360G · $179.99 · $179.99 · 4.88 / 5.0. 109 Reviews ; Ultra-Bright Outdoor Laser Level 3×36…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ceiling Level Laser

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ceiling Level Lasers
The global market for ceiling level lasers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in construction technology, increased demand for precision in building projects, and the growing adoption of smart building systems. These lasers, which are primarily used for alignment, leveling, and layout applications in commercial and residential construction, are evolving rapidly due to integration with digital tools and automation.
One of the dominant trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the integration of ceiling level lasers with Building Information Modeling (BIM) and augmented reality (AR) platforms. Contractors and architects are increasingly relying on digital workflows, and ceiling lasers that can sync with 3D models enable real-time layout projection directly onto work surfaces. This trend enhances accuracy, reduces rework, and improves overall project efficiency.
Another key development is the miniaturization and enhanced durability of laser units. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to offer more compact, lightweight, and rugged ceiling lasers designed for ease of use in challenging environments. Improved battery life and wireless connectivity (e.g., Bluetooth and Wi-Fi) allow remote control via mobile apps, enabling a single operator to manage multiple layout tasks with minimal setup time.
Sustainability and energy efficiency are also influencing product design. With green building certifications like LEED gaining prominence, equipment manufacturers are focusing on energy-efficient components and recyclable materials in laser construction. Additionally, the trend toward rental and equipment-as-a-service (EaaS) models is gaining traction, especially among small and mid-sized contractors looking to access high-end ceiling lasers without large capital investments.
Regionally, the Asia-Pacific market is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. Meanwhile, North America and Western Europe will maintain strong demand, fueled by renovation projects and stringent building codes requiring precise installation techniques.
In summary, by 2026, the ceiling level laser market will be characterized by smarter, more connected, and user-centric tools. The convergence of digital construction technologies, sustainability demands, and evolving business models will define the competitive landscape, favoring innovators who can deliver integrated, efficient, and scalable laser solutions.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ceiling Level Lasers (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing ceiling level lasers for industrial applications—such as alignment, grading, or positioning—requires careful evaluation of both quality and intellectual property (IP) factors. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, legal risks, and long-term cost overruns. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Durability
Many low-cost ceiling level lasers are constructed with substandard materials and lack rigorous testing. This results in premature failure, inconsistent beam accuracy, and susceptibility to environmental factors like vibration or temperature shifts—common in industrial environments.
Inadequate Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
One of the most frequent oversights is selecting a laser without an appropriate IP rating. Ceiling-mounted units may be exposed to dust, moisture, or cleaning processes. Lasers with insufficient IP ratings (e.g., below IP54) risk internal contamination, leading to calibration drift or complete failure.
Misrepresentation of IP Certification
Some suppliers falsely claim high IP ratings without independent verification. Always request certified test reports from accredited labs. Lasers that are merely “designed to meet” an IP standard—without formal certification—pose a significant reliability risk.
Lack of Thermal and Mechanical Stability
Low-quality lasers often lack proper thermal management and shock resistance. In ceiling installations, ambient temperature fluctuations and building vibrations can degrade alignment accuracy over time. High-quality units incorporate temperature compensation and robust mounting systems.
Insufficient Beam Visibility and Range
Cheaper models may emit dim or inconsistent laser beams, especially in well-lit or large spaces. This undermines usability and safety. Ensure the laser meets required visibility and range specifications for your application, and verify performance under real-world conditions.
Hidden IP Infringement Risks
Using lasers that incorporate patented technologies—such as specific optical designs, calibration methods, or software algorithms—without proper licensing can expose your company to legal action. This is especially critical when sourcing from generic manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement.
Reliance on Unverified OEMs or Copycat Products
Some suppliers rebrand or clone established laser systems without authorization. These products may mimic appearance but lack performance reliability and technical support. They also carry high IP infringement risks and are often unsupported in the long term.
Absence of Regulatory Compliance Documentation
Ensure the laser complies with relevant safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards (e.g., FDA/CDRH in the US, IEC 60825 internationally). Missing or falsified compliance documentation can delay projects and create liability issues.
No Long-Term Support or Calibration Services
Low-cost suppliers may disappear or offer no calibration, repair, or spare parts. Ceiling level lasers require periodic recalibration to maintain accuracy. Source from vendors with proven service networks and accessible technical support.
Overlooking Software and Firmware IP
Modern lasers often include proprietary firmware for self-leveling, remote control, or integration with other systems. Unauthorized use or reverse engineering of such software violates copyright and licensing agreements, potentially resulting in legal and operational consequences.
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: verify certifications, test units under real conditions, audit supplier credentials, and consult legal experts when IP concerns arise. Prioritize quality, compliance, and long-term support over initial cost savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ceiling Level Laser
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal handling, transportation, installation, and operation of Ceiling Level Laser systems.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to all applicable international, national, and local regulations governing laser devices. Key standards include:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10/1040.11: U.S. regulations for laser products, including mandatory reporting and labeling.
– CE Marking Requirements: Compliance with the EU’s Laser Products Directive (2014/53/EU) and relevant health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– RoHS & REACH: Confirm that materials used in the laser system comply with restrictions on hazardous substances.
All Ceiling Level Laser units must be properly classified (typically Class 1, 1M, 2, or 2M depending on design) and carry required warning labels and user information.
Transportation & Handling
- Packaging: Ship units in manufacturer-approved, anti-static, and shock-resistant packaging to prevent damage during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and laser classification labels as required. Include handling instructions and hazard symbols where applicable.
- Temperature & Humidity: Maintain storage and transport conditions within the specified range (typically 0°C to 40°C, 10% to 80% non-condensing humidity).
- Battery Safety (if applicable): If the unit includes rechargeable batteries, comply with IATA/IMDG/ADR regulations for lithium battery transport.
Import & Export Documentation
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of conformity.
- Obtain necessary export licenses if required based on destination country and laser classification.
- Confirm compliance with customs regulations, including tariff codes (e.g., HS Code 9013.20 for laser devices).
- Provide technical specifications and safety documentation to facilitate customs clearance.
Installation & Site Compliance
- Qualified Personnel: Installation must be performed by trained technicians familiar with laser safety and electrical codes.
- Height & Clearance: Install at the specified ceiling height with unobstructed line-of-sight as per operational requirements.
- Electrical Safety: Ensure proper grounding and compliance with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC standards internationally).
- Safety Interlocks: Verify that safety features (e.g., motion sensors, automatic shutoff) are functional.
- Warning Signs: Post appropriate laser warning signs in visible locations near installation zones.
Operational Safety & Training
- Conduct laser safety training for all personnel involved in operation or maintenance.
- Provide operators with safety manuals, emergency procedures, and personal protective equipment (PPE) if needed.
- Restrict access to authorized personnel only during operation.
- Perform routine safety checks and maintain a log of inspections and maintenance.
Maintenance & Servicing
- Schedule regular preventive maintenance per manufacturer guidelines.
- Use only authorized replacement parts and service tools.
- Deactivate and lock out the laser during servicing.
- Maintain records of all servicing, repairs, and safety audits for compliance reporting.
Disposal & End-of-Life
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives for proper recycling.
- Handle laser components (especially optical and electronic modules) as e-waste.
- Document disposal procedures and obtain certificates from certified recyclers.
Adhering to this guide ensures regulatory compliance, promotes workplace safety, and supports efficient logistics throughout the lifecycle of Ceiling Level Laser systems.
Conclusion on Sourcing Ceiling-Level Lasers
In conclusion, sourcing ceiling-level lasers requires a strategic approach that balances technical requirements, safety standards, budget constraints, and long-term usability. These specialized lasers are essential for applications such as indoor positioning, architectural alignment, automation, and laser guidance systems, where precision at elevated levels is critical.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include beam visibility, mounting compatibility, alignment accuracy, durability in various environmental conditions, and compliance with laser safety regulations (such as IEC 60825). Evaluating both established industrial suppliers and emerging technology providers ensures access to reliable, innovative solutions.
Opting for reputable manufacturers with proven track records in precision laser technology can minimize maintenance issues and enhance system reliability. Additionally, integrating features like self-leveling mechanisms, remote control, and wireless connectivity can significantly improve operational efficiency.
Ultimately, successfully sourcing ceiling-level lasers involves thorough due diligence, clear specification of project needs, and collaboration with suppliers who offer technical support and quality assurance. Making informed decisions in the procurement phase will result in improved performance, safety, and return on investment across the intended application.