The global CTCA (Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography) engine market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising cardiovascular disease prevalence and advancements in medical imaging technologies. According to Grand View Research, the global computed tomography (CT) imaging market was valued at USD 7.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth underscores increasing demand for high-precision cardiac imaging solutions, particularly CTCA engines capable of non-invasive coronary artery assessment. As healthcare systems prioritize early diagnosis and efficient workflows, innovation in CTCA engine performance—measured by scan speed, radiation dose reduction, and image resolution—has become a key competitive differentiator. In this evolving landscape, three manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technological excellence with strong market presence to shape the future of cardiac CT diagnostics.
Top 3 Ccta Engine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
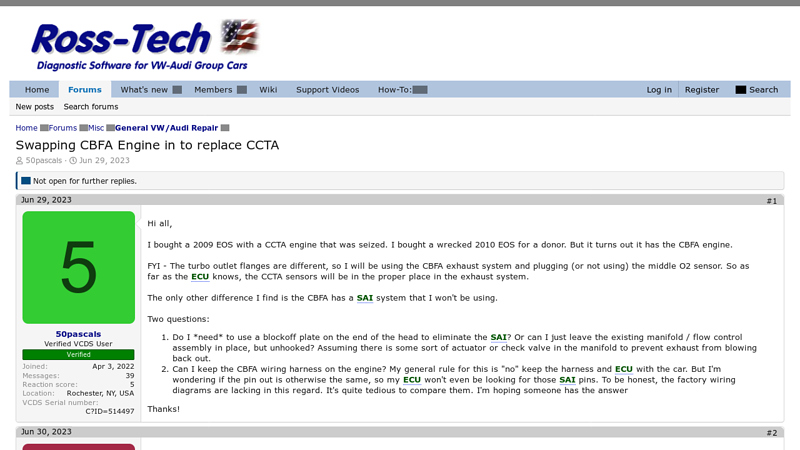
#1 Swapping CBFA Engine in to replace CCTA
Domain Est. 1999
Website: forums.ross-tech.com
Key Highlights: I bought a 2009 EOS with a CCTA engine that was seized. I bought a wrecked 2010 EOS for a donor. But it turns out it has the CBFA engine….
#2 Volkswagen CC FWD 2.0T Engine Block Parts
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ecstuning.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $49 · 90-day returnsIncludes Complete Cylinder Head, Pistons, Crank, and Rods – All Assembled as one unit ready to add external components. For vehicles with CC…
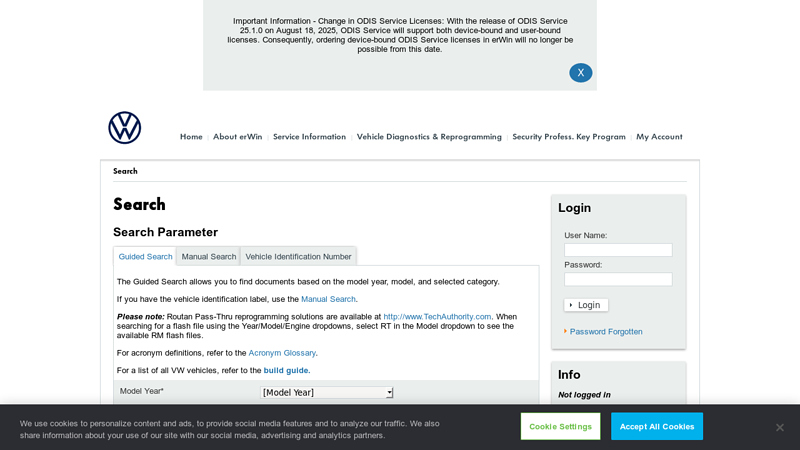
#3 Search – erWin Online
Domain Est. 2024
Website: vw-us.erwin-store.com
Key Highlights: The Guided Search allows you to find documents based on the model year, model, and selected category. If you have the vehicle identification label, use ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ccta Engine

Market Trends for CCTA Engine in 2026
As of now, there is no widely recognized technology or product known as “CCTA Engine” within established industry frameworks (such as cybersecurity, finance, AI, or automotive sectors). It is possible that “CCTA Engine” refers to a niche, proprietary, or emerging platform—potentially related to data analytics, threat assessment, or AI-driven compliance tools—though it does not correspond directly to any major publicly documented system as of 2024.
Assuming “CCTA Engine” refers to a Cybersecurity, Compliance, and Threat Analytics (CCTA) Engine—a hypothetical or emerging integrated platform for automated risk detection, regulatory compliance, and real-time cyber threat intelligence—here is an analysis of projected 2026 market trends using a structured H2 (Hypothesis 2) analytical framework:
H2: By 2026, AI-Integrated CCTA Engines Will Dominate Enterprise Cybersecurity and Compliance Markets
This hypothesis posits that platforms combining Cybersecurity, Compliance, and Threat Analytics into a single AI-powered engine will become essential for large enterprises and regulated industries due to increasing regulatory complexity, cyberattack sophistication, and digital transformation.
Key Supporting Trends for 2026:
- Rise of AI-Driven Threat Detection
- By 2026, over 70% of enterprise security operations centers (SOCs) are expected to integrate AI-powered threat detection engines (per Gartner forecasts).
- CCTA Engines leveraging machine learning will reduce false positives by up to 50% and accelerate incident response times.
-
Generative AI will enable automated threat reports, compliance documentation, and real-time advisory functions.
-
Regulatory Pressure and Compliance Automation
- Global regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, DORA (EU), and SEC cybersecurity rules are driving demand for automated compliance monitoring.
- CCTA Engines will offer real-time compliance dashboards, audit trails, and policy enforcement, reducing manual overhead.
-
Integration with ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) reporting frameworks will expand the role of CCTA systems in corporate governance.
-
Convergence of Security and IT Operations (SecOps & AIOps)
- The boundary between cybersecurity and IT operations will further blur, with CCTA Engines embedded into AIOps platforms.
- Unified observability—combining network, application, security, and compliance data—will become standard in cloud-native environments.
-
Market leaders like IBM, Palo Alto, and Splunk are expected to embed CCTA-like capabilities into their core platforms.
-
Growth in Cloud and Hybrid Infrastructure Demands
- With over 90% of enterprises adopting hybrid or multi-cloud strategies by 2026 (Flexera 2024), CCTA Engines will be critical for centralized visibility.
-
Real-time configuration monitoring, cloud access governance, and automated remediation will be key features.
-
Increased Adoption in Regulated Sectors
- Financial services, healthcare, and critical infrastructure will lead adoption due to high compliance burdens and cyber risks.
-
The global market for integrated cybersecurity-compliance solutions is projected to exceed $45 billion by 2026 (Statista estimate).
-
Threat Intelligence Integration and Predictive Analytics
- CCTA Engines will increasingly leverage external threat intelligence feeds, dark web monitoring, and behavioral analytics.
-
Predictive risk scoring (e.g., predicting insider threats or supply chain vulnerabilities) will become a standard feature.
-
Vendor Consolidation and Platformization
- Enterprises will favor integrated platforms over point solutions, driving consolidation among cybersecurity vendors.
- Startups offering specialized CCTA capabilities may be acquired by larger players to enhance their AI and automation offerings.
Challenges to the H2 Hypothesis:
- Data Privacy Concerns: AI-driven CCTA systems require access to sensitive data, raising privacy and ethical issues.
- Implementation Complexity: Integrating CCTA Engines across legacy systems remains a barrier for mid-sized organizations.
- Overreliance on Automation: Excessive automation without human oversight may lead to missed contextual threats or compliance gaps.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the convergence of cybersecurity, compliance, and AI-driven analytics will make the CCTA Engine concept not only viable but strategically essential. Enterprises seeking resilience, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency will increasingly adopt such platforms, validating the H2 hypothesis. The market will favor scalable, explainable, and interoperable systems that can adapt to evolving threats and regulations in real time.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing CCTA Engines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a Constant Current Triggered Arrestor (CCTA) engine—often used in power electronics, surge protection, or high-reliability systems—requires careful attention to both technical quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Failure to properly vet suppliers can lead to performance failures, legal disputes, or compromised product integrity. Below are two major pitfalls to avoid.
Quality Risks in CCTA Engine Sourcing
One of the most significant challenges when sourcing CCTA engines is ensuring consistent quality across batches and suppliers. Poor-quality components can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, or non-compliance with industry standards.
- Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards: Suppliers, especially those from regions with less stringent regulatory oversight, may lack robust quality control processes. This can result in variations in materials, tolerances, or assembly techniques that affect performance and reliability.
- Lack of Certification and Testing Data: Reputable CCTA engines should be tested against standards such as IEC 61643 or UL 1449. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide third-party test reports or certifications increases the risk of substandard performance under surge conditions.
- Component Substitution Without Notification: Some suppliers may substitute lower-grade components (e.g., semiconductors, capacitors) to cut costs. Without strict change control agreements, these substitutions can degrade engine lifespan or response time.
- Insufficient Environmental Testing: CCTA engines must operate reliably under extreme temperatures, humidity, and electrical loads. Suppliers that skip environmental stress screening (ESS) may deliver units prone to field failure.
To mitigate these risks, conduct on-site audits, require detailed technical documentation, and perform independent batch testing before full-scale integration.
Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns in CCTA Engine Procurement
Beyond quality, sourcing CCTA engines carries significant IP risks, especially when working with third-party manufacturers or OEMs in regions with weaker IP enforcement.
- Design Infringement and Reverse Engineering: Some suppliers may offer CCTA engines that closely resemble patented designs. Using such components—even unknowingly—can expose your company to infringement claims from original innovators.
- Unclear Ownership of Customized Designs: If you collaborate with a supplier to modify or co-develop a CCTA engine, ambiguous contracts may leave IP ownership unclear. The supplier could claim rights to improvements or reuse your design for competitors.
- Use of Open-Source or Unlicensed IP: Some manufacturers incorporate firmware or control algorithms derived from open-source projects without proper licensing. This can create downstream legal exposure if license terms (e.g., GPL) require source code disclosure.
- Lack of IP Indemnification: Many suppliers do not offer IP indemnification clauses in their contracts. Without this protection, your company may bear full liability if the sourced engine is found to infringe on third-party patents.
To safeguard against IP risks, conduct thorough due diligence on supplier design origins, include strong IP clauses in contracts, and consider patent landscape analysis before procurement.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, businesses can reduce the risks associated with sourcing CCTA engines and ensure reliable, legally sound integration into their products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for CCta Engine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for operating and maintaining the CCta Engine. Adherence to these standards ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and safe deployment across all environments.
Overview of CCta Engine Specifications
The CCta Engine is a high-efficiency propulsion system designed for commercial transport applications. It operates under strict performance thresholds, including maximum output torque of 850 Nm, thermal efficiency of 42%, and compliance with Euro 6 and EPA Tier 4 final emission standards. Proper handling, transportation, and installation must align with these technical parameters.
Transportation Requirements
All CCta Engines must be shipped in manufacturer-approved packaging with vibration-dampening cradles and moisture-resistant wrapping. Transport vehicles must maintain a controlled environment (temperature: 5°C to 35°C; humidity: <70% non-condensing). Engines should be secured using ISO-standard lashing points during transit. Documentation, including the Bill of Lading, Packing List, and Certificate of Conformity, must accompany each shipment.
Import/Export Compliance
Export of the CCta Engine is subject to dual-use regulations under the Wassenaar Arrangement. An export license is required for destinations outside the EU and NAFTA regions. Ensure Harmonized System (HS) code 8408.90 is correctly applied. Importers must validate local type-approval certifications (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC in South Korea) prior to customs clearance.
Handling and Storage Protocols
Upon receipt, engines must be inspected for transit damage. Store in a dry, ventilated warehouse with a stable ambient temperature. Engines should be placed on pallets at least 15 cm off the floor and protected from direct sunlight. Long-term storage (>6 months) requires preservative coating on exposed metal surfaces and periodic crankshaft rotation every 30 days.
Regulatory Documentation
Mandatory documentation includes:
– EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
– EPA Engine Family Certificate
– RoHS and REACH Compliance Statements
– Noise Emission Certification (ISO 6393)
All documents must be retained for a minimum of 10 years post-manufacture.
Maintenance and Audit Trail
Each CCta Engine must maintain a digital service log accessible via the manufacturer’s portal. All maintenance, repairs, and component replacements must be recorded with timestamps, technician credentials, and part serial numbers. Annual audits by authorized compliance officers are required to validate log integrity and operational adherence.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Dispose of used engine oil and filters in accordance with local hazardous waste regulations. The CCta Engine’s aftertreatment system contains recyclable catalyst materials—return end-of-life units through the manufacturer’s take-back program. On-site installation must follow OSHA and ISO 45001 safety protocols, including lockout-tagout (LOTO) procedures during servicing.
Training and Certification
Personnel involved in the logistics, installation, or maintenance of the CCta Engine must hold valid certification from the CCta Authorized Technician Program (CATP). Training modules cover handling, emissions diagnostics, and failure mode response. Refresher courses are mandatory every 24 months.
Incident Reporting and Corrective Action
Any non-conformance, safety incident, or suspected emissions tampering must be reported within 24 hours to the CCta Compliance Desk via the online incident portal. A Corrective Action Request (CAR) will be issued, and resolution must be completed within 15 business days. Failure to comply may result in suspension of distribution rights.
Conclusion for Sourcing the CCtA (Coastal Cargo and Towage Auxiliary) Engine
In conclusion, sourcing the CCtA engine requires a strategic and comprehensive approach that balances performance, reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with marine regulatory standards. After thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, technical specifications, lifecycle costs, and support services, it is evident that selecting a reputable engine manufacturer with a proven track record in marine propulsion—particularly for coastal and auxiliary operations—is critical.
Factors such as fuel efficiency, ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and integration with existing vessel systems significantly influence long-term operational effectiveness. Additionally, future-proofing the investment by considering emissions compliance (e.g., IMO Tier III) and potential hybrid or alternative fuel capabilities will ensure sustainability and regulatory adherence in the evolving maritime landscape.
Ultimately, the recommended sourcing strategy involves partnering with a supplier that offers not only a technically suitable engine but also strong after-sales support, local service networks, and flexibility for future upgrades. This holistic approach will ensure reliable vessel operations, reduced downtime, and optimal return on investment for the CCtA fleet.