The global clinical laboratory equipment market, driven by rising demand for accurate and rapid diagnostic tools, is witnessing robust growth—projected to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. Within this landscape, Complete Blood Count (CBC) test machines have emerged as critical components in routine medical diagnostics, supporting early detection of conditions such as anemia, infections, and blood cancers. With increasing healthcare infrastructure development and a growing emphasis on preventive medicine, the CBC analyzer segment is experiencing heightened adoption across hospitals, diagnostic centers, and point-of-care facilities. As demand surges, several manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, reliability, and automation. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and industry performance metrics, the following seven companies represent the leading forces shaping the future of CBC testing worldwide.
Top 7 Cbc Test Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
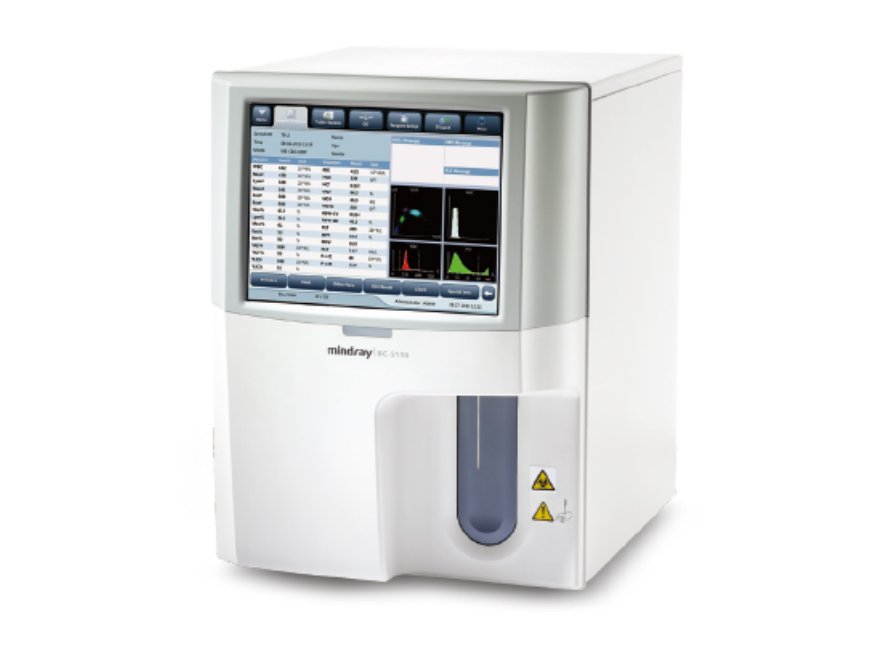
#1 Mindray
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mindray.com
Key Highlights: As a medical equipment and solutions supplier with a deep focus on healthcare, Mindray strives to develop and share medical technologies and devotes to ……
#2 Hematology Analyzer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: genrui-bio.com
Key Highlights: Genrui Hematology machines come with advanced capabilities and can process hundreds of samples accurately within a short span of time. Hematology lab tests ……
#3 CBC Machines
Domain Est. 1995
Website: henryschein.com
Key Highlights: Shop & browse Henry Schein medical for Hematology analyzers from various high quality brands such as Abbott and Beckman Coulter….
#4 ProCyte Dx Veterinary CBC Hematology Analyzer
Domain Est. 1995
Website: idexx.com
Key Highlights: The ProCyte Dx Veterinary Hematology Analyzer gives the most comprehensive CBC (complete blood count) available in veterinary medicine….
#5 Hematology Analyzers & Systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sysmex.com
Key Highlights: Our automated cell image analysis systems offer hematology labs of all sizes improved consistency of cell identification, efficient resource utilization….
#6 Beckman Coulter Diagnostics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: beckmancoulter.com
Key Highlights: Beckman Coulter Diagnostics helps healthcare professionals provide better patient care by delivering the accurate diagnostic information they need….
#7 HemoScreen
Domain Est. 2010
Website: pixcell-medical.com
Key Highlights: Fast automatic blood count sample results. A 5-part complete blood test (CBC) analyzer machine. HemoScreen FDA approved – simple blood tester….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cbc Test Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for CBC Test Machines
The market for Complete Blood Count (CBC) test machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in diagnostic technologies, rising demand for point-of-care (POC) testing, and growing global focus on early disease detection. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the CBC test machine industry in 2026:
-
Expansion of Point-of-Care Testing
By 2026, CBC test machines are increasingly being deployed in decentralized healthcare settings such as clinics, pharmacies, and even home environments. Portable and handheld CBC analyzers are gaining traction due to their rapid turnaround time and ease of use. This shift is fueled by the need for immediate diagnostic results in emergency care, rural healthcare, and pandemic preparedness. -
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI-powered CBC machines are emerging as a dominant trend, enabling automated sample analysis, error reduction, and predictive diagnostics. Machine learning algorithms improve accuracy by identifying abnormal blood cell patterns and flagging potential conditions like anemia, infections, or leukemia. Fully automated systems reduce manual intervention, enhancing throughput in high-volume laboratories. -
Growth in Emerging Economies
Developing regions in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to witness robust growth in the CBC test machine market. Increased healthcare spending, government initiatives for universal health coverage, and rising prevalence of infectious and chronic diseases are driving demand. Local manufacturing and cost-effective models are making CBC technology more accessible. -
Focus on Multiplexing and Comprehensive Diagnostics
Next-generation CBC machines are integrating additional biomarker testing capabilities beyond standard hematology parameters. Devices that combine CBC with inflammatory markers, coagulation profiles, or glucose levels offer holistic patient assessments. This trend supports value-based care models that prioritize comprehensive diagnostics in fewer tests. -
Regulatory Advancements and Standardization
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and CE are streamlining approvals for innovative CBC devices, particularly those used in POC settings. Harmonization of global standards ensures device reliability, interoperability, and data security—critical factors for integration into electronic health records (EHRs) and telemedicine platforms. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Design
Manufacturers are prioritizing sustainability by developing CBC machines with reduced reagent consumption, longer-lasting components, and recyclable materials. Energy-efficient designs and cartridge-based systems minimizing biohazard waste are becoming competitive differentiators. -
Impact of Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
The convergence of CBC testing with digital health platforms allows remote result sharing with healthcare providers. In 2026, patients in home or community settings can perform CBC tests with connected devices, transmitting data securely for virtual consultations—enhancing chronic disease management and preventive care.
In summary, the 2026 CBC test machine market is characterized by innovation, accessibility, and integration. As healthcare systems prioritize speed, accuracy, and patient-centric care, CBC technology will play a pivotal role in transforming diagnostic pathways worldwide.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a CBC Test Machine: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test machine, especially from overseas or less-regulated markets, presents several critical risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these pitfalls is essential to ensure patient safety, regulatory compliance, and long-term business success.
Compromised Quality and Regulatory Non-Compliance
One of the most significant risks when sourcing CBC analyzers is receiving machines that do not meet international performance and safety standards. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners in materials, manufacturing processes, or calibration, resulting in:
- Inaccurate test results: Poorly calibrated or substandard sensors can lead to false diagnoses, endangering patient health and exposing healthcare providers to liability.
- Lack of regulatory certification: Machines may not comply with essential standards such as CE marking (Europe), FDA 510(k) clearance (USA), or ISO 13485 (quality management for medical devices). Using non-compliant devices can result in legal penalties and facility shutdowns.
- Unreliable after-sales support: Poor-quality suppliers often lack trained technical support, making maintenance, repairs, and software updates difficult or impossible, leading to prolonged downtime.
To mitigate this, always verify regulatory certifications, request third-party test reports, and conduct factory audits before committing to a supplier.
Intellectual Property Infringement and Counterfeit Devices
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of purchasing counterfeit or cloned CBC machines that infringe on patented technology. These devices may:
- Replicate branded designs and software: Imitation analyzers often copy the interface, functionality, and appearance of established brands without licensing the underlying technology, exposing buyers to legal risk.
- Use unauthorized software or algorithms: The hematological analysis algorithms in CBC machines are often proprietary. Unauthorized use can constitute IP theft and may lead to software instability or diagnostic errors.
- Lack proper licensing: Using an IP-infringing device may violate local laws and result in seizure of equipment, fines, or injunctions, especially in regulated healthcare environments.
To protect your organization, require suppliers to provide proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements, conduct due diligence on brand authenticity, and avoid unusually low-priced machines that seem too good to be true.
Hidden Costs from Poor Validation and Integration
Even if a CBC machine appears functional, hidden quality issues can emerge during integration and daily use:
- Incompatibility with LIS/HIS systems: Poorly documented APIs or non-standard data formats can prevent seamless integration with hospital information systems, increasing IT workload and operational delays.
- Lack of traceability and documentation: Inadequate manufacturing records or missing calibration certificates can complicate audits and regulatory inspections.
- Short product lifecycle: Low-cost machines may be discontinued quickly, leaving users without spare parts or software updates.
Always request full technical documentation, evaluate compatibility with existing infrastructure, and confirm long-term support availability before procurement.
By proactively addressing quality assurance and IP concerns, organizations can avoid costly mistakes and ensure they invest in reliable, legally compliant CBC testing solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for CBC Test Machine
Shipping and Handling Instructions
Ensure the CBC test machine is packaged in its original protective casing or an equivalent shock-resistant container. Use certified freight carriers with experience in medical equipment transport. Maintain the machine in an upright position during transit to prevent internal component damage. Climate-controlled shipping is required when ambient temperatures are expected to fall below 10°C (50°F) or exceed 40°C (104°F). Include desiccants in packaging to control moisture and attach handling labels indicating “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
Import and Export Compliance
Verify that the CBC test machine complies with the import regulations of the destination country, including registration with local health authorities (e.g., FDA in the U.S., CE marking in the EU, or CDSCO in India). Obtain necessary export licenses if shipping from a regulated jurisdiction, especially when the device contains sensitive technology. Ensure Harmonized System (HS) Code 9018.19.00 (for medical diagnostic instruments) is correctly declared on shipping documentation. Provide a Certificate of Conformity and technical specifications to customs authorities upon request.
Regulatory Documentation Requirements
Maintain a complete technical file including the Declaration of Conformity, User Manual, Software Version Log, and Risk Management File per ISO 14971. The device must be registered in the destination country’s medical device database prior to delivery. For U.S. shipments, include FDA Establishment Registration and Device Listing numbers. For EU shipments, ensure the CE Certificate issued by a Notified Body is current and provide an EU Representative contact. Retain all documentation for a minimum of 10 years post-discontinuation.
Installation and Site Readiness
Confirm that the installation site meets environmental requirements: stable power supply (100–240 V AC, 50/60 Hz), temperature range of 15–30°C, humidity between 20–80% non-condensing, and a clean, dust-free workspace. Ensure network connectivity for data transfer and LIS integration if applicable. Perform a site acceptance test (SAT) upon installation to verify operational integrity. Only trained biomedical engineers or manufacturer-certified technicians should conduct setup and calibration.
Post-Installation Compliance and Maintenance
Schedule routine maintenance as specified in the manufacturer’s service manual, typically every 6 months or after 10,000 tests. Keep a detailed service log documenting all repairs, calibrations, and software updates. Ensure the device remains compliant with IVD (In Vitro Diagnostic) regulations throughout its lifecycle. Report any adverse incidents or malfunctions to relevant regulatory bodies within required timelines (e.g., FDA MedWatch within 30 days). Retain records of quality control runs and preventive maintenance for audit purposes.
Conclusion for Sourcing a CBC Test Machine
After a thorough evaluation of available options, it is concluded that sourcing an automated Complete Blood Count (CBC) test machine is a strategic and necessary investment to enhance diagnostic efficiency, accuracy, and patient care. The selected CBC analyzer should meet key criteria including reliability, speed, ease of maintenance, regulatory compliance (such as FDA or CE marking), and compatibility with existing laboratory systems.
Based on the assessment of technical specifications, cost-effectiveness, vendor reputation, and after-sales support, the recommended CBC machine offers a balanced combination of high throughput, minimal reagent waste, user-friendly interface, and robust data management capabilities. This aligns with the laboratory’s operational needs and growth objectives.
Furthermore, integrating an in-house CBC testing system will reduce turnaround time, decrease reliance on external laboratories, and improve overall workflow efficiency. The long-term benefits—such as cost savings, improved diagnostic autonomy, and enhanced service quality—outweigh the initial investment.
It is therefore recommended to proceed with the procurement of the selected CBC analyzer, along with appropriate staff training and validation protocols, to ensure seamless implementation and sustained performance. Regular performance monitoring and preventive maintenance will be essential to maintain the machine’s reliability and diagnostic accuracy over time.