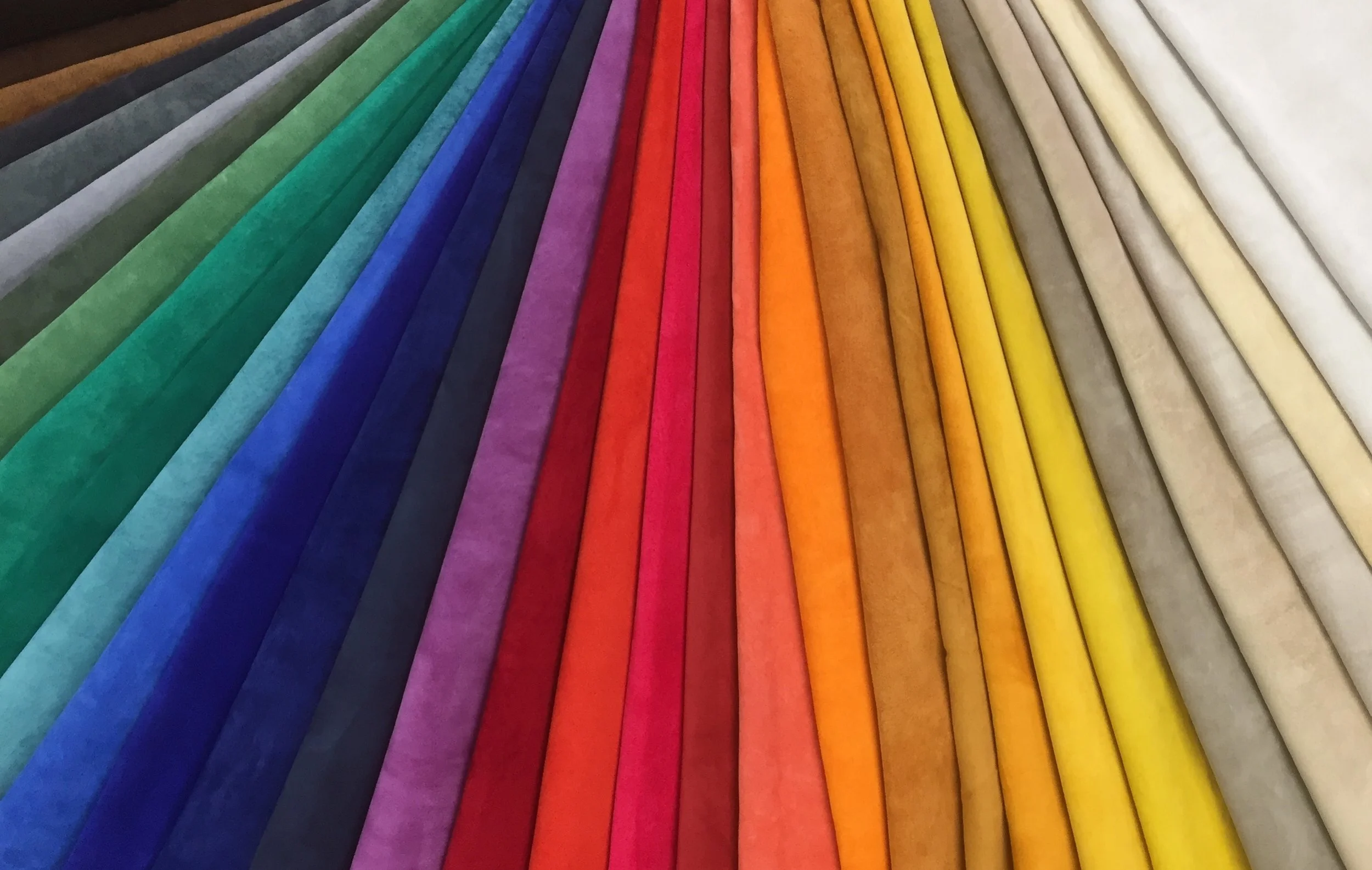
The global leather market, valued at USD 45.6 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.3% through 2030, driven by rising demand for high-quality, durable materials in fashion, automotive, and furniture industries (Grand View Research, 2023). Within this landscape, cattlehide leather remains the most dominant type, accounting for over 65% of total leather production due to its superior strength, texture, and versatility. As consumer preferences shift toward sustainable and traceable sourcing, leading manufacturers are investing in eco-friendly tanning technologies and vertical integration to meet stringent regulatory and ethical standards. This growing demand, coupled with innovations in processing and rising production in key regions like Asia-Pacific and South America, underscores the strategic importance of selecting proven cattlehide leather suppliers. Based on production capacity, global reach, quality certifications, and sustainability initiatives, here are the top 7 cattlehide leather manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 7 Cattlehide Leather Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CK International, Ltd. Pigskin Page
Domain Est. 2011
Website: ckinternationalltd.com
Key Highlights: Pigskin is economical and provides a cost-effective material for leather producers. … Cattle hide occupies the leather market share and the consumer mind space….
#2 Conceria Cervinia is Doing Business in Russia as Usual
Domain Est. 2022
Website: leave-russia.org
Key Highlights: In summer 2022, the military footwear manufacturer received 1.3 tons of cattle hide leather from Conceria Cervinia, based in Verona….
#3 Animal Hides For Leather Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bakercommodities.com
Key Highlights: Baker Commodities collects animal hides & prepares them for the companies who create leather products. Contact us if you need any leather products!…
#4 High
Domain Est. 2000
Website: montanaleather.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 30-day returns…
#5 COUNTRY COW
Domain Est. 2006
Website: aacrack.com
Key Highlights: In stockCountry Cow is a Vegetable Re-Tanned, heavy weight, waxy pull up leather. The hides are tanned within Europe on heavy Ox hides….
#6 Leather and Hide Council of America
Domain Est. 2019
Website: usleather.org
Key Highlights: The Leather & Hide Council of America represents the entire US leather and hide sector. We are a powerful voice for packers, processors, tanners, traders, ……
#7 Rolford Leather
Domain Est. 2012
Website: rolfordleather.com
Key Highlights: Discover our variety of high-quality leather hides at affordable prices available to buy online for immediate worldwide delivery….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cattlehide Leather
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cattlehide Leather
The global cattlehide leather market in 2026 is expected to navigate a complex landscape shaped by evolving consumer preferences, sustainability pressures, technological advancements, and shifting economic dynamics. While facing significant challenges, particularly from alternative materials, the market will likely see nuanced trends defining its trajectory.
1. Sustainability & Traceability as Core Imperatives:
* Heightened Scrutiny: Consumer and regulatory pressure will intensify regarding the environmental impact of livestock farming (deforestation, methane emissions, water usage) and tanning processes (chemical pollution). Brands will be forced to prioritize transparency.
* Demand for Provenance: “Traceability” will move from a niche concern to a mainstream expectation. Buyers will demand verifiable proof of ethical sourcing (e.g., deforestation-free supply chains, animal welfare standards) and low-impact tanning (e.g., chrome-free, vegetable-tanned, or innovative enzymatic processes).
* Certification Growth: Industry certifications (e.g., Leather Working Group – LWG, ZDHC) will become essential market access requirements, driving investment in cleaner production and supply chain audits.
2. Premiumization vs. Cost-Effectiveness Dichotomy:
* Premium Segment Resilience: High-end fashion houses, luxury automotive interiors, and bespoke furniture makers will continue to value the unique qualities, durability, and natural beauty of premium full-grain and corrected-grain cattlehide. This segment will focus on craftsmanship, heritage, and storytelling linked to quality.
* Mid/Low-Tier Pressure: Mass-market segments (e.g., fast fashion footwear, budget furniture) will face intense competition from synthetic alternatives and innovative bio-based leathers (e.g., mushroom, cactus, lab-grown). Price sensitivity here will be high, squeezing margins for standard cattlehide.
* Value Proposition Shift: Suppliers will need to articulate the long-term value (durability, repairability, aging characteristics) of genuine leather more effectively against cheaper, less durable synthetics.
3. Technological Innovation Driving Efficiency & Novelty:
* Advanced Tanning & Finishing: Adoption of more sustainable and efficient tanning technologies (e.g., vacuum tanning, plasma treatment, digital printing for intricate finishes) will increase to reduce resource consumption and waste.
* Waste Valorization: Innovations in utilizing leather production by-products (e.g., collagen for cosmetics/pharma, gelatin, biofuels) will gain traction, improving the overall sustainability footprint and creating new revenue streams.
* Hybrid Materials: Development of leather-composite materials (combining leather with recycled synthetics or bio-polyesters) may emerge to enhance performance (water resistance, durability) or reduce environmental impact while retaining leather’s aesthetic.
4. Regional Market Divergence:
* Asia-Pacific (APAC): Remains the dominant production hub (China, India, Vietnam, Bangladesh) and a growing consumption market. Growth will be driven by rising disposable incomes, infrastructure development (furniture, automotive), and evolving fashion tastes. Sustainability compliance will be a major challenge and focus.
* Europe & North America: Mature markets with strong emphasis on sustainability, quality, and ethical sourcing. Demand will be concentrated in premium/luxury segments. Regulatory frameworks (e.g., EU Green Deal, CBAM) will significantly impact imports and production standards.
* Emerging Markets: Regions like Latin America and Africa present growth opportunities, particularly in automotive (local manufacturing) and footwear, but infrastructure and sustainability challenges remain.
5. Competitive Landscape & Supply Chain Dynamics:
* Consolidation & Vertical Integration: Pressure may drive consolidation among tanneries and increased vertical integration by large brands seeking greater control over sustainability and quality.
* Sourcing Shifts: Diversification of sourcing regions (e.g., increased focus on South America for sustainably raised cattle) may occur to mitigate risks related to environmental regulations or geopolitical factors in traditional hubs.
* Transparency Tech: Blockchain and other digital tools for supply chain tracking will become more prevalent, enabling brands to verify claims and meet consumer demand for proof.
Conclusion for 2026:
Cattlehide leather will not disappear but will operate in a more polarized and scrutinized market. Its future hinges on its ability to demonstrably address sustainability concerns through transparent, traceable, and low-impact production. Success will belong to suppliers and brands that cater effectively to the premium segment’s demand for quality and ethics, while finding innovative ways to compete on value and environmental performance in mid-tier markets. The rise of alternatives will continue to challenge, but the inherent durability and unique sensory qualities of high-quality cattlehide will ensure its relevance, particularly where longevity and luxury are prioritized. The market in 2026 will be defined by adaptation, transparency, and a clear focus on responsible production.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cattlehide Leather (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing cattlehide leather involves navigating several challenges related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to product defects, legal disputes, reputational damage, and financial loss. Here are key issues to watch for:
Inconsistent or Substandard Quality
One of the most frequent challenges in sourcing cattlehide leather is ensuring consistent quality. Variations can arise due to differences in raw material origin, tanning processes, and supplier standards.
- Natural Variability: Cattlehide is a natural product, and each hide has unique markings, scars, and grain patterns. Buyers may receive batches that differ significantly from approved samples, especially if suppliers do not grade hides rigorously.
- Poor Tanning and Finishing: Inadequate tanning can result in leather that is stiff, prone to cracking, or discolored. Low-quality dyes or coatings may fade or peel, reducing product lifespan.
- Lack of Standardization: Suppliers may use different grading systems (e.g., full grain, top grain, corrected grain), leading to misunderstandings about the actual quality being purchased.
Misrepresentation of Leather Type and Origin
Suppliers may mislabel or exaggerate the type or origin of leather to command higher prices.
- False “Full Grain” Claims: Some suppliers market corrected or buffed leather as “full grain,” which is the highest quality. True full grain retains the original surface and is more durable.
- Geographic Mislabeling: Leather may be falsely advertised as coming from premium regions (e.g., Italian or French leather) when it is actually sourced from lower-cost regions with less stringent quality controls.
- Blended or Composite Leathers: Some materials marketed as “genuine leather” may contain significant non-leather components (e.g., bonded leather), misleading buyers about the product’s composition and performance.
Intellectual Property Infringement
When sourcing leather for branded or design-sensitive products, IP risks are significant.
- Unauthorized Use of Trademarked Finishes or Textures: Some tanneries develop proprietary finishes or embossing patterns protected by trademarks or design patents. Using these without permission—especially when sourcing through third-party suppliers—can lead to legal action.
- Counterfeit or Pirated Materials: In some cases, suppliers may offer leather that mimics the appearance of high-end branded leathers (e.g., imitating signature textures from luxury fashion houses), exposing buyers to IP liability.
- Lack of Documentation and Traceability: Without proper documentation from suppliers (e.g., certificates of authenticity, tannery invoices), it can be difficult to prove the legitimacy and legal sourcing of materials in case of an IP dispute.
Ethical and Sustainability Misrepresentation
Buyers increasingly demand ethically and sustainably sourced leather, but greenwashing is common.
- Fake Certifications: Suppliers may claim compliance with environmental or animal welfare standards (e.g., LWG certification) without valid documentation.
- Untraceable Supply Chains: Lack of transparency in the supply chain can hide unethical practices such as illegal deforestation, poor working conditions, or inhumane animal treatment.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and tannery verification.
– Request material certifications and batch testing for quality consistency.
– Use clear, legally binding contracts specifying leather type, grade, origin, and IP compliance.
– Work directly with reputable tanneries when possible, rather than intermediaries.
– Consult legal experts to review IP risks, especially when replicating textures or finishes.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP concerns, businesses can ensure they source authentic, high-performance cattlehide leather while minimizing legal and reputational risks.
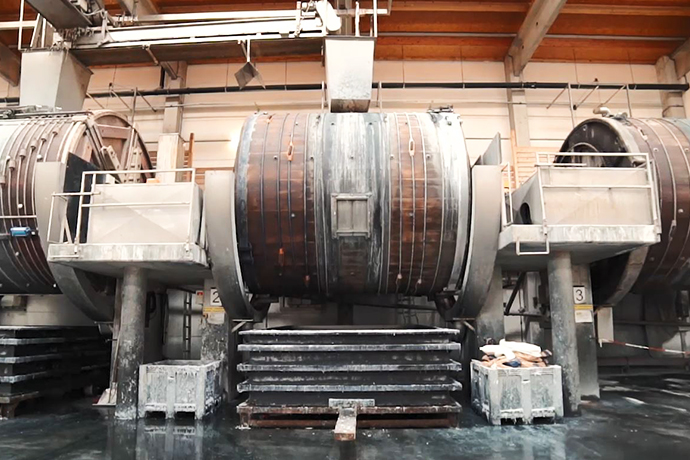

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cattlehide Leather
Overview
Cattlehide leather, derived from bovine animals, is a widely traded raw material used in apparel, footwear, furniture, and automotive interiors. Transporting and trading cattlehide leather involves adherence to international and regional regulations concerning animal health, environmental standards, customs procedures, and product safety. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for businesses involved in the import, export, and distribution of cattlehide leather.
Regulatory Compliance
Animal Health & Disease Control
Cattlehide leather is subject to veterinary and sanitary regulations to prevent the spread of animal diseases such as Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD), Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), and Anthrax. Key requirements include:
– Export Certificates: Most countries require an official veterinary health certificate issued by the national authority of the exporting country.
– Processing Standards: Raw hides must be tanned or otherwise processed to render them non-infectious. Many markets require that hides be salted, dried, or chemically treated.
– Approved Countries: Importers must ensure that the country of origin is on the importing country’s list of approved sources. For example, the EU maintains strict lists of eligible third countries for raw hides.
CITES and Wildlife Protection
While cattle (Bos taurus) are not listed under CITES, it’s important to verify that leather products do not include materials from protected species. Mislabeling or inclusion of exotic skins can result in seizure and legal penalties.
REACH and Chemical Compliance (EU)
Under the EU’s REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation:
– Leather products must not contain restricted substances above permitted thresholds, such as azo dyes, chromium(VI), formaldehyde, and certain phthalates.
– Importers and manufacturers must conduct chemical testing and maintain documentation for compliance.
Prop 65 (California, USA)
Leather products sold in California must comply with Proposition 65, which requires warning labels if products contain chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm, such as certain chromium compounds.
Import & Export Documentation
Required Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Veterinary Health Certificate (for raw or semi-processed hides)
- Fumigation Certificate (if required by destination country)
- REACH or SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) Declaration (EU-bound shipments)
Harmonized System (HS) Codes
Accurate classification is critical for customs clearance. Common HS codes include:
– 4103.20: Tanned or crust hides and skins of bovine animals
– 4107.12: Finished leather of bovine animals
– 4114.20: Patent leather and metallized leather
Classification may vary by country and leather finish, so consult local customs authorities.
Logistics & Transportation
Packaging Requirements
- Raw and wet-salted hides: Packed in moisture-resistant plastic or jute bags to prevent mold and contamination.
- Finished leather: Typically rolled or folded and wrapped in protective paper or film to avoid scratches and moisture damage.
- Use sturdy containers or pallets for bulk shipments.
Storage Conditions
- Store in dry, ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Maintain humidity levels to prevent mold growth (ideally 45–60% RH).
- Finished leather should be stored off the ground and covered to avoid dust and physical damage.
Transportation Modes
- Ocean Freight: Most cost-effective for bulk shipments. Use dry or refrigerated containers depending on hide condition.
- Air Freight: Suitable for high-value or time-sensitive finished leather goods.
- Land Transport: Common for regional distribution; ensure proper vehicle sealing and climate control if needed.
Sustainability & Traceability
Deforestation & Land Use
Ensure supply chains do not contribute to illegal deforestation, especially in regions like the Amazon. Increasingly, importers are required to demonstrate due diligence under regulations like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR).
Traceability Systems
Implement traceability from ranch to tannery to demonstrate:
– Legal origin of hides
– Animal welfare standards
– Environmental compliance in tanning processes
Blockchain and certification programs (e.g., Leather Working Group – LWG) support traceability and sustainability claims.
Certification & Standards
Leather Working Group (LWG)
The LWG audits tanneries for environmental performance, including water usage, chemical management, and emissions. LWG-certified leather is preferred by many global brands.
ISO Standards
- ISO 17078: Test methods for leather
- ISO 17228: Environmental management in leather manufacturing
Compliance with ISO standards enhances product quality and market access.
Risk Mitigation
Customs Delays
- Ensure all documentation is complete and consistent.
- Use licensed customs brokers familiar with agricultural and textile products.
- Pre-clear shipments where possible.
Product Rejection
- Conduct pre-shipment inspections for quality and compliance.
- Verify chemical content through third-party labs.
- Monitor regulatory changes in target markets.
Insurance
Cover shipments against common risks such as water damage, theft, and contamination. Specify coverage for perishable or chemically treated goods.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of cattlehide leather requires a proactive approach to regulatory requirements, documentation, and sustainable sourcing. Staying informed about evolving global standards—especially in chemical safety, animal health, and environmental protection—is essential for uninterrupted trade and brand integrity. Partnering with certified suppliers and logistics experts can significantly reduce risks and enhance supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, sourcing cattlehide leather requires a careful balance between quality, sustainability, cost, and ethical considerations. As a durable and versatile material widely used in fashion, furniture, and automotive industries, cattlehide leather must be procured from reliable suppliers who adhere to high environmental and animal welfare standards. Prioritizing transparency in the supply chain, ensuring proper tanning methods (preferably eco-friendly like vegetable tanning), and verifying certifications (such as ISO, LWG, or REACH compliance) are essential steps in responsible sourcing. Additionally, building long-term relationships with reputable tanneries and staying informed about market trends and regulations can enhance supply chain resilience and product integrity. Ultimately, a well-considered sourcing strategy not only supports business objectives but also aligns with growing consumer demand for ethically and sustainably produced materials.