The global cast iron furnace market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising industrialization, increasing demand for efficient metal melting solutions, and expanding applications in foundries, steel plants, and heavy manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global industrial furnace market—which includes cast iron furnaces—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on energy-efficient heating systems. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global industrial furnace market at USD 58.3 billion in 2022 and forecasts continued expansion due to heightened infrastructure development and industrial activities, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America. With these dynamics shaping the sector, select manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, durability, and performance. Here are the top 9 cast iron furnace manufacturers leading the industry through advanced engineering and global market reach.
Top 9 Cast Iron Furnace Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mestek
Domain Est. 1995
Website: mestek.com
Key Highlights: Our HVAC equipment group and controls group is a leading manufacturer of heating, ventilation and cooling products including residential and commercial hydronic ……
#2 Wirco Inc.
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1978
Website: wirco.com
Key Highlights: Since 1978 Wirco, Inc. has been committed to providing high-temperature tooling and furnace replacement parts for our heat treating and steel manufacturing ……
#3 DELTA H
Domain Est. 1998
Website: delta-h.com
Key Highlights: DELTA H designs and manufactures industrial furnaces and ovens for aerospace, defense, and manufacturing. Explore our USA-made thermal processing solutions….
#4 All Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: weil-mclain.com
Key Highlights: Cast Iron. Heating Range: 346 – 1,674 MBH. Mediums: Steam; /; Water. 88 High Efficiency Series 3 Commercial Gas Oil Boiler. Fuel Type: Gas; /; Oil. Heat ……
#5 Smith Boilers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: smithboiler.com
Key Highlights: Smith Cast Iron Boilers are known throughout North America for their rugged reliability, operating efficiencies and longevity….
#6 Pennco
Domain Est. 2000
Website: penncoboilers.com
Key Highlights: Built with high quality components and standards, Pennco gas and oil-fired boilers are manufactured by our dedicated workforce in the U.S.A. to ensure that our ……
#7 Inductotherm Corp.
Domain Est. 2002
Website: inductothermgroup.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture the most advanced induction melting, heating, holding and pouring systems for virtually all metal and material processing….
#8 Northern Iron a Lawton Standard foundry in St. Paul, MN
Domain Est. 2006
Website: northernim.com
Key Highlights: We produce the highest quality iron castings in our five-furnace foundry. Grey, ductile, and austempered ductile iron castings up to 250 lbs….
#9
Domain Est. 2007
Website: trioboiler.com
Key Highlights: TRIO offers the best value on the market today. Combining European design, American engineering and 50 years of manufacturing expertise….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cast Iron Furnace
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cast Iron Furnaces
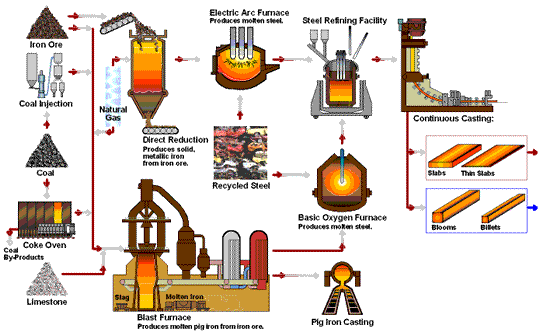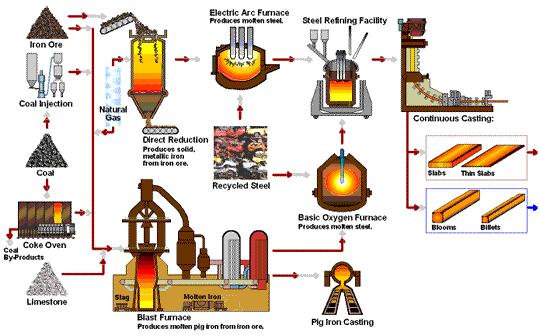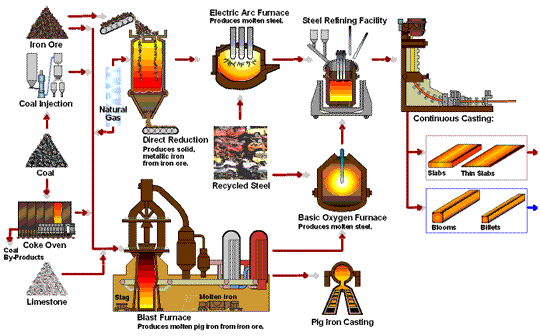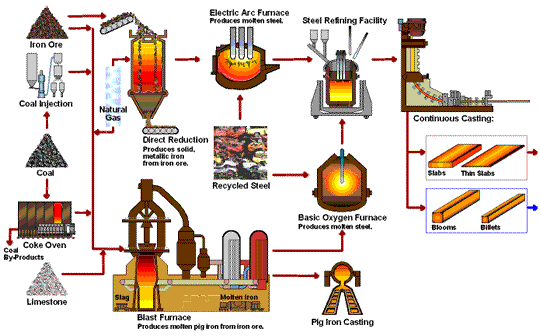
The global cast iron furnace market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by a confluence of industrial modernization, environmental regulations, and shifting manufacturing dynamics. Cast iron furnaces—primarily used in foundries for melting scrap iron and producing cast iron components—continue to play a vital role in heavy industries such as automotive, construction, and machinery. However, several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape in 2026:
-
Increased Demand from Automotive and Infrastructure Sectors
The ongoing recovery and expansion of the automotive industry, especially in emerging economies, are driving demand for durable cast iron components like engine blocks and brake systems. Additionally, increased infrastructure investments in regions such as Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America are fueling the need for heavy-duty construction machinery and pipelines, boosting the demand for cast iron products and, by extension, cast iron furnaces. -
Shift Toward Energy Efficiency and Emission Reduction
Environmental regulations are becoming more stringent worldwide, particularly in Europe and North America. Foundries are under pressure to reduce carbon emissions and energy consumption. As a result, manufacturers are investing in modernized cast iron furnaces with improved thermal efficiency, waste heat recovery systems, and cleaner combustion technologies. Induction furnaces are gaining market share over traditional cupolas, but hybrid systems that integrate cast iron melting capabilities with lower emissions are emerging as a transitional solution. -
Adoption of Smart Manufacturing and IoT Integration
The Industry 4.0 revolution is impacting foundry operations. By 2026, an increasing number of cast iron furnace installations are expected to feature IoT-enabled sensors, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These technologies enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve metal quality consistency—critical factors for high-precision industries like automotive and aerospace. -
Regional Market Shifts and Emerging Hubs
While traditional markets in North America and Western Europe are seeing moderate growth due to market saturation and environmental constraints, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia—is emerging as the dominant region for cast iron furnace demand. Localized production, government support for manufacturing, and rising domestic consumption are key drivers. Additionally, countries in Eastern Europe and the Middle East are investing in industrial capacity, creating new opportunities. -
Recycling and Circular Economy Influence
The growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing is increasing the use of recycled scrap metal in cast iron production. Cast iron furnaces that efficiently process scrap with minimal energy input and pollution are in higher demand. This trend supports the proliferation of electric arc furnaces (EAFs) and induction furnaces, though cupola furnaces are being retrofitted to handle higher scrap ratios more cleanly. -
Material Substitution Challenges and Opportunities
While alternative materials like aluminum and composites are replacing cast iron in some lightweight applications, cast iron remains irreplaceable in high-stress, high-temperature environments. This resilience ensures continued relevance for cast iron furnaces, especially in industrial machinery, heavy trucks, and power generation equipment.
In summary, the 2026 cast iron furnace market will be shaped by sustainability imperatives, technological innovation, and regional industrial growth. While facing competition from alternative melting technologies and materials, cast iron furnaces that evolve to meet modern efficiency and environmental standards will retain a strategic role in global manufacturing.
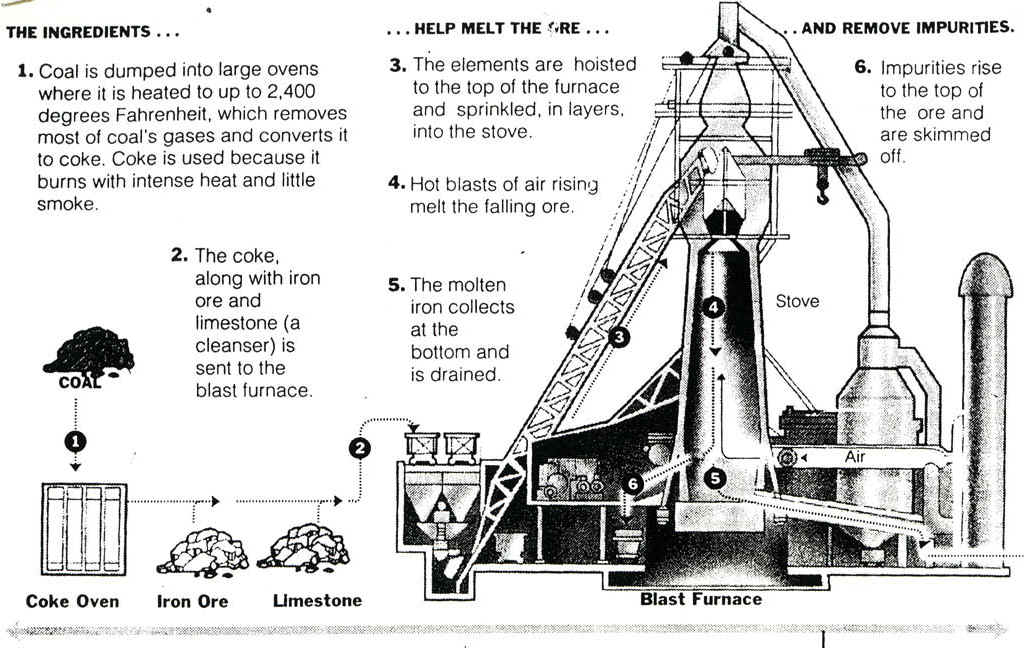
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cast Iron Furnaces: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing cast iron furnaces, particularly from international or less-regulated suppliers, involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, financial losses, and legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Composition and Casting Integrity
One of the most critical risks is receiving cast iron furnaces made from substandard or inconsistent materials. Poor-quality cast iron—such as gray iron with incorrect carbon/silicon ratios or inadequate tensile strength—can lead to premature cracking, warping, or catastrophic failure under high thermal stress. Suppliers may use recycled or uncertified scrap metal, resulting in variable mechanical properties. Without third-party material certifications (e.g., ASTM A48 or ISO 185) and verified metallurgical reports, buyers cannot ensure the furnace will withstand operating temperatures and cycles.
Inadequate Heat Treatment and Stress Relieving
Proper heat treatment is essential to relieve internal stresses in cast components after molding. Inadequate or skipped stress-relieving processes increase the risk of distortion or cracking during furnace operation. Sourcing from suppliers without documented heat treatment protocols or quality control records exposes buyers to unreliable products that may fail prematurely.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Fit Issues
Low-cost suppliers may lack precision tooling or quality control, leading to dimensional inaccuracies in flanges, ports, or mounting surfaces. These inconsistencies can result in misalignment with auxiliary equipment (e.g., ductwork, burners), causing leaks, inefficient combustion, and safety hazards. Without proper inspection reports or first-article testing, such defects may go unnoticed until installation.
Lack of Performance Testing and Documentation
Many suppliers do not conduct or provide evidence of performance testing—such as pressure testing, thermal cycling, or combustion efficiency validation. Buyers may receive furnaces that look correct but fail under real operating conditions. Insist on factory acceptance tests (FAT) and comprehensive documentation, including thermal expansion data and refractory lining details.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Replication of Proprietary Designs
When sourcing custom or engineered cast iron furnaces, there is a significant risk that your proprietary designs, engineering specifications, or patented features may be copied without authorization. Unethical suppliers may reverse-engineer your designs and sell identical or similar units to competitors, undermining your market advantage. This risk is especially high in regions with weak IP enforcement.
Insufficient Legal Protections in Contracts
Many procurement agreements lack explicit IP clauses that assign ownership of design modifications or prohibit reverse engineering. Without a robust Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA), clear IP assignment terms, and restrictions on third-party production, suppliers may legally use your technical data for other clients.
Use of Counterfeit or Non-Licensed Technology
Some suppliers integrate branded components (e.g., burners, control systems) without proper licensing, exposing the buyer to liability for using counterfeit or infringing technology. Ensure all integrated components are genuine and supplied with valid certification.
Inadequate Traceability and Documentation Control
Poor document control at the supplier level can lead to unapproved design changes or undocumented modifications. Without version-controlled drawings and change management processes, it becomes difficult to protect or enforce your IP rights if infringement occurs.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Require material test reports (MTRs), heat treatment records, and dimensional inspection reports.
– Conduct on-site audits or engage third-party inspection agencies.
– Include strong IP clauses in contracts—specifying ownership, confidentiality, and usage rights.
– File design patents or utility models where applicable.
– Use legally binding NDAs and limit technical data disclosure to what is strictly necessary.
Proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns during the sourcing process ensures long-term reliability, legal safety, and competitive advantage.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cast Iron Furnace
Overview
Transporting and operating a cast iron furnace—whether for industrial production, foundry use, or restoration—requires careful attention to logistics, regulatory compliance, and safety standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and legal handling, transportation, installation, and operation of cast iron furnaces.
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
Cast iron furnaces, especially those used in melting operations, are subject to environmental controls due to emissions of particulates, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and potentially hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). Compliance with the following regulations is essential:
– EPA Standards (US): Ensure adherence to the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) and New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) under the Clean Air Act. Permitting may be required for air emissions.
– EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED): Facilities in the EU must operate under an environmental permit, monitoring emissions and applying Best Available Techniques (BAT).
– Local Air Quality Permits: Check with regional or municipal environmental agencies for additional permitting and emission limits.
Occupational Safety and Health
Worker safety during furnace operation and maintenance is governed by occupational health standards:
– OSHA (US): Comply with 29 CFR 1910.1000 (air contaminants), 1910.132 (personal protective equipment), and 1910.156 (foundry operations). Heat stress, fall protection, and lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures are critical.
– Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs): Monitor exposure to iron oxide fumes, carbon monoxide, and other byproducts. Implement proper ventilation and respirator programs where needed.
– Machine Guarding: Ensure moving parts, hot surfaces, and charging mechanisms are properly guarded.
Equipment Standards and Certification
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (if applicable): While most cast iron furnaces are not pressure vessels, any associated pressure systems (e.g., steam jackets or cooling systems) must meet ASME standards.
- CE Marking (EU): Equipment placed on the EU market must comply with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, including safety design, risk assessment, and technical file documentation.
- Third-Party Inspection: Consider third-party certification for structural integrity and operational safety, especially for refurbished or vintage units.
Transportation and Logistics
Pre-Shipment Preparation
- Disassembly and Packaging: If transporting a large furnace, disassemble into manageable sections. Protect fragile cast iron components with wood crating or foam padding to prevent cracking during transit.
- Weight and Dimensions: Confirm the gross weight and dimensions of each component. Cast iron is extremely dense—accurate load data is essential for selecting proper transport vehicles and rigging equipment.
- Lifting Points: Ensure integral lifting lugs or attachment points are present and rated for the load. Never lift directly from non-rated sections (e.g., flue pipes or refractory linings).
Transport Requirements
- Heavy Haul Permits: Oversize or overweight loads may require special permits from state/provincial transportation departments. Route surveys may be necessary to avoid low bridges or weak infrastructure.
- Specialized Carriers: Use flatbed trailers with air-ride suspension and secure lashing points. Employ rigging professionals experienced in handling heavy industrial equipment.
- Hazardous Materials (if applicable): If the furnace contains residual oils, refractory dusts, or lead-based paints, classify and label accordingly under DOT (US) or ADR (EU) regulations.
Import/Export Compliance
- Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Identify the correct HS code (e.g., 8454.30 for furnaces for melting metal).
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures: Wooden packaging must comply with ISPM 15 (heat-treated and stamped) to prevent pest transfer.
- Embargo and Sanctions Checks: Verify that destination countries are not subject to trade restrictions.
Installation and Commissioning
Site Preparation
- Foundation Requirements: Cast iron furnaces require a stable, level foundation capable of supporting dynamic loads. Reinforced concrete pads with vibration isolation may be needed.
- Clearance and Ventilation: Maintain adequate clearance for maintenance, emergency access, and heat dissipation. Install exhaust hoods and ductwork connected to emission control systems.
- Utility Connections: Verify availability of required utilities—natural gas, propane, electricity, water cooling—within specifications.
Safety Systems Integration
- Fire Suppression: Install automatic fire detection and suppression systems in proximity to the furnace.
- Emergency Shutoffs: Provide manual and automatic shutoffs for fuel, power, and cooling systems.
- Alarms and Monitoring: Equip with temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and alarm systems for overheating or gas leaks.
Ongoing Compliance and Maintenance
Operational Documentation
- Maintain logs of furnace operation, maintenance, emissions monitoring, and safety inspections.
- Keep up-to-date risk assessments and method statements (RAMS) for all furnace-related tasks.
Periodic Inspections
- Conduct regular inspections for cracks, corrosion, refractory wear, and structural integrity.
- Follow a preventive maintenance schedule aligned with manufacturer recommendations or industry best practices (e.g., AFS guidelines for foundry equipment).
Training and Certification
- Train operators and maintenance staff on safe operating procedures, emergency response, and compliance requirements.
- Document training and ensure refresher courses are scheduled annually.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance aspects of a cast iron furnace demands proactive planning, adherence to regulations, and collaboration with qualified professionals. By following this guide, organizations can ensure safe, legal, and efficient deployment and operation of cast iron furnaces in compliance with all applicable standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cast Iron Furnace:
Sourcing a cast iron furnace requires careful consideration of several critical factors, including the quality and specifications of the furnace, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, lead times, and compliance with industry standards. Cast iron furnaces are valued for their durability, heat retention, and efficiency, making them a preferred choice in various industrial and residential heating applications.
After evaluating multiple suppliers, conducting material and performance assessments, and analyzing logistical and financial implications, it is evident that selecting a reputable manufacturer with proven experience in producing high-grade cast iron equipment is paramount. Establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers who offer technical support, warranties, and adherence to safety and environmental regulations further ensures operational reliability and cost savings over the furnace’s lifecycle.
In conclusion, a strategic and well-informed sourcing approach—balancing quality, cost, and service—will ensure the successful acquisition of a cast iron furnace that meets technical requirements and contributes to long-term operational efficiency and sustainability.