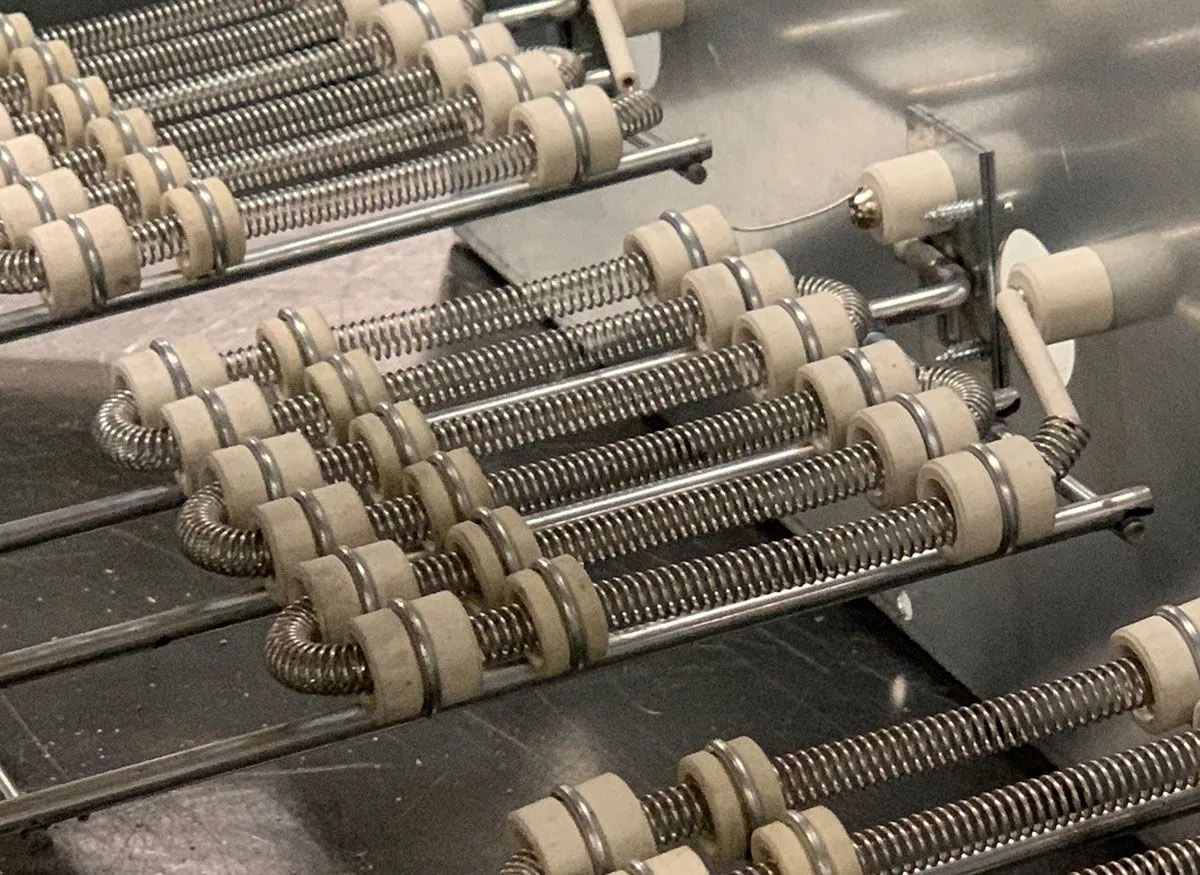
The global cartridge heater market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for efficient thermal solutions across industrial manufacturing, plastics, and automation sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.5% over the forecast period (2024–2029), underpinned by increasing adoption in injection molding, semiconductor production, and process heating applications. As industries prioritize precision temperature control and energy efficiency, cartridge heating elements—valued for their compact design and high thermal performance—have become a critical component in equipment ranging from packaging machines to CNC tooling systems. With North America and Asia-Pacific leading in both production and consumption, the competitive landscape is shaped by innovation in materials, watt density, and customization capabilities. In this dynamic environment, four manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining technological expertise, global reach, and robust R&D to maintain a dominant share of the market.
Top 4 Cartridge Heating Element Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Heaters
Domain Est. 1995
Website: watlow.com
Key Highlights: Watlow is a leader in the industrial heater industry manufacturing high quality cartridge heaters, immersion heaters, advanced ceramic heaters and other ……
#2 Custom Heater Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: durexindustries.com
Key Highlights: A leading manufacturer of high quality custom & industry standard designed electric heaters, temperature sensors, process heating systems & temperature ……
#3 ProTherm Industries
Domain Est. 1998
Website: prothermind.com
Key Highlights: Heating Elements … ProTherm Industries provides a wide range of heating elements, band heaters, cartridge heaters, formed and finned tubular heaters, bolt ……
#4 Electrified Heating Solutions
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tutco.com
Key Highlights: TUTCO is one of the worlds largest suppliers of electric resistive heating elements and holds 80% of the US patents in open coil heating products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cartridge Heating Element
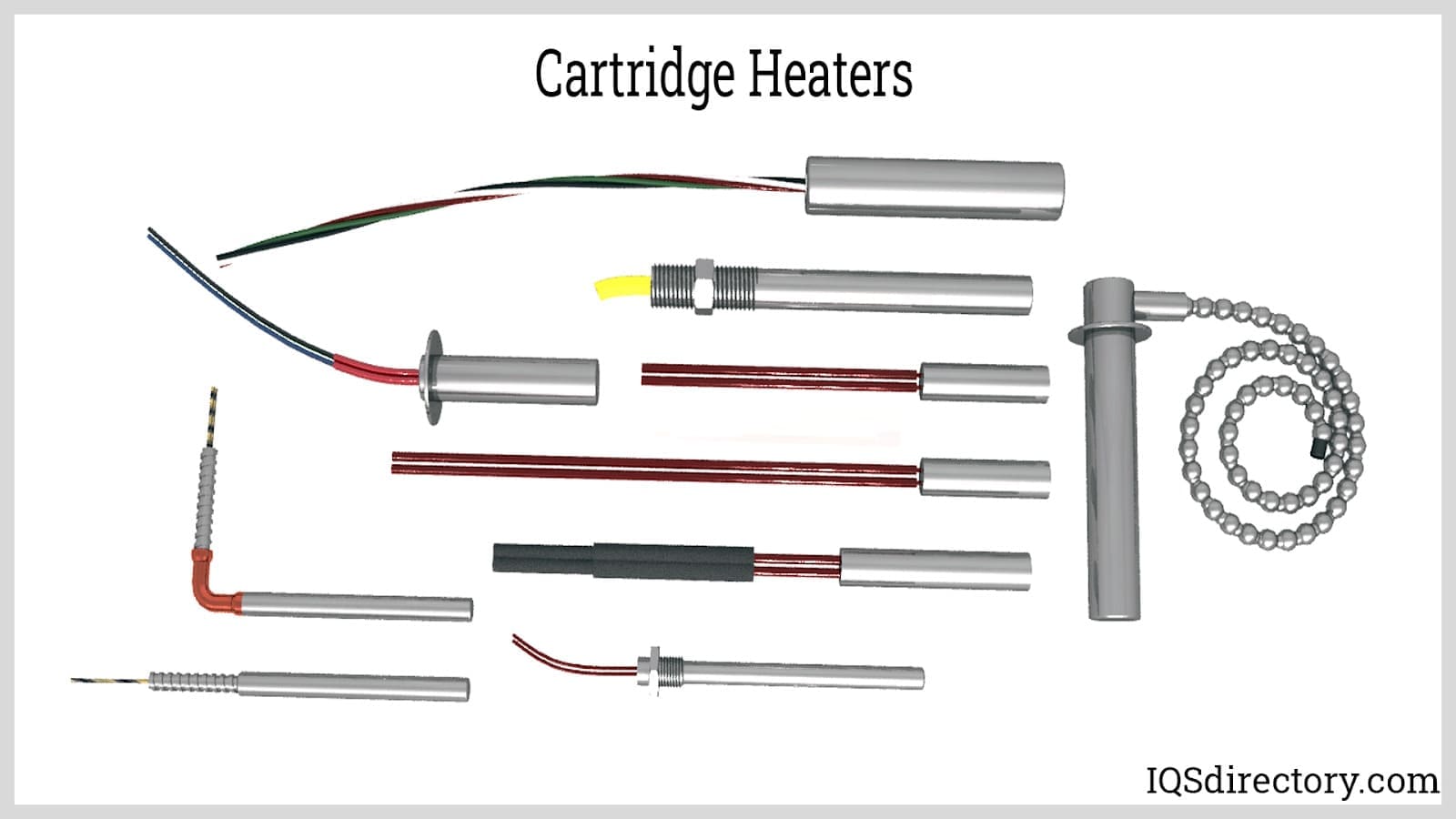
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cartridge Heating Elements
The global market for cartridge heating elements is poised for notable transformation and expansion by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing industrial automation, and increasing energy efficiency demands across key sectors. Several macroeconomic and industry-specific trends are shaping the trajectory of this market, positioning cartridge heaters as essential components in diverse applications ranging from plastics and packaging to aerospace and medical devices.
-
Rising Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
With the global push toward Industry 4.0, manufacturers are integrating smart, connected systems that require reliable and precise thermal solutions. Cartridge heating elements, known for their compact design and high thermal efficiency, are increasingly used in automated machinery such as injection molding equipment, semiconductor processing units, and automated food processing systems. By 2026, demand is expected to grow as industries prioritize consistent, responsive, and energy-efficient heating solutions that integrate seamlessly with IoT-enabled monitoring systems. -
Expansion in the Plastics and Packaging Industry
The plastics manufacturing sector remains the largest consumer of cartridge heating elements, particularly in extrusion and injection molding machines. As emerging economies continue to urbanize and consumer demand for packaged goods rises, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, production capacity is expanding. This growth will directly fuel demand for high-performance cartridge heaters capable of withstanding prolonged operational cycles and high temperatures—up to 1,200°F (649°C) in some advanced models. -
Emphasis on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Global regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are driving innovation in energy-efficient heating technologies. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to focus on developing low-watt-density cartridge heaters with improved thermal transfer and reduced heat loss. Advanced materials such as magnesium oxide with higher purity and optimized sheath alloys (e.g., Incoloy, stainless steel) will enable longer lifespans and lower maintenance costs, aligning with green manufacturing standards. -
Adoption of Customized and Application-Specific Designs
As end-user requirements become more specialized, there is a rising trend toward custom-engineered cartridge heaters. OEMs and industrial users are demanding heaters tailored to unique dimensions, voltage configurations, and thermal profiles. This shift is particularly evident in high-tech industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where precision and reliability are paramount. By 2026, companies offering rapid prototyping, 3D modeling, and modular design platforms will gain a competitive edge. -
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics
The global supply chain for heating elements continues to evolve post-pandemic, with regionalization and nearshoring gaining momentum. While China remains a major producer of cartridge heaters, North America and Europe are investing in domestic manufacturing to reduce dependency and enhance supply resilience. This trend is expected to accelerate through 2026, supported by government incentives for onshoring critical industrial components. -
Technological Innovations and Material Advancements
Next-generation cartridge heaters are incorporating innovations such as braided heating wires, improved dielectric insulation, and ceramic-to-metal seals for enhanced thermal stability and vibration resistance. Additionally, R&D efforts are focusing on integrating sensors for real-time temperature feedback, enabling predictive maintenance and closed-loop control systems. These features will be increasingly adopted in high-reliability applications, further expanding market opportunities. -
Growth in Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional industrial uses, new applications in renewable energy systems (e.g., hydrogen production, battery thermal management), electric vehicle manufacturing, and 3D printing are emerging as growth drivers. Cartridge heaters are being adapted for use in thermal management units for lithium-ion batteries and in additive manufacturing systems requiring precise zone heating.
Conclusion
By 2026, the cartridge heating element market will be characterized by increased demand for smarter, more efficient, and application-specific solutions. Key growth will be fueled by industrial modernization, sustainability mandates, and diversification into high-tech sectors. Companies that invest in R&D, supply chain resilience, and digital integration are likely to lead in this evolving landscape. The global market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% from 2021 to 2026, reaching an estimated value of USD 1.8 billion by the end of the period, according to industry forecasts.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cartridge Heating Elements (Quality & IP)
Sourcing cartridge heating elements involves more than just matching basic specifications. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, supply chain disruptions, and legal risks. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Lowest Price Over Total Cost of Ownership
- Pitfall: Selecting suppliers based solely on the lowest initial unit cost.
- Consequences: Cheap elements often use inferior materials (e.g., low-grade resistance wire, insufficient MgO insulation, thin sheaths) and poor manufacturing processes. This leads to:
- Premature Failure: Shorter lifespan due to oxidation, hot spots, or sheath degradation.
- Inconsistent Performance: Variable watt density, inaccurate temperature control.
- Higher Downtime & Replacement Costs: Frequent failures increase maintenance costs and production losses.
- Solution: Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), including lifespan, reliability, energy efficiency, and impact on production uptime. Invest in quality from reputable suppliers.
2. Inadequate Verification of Material Specifications & Tolerances
- Pitfall: Accepting supplier claims without independent verification or detailed material certifications (e.g., Mill Test Certificates – MTCs).
- Consequences:
- Unknown Sheath Material: Risk of using incorrect alloy (e.g., non-304/316 SS when required), leading to corrosion, contamination, or mechanical failure.
- Substandard Resistance Wire: Lower purity wire (e.g., not Kanthal A-1) degrades faster and has inconsistent resistivity.
- Insufficient MgO Purity/Density: Impure or poorly compacted MgO reduces electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and moisture resistance, increasing failure risk.
- Poor Dimensional Tolerances: Elements not fitting properly cause poor thermal contact, hot spots, and potential damage to the host component.
- Solution: Demand and verify material certifications (MTCs for sheath, wire, MgO). Specify required purity standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Conduct incoming inspection for critical dimensions and visual quality. Consider third-party testing for critical applications.
3. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
- Pitfall: Sourcing generic “equivalent” parts without understanding the IP landscape, especially from suppliers in regions with lax IP enforcement.
- Consequences:
- Infringement Liability: Using a component that copies patented designs (e.g., specific termination styles, internal construction, manufacturing processes) exposes your company to lawsuits from the patent holder, even if the supplier provided it.
- Counterfeit Parts: Receiving elements falsely branded as from a reputable OEM, potentially with unknown quality and safety risks.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Suppliers relying on IP infringement may disappear if sued, disrupting your supply.
- Solution:
- Due Diligence: Research if the specific cartridge heater design is patented. Use patent databases.
- Supplier Vetting: Choose suppliers with strong reputations for ethical sourcing and IP compliance. Ask for warranties against IP infringement.
- Direct Sourcing: Source complex or patented designs directly from the OEM or authorized distributors whenever possible.
- Clear Contracts: Include IP indemnification clauses in supplier agreements.
4. Underestimating the Importance of Proper Design for Application
- Pitfall: Treating cartridge heaters as simple commodities and not ensuring the design (watt density, sheath material, length, diameter, voltage, termination) is truly optimized for the specific operating environment.
- Consequences:
- Excessive Watt Density: Causes overheating of the sheath surface, leading to rapid oxidation, shortened life, and potential damage to the heated material.
- Incorrect Sheath Material: Corrosion in aggressive environments or contamination in food/pharma applications.
- Poor Thermal Contact: Inadequate hole fit or lack of thermal paste reduces heat transfer efficiency and causes element overheating.
- Inadequate Termination: Leads to connection failures, arcing, and fire hazards.
- Solution: Engage with suppliers early in the design phase. Provide full application details (material, temperature profile, environment, duty cycle, hole size/depth, required lifespan). Use supplier selection tools or consult engineering support.
5. Neglecting Certifications and Compliance Requirements
- Pitfall: Assuming standard industrial heaters meet specific industry standards or safety certifications needed for the end application.
- Consequences:
- Failure to Meet Safety Standards: Risk of fire, electric shock, or toxic fumes if heaters lack required safety certifications (e.g., UL, CSA, CE, EAC, RoHS, REACH).
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Products incorporating non-compliant heaters may be barred from sale in certain markets (e.g., medical, food processing, aerospace).
- Voided Equipment Warranties: Using uncertified components can void the warranty on the larger system.
- Solution: Clearly specify required certifications and compliance standards before sourcing. Verify certificates are valid and specific to the heater model/series. Request test reports if necessary.
By proactively addressing these common pitfalls related to quality assurance and intellectual property, you can ensure the reliable, safe, and legally compliant operation of your equipment and protect your business from significant downstream risks.
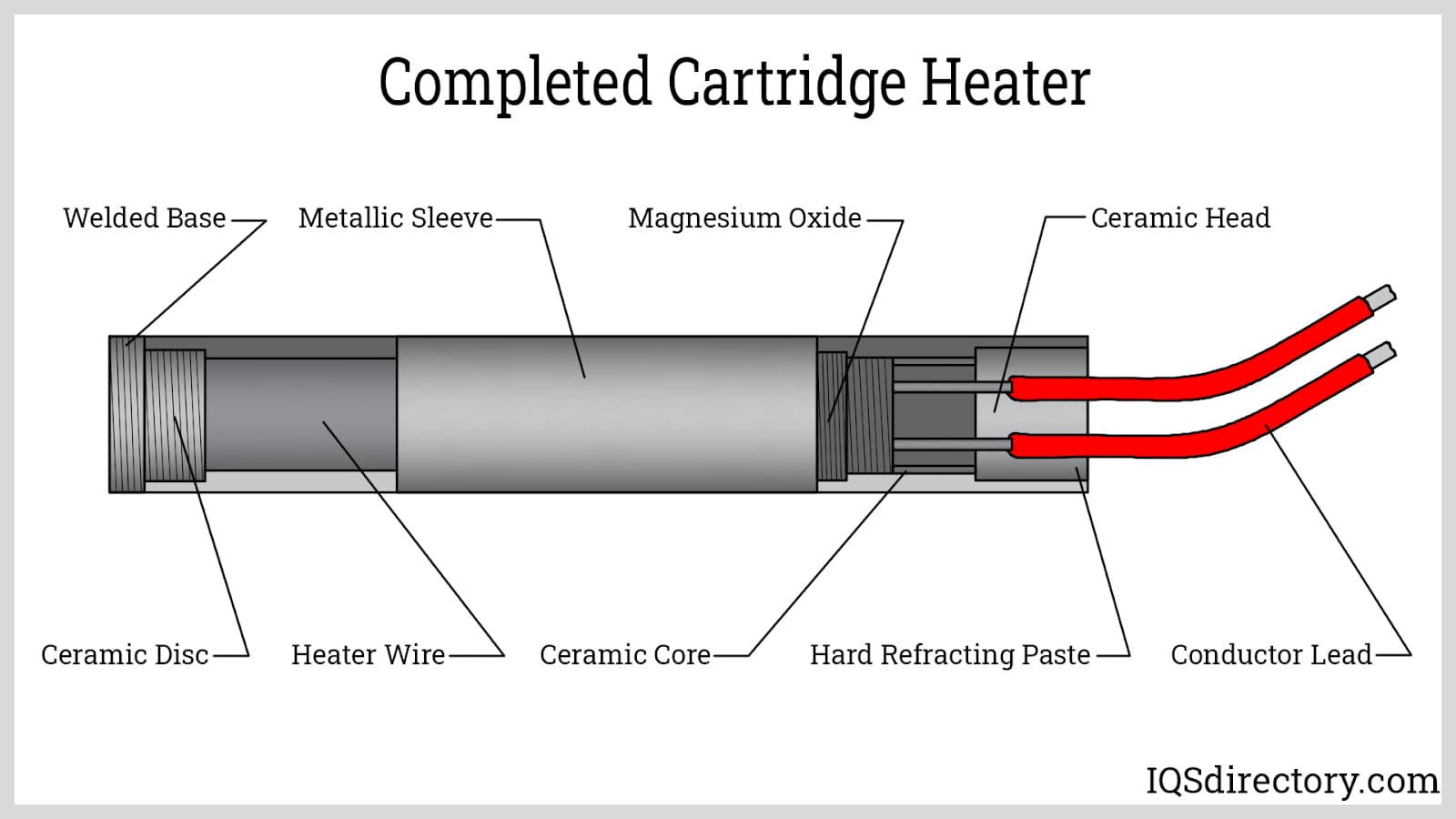
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cartridge Heating Elements
Cartridge heating elements are widely used in industrial, commercial, and manufacturing applications for efficient and localized heat transfer. Due to their electrical nature, material composition, and operational characteristics, proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential for safe transportation, storage, and use. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for cartridge heating elements under the H2 classification framework.
H2: Safety Data, Handling, and Regulatory Compliance
While cartridge heating elements are not typically classified as hazardous materials under transport regulations (e.g., IATA, IMDG, ADR), certain conditions and configurations may trigger specific handling and documentation requirements. The “H2” designation may refer to internal company hazard classification or allude to hydrogen-related safety concerns—however, cartridge heaters do not contain hydrogen gas. This section clarifies compliance under standard interpretations.
1. Classification and Hazard Identification
- UN Classification: Cartridge heating elements are generally not classified as dangerous goods for transport when shipped without power sources or flammable components.
- Electrical Components: As electrical devices, they may fall under machinery or equipment classifications (HTS Code: 8516.79 or similar).
- No H2 Gas Involved: Despite the “H2” reference, standard cartridge heaters do not contain or produce hydrogen (H₂) gas. If H2 is referenced in relation to hydrogen-compatible heater designs (e.g., for hydrogen processing systems), additional material compatibility and safety protocols apply.
⚠️ Note: If heaters are specifically designed for hydrogen (H₂) service (e.g., in fuel cells or hydrogen reformers), they must comply with:
– ASME B31.12 (Hydrogen Piping and Pipelines)
– ISO 11114-4 (Cylinder material compatibility with hydrogen)
– Pressure Equipment Directive (PED 2014/68/EU) if applicable
2. Packaging and Logistics
- Packaging Requirements:
- Use anti-static or protective packaging to prevent terminal damage.
- Seal terminals to prevent short-circuiting during transit.
- Use robust cartons with cushioning to avoid mechanical stress.
- Labeling:
- Include product specifications (voltage, wattage, dimensions).
- Mark “Fragile” and “This Side Up” if applicable.
-
No GHS hazard labels required unless accessories (e.g., thermal paste) are classified.
-
Storage Conditions:
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (typically 10°C to 35°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture to prevent oxidation of sheath materials (e.g., stainless steel, Incoloy).
3. Transportation Regulations
- Air (IATA): Cartridge heaters are typically permitted as non-hazardous cargo. No Shipper’s Declaration required.
- Sea (IMDG): Not regulated as dangerous goods unless packaged with batteries or flammable materials.
- Road (ADR): Exempt from hazardous goods classification under ADR if no dangerous components are present.
✅ Compliance Tip: Confirm with freight forwarders that heaters are classified as “machinery” or “electrical components” to avoid delays.
4. Compliance with International Standards
Cartridge heating elements must comply with relevant electrical and product safety standards:
- Electrical Safety:
- IEC 60335-1 (Safety of household and similar electrical appliances)
- UL 1312 (Bare Element Heaters, USA)
-
CSA C22.2 No. 44 (Heaters, Canada)
-
Material & Environmental Compliance:
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – EU Directive 2011/65/EU
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation of Chemicals) – Ensure no SVHCs in materials
- Conflict Minerals reporting (if applicable under SEC Rule 13p-1)
5. Customs and Trade Documentation
- HS Code: 8516.79 (Other electro-thermic appliances)
- Required Documents:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Conformity (if required by destination country)
- CE Marking Declaration (for EU)
- UL/CSA Certification (for North America)
⚠️ Export Controls: Check if high-wattage or industrial heaters are subject to export regulations (e.g., EAR99 under U.S. Export Administration Regulations).
6. Special Considerations for H2-Compatible Heaters
If the cartridge heater is designed for use in hydrogen (H₂) environments, additional compliance steps are required:
- Material Compatibility: Use H₂-resistant alloys (e.g., 316L stainless steel, Inconel) to prevent hydrogen embrittlement.
- Pressure Rating: Validate heater design for H₂ system pressure (per ASME BPVC).
- Leak Testing: Perform helium or H₂ leak tests before deployment.
- ATEX/IECEx Certification: Required if used in potentially explosive atmospheres (e.g., hydrogen processing plants).
7. End-of-Life and Recycling
- WEEE Compliance (EU): Cartridge heaters with electrical components may fall under WEEE Directive 2012/19/EU.
- Recycling: Metals (copper, steel, magnesium oxide) should be recovered through approved e-waste channels.
Summary Checklist
| Item | Requirement |
|——|————-|
| Hazard Classification | Not hazardous (unless H₂ service) |
| Packaging | Protective, anti-static, moisture-resistant |
| Transport | IATA/IMDG/ADR compliant as non-dangerous goods |
| Certifications | CE, UL, RoHS, REACH (as applicable) |
| H2 Service Heaters | ASME B31.12, hydrogen compatibility testing |
| Export Docs | Commercial invoice, CoC, HS code 8516.79 |
Conclusion
Cartridge heating elements are generally low-risk in logistics but must meet electrical safety and material compliance standards. When designed for hydrogen (H₂) service, additional engineering and regulatory steps are mandatory. Always verify application-specific requirements and consult with compliance experts for international shipments.
For further assistance, contact your manufacturer or regulatory advisor to ensure full adherence to local and global standards.
Conclusion:
In sourcing cartridge heating elements, it is essential to consider key factors such as watt density, material compatibility, thermal response, operational temperature range, and dimensional specifications to ensure optimal performance and longevity in the intended application. Selecting a reliable supplier that adheres to quality standards and offers customization options can significantly enhance system efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. Additionally, evaluating certifications, lead times, and technical support contributes to a successful integration into industrial, commercial, or specialized heating systems. A well-informed sourcing strategy ensures that the chosen cartridge heaters meet both technical requirements and cost-effectiveness, ultimately supporting consistent and reliable thermal performance.