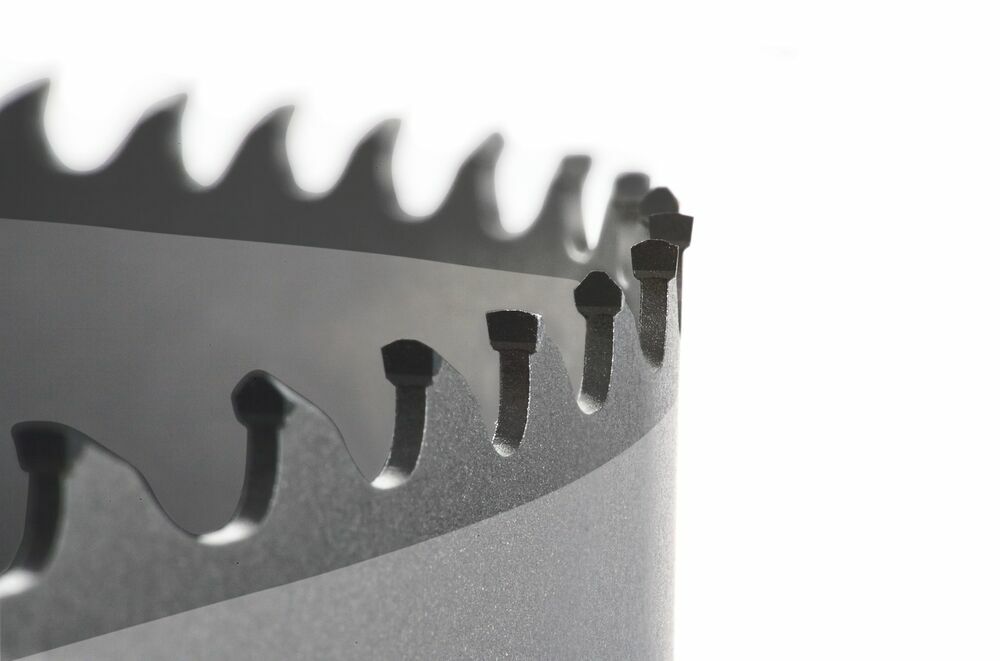
The global bandsaw blades market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand from key industries such as metal fabrication, automotive, aerospace, and construction. According to Grand View Research, the global saw blades market size was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. A key contributor to this expansion is the increasing preference for high-performance cutting tools, particularly carbide-tipped bandsaw blades, which offer superior durability, precision, and efficiency compared to traditional high-speed steel blades. With metal cutting accounting for the largest application segment, manufacturers are investing heavily in advanced materials and coating technologies to meet the evolving demands of industrial cutting processes. As the need for energy-efficient and cost-effective machining grows, carbide-tipped bandsaw blades have become a critical component in modern production environments. This growing market landscape has spurred innovation and competition among leading manufacturers worldwide. The following list highlights the top 10 carbide-tipped bandsaw blade manufacturers shaping the industry through technological advancement, product reliability, and global reach.
Top 10 Carbide Tipped Bandsaw Blades Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Bandsaw Blade Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: forrestmfg.com
Key Highlights: Forrest carries the following types of industrial bandsaw blades: Carbon steel; Carbide tipped; Carbide grite edge. Visit our Understanding Bandsaw Blades page ……
#2 Diamond Saw Works
Domain Est. 1998
Website: diamondsaw.com
Key Highlights: We’re proud to produce high-quality, industrial-grade Sterling saw blades to manufacturing companies, sawmill workers, and builders across the country….
#3 LENOX®
Domain Est. 2017
Website: cutwithlenox.com
Key Highlights: Designed for difficult-to-cut situations. Carbide-grade band saw blades treated with HONEX Technology™ reduce edge chipping for more cuts in high-strength steel ……
#4 The M.K. Morse Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mkmorse.com
Key Highlights: Featured Products. Jawbreaker Carbide Tipped Band Saw Blades. Jawbreaker. Designed for production cutting of large billets of super alloys and other very hard ……
#5 Carbide Tipped Band Saw Blades
Domain Est. 1998
Website: starrett.com
Key Highlights: Starrett Carbide Tipped Band Saw Blades deliver maximum cutting performance for high volume, production cutting of high nickel alloys and exotic metals….
#6 Pat Mooney Saws: Metal Sawing Machinery
Domain Est. 2001
Website: patmooneysaws.com
Key Highlights: Pat Mooney Saws provides band saw machines, cnc centers, circular saw machines, upcut saw machines, saw blades, and more….
#7 Timber Wolf® blades from 1/8” to 1” for every cutting application …
Domain Est. 2004
Website: timberwolfblades.com
Key Highlights: A perfect balance of superior steel, blade width and thickness plus precision set teeth produce a superior cutting blade with exceptional overall life….
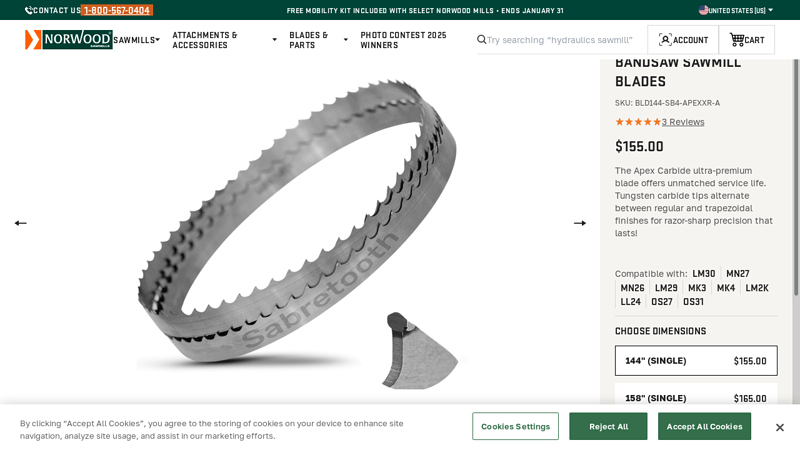
#8 Apex Carbide Bandsaw Sawmill Blades
Domain Est. 2006
Website: norwoodsawmills.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (3) Sabretooth Apex Carbide Blade offers durability with tungsten carbide tips, razor-sharp precision, and ultra-premium performance. Sizes: 144″, 158″, 167″….
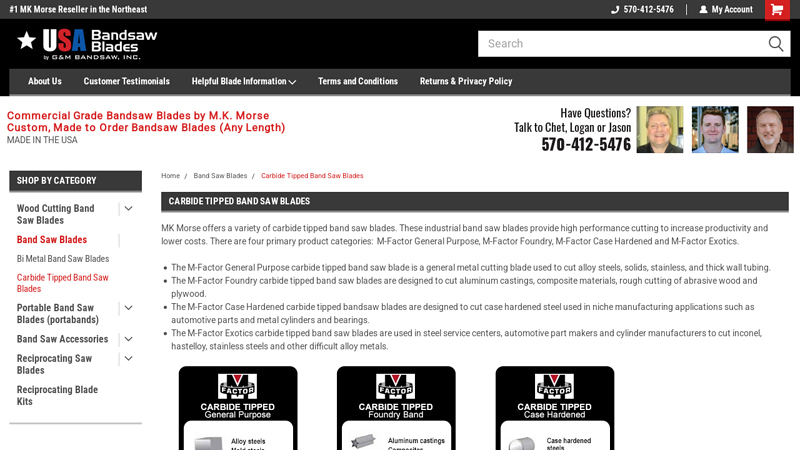
#9 Carbide Tipped Band Saw Blades
Domain Est. 2013
Website: usabandsawblades.com
Key Highlights: The M-Factor General Purpose carbide tipped band saw blade is a general metal cutting blade used to cut alloy steels, solids, stainless, and thick wall tubing….
#10 Carbide Band Saw Blades
Website: wikus.de
Key Highlights: Carbide-tipped band saw blades. Excellent results in every application thanks to the different degrees of hardness and compositions of the carbides used….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Carbide Tipped Bandsaw Blades

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Carbide Tipped Bandsaw Blades
The global market for carbide tipped bandsaw blades is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing industrial automation, and growing demand across key end-use sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and energy. This analysis explores the primary trends shaping the carbide tipped bandsaw blade market in 2026 under the H2 framework.
1. Rising Demand in High-Precision Manufacturing
By 2026, the need for high-precision cutting tools in advanced manufacturing will continue to surge. Carbide tipped bandsaw blades, known for their superior hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain sharpness at elevated temperatures, are becoming the preferred choice for cutting tough alloys like titanium, Inconel, and high-strength steels. This trend is particularly pronounced in the aerospace and defense industries, where material integrity and dimensional accuracy are critical.
2. Adoption of Smart and Automated Cutting Systems
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies into metal fabrication is accelerating the demand for intelligent cutting tools. In 2026, manufacturers are increasingly deploying carbide tipped bandsaw blades in automated bandsaw machines equipped with IoT sensors and predictive maintenance systems. These smart tools can monitor blade wear, optimize cutting parameters in real time, and reduce downtime—enhancing productivity and lowering operational costs.
3. Focus on Sustainability and Tool Longevity
Environmental regulations and cost-efficiency goals are pushing industries to adopt longer-lasting cutting tools. Carbide tipped blades offer a significantly longer lifespan compared to traditional bi-metal blades, reducing the frequency of replacements and material waste. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to emphasize recyclable carbide grades and sustainable production processes, aligning with broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) objectives.
4. Regional Market Expansion
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the carbide tipped bandsaw blade market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization in countries like China, India, and Vietnam. Growth in infrastructure development, automotive manufacturing, and renewable energy projects is boosting demand for high-performance cutting solutions. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on replacing aging tooling infrastructure with advanced carbide products to support high-mix, low-volume production models.
5. Innovation in Blade Design and Coatings
Ongoing R&D efforts are leading to new blade geometries, micro-grain carbide formulations, and advanced coatings (e.g., TiAlN, AlCrN) that enhance performance in high-speed and dry-cutting applications. By 2026, customized blade designs tailored to specific materials and cutting conditions are expected to become more prevalent, offering end-users greater flexibility and efficiency.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical uncertainties and logistical disruptions have prompted a shift toward localized production of critical industrial components. In 2026, leading carbide blade manufacturers are investing in regional production hubs to reduce dependency on global supply chains and ensure faster delivery times. This trend supports just-in-time manufacturing and strengthens customer relationships.
Conclusion
The 2026 outlook for carbide tipped bandsaw blades is characterized by innovation, automation, and sustainability. As industries demand higher efficiency and precision, the adoption of advanced carbide solutions is set to accelerate. Companies that invest in smart tooling, sustainable practices, and regional market development will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging trends.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Carbide Tipped Bandsaw Blades (Quality, IP)
Sourcing carbide tipped bandsaw blades requires careful attention to avoid compromising on performance, longevity, and legal compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to unexpected costs, downtime, and even intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are critical pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Blade Quality and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues is receiving blades that fail to meet advertised specifications. Low-quality carbide tips may have inconsistent hardness or improper brazing, leading to rapid chipping or delamination during cutting. Substandard steel backing can warp under heat or stress, reducing blade life and cutting accuracy. Buyers often focus on upfront price, only to face higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements and machine downtime.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Many suppliers, especially from less-regulated markets, provide blades without proper documentation or quality certifications. This absence makes it difficult to verify material origins, heat treatment processes, or compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN). Without traceability, diagnosing blade failure becomes challenging, and warranty claims may be unenforceable.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Purchasing from unverified suppliers increases the risk of acquiring counterfeit or cloned blades that mimic patented designs from reputable manufacturers (e.g., LENOX, Amada, or Conval). These copies may replicate tooth geometry, branding, or performance specs without authorization. Using such blades can expose your company to legal liability, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement. Additionally, counterfeit products often underperform and lack technical support.
Inadequate Technical Support and Application Matching
Some suppliers fail to provide proper guidance on blade selection for specific materials or machines. Using a blade not optimized for your application—such as cutting hardened steel with a blade designed for aluminum—leads to poor cut quality and premature wear. Reliable suppliers should offer technical data sheets and expert consultation to ensure proper fit and function.
Hidden Costs from Short Blade Lifespan
While low-cost blades may appear economical initially, their shorter service life increases total cost of ownership. Frequent changeouts reduce productivity, increase labor costs, and may damage equipment due to vibration or improper tracking. Investing in high-quality, properly sourced blades typically results in better ROI over time.
Supply Chain and After-Sales Service Gaps
Unreliable suppliers may have inconsistent stock, long lead times, or no local support network. If a blade fails mid-production, delays in replacement can halt operations. Additionally, lack of after-sales service—such as sharpening recommendations or failure analysis—limits your ability to optimize blade usage.
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct due diligence on suppliers, request product certifications, verify IP legitimacy, and prioritize long-term value over initial price. Partnering with authorized distributors or established manufacturers helps ensure quality, compliance, and reliable support.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Carbide Tipped Bandsaw Blades
Carbide tipped bandsaw blades are precision cutting tools widely used in metalworking, woodworking, and other industrial applications. Due to their composition, value, and regulated materials, proper logistics and compliance management are essential for safe, legal, and efficient handling. This guide outlines best practices and regulatory considerations.
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Carbide tipped bandsaw blades contain tungsten carbide, a strategic material subject to international trade regulations and export controls. Key considerations include:
- HS Code (Harmonized System): Typically classified under 8202.20 (bandsaws with interchangeable cutting elements) or 8202.91 (other saw blades). Final classification may vary by country and blade specification.
- Export Controls: Tungsten carbide may be subject to export control regulations such as:
- EAR (Export Administration Regulations, USA): Check ECCN (Export Control Classification Number); tungsten carbide tools may fall under 9A005 or 3A001, depending on application and specifications.
- ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): Generally not applicable unless blades are designed for military or defense applications.
- Dual-Use Concerns: Blades used in aerospace, defense, or nuclear industries may trigger additional scrutiny. Documentation must clearly state end-use to avoid delays.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and safe transport:
- Protective Wrapping: Blades must be individually wrapped in anti-corrosion paper or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) film to prevent rust and damage.
- Rigid Packaging: Use sturdy cardboard sleeves or plastic cases to prevent bending or edge chipping. Avoid loose stacking.
- Labeling:
- Clearly label with product specifications (length, width, TPI, tooth geometry).
- Include handling warnings: “Fragile – Sharp Edges,” “Do Not Stack,” “This Side Up.”
- Add compliance labels (e.g., CE marking if applicable, RoHS compliance statement for EU markets).
- Unit Load Stability: Secure packaged blades on pallets using stretch wrap and corner boards. Maximum stack height should not exceed manufacturer recommendations.
Transportation & Shipping
Transport logistics should account for size, weight, and regulatory compliance:
- Mode of Transport:
- Air Freight: Suitable for urgent or high-value shipments. Requires proper blade securing and IATA-compliant labeling (sharp objects may require special declaration).
- Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments. Use moisture-resistant packaging and desiccants in containers to prevent corrosion.
- Ground Transport: Ideal for regional distribution. Ensure secure vehicle loading to avoid blade vibration and impact.
- Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice (with detailed description, HS code, value).
- Packing List (quantities, weights, dimensions).
- Certificate of Origin (required by some countries for duty assessment).
- Export License (if required based on destination and ECCN).
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities (e.g., FOB, DDP) to avoid disputes. Use Incoterms® 2020 for clarity.
Import & Customs Clearance
Efficient customs clearance depends on accurate documentation and compliance:
- Duty & Tax Assessment: Confirm applicable tariffs based on HS code and country of import. Some regions offer reduced rates for industrial tools.
- Compliance Certifications:
- RoHS (EU): Confirm blades contain no restricted hazardous substances.
- REACH (EU): Declare substances of very high concern (SVHC) if applicable.
- Proposition 65 (California): Required if products contain listed chemicals (e.g., cobalt in carbide).
- Customs Inspections: Be prepared for physical inspection, especially for high-value or dual-use items. Maintain detailed technical specifications and end-use declarations.
Storage & Inventory Management
Proper storage preserves blade performance and ensures traceability:
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled area (ideally 15–25°C, RH < 60%) to prevent carbide degradation and steel body warping.
- Racking: Store vertically or on edge using blade racks. Never lay flat in stacks.
- Inventory Tracking: Use barcode or RFID systems to track lot numbers, expiry (if applicable), and compliance status. Maintain records for at least 5 years for audit purposes.
Environmental & Safety Compliance
Adhere to occupational health and environmental standards:
- MSDS/SDS (Safety Data Sheet): Provide SDS for carbide dust and blade handling, especially for end-users performing blade changes or grinding.
- Waste Disposal: Carbide blades are recyclable. Partner with certified metal recyclers for proper end-of-life handling. Do not dispose of in regular waste streams.
- OSHA/Workplace Safety (USA): Ensure safe handling practices; provide training for employees on sharp object risks and PPE requirements.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for carbide tipped bandsaw blades require attention to material regulations, proper packaging, accurate documentation, and adherence to international trade standards. Proactive planning and documentation not only ensure smooth operations but also mitigate legal and financial risks. Partner with experienced freight forwarders and compliance experts to stay current with evolving regulations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Carbide-Tipped Bandsaw Blades
Sourcing high-quality carbide-tipped bandsaw blades is essential for achieving optimal cutting performance, durability, and cost-efficiency in industrial and precision machining applications. These blades offer superior hardness, heat resistance, and longevity compared to traditional bi-metal blades, making them ideal for cutting tough materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and exotic alloys. When sourcing, key factors to consider include blade geometry, tooth design, carbide grade, weld quality, and the reputation of the manufacturer or supplier.
Partnering with reliable suppliers who offer technical support, consistent quality control, and customization options can significantly enhance operational productivity and reduce downtime. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—factoring in blade life, maintenance, and feed rates—rather than focusing solely on upfront cost ensures better long-term value.
In conclusion, investing time and resources in selecting the right carbide-tipped bandsaw blades from reputable sources will result in improved cut quality, increased efficiency, and reduced production costs, ultimately supporting superior performance across demanding cutting applications.