The global carbide market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand from industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where precision cutting tools and wear-resistant components are critical. According to Mordor Intelligence, the tungsten carbide market was valued at USD 11.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increased industrial automation, a surge in metalworking applications, and the push for longer-lasting tooling solutions that reduce downtime and operational costs. As demand escalates, manufacturers capable of delivering high-quality tungsten carbide at competitive prices are gaining strategic advantage. This list highlights the top 10 carbide price manufacturers—evaluated based on production scale, global pricing benchmarks, material consistency, and market share—who are shaping the competitive landscape amid this upward trajectory.
Top 10 Carbide Price Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
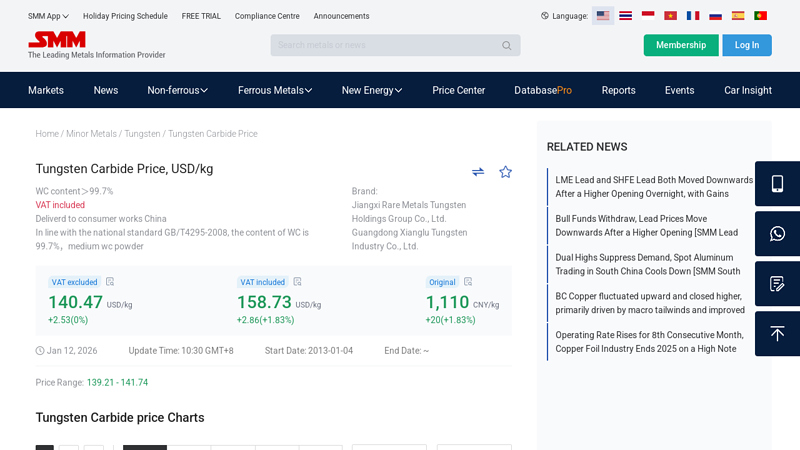
#1 Tungsten Carbide Price, USD/kg
Domain Est. 1995
Website: metal.com
Key Highlights: Tungsten Carbide Price, USD/kg ; VAT excluded · 140.47. USD/kg. +2.53(0%) ; VAT included · 158.73. USD/kg. +2.86(+1.83%) ; Original · 1,110. CNY/kg. +20(+1.83%)….
#2 Tungsten Carbide Materials
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kennametal.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide variety of carbide grades including submicron, fine, medium, and coarse-grained tungsten carbides with a mixture of binders and additives….
#3 Router Bits, Saw Blades, Carbide, Drill Bits
Domain Est. 1996
Website: carbideprocessors.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 · 90-day returnsSupplier of woodworking tools including; router bits, saw blades, drill bits, Woodpecker tools, hand tools and more….
#4 Horizon Carbide Tool, Inc
Domain Est. 1997
Website: horizoncarbide.com
Key Highlights: Horizon Carbide Tool has built its reputation on quality, service, dependability and price. We take great pride in manufacturing indexable cutting tools and ……
#5 Element Six
Domain Est. 1998
Website: e6.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Element Six, a world leader in synthetic diamond and tungsten carbide supermaterials. Find out more about our excellent range today….
#6 Carbide Cutting Tools
Domain Est. 1999
Website: carbidecuttingtools.com
Key Highlights: Made in the USA! Over 15 years of supplying quality carbide cutting tools you can count on….
#7 Carbide 3D
Domain Est. 2013
Website: carbide3d.com
Key Highlights: Carbide Create is our free CAD/CAM software that’s easy to learn and powerful enough to grow with you. Don’t have a Carbide machine? Do you want 3D design and ……
#8 PCT
Domain Est. 2018
Website: pct-imc.com
Key Highlights: High Performance Carbide Endmills. Various geometries to choose from to fit your application and material to maximize performance….
#9 Current Scrap Prices for Carbide, Tungsten, & Other Rare Metals
Domain Est. 2021
Website: rrcarbide.com
Key Highlights: Types & Grades of Carbide and Tungsten-Based Materials. These prices are updated regularly based on market conditions….
#10 MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORPORATION
Domain Est. 2022
Website: mmc-carbide.com
Key Highlights: This homepage offers Mitsubishi Materials cutting tools information….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Carbide Price
2026 Market Trends for Carbide Price: H2 Analysis
As we move into the second half of 2026 (H2 2026), the global tungsten carbide market continues to experience dynamic shifts driven by raw material availability, technological advancements, industrial demand, and geopolitical factors. This analysis examines key trends shaping carbide prices during this period, with a focus on supply-demand dynamics, manufacturing innovations, regional market behavior, and macroeconomic influences.
Supply Chain and Raw Material Constraints
Tungsten, a primary component of carbide, remains central to price volatility. In H2 2026, China—responsible for over 80% of global tungsten production—maintains strict export controls and environmental regulations, limiting supply availability. Additionally, disruptions in Myanmar and Vietnam, secondary sources of tungsten concentrate, have tightened supply chains. These constraints have led to a sustained upward pressure on raw material costs, contributing to elevated carbide prices.
Recycling efforts have increased, with the secondary carbide recycling rate reaching approximately 35% globally. However, recycled material cannot fully offset primary supply shortages, especially in high-purity applications used in aerospace and medical tools. As a result, refined tungsten and cobalt prices remain elevated, feeding directly into higher carbide product costs.
Industrial Demand Drivers
Demand for carbide tools remains robust across several key sectors:
-
Manufacturing & Automotive: The global push for precision machining and high-efficiency tooling in electric vehicle (EV) production continues to boost demand for carbide cutting tools. In H2 2026, automotive manufacturers in North America and Europe are investing in advanced machining centers that rely heavily on durable carbide inserts.
-
Oil & Gas: Despite the energy transition, exploration and drilling activities in deepwater and unconventional reserves remain active. Carbide-tipped drill bits are essential in these high-stress environments, supporting steady demand—particularly in the U.S. shale sector and offshore projects in the Middle East and Latin America.
-
Aerospace & Defense: The aerospace industry’s recovery and expansion, especially in Asia-Pacific and North America, are driving demand for high-performance carbide components used in turbine engine machining and composite material processing.
These demand trends are contributing to strong order backlogs among major carbide producers, enabling them to pass on input cost increases through higher prices.
Technological Advancements and Product Differentiation
H2 2026 sees accelerated adoption of advanced carbide grades featuring nanostructured binders, coated substrates (e.g., TiAlN, AlCrN), and digitally optimized geometries. These innovations improve tool life and machining efficiency, justifying premium pricing. Leading manufacturers such as Sandvik, Kennametal, and Mitsubishi Materials are increasingly marketing performance-based pricing models, where tool cost is justified by total cost savings in production.
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as IoT-enabled tool monitoring and predictive maintenance—is also influencing carbide pricing. Smart tools embedded with sensors or tracking features command price premiums, particularly in high-value manufacturing environments.
Regional Market Dynamics
-
Asia-Pacific: China and India remain the fastest-growing markets for carbide consumption. However, China’s domestic carbide production has plateaued due to emissions regulations, leading to increased imports of high-end carbide products from Europe and Japan—supporting global price levels.
-
North America: Reshoring of manufacturing and defense spending are driving carbide demand. U.S. producers are investing in near-shoring of tool production, but reliance on imported tungsten persists, keeping prices sensitive to trade policies.
-
Europe: The EU’s Green Deal and digitalization initiatives are spurring demand for efficient machining solutions. However, energy costs and carbon compliance regulations are adding to production costs, further contributing to price firmness.
Geopolitical and Trade Factors
Export licensing requirements for strategic materials, including tungsten, have tightened under U.S.-China tech competition frameworks. The U.S. Department of Commerce has added certain high-performance carbide grades to restricted lists, impacting global supply flows. Meanwhile, the EU is reviewing critical raw material dependencies, potentially leading to stockpiling initiatives that could increase short-term demand volatility.
Price Outlook for H2 2026
Carbide prices in H2 2026 are expected to remain stable to slightly increasing, with an average year-over-year increase of 5–8% depending on grade and region. Premium grades used in aerospace and medical applications may see price increases up to 10%, reflecting supply bottlenecks and high performance requirements.
Long-term contracts between tooling suppliers and end-users are becoming more common, providing price stability but limiting spot market liquidity. This trend is reducing price transparency but supporting investment in production capacity.
Conclusion
The H2 2026 carbide market is characterized by tight supply, resilient demand, and technological premiumization. While recycling and efficiency gains are mitigating some cost pressures, fundamental constraints in tungsten supply and robust industrial demand are sustaining elevated price levels. Stakeholders should prepare for continued volatility and consider strategic sourcing, long-term agreements, and investment in alternative materials or tool life optimization to manage costs effectively.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Carbide Prices (Quality, IP)
Sourcing carbide—especially for industrial applications like cutting tools, wear parts, or mining equipment—requires careful evaluation beyond just the price tag. Overlooking critical factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant long-term costs, performance issues, or legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Underestimating Quality Variability Despite Similar Pricing
Carbide prices can appear competitive across multiple suppliers, but the actual material quality may vary widely. Low-cost carbide often uses inconsistent raw materials, suboptimal sintering processes, or lacks rigorous quality control. This can result in premature tool failure, inconsistent performance, and increased downtime. Always request material certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), microstructure analysis, and performance test data to verify quality claims.
Ignoring Grain Structure and Binder Content Specifications
The performance of carbide is highly dependent on grain size and cobalt (or other binder) content. Slight deviations can drastically affect hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. Suppliers may not disclose full composition details or may use proprietary blends without performance validation. Ensure technical specifications are clearly defined in contracts and independently verified through third-party testing when sourcing from new or unfamiliar vendors.
Falling for Counterfeit or Recycled Carbide Misrepresented as Virgin Material
Some suppliers offer “virgin” carbide at suspiciously low prices, but the material may be recycled or counterfeit. Recycled carbide, while usable in certain applications, typically has impurities and inconsistent properties. Counterfeit products may mimic branding or certifications without meeting original standards. Verify supplier authenticity, check for batch traceability, and consider conducting spectrographic analysis to confirm material composition.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Tool Design and Composition
Many high-performance carbide formulations and tool geometries are protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing tools or materials from suppliers that replicate patented designs—even unintentionally—can expose your company to IP infringement claims. Always confirm that the supplier has the right to manufacture and sell the product, and request documentation proving freedom to operate, especially when sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement.
Relying on Incomplete or Unverified Certifications
Suppliers may present certifications that appear legitimate but are outdated, falsified, or issued by unrecognized bodies. This is particularly common with ISO, RoHS, or REACH compliance claims. Conduct due diligence by verifying certifications through official databases or using third-party audit services. Lack of proper documentation can result in supply chain disruptions or non-compliance penalties.
Failing to Secure IP Rights in Custom Tooling or Formulations
When developing custom carbide tools or requesting proprietary blends, companies often assume ownership of the design or composition. However, without clear contractual agreements, the supplier may retain IP rights, limiting your ability to switch vendors or scale production. Always include IP assignment clauses in development contracts and ensure all custom formulations are documented and legally protected.
Prioritizing Short-Term Cost Savings Over Total Cost of Ownership
The cheapest carbide may lead to higher operational costs due to frequent replacements, machining inaccuracies, or production delays. A comprehensive cost analysis should include tool life, performance consistency, and downtime. Investing in higher-quality, IP-compliant carbide often results in lower total cost of ownership and reduced legal exposure.
By recognizing and mitigating these pitfalls, businesses can make more informed sourcing decisions that balance cost, quality, and risk—ensuring reliable performance and legal compliance in their carbide supply chain.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Carbide Price
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations when managing carbide pricing, procurement, shipping, and regulatory adherence. Ensuring alignment across these areas is critical for cost control, supply chain efficiency, and legal conformity.
Shipping and Transportation
Carbide materials—particularly in powder, scrap, or finished tool forms—require specialized handling due to their weight, value, and potential classification as hazardous materials. Use secure, tamper-evident packaging and consider temperature and moisture control during transit. Partner with carriers experienced in industrial goods and capable of providing real-time tracking. Air freight may be necessary for high-value or urgent shipments, but sea freight is cost-effective for bulk quantities. Always declare accurate weights and material types to avoid customs delays.
Import/Export Regulations
Carbide (especially tungsten carbide) may be subject to export controls due to dual-use applications in defense and advanced manufacturing. Verify compliance with international regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or the EU Dual-Use Regulation. Obtain required licenses when exporting to restricted countries or end-users. Maintain detailed records of transactions and end-use certifications. Monitor changes in trade policies, particularly involving key carbide-producing nations such as China.
Customs Documentation and Duties
Accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes are essential for proper classification of carbide products (e.g., 8208 for cutting tools, 8101 for tungsten carbide powders). Provide complete commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Misclassification can lead to duty discrepancies, penalties, or shipment seizures. Work with customs brokers to anticipate and manage duty rates, which can vary significantly by country and product form.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Carbide dust is hazardous if inhaled. Ensure all handling, packaging, and transport comply with OSHA (in the U.S.) or equivalent occupational safety standards. Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) with every shipment. Confirm that recycling and disposal of carbide scrap follow local environmental regulations, such as RCRA in the U.S. or the EU Waste Framework Directive. Consider closed-loop recycling programs to reduce environmental liability and raw material costs.
Anti-Bribery and Ethical Sourcing
Carbide raw materials (e.g., tungsten, cobalt) may originate from regions with high risk for conflict minerals or unethical labor practices. Adhere to frameworks like the OECD Due Diligence Guidance and comply with the U.S. Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502. Conduct supplier audits and require certifications to confirm responsible sourcing. Maintain transparency in pricing and contracts to prevent corruption risks.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain comprehensive records of all transactions, compliance certifications, shipping documents, and communication with regulatory bodies. These records support internal audits and regulatory inspections. Implement a digital document management system to ensure traceability and quick retrieval. Regular internal audits help identify and correct compliance gaps before they escalate.
By integrating these logistics and compliance practices, organizations can ensure accurate carbide pricing models reflect true operational costs while minimizing legal and supply chain risks.
Conclusion on Sourcing Carbide Pricing:
Sourcing carbide at a competitive price requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, and supply chain reliability. Market prices for carbide are influenced by fluctuating raw material costs—particularly tungsten, cobalt, and other critical metals—as well as manufacturing capabilities, geographic location, and global demand. While suppliers from regions like China often offer lower prices due to scale and lower production costs, they may present risks related to quality consistency and longer lead times. In contrast, European or North American suppliers may charge a premium but typically offer higher quality standards, better technical support, and faster delivery.
Effective sourcing also involves building strong supplier relationships, negotiating long-term contracts to hedge against price volatility, and considering total cost of ownership—factoring in shipping, duties, certifications, and potential rework or downtime from subpar materials. Additionally, recycling scrap carbide can significantly reduce costs and support sustainability initiatives.
In conclusion, the optimal carbide sourcing strategy involves a diversified supplier base, continuous market monitoring, and a focus on total value rather than unit price alone. This ensures not only cost-efficiency but also consistent quality and supply resilience in the long term.