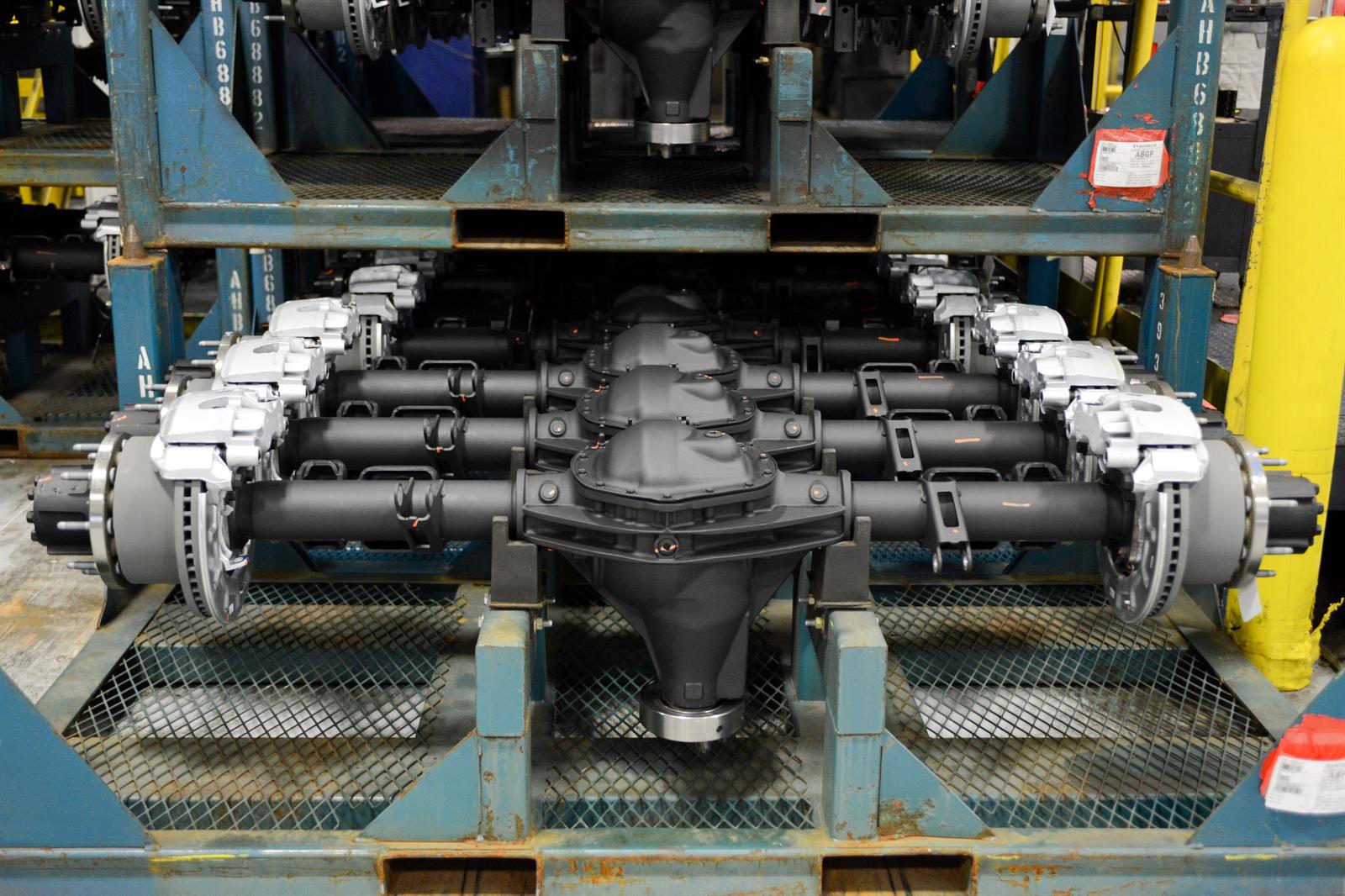
The global automotive front axle market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising vehicle production, advancements in axle technology, and increasing demand for fuel-efficient and lightweight components. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the automotive axle market was valued at USD 53.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by expanding electric vehicle (EV) adoption, which demands high-performance axles capable of handling increased torque and weight distribution. As manufacturers focus on enhancing vehicle safety, durability, and efficiency, the role of front axle systems has become more critical than ever. In this evolving landscape, key players are investing in R&D and strategic partnerships to maintain competitiveness. Below are the top 10 car front axle manufacturers leading innovation and market share in this high-growth sector.
Top 10 Car Front Axle Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Currie Enterprises
Domain Est. 1997
Website: currieenterprises.com
Key Highlights: Currie Enterprises is a premier manufacturer of high-performance direct replacement, and custom muscle car, and truck rearend axle assemblies….
#2 TEN Factory
Domain Est. 2008
Website: tenfactory.com
Key Highlights: The TEN Factory product line includes: chromoly front and rear axle pair kits, performance single axle kits, and replacement axle shafts….
#3 Aftermarket
Domain Est. 1993
Website: dana.com
Key Highlights: Dana’s specialized Crate Axle distributor program provides a prepackaged solution for many light vehicle drivetrain builds that are manufactured to exacting ……
#4 Axle Assemblies
Domain Est. 1996
#5 American Axle & Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: aam.com
Key Highlights: As a leading global Tier 1 Automotive and Mobility Supplier, AAM designs, engineers and manufactures Driveline and Metal Forming technologies to support ……
#6 Automotive Axles Limited
Domain Est. 1999
Website: autoaxle.com
Key Highlights: Automotive Axles Limited has been manufacturing reliable & long-life light Medium & Heavy duty Drive axles, Front Steer axles, Non-Drive axles, axles for ……
#7 RCV Performance
Domain Est. 2003
#8 New Premium CV Axles
Domain Est. 2013
Website: trakmotive.com
Key Highlights: TrakMotive® Automotive CV Axles transfer power from the transmission to the drive wheels of a vehicle. They consist of a CV Joint and Drive Shaft….
#9 American Axle & Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2013
Website: demandaam.com
Key Highlights: AAM has developed a series of axle and driveshaft components to make it easier for the installer to perform a repair or a complete replacement job….
#10 BRIST • Axle and Transmission for the Future of Bus & Truck
Domain Est. 2014
Website: bristaxle.com
Key Highlights: BRIST is a full-system supplier of axles and transmission for vans, trucks and buses, with a lot of activities going on in e-mobility sphere….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Car Front Axle

H2 2026 Market Trends for Car Front Axle
The global car front axle market in H2 2026 is expected to be shaped by accelerating technological shifts, evolving regulatory landscapes, and changing consumer preferences, driven primarily by the ongoing transformation of the automotive industry. Key trends include:
1. Accelerated Electrification Driving Axle Design Innovation:
With EV adoption surpassing 25% of global new car sales in 2026, front axles are increasingly being redesigned for electric powertrains. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, battery electric vehicles (BEVs) often utilize front-mounted electric motors, requiring integrated e-axles that combine motor, inverter, gearbox, and differential into a single compact unit. This shift favors lightweight, high-efficiency designs using advanced materials like high-strength aluminum alloys and composite components to maximize vehicle range. Suppliers are focusing on modular e-axle platforms to serve multiple OEMs, reducing development costs and accelerating time-to-market.
2. Rise of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and Vehicle Dynamics Integration:
Front axles are becoming critical enablers of ADAS and automated driving functions. In H2 2026, there is growing integration of sensors, actuators, and software-controlled suspension and steering systems within the front axle assembly. Features like torque vectoring, adaptive damping, and steer-by-wire systems are increasingly common in premium and high-performance EVs, enhancing handling, safety, and ride comfort. This trend demands smarter, more connected front axle systems capable of real-time data exchange with the vehicle’s central control unit.
3. Lightweighting and Sustainability Pressures:
Regulatory mandates for lower CO₂ emissions and extended EV range are pushing OEMs and suppliers to prioritize lightweighting. In H2 2026, front axles are seeing increased use of forged aluminum control arms, hollow anti-roll bars, and high-tensile steel components. Simultaneously, sustainability initiatives are driving demand for recyclable materials and greener manufacturing processes, including reduced energy consumption and lower-emission surface treatments.
4. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization:
Geopolitical tensions and lessons from recent disruptions have led to a strategic shift toward regionalized supply chains. In H2 2026, major axle manufacturers are expanding localized production capacity—particularly in North America and Southeast Asia—to serve EV-focused OEMs and reduce dependency on long global supply lines. This trend supports faster response times and compliance with regional content requirements, especially under policies like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships Among Suppliers:
The complexity and capital intensity of developing next-generation e-axles are driving consolidation in the supplier base. In H2 2026, Tier 1 suppliers are forming strategic alliances with EV startups, battery manufacturers, and software firms to co-develop integrated powertrain solutions. Mergers and acquisitions are also increasing, as smaller players seek scale to compete in the rapidly evolving market.
Conclusion:
By H2 2026, the car front axle is no longer a purely mechanical component but a technologically advanced, electrified, and intelligent system central to vehicle performance, efficiency, and safety. OEMs and suppliers that embrace modularity, electrification, connectivity, and sustainability will lead the market, while those slow to adapt risk obsolescence in an increasingly competitive and innovation-driven landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Car Front Axles: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing car front axles, especially from international or non-OEM suppliers, involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to safety issues, costly recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, may not adhere to stringent automotive quality management systems such as IATF 16949. This can result in inconsistent material composition, improper heat treatment, or poor machining tolerances—compromising the axle’s durability and safety under stress.
Use of Substandard Materials
To reduce costs, some manufacturers may use inferior-grade steel or fail to meet required metallurgical specifications. This increases the risk of premature fatigue, cracking, or catastrophic failure during operation.
Lack of Rigorous Testing and Certification
Reputable front axles undergo extensive testing—including fatigue testing, load testing, and dynamic simulations. Suppliers that skip or falsify test reports may deliver components that fail under real-world conditions, posing serious safety hazards.
Poor Quality Control and Inspection Processes
Inadequate in-process and final inspections can allow defective axles (e.g., with micro-cracks, misaligned components, or incorrect dimensions) to reach the market. Relying solely on supplier-provided documentation without third-party validation heightens this risk.
Insufficient Traceability
Without proper batch or serial traceability, identifying and recalling faulty axles becomes nearly impossible. This lack of traceability also complicates root cause analysis during failure investigations.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Replication of OEM Designs
Many aftermarket front axles are reverse-engineered copies of original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. Sourcing such components may involve using patented designs, trademarks, or technical specifications without permission, exposing buyers to IP infringement claims.
Trademark and Branding Violations
Suppliers may use logos, part numbers, or packaging that mimic OEM branding, misleading customers and violating trademark laws. Even if unintentional, purchasing these parts can implicate the buyer in contributory infringement.
Lack of IP Due Diligence
Buyers often fail to verify whether suppliers have legitimate rights to produce and sell the axle designs. Without proper licensing agreements or design ownership documentation, the supply chain becomes vulnerable to legal action, customs seizures, or forced product withdrawal.
Grey Market and Counterfeit Goods
Purchasing through unauthorized distributors increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or grey-market axles. These parts not only lack quality assurance but are frequently associated with IP violations and can void vehicle warranties.
Exposure to Legal and Financial Liability
In the event of an IP dispute, the end buyer or distributor—not just the manufacturer—can face lawsuits, fines, or injunctions. This is especially critical in regulated markets like the EU or North America, where enforcement of IP rights is strict.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and require certifications (e.g., IATF 16949).
– Demand material test reports and independent quality inspections.
– Perform IP risk assessments and require suppliers to warrant design legality.
– Source through authorized channels and use legal agreements that include IP indemnification clauses.
– Partner with reputable third-party verification services for both quality and IP compliance.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, companies can safeguard their supply chains, ensure vehicle safety, and avoid costly legal and operational setbacks.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Car Front Axle
Overview
The car front axle is a critical automotive component responsible for supporting the vehicle’s weight, enabling steering (in most configurations), and transmitting driving force (in front-wheel-drive vehicles). Due to its structural importance and mechanical complexity, transporting and importing/exporting front axles requires adherence to specific logistics protocols and regulatory compliance standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling of car front axles across the supply chain.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transportation. Front axles are heavy, often weighing between 20–50 kg, and have precision-machined surfaces susceptible to corrosion and impact.
- Use robust wooden crates or steel-reinforced containers to protect against crushing and impact.
- Apply anti-corrosion coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper to prevent rust, especially in maritime or humid environments.
- Secure the axle with foam padding, straps, or custom fixtures to minimize movement during transit.
- Label packages clearly with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Invert,” “This Side Up”) and include part numbers and serial identifiers.
Transportation Requirements
Due to weight and size, transport planning must account for mode-specific constraints.
- Road Transport: Use flatbed or enclosed trailers with proper load securing (e.g., ratchet straps, load bars). Ensure compliance with weight distribution regulations (e.g., ADR in Europe, FMCSA in the U.S.).
- Maritime Shipping: Palletize units and secure within 20’ or 40’ containers. Comply with International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) code if lubricants or treated metals are present.
- Air Freight: Rarely used due to weight and cost, but if required, use IATA-compliant packaging and ensure proper documentation for customs clearance.
Regulatory Compliance
Export/Import Regulations
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Typically classified under 8708.80 (Axles and axle components for motor vehicles). Confirm with local customs authority for accuracy.
- Import Duties & Taxes: Vary by country. For example, the U.S. applies a standard duty rate of 2.5% under HTSUS 8708.80.60, while the EU may apply 4–6% depending on origin.
- Rules of Origin: Comply with trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) to qualify for preferential tariffs. Maintain detailed Bills of Materials (BOM) and manufacturing records.
Safety & Environmental Standards
- REACH (EU): Disclose substances of very high concern (SVHC) if present in coatings or materials.
- RoHS Compliance: Ensure electronic components (e.g., sensor-equipped axles) meet restrictions on hazardous substances.
- EPA & DOT (U.S.): While front axles are not directly regulated like emissions systems, manufacturers must follow general automotive safety standards under FMVSS.
Documentation Requirements
Complete and accurate paperwork is essential for customs clearance and traceability.
- Commercial Invoice: Include item description, quantity, value, HS code, and Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, CIF).
- Packing List: Detail weight, dimensions, and number of packages.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for tariff preference claims.
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS): If the axle contains lubricants or treated surfaces.
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Proof of shipment and carrier contract.
Incoterms® Considerations
Select the appropriate Incoterms® rule to define responsibilities:
- EXW (Ex Works): Buyer arranges pickup and assumes all risk.
- FCA (Free Carrier): Seller delivers to a carrier; risk transfers at that point.
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Seller pays freight and insurance to destination; recommended for long-distance shipments.
Quality & Traceability
Maintain traceability from manufacturing to delivery.
- Lot/Batch Tracking: Use serialized labels or RFID tags for recall readiness.
- Inspection Reports: Provide pre-shipment inspection certificates (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) if required by buyer or customs.
- Warranty & Recall Protocols: Ensure systems are in place to address compliance issues or defects post-shipment.
Conclusion
Transporting car front axles demands a coordinated approach that balances logistics efficiency with strict regulatory compliance. By adhering to proper packaging, documentation, and international standards, manufacturers and logistics providers can ensure timely delivery while minimizing risks of damage, customs delays, or non-compliance penalties. Regular review of trade regulations and supply chain practices is recommended to maintain compliance in a dynamic global market.
Conclusion for Sourcing Car Front Axle:
In conclusion, sourcing a car front axle requires a comprehensive approach that balances quality, cost, availability, and compatibility. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their reputation, manufacturing standards, and adherence to industry regulations to ensure the durability and safety of the component. Conducting thorough market research, considering both OEM and aftermarket options, and assessing total cost of ownership—including logistics, lead times, and after-sales support—will enable informed decision-making. Ultimately, selecting a reliable and efficient front axle supplier contributes significantly to vehicle performance, safety, and long-term customer satisfaction. A strategic sourcing process ensures that the chosen axle meets technical specifications while supporting operational efficiency and competitive advantage in the automotive supply chain.