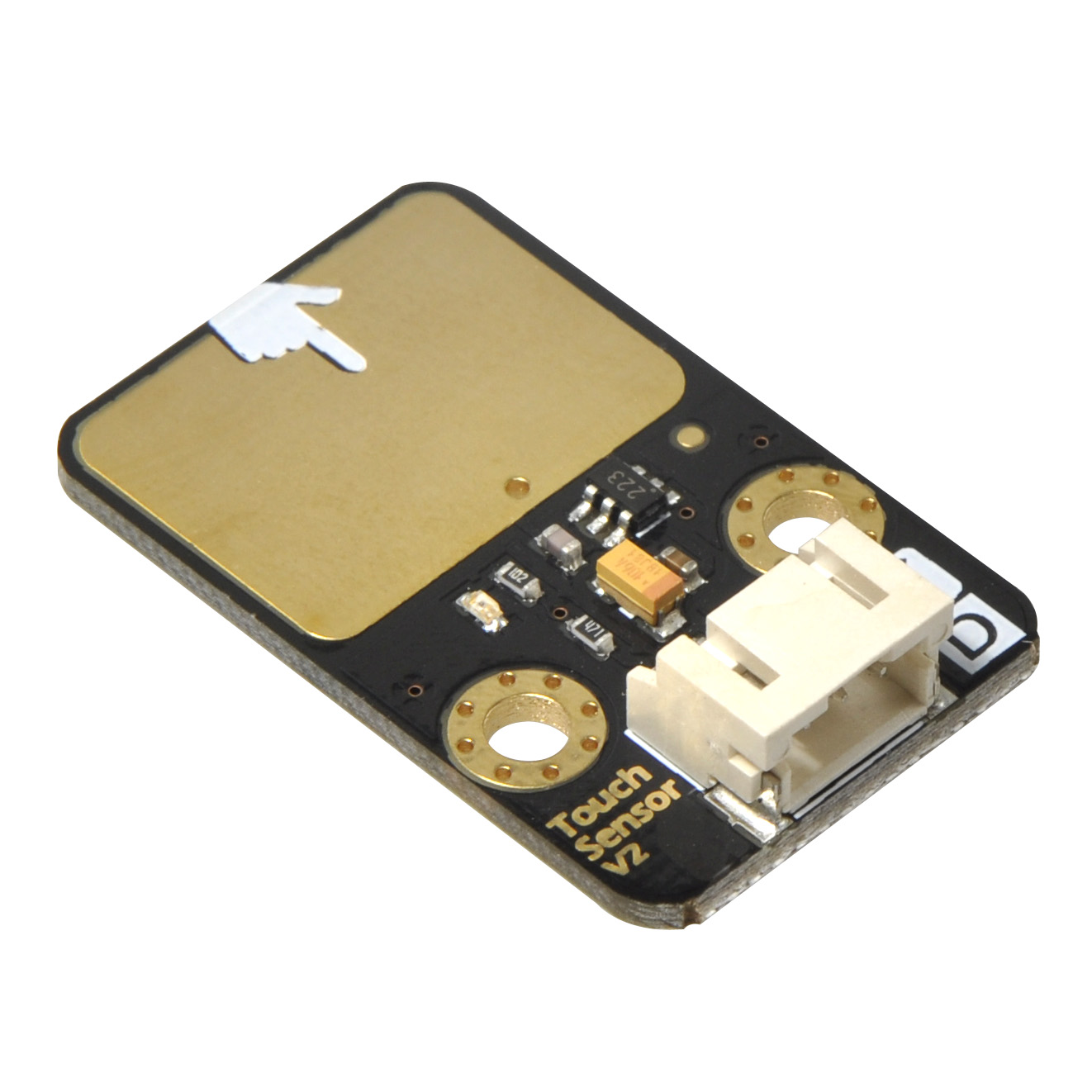
The global capacitive touch sensor market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 8.67 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 14.37 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8.9% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of touch-enabled devices, advancements in human-machine interface (HMI) technologies, and the proliferation of touchscreens in automotive infotainment and control systems. As innovation accelerates and performance expectations rise, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in developing high-sensitivity, energy-efficient, and durable capacitive touch solutions. Below, we spotlight the top 10 capacitive touch sensor manufacturers shaping the future of intuitive interface technology.
Top 10 Capacitive Touch Sensor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Capacitive Touch Sensing Technology Overview
Domain Est. 1989
Website: synaptics.com
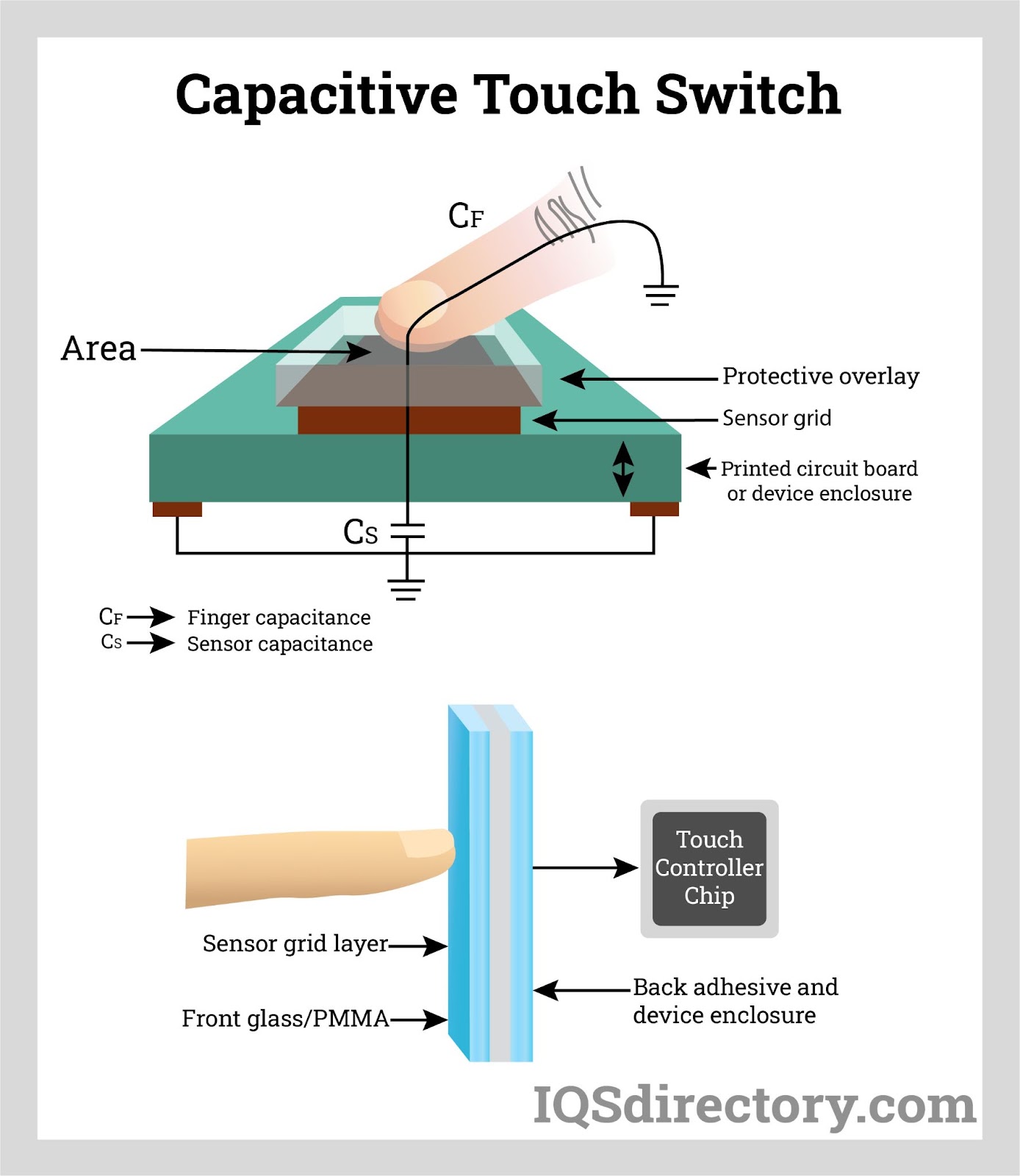
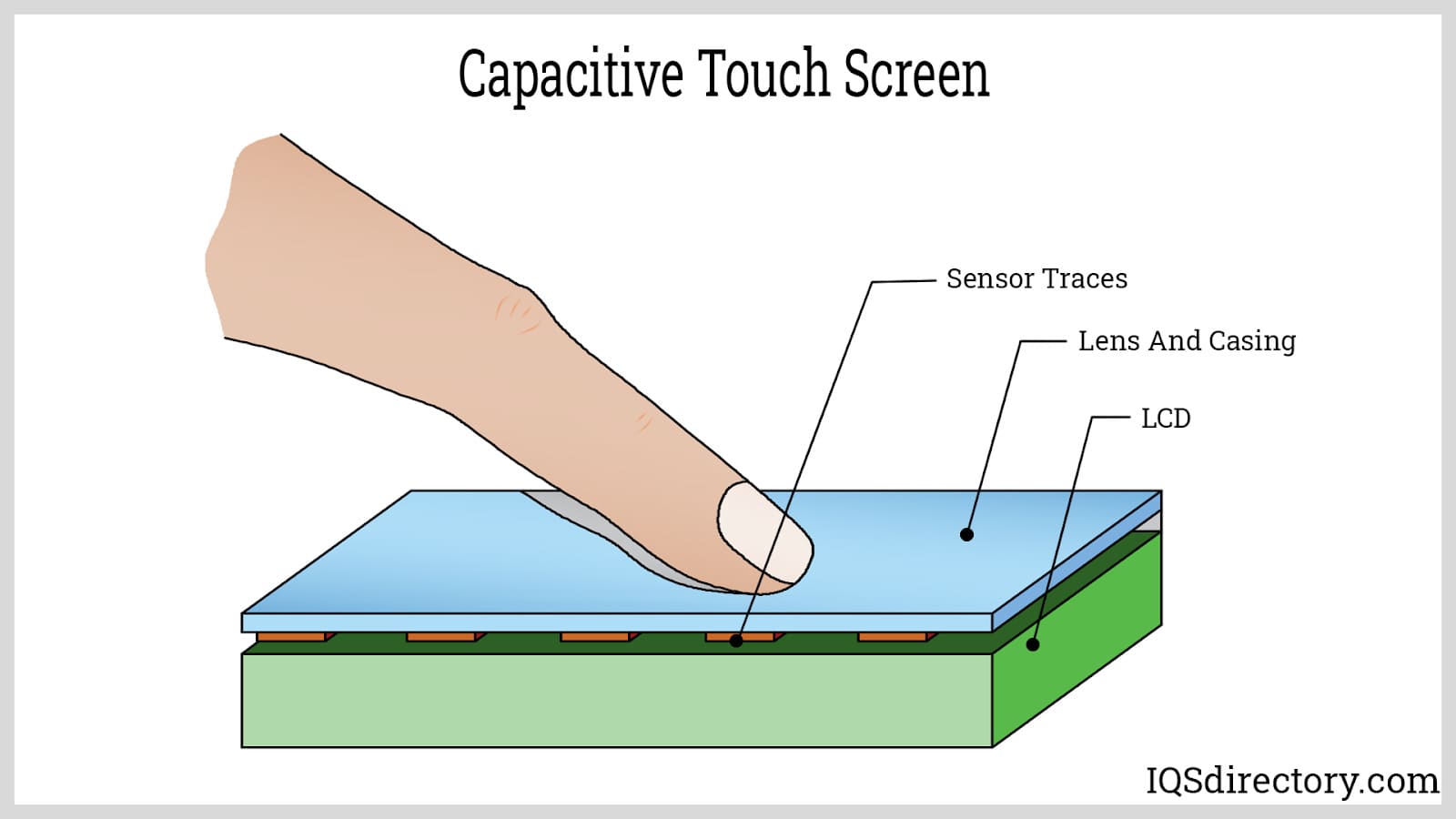
Key Highlights: Synaptics capacitive touch sensors create an electric field above of the glass surface of a touchscreen. Materials science, antenna theory, and electromagnetism ……
#2 Sensors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata develops and manufactures high-performance inertial sensors, including accelerometers, inclinometers, and combined gyroscope-accelerometer sensors….
#3 CAPTRON world market leader for capacitive touch buttons …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: captron.com
Key Highlights: CAPTRON is the world market leader for capacitive touch buttons and manufacturer of high-quality sensors and sensor solutions….
#4 Capacitive Touch
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cirque.com
Key Highlights: The Technology of Touch Cirque solutions are all built upon the technology of capacitive touch sensing. By sensing the minute difference in electrical fields ……
#5 Nissha Co., Ltd.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: nissha.com
Key Highlights: Our film-based capacitive-type touch sensor is thin and light, while providing high visibility and narrow frames. It has been widely adopted in applications ……
#6 Capacitive Touch Sensor
Domain Est. 2000
Website: shinpoly.com
Key Highlights: Shin-Etsu Polymer developed a range of touch sensors based on various conductive materials printed or deposited on ultra thin films….
#7 Capacitive touch panel & Overlay
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jae.com
Key Highlights: JAE’s automotive capacitive touch panels began mass production in 2012, which is earlier than other companies, and have more than seven years of results….
#8 Capacitive Touch Panels
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hosiden.com
Key Highlights: Touch Sensors | | │Hosiden is electronic parts maker manufacturing and selling connector, switch, acoustic parts and capacitive touch panel….
#9 Capacitive Touch HMIs
Domain Est. 2002
Website: renesas.com
Key Highlights: Explore Renesas’ advanced capacitive touch solutions for human-machine interfaces (HMIs), offering high sensitivity, noise tolerance, easy development tools ……
#10 Capacitive Touch Sensors
Website: rafi-northamerica.com
Key Highlights: Our cap touch designs provide a seamless interaction between man and machine, putting the end user in complete control of the experience….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Capacitive Touch Sensor
H2: Projected Market Trends for Capacitive Touch Sensors in 2026
By 2026, the global capacitive touch sensor market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, expanding applications, and evolving consumer demands. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Proliferation in Consumer Electronics & Smart Devices:
Capacitive touch sensors will remain dominant in smartphones, tablets, and laptops, with increased adoption in emerging smart home devices (smart thermostats, appliances, lighting controls), wearables (smartwatches, AR/VR headsets), and smart speakers. Demand will be fueled by the need for sleek, durable, and intuitive user interfaces.
2. Growth in Automotive Applications:
The automotive sector will be a major growth driver. By 2026, capacitive touch sensors will be increasingly integrated into center consoles, infotainment systems, climate controls, steering wheels (for gesture control), and digital instrument clusters. This shift supports the trend toward minimalist, high-tech cabin designs and enhanced driver safety through haptic feedback integration.
3. Advancements in Sensing Technology:
Technological improvements will enhance performance and reliability. Expect wider adoption of:
– Projected Capacitive (PCAP) Technology: Offering multi-touch capability, high sensitivity, and support for gesture recognition.
– In-Cell and On-Cell Integration: Reducing device thickness and improving optical clarity in displays.
– Wet Tolerance and Glove Mode: Enabling reliable operation in challenging environments (rain, cold weather), expanding usability in outdoor and industrial settings.
4. Expansion into Industrial and Medical Sectors:
Capacitive sensors will see increased use in industrial control panels, medical devices (patient monitors, diagnostic equipment), and public kiosks due to their durability, ease of cleaning, and resistance to mechanical wear—critical in hygienic and rugged environments.
5. Emphasis on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
As energy regulations tighten and sustainability becomes a priority, low-power capacitive controllers and sensors designed for battery-operated devices (e.g., IoT sensors, wearables) will gain prominence. Manufacturers will also focus on recyclable materials and reduced environmental impact in production.
6. Regional Market Dynamics:
Asia-Pacific will continue to lead market growth, driven by robust electronics manufacturing in China, South Korea, and India. North America and Europe will see steady growth, supported by automotive innovation and smart home adoption. Emerging markets will expand access to touch-enabled consumer devices.
7. Competitive Landscape and Innovation:
The market will remain competitive, with key players focusing on miniaturization, improved signal-to-noise ratios, and integration with AI for predictive touch and context-aware interfaces. Strategic partnerships between sensor manufacturers, IC designers, and OEMs will accelerate innovation.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the capacitive touch sensor market will be characterized by broader application reach, enhanced functionality, and deeper integration into everyday technologies. As human-machine interaction evolves, capacitive touch sensors will remain a foundational technology, adapting to new form factors and user experience demands across industries.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Capacitive Touch Sensors: Quality and IP Concerns
Sourcing capacitive touch sensors involves more than just selecting a component based on specifications. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and delayed time-to-market. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, may lack rigorous quality control processes. This can result in inconsistent sensor performance across batches—such as varying sensitivity, response time, or false triggering—due to poor calibration, substandard materials, or inadequate testing. Always verify a supplier’s quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and request sample testing under real-world conditions before mass production.
Lack of Environmental and Durability Testing
Capacitive touch sensors are often used in demanding environments (e.g., industrial, automotive, outdoor). A common pitfall is selecting sensors not adequately tested for temperature extremes, humidity, EMI/RFI interference, or mechanical wear. Without proper ingress protection (IP) ratings (e.g., IP65, IP67), sensors may fail when exposed to dust, moisture, or cleaning agents. Ensure the supplier provides full environmental test data and specifies appropriate sealing or coating methods.
Inadequate or Missing IP Protection in Supplier Components
Some off-the-shelf capacitive touch controllers or firmware are based on open-source or unlicensed IP. Using such components can expose your product to intellectual property infringement claims. Always verify that the sensor module and its embedded firmware are fully licensed and free from third-party IP conflicts. Request documentation such as IP indemnification clauses in supply agreements.
Hidden Dependence on Proprietary Algorithms Without Licensing Clarity
Many advanced capacitive sensors rely on proprietary noise filtering, gesture recognition, or proximity algorithms. Suppliers may not clearly disclose whether these algorithms are licensed or if additional royalty fees apply—especially in high-volume production. Failing to address this upfront can lead to unexpected costs or legal challenges. Clarify licensing terms and scalability of fees before finalizing the supplier.
Insufficient Design Support and Documentation
Low-quality suppliers often provide incomplete or inaccurate technical documentation, including schematics, PCB layout guidelines, and firmware integration instructions. Poorly documented sensors can lead to integration issues, prolonged debugging, and suboptimal performance. Choose suppliers who offer comprehensive design support, reference designs, and accessible engineering teams.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, companies can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legally compliant integration of capacitive touch sensors into their products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Capacitive Touch Sensors
Product Classification and HS Code
Capacitive touch sensors are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 8536.50 or 8542.31, depending on function and integration level. If the sensor is part of a larger assembly (e.g., integrated into a control panel), the classification may shift based on the primary function of the end product. Accurate classification is critical for customs clearance, duty calculation, and import/export compliance. Confirm the correct HS code with a licensed customs broker or trade authority in the destination country.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Capacitive touch sensors must comply with regional and international regulatory standards to ensure safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and environmental protection. Key regulations include:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC 2014/30/EU) is mandatory. RoHS (2011/65/EU) and REACH regulations apply to restricted substances.
– FCC Certification (USA): Required under Part 15 of the FCC rules for unintentional radiators. Ensures electromagnetic interference (EMI) does not disrupt other devices.
– UKCA Marking (UK): Post-Brexit equivalent to CE marking; required for products sold in Great Britain.
– KC Certification (South Korea): Mandatory for electronic components sold in Korea, covering safety and EMC.
– PSE Mark (Japan): Required for electrical products under the DENAN Law; touch sensors may fall under Class B (non-specified products).
Ensure all certifications are current and documentation is available for customs and market surveillance authorities.
Packaging and Shipping Considerations
Capacitive touch sensors are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD), moisture, and physical damage. Use the following packaging standards:
– ESD-Safe Packaging: Employ static-shielding bags (e.g., metallized or pink poly), conductive foam, or static-dissipative containers.
– Moisture Protection: Include desiccant packs and moisture barrier bags (MBB), especially for sensors with exposed circuits or during ocean freight.
– Physical Protection: Use rigid outer cartons with cushioning (e.g., foam inserts or corrugated dividers) to prevent impact damage.
– Labeling: Clearly mark packages with ESD-sensitive symbols, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”), and compliance labels (e.g., CE, FCC).
Ship via carriers experienced in handling electronic components, and consider climate-controlled transport for high-humidity routes.
Import/Export Documentation
Accurate documentation is essential for smooth cross-border logistics. Required documents include:
– Commercial Invoice: Must detail product description, HS code, value, country of origin, and terms of sale (e.g., FOB, DDP).
– Packing List: Specifies weight, dimensions, and quantity per package.
– Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries for tariff assessment or trade agreements.
– Compliance Certificates: Copies of FCC, CE, RoHS, or other relevant certifications.
– Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Provides shipping and tracking details.
Ensure all documents are consistent in product naming and technical specifications to avoid customs delays.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Capacitive touch sensors must adhere to environmental directives limiting hazardous substances:
– RoHS (EU): Restricts lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain flame retardants.
– REACH (EU): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– WEEE (EU): Mandates proper end-of-life recycling; producers may need to register and contribute to take-back programs.
– China RoHS: Applies similar restrictions for products sold in China.
Maintain a bill of materials (BOM) with substance declarations from suppliers to support compliance audits.
Supply Chain and Vendor Management
Ensure suppliers and contract manufacturers adhere to quality and compliance standards:
– Require ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) certifications.
– Conduct regular audits for RoHS and REACH compliance.
– Verify ESD control procedures in manufacturing and packaging areas.
– Maintain traceability through lot numbering and batch records for recall readiness.
Collaborate with vendors to align logistics practices, including labeling, packaging, and documentation.
End-of-Life and Recycling
Capacitive touch sensors contain electronic components requiring responsible disposal:
– Design for disassembly where possible.
– Partner with certified e-waste recyclers compliant with R2 or WEEELABEX standards.
– Provide customers with take-back options or recycling instructions, especially in regulated markets (e.g., EU, California).
This supports circular economy goals and regulatory obligations under WEEE and similar laws.
Conclusion on Sourcing Capacitive Touch Sensors
After evaluating various options for sourcing capacitive touch sensors, it is evident that a balanced approach considering performance, cost, reliability, and supply chain stability is essential. Capacitive touch sensors are widely available from multiple global suppliers, including established manufacturers in Asia (e.g., China, Taiwan), Europe, and North America. Key players such as Texas Instruments, Analog Devices, Microchip, and specialized OEMs offer both standalone sensor ICs and integrated modules with varying levels of customization and support.
When selecting a supplier, factors such as sensitivity, power consumption, environmental durability (e.g., water resistance, glove operation), and compatibility with desired materials (glass, plastic) must align with the application requirements. Additionally, evaluating lead times, minimum order quantities (MOQs), technical support, and long-term availability is crucial—especially for volume production.
For prototyping and low-volume production, distributors like Digi-Key, Mouser, or SparkFun provide quick access to off-the-shelf solutions. For high-volume manufacturing, direct engagement with manufacturers or contract suppliers may offer better pricing and customization options.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of capacitive touch sensors requires a strategic assessment of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Partnering with reputable suppliers and maintaining flexibility in design to accommodate component availability will ensure timely development and robust end-product performance.