The global fastener market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand from automotive, construction, industrial machinery, and aerospace sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global fastener market size was valued at USD 103.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. A significant portion of this demand stems from high-precision threaded fasteners such as cap screws and bolts, which are critical for structural integrity and performance in engineered applications.
Cap screws and bolts, while often used interchangeably, differ in design, application, and load capacity, making the choice of manufacturer crucial for quality, consistency, and compliance with international standards like ISO, DIN, and ASTM. With Asia Pacific dominating production—accounting for over 50% of global output—the competitive landscape includes both established Western manufacturers and rapidly advancing suppliers from China, India, and Japan.
As industries prioritize reliability and supply chain resilience, selecting the right manufacturer has become a strategic decision. This analysis highlights the top 10 cap screw and bolt manufacturers based on production scale, innovation, global reach, and adherence to quality benchmarks, offering data-driven insights for procurement professionals and engineering teams.
Top 10 Cap Screw Vs Bolt Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hex Bolts vs. Hex Cap Screws
Domain Est. 1998
Website: portlandbolt.com
Key Highlights: Generally speaking, hex cap screws are used in precise applications like an OEM setting where tight tolerances are required….
#2 Custom Fasteners Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nationalbolt.com
Key Highlights: National Bolt and Nut Corporation is a ISO Certified Nationwide custom fasteners manufacturer of nuts, washers, bolts and fasteners. Contact us today!…
#3 Hex Bolts and Cap Screws
Domain Est. 2015
Website: stsindustrial.com
Key Highlights: Cap screws have a washer face under the head, while hex bolts do not. Hex bolts are typically manufactured using a hot-forging process and have a flat end. Cap ……
#4 Fasteners
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sae.org
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsThis SAE Part Standard covers selected metric screws, hex bolts, and nuts manufactured in accordance with American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) ……
#5 PEM – PennEngineering
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pemnet.com
Key Highlights: PEM offers innovative fastening solutions for a variety of applications across industries like Automotive Electronics, Consumer Electronics, Datacom and more….
#6 Cap Screws vs. Socket Screws
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mudgefasteners.com
Key Highlights: Cap screws offer robustness and high torque capabilities, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. On the other hand, socket screws provide a sleek ……
#7 The Difference Between Hex Head Cap Screws & Hex Bolts
Domain Est. 2005
Website: wilsongarner.com
Key Highlights: Hex head cap screws and hex bolts may look and sound like the same thing, but they’re different. Learn how to distinguish them using ASME’s ……
#8 12 Point Bolts vs. Hex Head Cap Screws
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: A 12-point bolt design offers the same bearing surface as a hex head cap screw of comparable size. There really is no difference between the two….
#9 What’s the Difference Between Hex Bolts and Hex Cap Screws?
Domain Est. 2024
Website: hrfastener.com
Key Highlights: The real difference between a hex bolt and a hex cap screw lies in two structural features: the cap screw has a bearing surface (also called ……
#10 [PDF] Fastener Catalog and Assortments
Website: dla.mil
Key Highlights: Bolts have good galvanic protection and excellent lubricity. CORROSION RESISTANT STEEL, PASSIVATED: Bolts have a high degree of corrosion resistance compared to ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cap Screw Vs Bolt
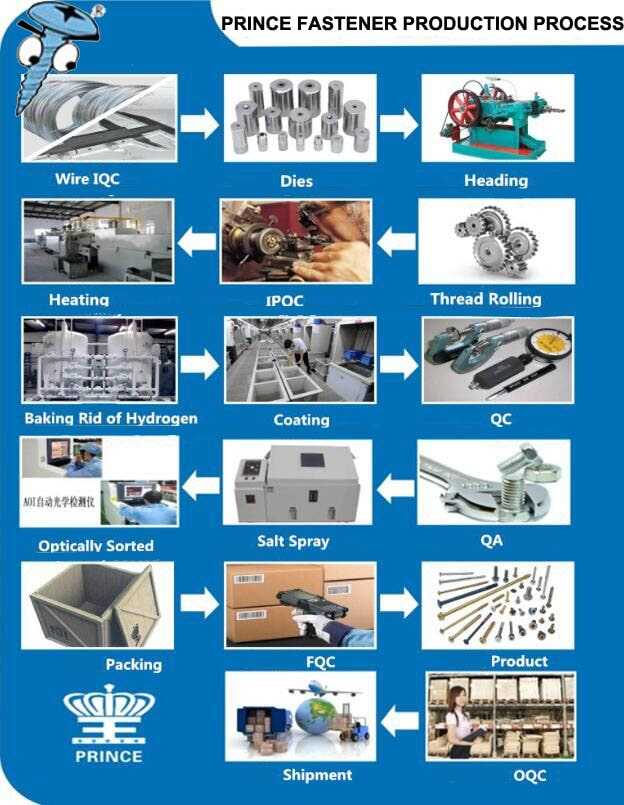
H2: Market Trends in 2026 – Cap Screws vs. Bolts
As the global industrial and construction sectors evolve through 2026, the market dynamics between cap screws and bolts are being shaped by technological advancements, material innovations, regulatory standards, and shifting demand across key industries. While both fasteners serve critical roles in mechanical assemblies, distinct trends are emerging that differentiate their applications, growth trajectories, and market preferences.
1. Rising Demand in Precision Engineering Favors Cap Screws
Cap screws, known for their precision fit, consistent thread quality, and superior finish, are gaining traction in high-performance industries such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and medical devices. The trend toward automation and miniaturization in these sectors is driving demand for fasteners that ensure tight tolerances and repeatable performance. In 2026, cap screws are increasingly preferred in applications where alignment, vibration resistance, and aesthetic finish matter—especially in robotics and electric vehicles (EVs), where reliability under dynamic loads is critical.
2. Bolts Maintain Dominance in Heavy-Duty and Infrastructure Applications
Bolts, particularly hex and structural bolts, continue to dominate in construction, heavy machinery, and oil & gas industries. With global infrastructure investment rising—especially in emerging economies—bolts remain the go-to choice for high-strength, load-bearing joints. The 2026 market sees ongoing demand for corrosion-resistant and high-tensile bolts, driven by stringent safety regulations and longer lifecycle expectations for industrial assets. Innovations in galvanization and alloy compositions are enhancing bolt durability, reinforcing their role in large-scale projects.
3. Material and Sustainability Trends Impact Both Segments
Both cap screws and bolts are experiencing a shift toward high-strength, lightweight materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and advanced composites. Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials and energy-efficient production methods. In 2026, the use of carbon footprint-labeled fasteners is gaining momentum, with cap screw producers leading in precision coating technologies that reduce waste and extend service life.
4. Regional Market Divergence
In North America and Europe, the cap screw market is growing faster due to advanced manufacturing ecosystems and stricter quality standards. Conversely, in Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia—bolts hold a larger market share, driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. However, as these regions upgrade their industrial capabilities, demand for precision fasteners like cap screws is expected to rise steadily.
5. Digitalization and Smart Fastening Solutions
The integration of IoT and smart monitoring systems in industrial equipment is creating new opportunities for intelligent fastening solutions. In 2026, cap screws are more frequently embedded with sensors or used in conjunction with torque-monitoring systems to ensure proper assembly in critical applications. While bolts are also seeing smart adaptations, the precision nature of cap screws makes them more compatible with automated quality control processes.
Conclusion
By 2026, the cap screw and bolt markets are diverging based on application specificity rather than direct competition. Cap screws are carving a niche in high-tech, precision-driven industries, while bolts remain indispensable in structural and heavy-duty applications. Manufacturers who align with these trends—offering specialized, sustainable, and technologically advanced fastening solutions—will be best positioned to capitalize on evolving market demands.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cap Screws vs Bolts (Quality and IP Considerations)
When sourcing fasteners, distinguishing between cap screws and bolts—and understanding their quality and IP (Ingress Protection) implications—is critical to ensuring performance, safety, and longevity. Misunderstanding these components can lead to costly mistakes. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Misidentifying Cap Screws and Bolts
A frequent error is treating cap screws and bolts as interchangeable. Cap screws are typically precision-engineered for close-tolerance applications and are designed to be threaded into a tapped hole, often with tighter dimensional and strength tolerances. Bolts, on the other hand, are generally used with a nut and may not require the same level of precision. Sourcing the wrong type can result in improper fit, reduced clamping force, or joint failure.
Overlooking Material and Grade Specifications
Both cap screws and bolts are available in various grades (e.g., ASTM A449, A325, ISO 898-1) and materials (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel). A common pitfall is assuming equivalent grades between cap screws and bolts without verifying mechanical properties. For example, a Grade 8 bolt does not have the same performance characteristics as a cap screw of similar appearance but different specification. Always match the fastener to the required strength, corrosion resistance, and environmental demands.
Confusing Thread Types and Engagement Requirements
Cap screws often rely on full thread engagement in a pre-tapped hole, while bolts depend on nut compatibility. Using a cap screw in a blind hole with insufficient thread depth—or selecting a bolt with incompatible thread pitch—can compromise joint integrity. Ensure thread type (coarse vs. fine), length, and engagement depth align with design requirements.
Neglecting Surface Finish and Corrosion Protection
Quality sourcing requires attention to surface treatments such as zinc plating, galvanization, or passivation, especially in harsh environments. A common oversight is selecting a fastener with inadequate corrosion resistance for outdoor or high-moisture applications. This is particularly important for stainless steel variants, where incorrect grade (e.g., 304 vs. 316) can lead to premature failure.
Ignoring IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings in Enclosure Applications
While IP ratings primarily apply to enclosures and housings, the fasteners used in sealing these systems play a critical role. Using standard bolts instead of specified cap screws (e.g., socket head cap screws with smooth shanks) can disrupt gasket compression or create gaps, reducing the overall IP rating of an assembly. Ensure fasteners contribute to maintaining the required environmental seal (e.g., dust and water resistance).
Assuming Interchangeability Across Standards
Cap screws and bolts are governed by different standards (e.g., ASME B18.2.1 for bolts, ASME B18.3 for socket cap screws). A key pitfall is assuming dimensional or performance equivalency across standards or regions (e.g., metric vs. imperial, ISO vs. ANSI). Always verify compliance with the relevant standard for your application.
Skipping Quality Certification and Traceability
In critical applications (e.g., aerospace, automotive, medical), sourcing fasteners without proper certification (e.g., ISO 898, ASTM, or DIN) or material traceability is a major risk. Low-cost suppliers may provide counterfeit or substandard products that fail under stress. Always require mill test reports, certification documentation, and batch traceability.
By recognizing these common pitfalls—particularly around terminology, specifications, environmental requirements, and quality assurance—procurement and engineering teams can make informed decisions that ensure reliability and compliance when sourcing cap screws versus bolts.

Logistics & Compliance Guide: Cap Screw vs Bolt
Understanding the distinctions between cap screws and bolts is crucial for logistics efficiency, regulatory compliance, and proper application in industrial and commercial settings. Although often used interchangeably, cap screws and bolts differ in design, function, and standards compliance, impacting procurement, inventory management, and end-use safety.
Definition and Key Differences
Cap Screw
A cap screw is a fastener with a domed or flat head (typically hex, socket head, or button head) designed to be tightened or loosened using a wrench or socket on the head. It is usually threaded along its entire length or has a partially threaded shank and is intended to be screwed into a pre-tapped hole. Cap screws often require no nut.
Bolt
A bolt is a fastener with a threaded shaft that is designed to be used with a nut. It typically features a plain (unthreaded) shank beneath the head and is meant to pass through unthreaded holes in mating parts, where a nut is then tightened to secure the assembly.
Material and Finish Standards
Both cap screws and bolts must comply with material and surface treatment standards to ensure durability and corrosion resistance.
- Common Materials: Carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel (e.g., AISI 304, 316), and aluminum.
- Finish Requirements:
- Zinc plating (ASTM B633)
- Hot-dip galvanizing (ASTM A153)
- Mechanical galvanizing (ASTM B695)
- Passivation for stainless steel (ASTM A967)
Compliance Note: When exporting or operating in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, automotive), adherence to RoHS, REACH, and conflict minerals regulations is mandatory. Certifications such as ISO 898-1 (mechanical properties) and ISO 3506 (stainless steel) must be documented.
Dimensional and Thread Specifications
- Cap Screws: Typically conform to ASME B18.2.1 (Square and Hex Bolts and Screws) or ASME B18.3 (Socket Head Cap Screws). Thread standards include UNC, UNF (Unified), or metric (ISO 68-1).
- Bolts: Governed by ASTM A307 (general-purpose carbon steel bolts), ASTM A325 (structural bolts), or ISO 4014/4017 (hex head bolts).
Logistics Impact: Mismatched thread types or dimensions can result in assembly failures and non-compliance. Ensure procurement aligns with project specifications and regional standards (e.g., metric vs. imperial).
Load and Performance Requirements
- Cap Screws: Often used in precision applications where high tensile strength and accurate torque control are essential (e.g., machinery, engines). Socket head cap screws (ASME B18.3) are rated for higher strength (e.g., Grade 8 or 12.9).
- Bolts: Used in structural or heavy-duty applications (e.g., construction, bridges). Structural bolts (e.g., ASTM A325 or A490) have specific load requirements and must meet ASTM F3125 standards.
Compliance Tip: Always verify load ratings and mechanical certifications (e.g., tensile strength, yield strength) during quality inspections and maintain traceability documentation.
Packaging, Labeling, and Traceability
Proper packaging ensures fasteners arrive undamaged and meet regulatory requirements.
- Packaging: Use moisture-resistant materials for corrosion-prone finishes. Separate mixed batches by grade, size, and finish.
- Labeling: Include:
- ASTM/ISO designation
- Material grade (e.g., 316 SS, Grade 8)
- Manufacturer ID
- Lot or heat number for traceability
- Country of origin (customs compliance)
Regulatory Note: In the EU, CE marking may be required for certain construction bolts. In North America, domestic preference rules (e.g., Buy American Act) may apply to public infrastructure projects.
Import/Export and Customs Compliance
- HS Codes:
- Bolts and screws typically fall under HS Code 7318.15 (hexagonal bolts and screws) or 7318.16 (other bolts and screws).
- Accurate classification avoids customs delays and tariff misapplication.
- Documentation: Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of conformance (CoC), and material test reports (MTRs) as needed.
- Country-Specific Rules: Some countries restrict certain platings (e.g., cadmium) or require third-party testing (e.g., UAE, Saudi Arabia).
Storage and Inventory Management
- Environmental Control: Store in dry, temperature-controlled areas to prevent corrosion, especially for plated or carbon steel fasteners.
- Inventory Segregation: Separate cap screws and bolts by type, size, and grade to prevent cross-use and ensure quality control.
- First Expired, First Out (FEFO): Apply for coated or treated fasteners with limited shelf life.
Summary: Best Practices for Logistics & Compliance
- Specify Correctly: Use precise terminology—“cap screw” vs. “bolt”—in purchase orders and technical drawings.
- Verify Standards: Confirm compliance with applicable ASTM, ISO, or DIN standards.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep CoCs, MTRs, and compliance declarations for audits.
- Train Procurement Teams: Ensure staff understand technical differences and regulatory implications.
- Audit Suppliers: Regularly assess suppliers for quality management (e.g., ISO 9001) and ethical sourcing.
By distinguishing cap screws from bolts in both specification and handling, organizations can enhance supply chain reliability, reduce compliance risks, and ensure product safety and performance.
Conclusion: Sourcing Cap Screws vs. Bolts
When deciding between sourcing cap screws and bolts, the choice ultimately depends on the specific application, performance requirements, and assembly conditions. Cap screws, with their precision fit, tighter tolerances, and variety of head styles (such as socket head and button head), are ideal for applications requiring high accuracy, repetitive assembly, and a clean, finished appearance—common in machinery, automation, and aerospace industries. They are typically used with pre-tapped holes and provide excellent clamping force with minimal protrusion.
Bolts, on the other hand, are better suited for structural applications where strength, durability, and ease of installation with nuts are priorities—such as in construction, heavy machinery, and infrastructure. They are generally more cost-effective for large-scale or less precise applications and offer greater flexibility in assembly with various nut types.
From a sourcing perspective, cap screws often come at a higher cost due to superior materials, tighter manufacturing tolerances, and specialized finishes. Bolts are generally more readily available and less expensive, especially in standard grades and sizes.
In summary, choose cap screws when precision, aesthetics, and performance under stress are critical. Opt for bolts when cost-efficiency, structural strength, and ease of field assembly are more important. Evaluating the design requirements, environmental conditions, and total cost of ownership will ensure the optimal fastener is selected for reliable, long-term performance.







![[PDF] Fastener Catalog and Assortments](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/pdf-fastener-catalog-and-assortments-706.jpg)

