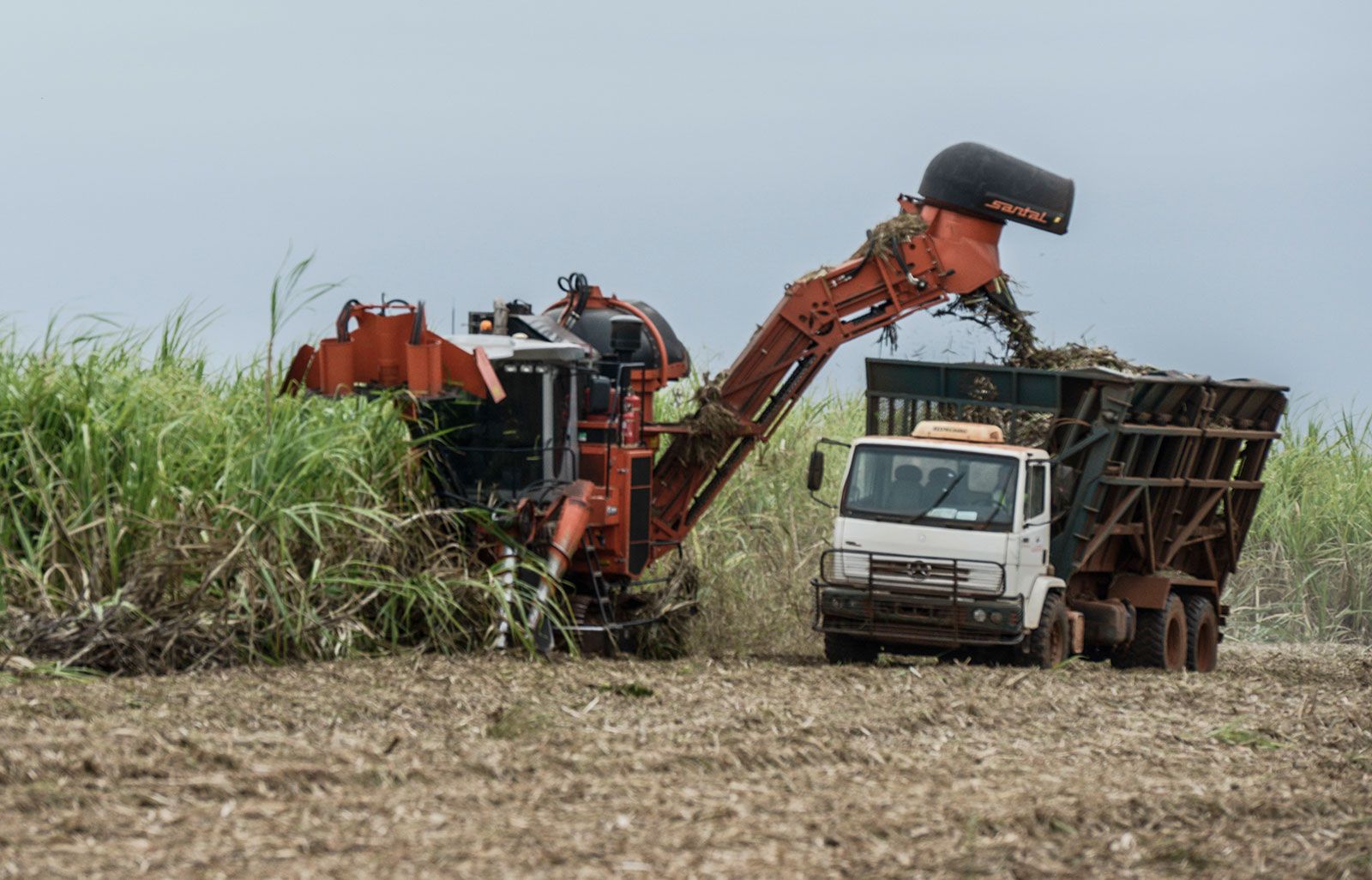
The global agricultural machinery market, driven by increasing demand for mechanization in farming, is witnessing robust growth, with the cane harvesting segment emerging as a key contributor. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the Agricultural Machinery Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by rising labor costs, advancements in automation, and government support for modern farming practices. Within this landscape, sugarcane harvesting machines are gaining traction as producers seek efficient, cost-effective alternatives to manual labor, particularly in large-scale operations across Brazil, India, and Australia. With sugarcane covering over 26 million hectares globally and production exceeding 1.9 billion tons annually (FAO, 2022), mechanized harvesting has become essential to meet output demands and improve operational efficiency. This growing adoption has spurred innovation among manufacturers, positioning the top nine cane harvesting machine producers at the forefront of technological advancement and market expansion.
Top 9 Cane Harvesting Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
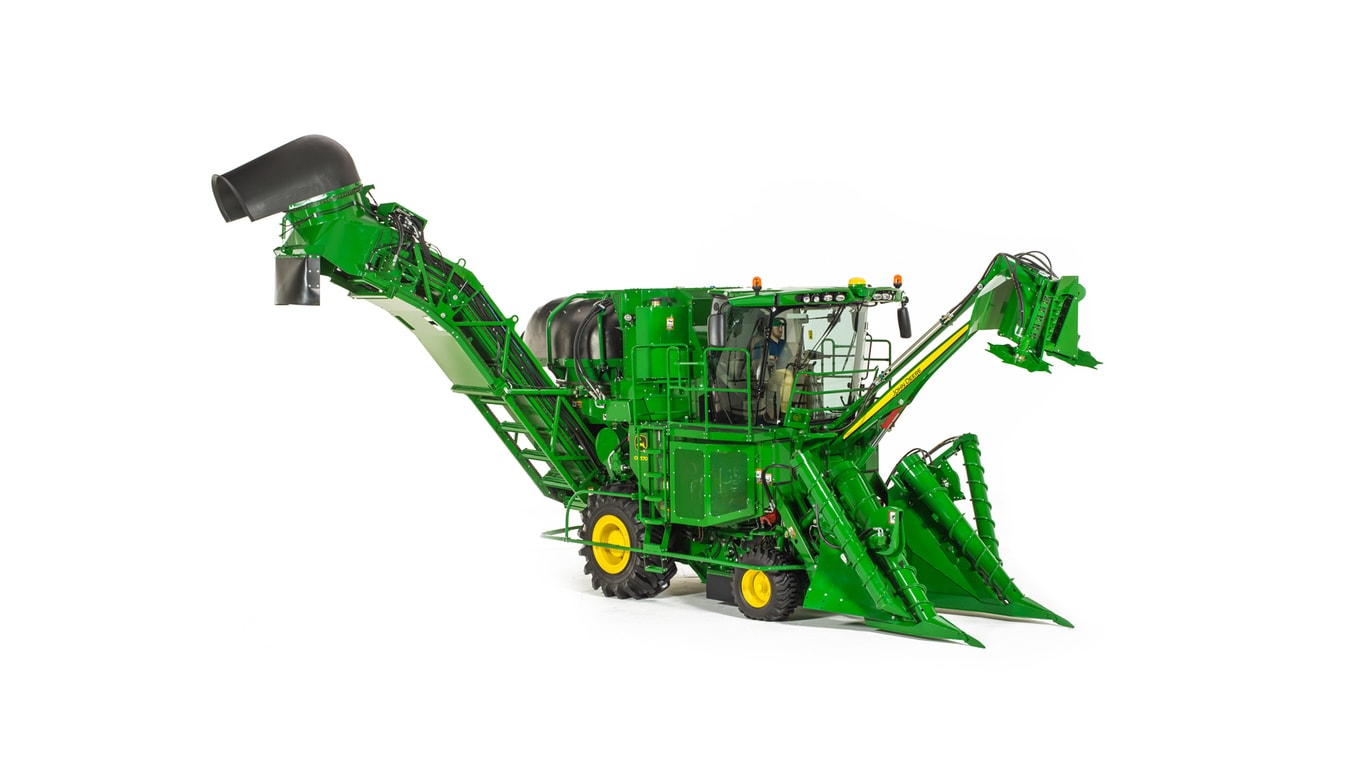
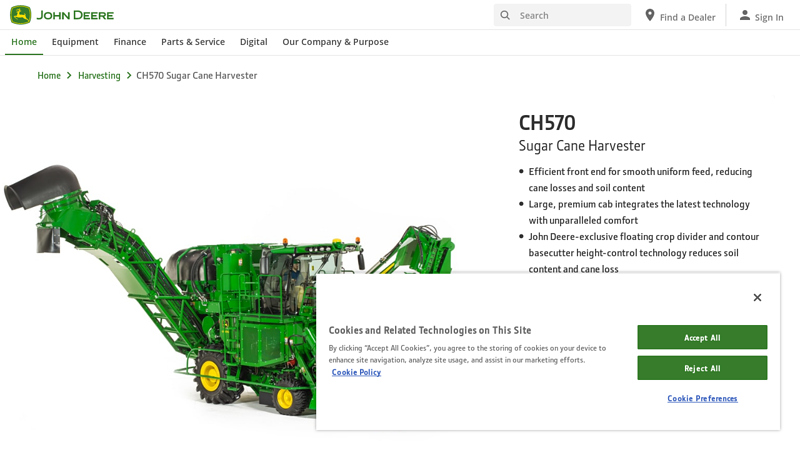
#1 CH570 Sugar Cane Harvester
Domain Est. 1990
Website: deere.com
Key Highlights: The 32.51-cm (12.8-in) G5Plus Display puts vital machine and harvesting information within easy reach. With touchscreen technology, it is simple to make quick ……
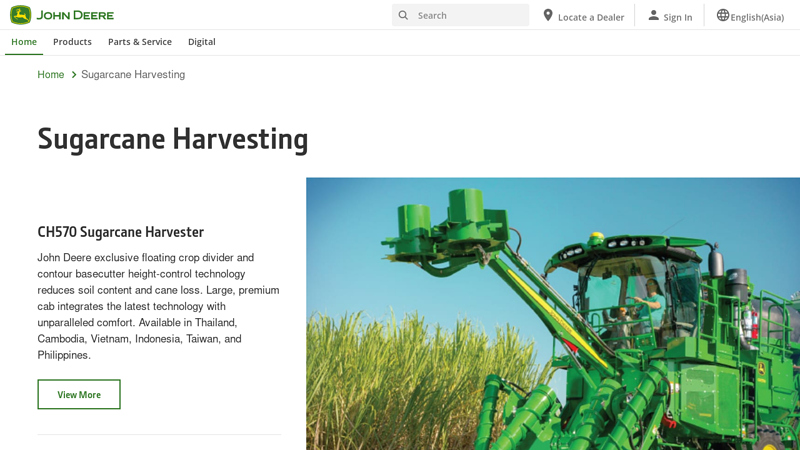
#2 Sugarcane Harvesting
Domain Est. 2007
Website: deere.asia
Key Highlights: CH570 Sugarcane Harvester. John Deere exclusive floating crop divider and contour basecutter height-control technology reduces soil content and cane loss….
#3 Compost Machine,Grain Machine,Cassava Machine,Sugarcane …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: tagrmfarming.com
Key Highlights: We are manufacturer of Compost Machine in China, if you want to buy Grain Machine, Cassava Machine, Sugarcane Machine, please contact us….
#4 Canetec
Website: canetec.com.au
Key Highlights: Canetec specialises in manufacturing Sugarcane Harvesters that are designed and built specially to help sugarcane growers enjoy more productive and ……
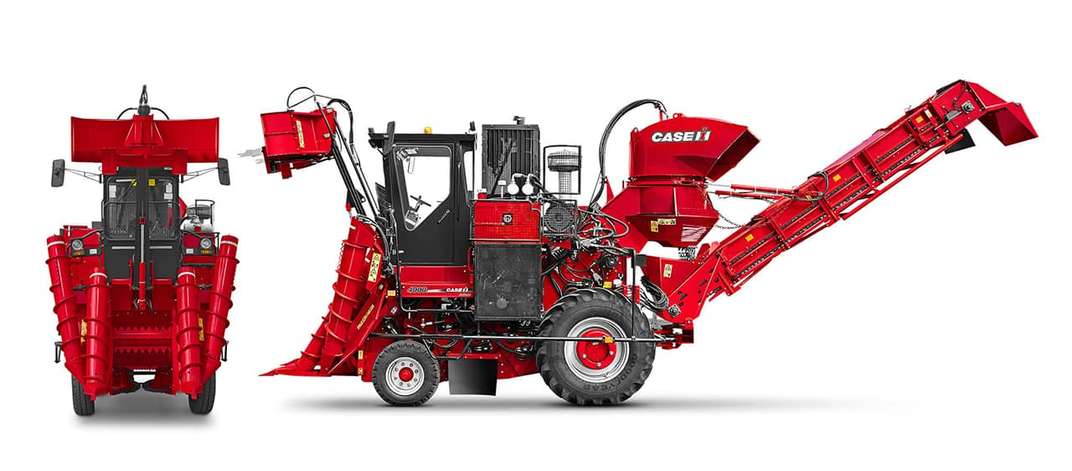
#5 Sugar Cane Harvester Austoft 4000
Domain Est. 1995
Website: caseih.com
Key Highlights: The Case IH Austoft 4000 is a compact sugar cane harvester designed to streamline the harvesting process in sugarcane fields that use reduced row spacing ……
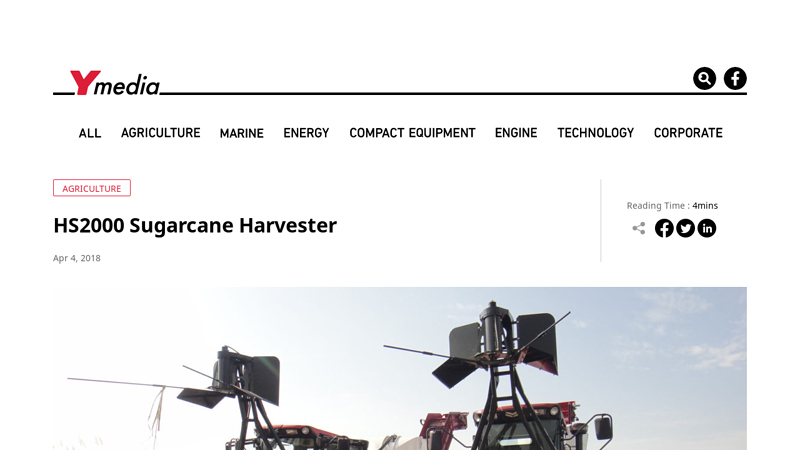
#6 HS2000 Sugarcane Harvester|Y media
Domain Est. 1996
Website: yanmar.com
Key Highlights: The HS2000 sugarcane harvester project started in 2015, and the final design was put into full scale production in 2017….
#7 Sugarcane Harvesters
Domain Est. 1997
Website: agriculture.newholland.com
Key Highlights: New Holland Agriculture Menu AUSTOFT 4010 MAXX SUGARCANE HARVESTER State of the art performance with a powerful legacy….
#8 ShaktimanAgro: Agriculture Equipment
Domain Est. 2005
Website: shaktimanagro.com
Key Highlights: Discover premium agriculture equipment and rotavators at Shaktiman Agro. Shop high-quality agricultural implements designed to boost your farming ……
#9 harvesting sugarcane
Domain Est. 2021
Website: fmworldagri.com
Key Highlights: FMWORLD Agricultural Machinery provide high quality, consistent harvesting sugarcane year round, contact us for more details!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cane Harvesting Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cane Harvesting Machines
The global cane harvesting machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, economic pressures, and evolving agricultural demands. Key trends shaping this market include:
1. Accelerated Automation and Smart Technology Integration:
By 2026, semi-automated and fully automated cane harvesters equipped with AI, GPS guidance, and real-time yield monitoring will become increasingly mainstream. Machine learning algorithms will optimize cutting height, speed, and load distribution based on terrain and crop conditions, boosting efficiency and reducing losses. Integration with farm management software (FMS) will enable predictive maintenance and data-driven decision-making, enhancing overall operational ROI.
2. Rising Demand for Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Solutions:
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals will push manufacturers toward electric and hybrid-powered harvesters. Battery technology improvements will make electric models more viable for longer operations, reducing carbon emissions and noise pollution. Additionally, emphasis will grow on machines that minimize soil compaction and support green cane harvesting (leaving trash on fields), preserving soil health and reducing burning practices.
3. Expansion in Emerging Markets and Smallholder Adoption:
While large plantations in Brazil, India, and Australia remain key markets, 2026 will see increased penetration in Southeast Asia and Africa. To cater to smallholder farmers, manufacturers will introduce more affordable, compact, and modular harvesting solutions—such as semi-mechanized or towed units—bridging the mechanization gap and improving productivity in labor-constrained regions.
4. Labor Shortages and Cost Pressures Driving Mechanization:
Persistent labor shortages and rising wages—especially in traditional cane-growing regions—will continue to accelerate the shift from manual to mechanical harvesting. Governments and cooperatives are expected to offer subsidies and financing schemes, making advanced machinery more accessible and reinforcing the economic case for investment in harvesting technology.
5. Focus on Durability and After-Sales Support:
With machines operating in harsh tropical conditions, reliability and low maintenance will be critical differentiators. Leading OEMs will expand localized service networks and offer digital support platforms, predictive diagnostics, and extended warranties to build customer trust and ensure high machine uptime during critical harvest seasons.
In summary, the 2026 cane harvesting machine market will be defined by smarter, greener, and more accessible technology, responding to global demands for efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in sugar and bioenergy supply chains.
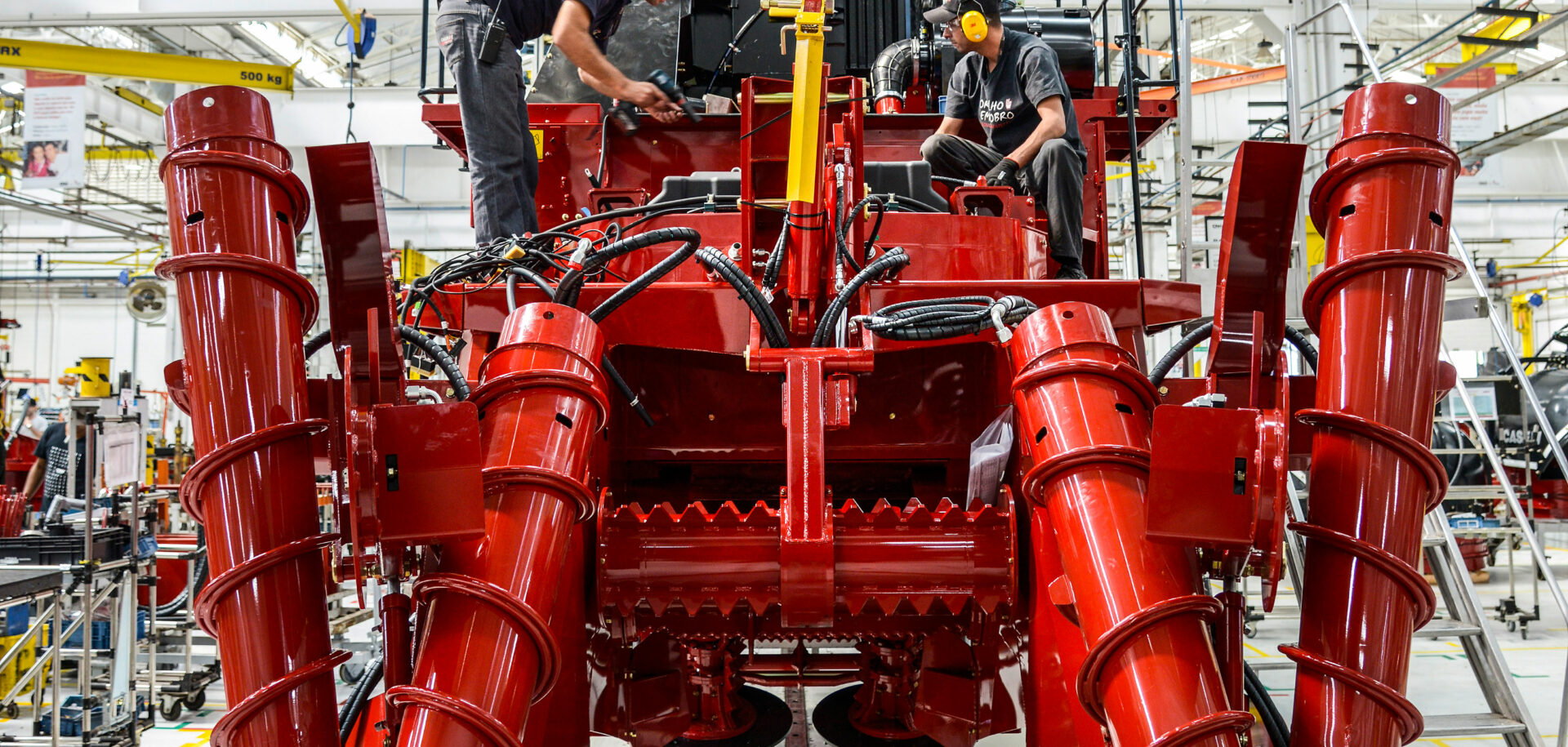

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cane Harvesting Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing cane harvesting machines from international suppliers, particularly from regions with less stringent regulatory oversight, exposes buyers to significant risks related to both machine quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Poor Build Quality and Component Standards
Many low-cost cane harvesters on the market use substandard materials and components to reduce manufacturing costs. This includes thin-gauge steel frames prone to cracking under stress, underpowered or unreliable engines, and hydraulics susceptible to leaks. Inferior welding and assembly practices further compromise structural integrity, leading to frequent breakdowns during harvesting seasons. Buyers may receive machines that fail to meet basic agricultural durability standards, resulting in costly downtime and repair expenses.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Suppliers, especially those operating without official distribution networks, often lack reliable after-sales service infrastructure. Spare parts may be difficult to source, with long lead times or complete unavailability. This forces operators to resort to makeshift repairs or third-party components that may not meet original specifications, further degrading machine performance and safety. The absence of trained technicians in the region compounds these challenges, undermining the long-term viability of the equipment.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Environmental Regulations
Many imported cane harvesters fail to meet international safety standards such as ISO or regional requirements (e.g., CE marking in Europe). Critical safety features—like emergency shutdown systems, rollover protection structures (ROPS), and proper guarding—may be missing or poorly implemented. Additionally, machines may emit excessive noise or pollutants, violating local environmental regulations and exposing operators and communities to health risks.
Intellectual Property Infringement
A major concern is the unauthorized replication of patented designs, technologies, and branding from established manufacturers (e.g., John Deere, New Holland, Case IH). Some suppliers produce “clone” harvesters that closely mimic the appearance and functionality of original equipment, potentially infringing on design patents, utility models, and trademarks. Purchasing such machines may expose the buyer to legal action, especially if the machines are imported into jurisdictions that enforce IP rights strictly. Customs authorities may seize shipments, and end-users could face liability for contributory infringement.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Origin
Suppliers may falsify technical specifications, overstating engine power, harvesting capacity, or fuel efficiency. Machines might be labeled as “original” or “certified” without valid documentation. In some cases, components are sourced from multiple unverified vendors and assembled without quality control, making traceability impossible. This misrepresentation undermines informed purchasing decisions and increases the risk of equipment failure.
Lack of Warranty and Legal Recourse
Contracts with unverified suppliers often include weak or unenforceable warranty terms. Disputes over defective machines are difficult to resolve due to jurisdictional challenges, language barriers, and the absence of legal presence in the buyer’s country. Recovering costs for non-conforming goods becomes nearly impossible, leaving the buyer financially exposed.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, verify supplier credentials, request third-party quality inspections, and consult legal experts regarding IP compliance before finalizing procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cane Harvesting Machine
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, operation, and maintenance of a cane harvesting machine. Whether importing, exporting, or operating domestically, adherence to regulatory standards and logistical best practices ensures efficiency, safety, and legal compliance.
Regulatory Compliance
Equipment Standards and Certification
Ensure the cane harvesting machine complies with international and local agricultural machinery standards, such as ISO 4254 (safety of agricultural machinery) or regional equivalents like CE marking (Europe) or ASABE standards (USA). Certification must include safety guards, emergency stops, operator protection structures (ROPS/FOPS), and emission controls.
Environmental Regulations
Harvesting operations must comply with environmental laws, including noise emission limits, dust control, and protection of nearby water bodies. In some regions, seasonal harvesting restrictions apply to minimize ecological impact. Confirm alignment with local environmental protection agency (EPA) or equivalent authority guidelines.
Emissions and Fuel Regulations
Verify that the machine meets applicable emissions standards (e.g., EU Stage V, U.S. EPA Tier 4 Final). Use of biodiesel or other alternative fuels may be encouraged or mandated in certain areas—check fuel compatibility and regulatory incentives.
Transportation Logistics
Pre-Shipment Preparation
Before transport, the machine must be cleaned of soil, plant matter, and contaminants to comply with biosecurity regulations. Drain fluids if required and secure all movable parts. Prepare documentation including bill of lading, packing list, and certificate of origin.
Domestic and International Shipping
For international movement, comply with phytosanitary regulations enforced by national agricultural departments. Obtain necessary import/export permits and ensure customs clearance by providing technical specifications, valuation documents, and applicable tariffs (e.g., HS Code 8433.51 for harvesting machinery).
Route Planning and Permits
Due to the size and weight of cane harvesters, special transport permits may be required for oversized loads. Coordinate with local transportation authorities for route approvals, especially when moving across state or provincial lines. Plan routes to avoid low bridges, weak roads, or restricted zones.
On-Site Operations and Safety Compliance
Operator Licensing and Training
Operators must be certified and trained in the safe use of the harvesting machine. Training should cover emergency procedures, machine-specific controls, and compliance with OSHA (or equivalent) safety standards.
Workplace Safety Protocols
Implement safety measures including lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance, proper signage, and personal protective equipment (PPE). Conduct regular safety audits and equipment inspections.
Field Operation Regulations
Adhere to local agricultural guidelines on harvesting hours, worker breaks, and field access. In some regions, burning of cane fields prior to harvest is regulated—ensure compliance with air quality laws if applicable.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Scheduled Maintenance Compliance
Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules to ensure machine reliability and regulatory compliance. Keep detailed logs of repairs, part replacements, and safety inspections.
Documentation and Audits
Maintain records of compliance certificates, transport permits, operator training, and environmental assessments. These documents may be required during regulatory audits or insurance claims.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of a cane harvesting machine requires careful attention to logistics planning and regulatory compliance across transportation, operation, and maintenance. Proactive engagement with local authorities, adherence to safety and environmental standards, and thorough documentation will minimize risks and ensure smooth, legal operation.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Cane Harvesting Machine
In conclusion, sourcing a cane harvesting machine is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of sugarcane operations. After evaluating key factors such as machine capacity, terrain compatibility, operational costs, maintenance requirements, and local support services, it becomes evident that selecting the right harvester involves a careful balance between upfront costs and long-term benefits.
Modern cane harvesters offer advanced features like GPS guidance, auto-levelling systems, and improved residue management, contributing to reduced labor dependency, minimized harvest losses, and better field management. Additionally, sourcing from reputable manufacturers or suppliers—whether locally or internationally—ensures access to reliable machinery, technical support, and spare parts, which are critical for minimizing downtime.
It is also essential to consider local climatic conditions, farm size, and harvesting windows when selecting the appropriate model. Engaging with agricultural experts, conducting cost-benefit analysis, and potentially exploring leasing or cooperative ownership models can further optimize the sourcing decision.
Ultimately, investing in the right cane harvesting machine not only improves operational efficiency but also supports the long-term competitiveness and sustainability of sugarcane farming in an increasingly mechanized agricultural landscape.