Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Can Filling Equipment
The beverage industry’s shift toward canned products shows no signs of slowing. From craft breweries in Colorado to kombucha producers in Germany, manufacturers across North America and Europe face a critical decision: selecting can filling equipment that balances production demands, product integrity, and budget constraints.
The Challenge
Choosing the wrong filling system costs more than capital—it impacts:
- Product quality: Carbonation loss, oxidation, and inconsistent fill levels damage brand reputation
- Operational efficiency: Mismatched equipment creates bottlenecks and increases labor costs
- Regulatory compliance: TTB requirements in the US and EU standards demand precise volume control
- Scalability: Equipment that can’t grow with demand becomes an expensive liability
Whether you’re filling carbonated beverages requiring counter-pressure technology, hot-fill products needing specialized high-temperature systems, or viscous liquids with particulates, the technical requirements vary significantly.
What This Guide Covers
| Section | Focus |
|———|——-|
| Equipment Types | Counter-pressure, volumetric, level, and specialty fillers |
| Selection Criteria | Matching technology to product characteristics |
| Capacity Planning | From small-batch to high-volume production |
| Compliance | US and European regulatory considerations |
| Total Cost Analysis | Beyond purchase price—maintenance, consumables, and ROI |
This guide provides the technical specifications, comparison frameworks, and evaluation criteria you need to make an informed purchasing decision. No sales pitch—just actionable intelligence for procurement teams and operations managers navigating an increasingly complex equipment landscape.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Can Filling Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for can filling equipment
- Understanding can filling equipment Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of can filling equipment
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘can filling equipment’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for can filling equipment
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for can filling equipment
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘can filling equipment’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for can filling equipment Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing can filling equipment With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for can filling equipment
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the can filling equipment Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of can filling equipment
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for can filling equipment
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Can Filling Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top 6 Can Filling Machine Manufacturers – Levapack
Domain: levapack.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Your Go-To Guide for the Best 6 Can Filling Machine Manufacturers · Preface · #1 Levapack · #2 Krones AG · #3 SIDEL · #4 Tetra Pak · #5 KHS Group · #6 ……
2. Top Filling Machine Manufacturers & Finbolink Events 2025
Domain: finbolink.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Groninge manufactures filling and packaging equipment with a focus on stability and hygiene. Recognized as reliable can filling machine manufacturers, they ……
3. Can filling machine – Micmachinery
Domain: micmachinery.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: As a leading supplier of china tin can filling machines, Micmachinery combines advanced technology with superior craftsmanship. Our machines are designed to ……
4. Top Can Filling Machine Companies | Reliable Manufacturers 2025
Domain: sznewcrownmachine.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Discover leading can filling machine companies offering automated, high-efficiency solutions for beverages & food. Compare trusted suppliers with PLC ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Beer filling machines – Comac Group
Domain: comacgroup.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Comac offers beer filling machines for kegs, bottles, and cans, with both semi-automatic and automatic options available….
6. Ideal Pase: Filling Machines
Domain: idealpase.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Specializing in delivering best-in-class packaging machinery, Massman Companies offers Unscramblers, Liquid Fillers, Pouch Fillers, Cappers, Lidders, Cartoners ……
7. Can Filling Machines Craft Beverage Canning
Domain: fillmore.beer
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Our simplified Hybrid can filling technology integrates counter pressure filling and atmospheric filling in an all in one easy to use canning machine….
8. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer | E-PAK Machinery
Domain: epakmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
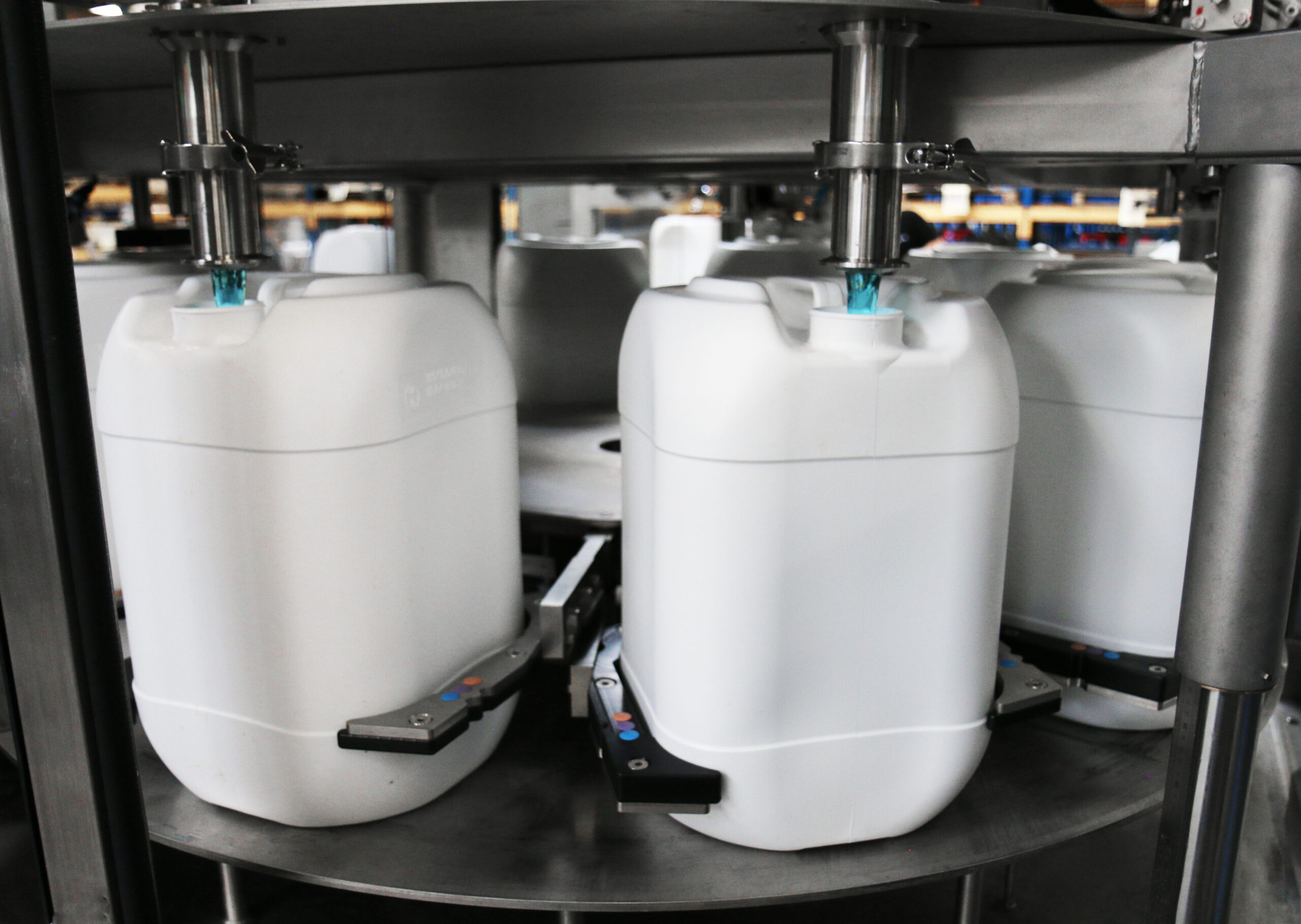

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
9. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer – ACASI Machinery – Acasi
Domain: acasi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: ACASI offers bottle unscramblers, fillers, cappers, labelers, neck banders, conveyors, accumulation tables, liquid filling, and bottle handling equipment….
10. Top 10 Carbonated Beverage Filling Machine Manufacturers 2025
Domain: suncrownmachine.com
Registered: 2025 (0 years)
Introduction: Here are the Top 10 Global Manufacturers in 2025, including Suncrown Machine, one of the most reliable names in turnkey beverage solutions….
Understanding can filling equipment Types and Variations
Understanding Can Filling Equipment Types and Variations
Selecting the right can filling equipment directly impacts your production efficiency, product quality, and regulatory compliance. This section breaks down the primary filling technologies available, helping you match equipment capabilities to your specific operational requirements.
Quick Comparison: Can Filling Equipment Types
| Type | Key Features | Best Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counter Pressure Fillers | Pressurised filling chamber; CO2 retention; fills from keg or brite tank | Beer, kombucha, soda, carbonated beverages | Maximises carbonation retention; handles crowlers and standard cans | Slower cycle times; higher equipment cost |
| Volumetric Fillers | Digital timer control; adjustable to 0.01 seconds; consistent volume dispensing | Spirits, juices, olive oil, vinegar | TTB compliance; precise volume control; flexible bottle/can sizing | Fill times vary with viscosity; requires calibration per product |
| Level Fillers | Sensor probe detection; automatic shut-off; adjustable shelf height | Wine, hot-fill products, specialty containers | Consistent fill levels regardless of container variations; ideal for non-standard containers | Volume may vary 3%+; not suitable for regulated volume requirements |
| Open Fillers (Gas Purge) | Gas purge cycle; automatic level sensor; minimal waste | Carbonated beverages (high-efficiency production) | Faster throughput; reduced product waste; efficient for volume operations | Less CO2 retention than counter pressure; requires gas supply |
| High-Temperature Particulate Fillers | Larger flow path; handles viscous liquids; accommodates particulates | Hot sauce, BBQ sauce, juices with pulp | Processes thick, chunky products; works with glass or plastic | Specialised application; not for thin liquids or carbonated products |
Counter Pressure Fillers
Counter pressure filling technology is the gold standard for carbonated beverages. The system pre-pressurises the can with CO2 before introducing the liquid, preventing foaming and preserving dissolved carbonation throughout the fill cycle.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How it works: The can is sealed against the fill head, purged with CO2, then pressurised to match the source vessel (keg or brite tank). Liquid flows under isobaric conditions, maintaining carbonation levels from source to sealed can.
Ideal for:
– Craft breweries packaging from kegs
– Kombucha producers requiring live carbonation
– Soda manufacturers prioritising fizz retention
– Crowler operations at taprooms and brewpubs
Considerations: Counter pressure systems require more operator training and typically have longer cycle times per can compared to atmospheric fillers. However, for carbonated products, the quality trade-off is non-negotiable.
Volumetric Fillers
Volumetric fillers dispense a precise, predetermined volume of liquid into each container. Digital timer controls allow adjustments down to 0.01 seconds, with settings stored in memory until manually changed.
How it works: The system calculates fill volume based on flow rate and time. Operators calibrate the timer to achieve target volumes, accounting for product viscosity and temperature.
Ideal for:
– Distilled spirits requiring TTB compliance
– Juice and beverage producers with strict volume labelling
– Olive oil and vinegar bottlers
– Any operation where regulatory volume accuracy is mandatory
Considerations: Viscosity changes (due to temperature or product variation) require recalibration. This technology excels when filling consistent products into standardised containers.
Level Fillers
Level filling technology uses sensor probes to detect when liquid reaches a predetermined height within the container, triggering automatic shut-off. This approach prioritises visual consistency over volumetric precision.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How it works: An adjustable shelf positions the container at the correct height relative to the sensor probe. When liquid contacts the probe, filling stops—regardless of the actual volume dispensed.
Ideal for:
– Wine producers using hand-blown or artisan bottles
– Hot-fill applications where product expansion occurs
– Specialty containers with wall thickness variations
– Products where visual fill line matters more than exact volume
Considerations: Volume variance can exceed 3% between containers, making this technology unsuitable for TTB-regulated spirits or products with strict net-weight requirements. It excels where container inconsistency is the norm rather than the exception.
Open Fillers with Gas Purge
Open fillers adapted for carbonated beverages incorporate a gas purge cycle to displace oxygen before filling. An automatic level sensor minimises product waste by stopping the fill at the optimal point.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How it works: The system purges the can with inert gas (typically CO2 or nitrogen), then fills to a sensor-detected level. While not fully isobaric like counter pressure systems, the gas purge significantly reduces oxidation and foam formation.
Ideal for:
– Mid-volume carbonated beverage operations
– Producers prioritising speed over maximum carbonation retention
– Operations filling lightly carbonated products
– Facilities scaling up from manual to semi-automated production
Considerations: Expect some carbonation loss compared to counter pressure filling. This trade-off often makes sense for operations where throughput efficiency outweighs marginal quality differences.
High-Temperature Particulate Fillers
Specialised for viscous liquids containing solid particles, high-temperature particulate fillers feature enlarged flow paths that prevent clogging and ensure smooth, consistent fills.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How it works: A wider bore filling system accommodates thick products and suspended particulates without blockage. Temperature controls maintain product fluidity throughout the filling process.
Ideal for:
– Hot sauce and BBQ sauce manufacturers
– Juice producers with pulp or fruit pieces
– Salsa and chunky condiment operations
– Any thick, particulate-laden product requiring heat during filling
Considerations: These systems are purpose-built for challenging products. They’re not interchangeable with standard liquid fillers and represent a specialised investment for specific product categories.
Selecting the Right Technology
Your choice depends on three primary factors:
- Product characteristics: Carbonation level, viscosity, particulate content, and temperature requirements
- Regulatory requirements: TTB compliance, net-weight labelling accuracy, and industry-specific standards
- Container variables: Standardised cans vs. specialty containers, volume consistency requirements
Many operations benefit from multiple filling technologies to accommodate diverse product lines. Evaluate your current production needs alongside anticipated growth to ensure equipment investments support long-term operational goals.
Key Industrial Applications of can filling equipment
Key Industrial Applications of Can Filling Equipment
Can filling equipment serves diverse industries, each with specific requirements for product integrity, compliance, and operational efficiency. Understanding these applications helps manufacturers select the right filling technology for their production needs.
Industry Applications Overview
| Industry | Primary Products | Filling Method | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Craft Beer & Brewing | Beer, ale, lager, hard seltzer | Counter pressure | CO2 retention, oxygen exclusion, foam control |
| Kombucha & Fermented Beverages | Kombucha, kefir, fermented teas | Counter pressure | Live culture preservation, carbonation maintenance |
| Soft Drinks & Soda | Carbonated beverages, sparkling water | Counter pressure / Open fill | High-speed filling, consistent carbonation levels |
| Wine & Cider | Canned wines, hard ciders | Level fill / Counter pressure | Oxygen-sensitive filling, precise fill levels |
| Spirits & RTD Cocktails | Ready-to-drink cocktails, canned spirits | Volumetric | TTB compliance, accurate volume control |
| Juice & Non-Carbonated Beverages | Fruit juices, cold-pressed drinks, coconut water | Volumetric / Level fill | Particulate handling, hot fill capability |
| Food & Condiments | Hot sauce, BBQ sauce, olive oil | High-temp particulate | Viscous product handling, temperature control |
Detailed Benefits by Application
Carbonated Beverages (Beer, Kombucha, Soda)
Counter pressure filling technology delivers critical advantages for carbonated products:
- Maximum CO2 retention — Filling under pressure prevents carbonation loss during the transfer process
- Reduced oxygen pickup — Gas purge cycles minimize oxidation, extending shelf life
- Crowler compatibility — Enables on-demand fills for taproom sales and special releases
- Direct keg/brite tank integration — Eliminates intermediate handling steps
Spirits & Regulated Beverages
Volumetric filling systems address strict compliance requirements:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- TTB regulatory compliance — Digital timer controls accurate to 0.01 seconds ensure consistent fill volumes
- Audit-ready precision — Documented volume accuracy for regulatory inspections
- Flexible bottle/can sizing — Adjustable shelf accommodates various container dimensions
- Viscosity adaptability — Timer-based controls compensate for different product flow rates
Wine & Specialty Beverages
Level filling technology solves challenges unique to premium products:
- Visual consistency — Sensor-controlled fills deliver uniform fill heights regardless of container variations
- Artisanal container compatibility — Accommodates hand-blown bottles and specialty cans with dimensional inconsistencies
- Hot fill capability — Supports pasteurization requirements for shelf-stable products
Food Products & Viscous Liquids
High-temperature particulate fillers handle challenging product characteristics:
- Thick product handling — Larger flow paths prevent clogging with sauces and pulpy liquids
- Particulate accommodation — Designed for products containing seeds, spices, or fruit pieces
- Temperature flexibility — Maintains product quality during hot fill applications
- Glass and plastic compatibility — Supports diverse packaging formats
Selecting Equipment by Production Scale
| Production Volume | Recommended Configuration | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Small batch / R&D | 2-head manual systems | Craft breweries, startups, test kitchens |
| Mid-volume production | 4-head semi-automatic | Regional beverage producers, specialty food manufacturers |
| High-volume operations | Multi-head automatic lines | Large-scale beverage production, national distribution |
Regional Considerations
North American Operations:
– TTB compliance requirements for alcoholic beverages
– FDA regulations for food-grade equipment
– 110V standard power configurations
European Operations:
– CE marking requirements
– 220V power compatibility available
– EU food contact material regulations
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘can filling equipment’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Can Filling Equipment & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Carbonation Loss During the Filling Process
Scenario: A craft brewery expanding into canned products discovers their initial filling setup results in flat, oxidized beer that fails to meet quality standards. Customers complain about inconsistent carbonation levels, damaging brand reputation.
Problem: Standard open-fill systems allow CO2 to escape during transfer from kegs or brite tanks to cans, resulting in:
– Reduced carbonation levels
– Increased oxidation and shortened shelf life
– Product waste from rejected batches
Solution: Implement counter pressure filling technology that fills cans under pressure, maximizing CO2 retention throughout the process. Systems like counter pressure can fillers maintain carbonation integrity from source vessel to sealed can, ensuring consistent product quality for beer, kombucha, soda, and other carbonated beverages.
Pain Point 2: Inconsistent Fill Volumes Across Variable Container Sizes
Scenario: A spirits producer filling multiple bottle formats (375ml, 750ml, 1L) struggles to maintain TTB-compliant fill volumes, facing potential regulatory penalties and product giveaway costs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem: Manual adjustments between production runs create:
– Compliance risks with Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau regulations
– Overfilling (profit loss) or underfilling (legal liability)
– Production downtime during changeovers
Solution: Deploy volumetric filling systems with digital timer controls adjustable to 0.01-second precision. These systems store volume settings in memory, enabling rapid changeovers while maintaining regulatory compliance across diverse container formats.
Pain Point 3: Filling Specialty or Inconsistent Containers
Scenario: A premium olive oil producer using hand-blown artisan bottles experiences frequent overfills and spills due to variations in bottle wall thickness and internal dimensions.
Problem: Standard volumetric systems cannot accommodate:
– Variations in punt size and bottle diameter
– Inconsistent neck heights
– Wall thickness differences exceeding 3% volume variance
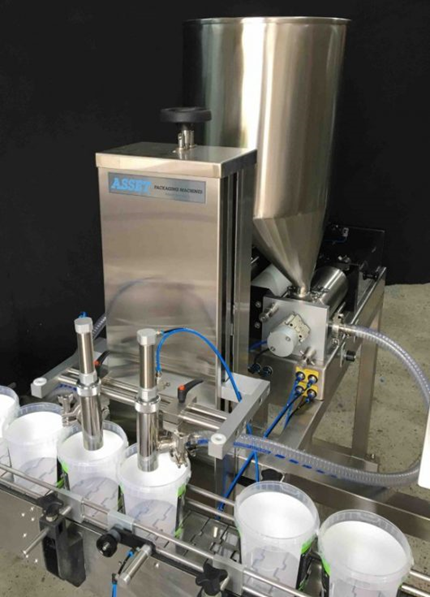

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution: Utilize level-fill technology with sensor probes that automatically shut off at the desired liquid height regardless of internal bottle dimensions. This ensures visually consistent fill levels across specialty containers while eliminating waste from overfills.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for can filling equipment
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Can Filling Equipment
Selecting the appropriate materials for can filling equipment directly impacts operational longevity, product integrity, and total cost of ownership. This guide examines critical material considerations for B2B buyers evaluating can filling systems.
Primary Contact Surface Materials
Stainless Steel (304 and 316 Grades)
Stainless steel remains the industry standard for product contact surfaces in can filling equipment. Grade 304 stainless steel offers adequate corrosion resistance for most beverage applications, while Grade 316 provides superior resistance to chlorides and acidic products—essential for facilities handling juices, kombucha, or products with high salt content.
Key considerations:
– 316 stainless steel commands a 20-30% price premium over 304
– Both grades meet FDA and EU food contact regulations
– Electropolished finishes reduce bacterial adhesion and simplify CIP procedures
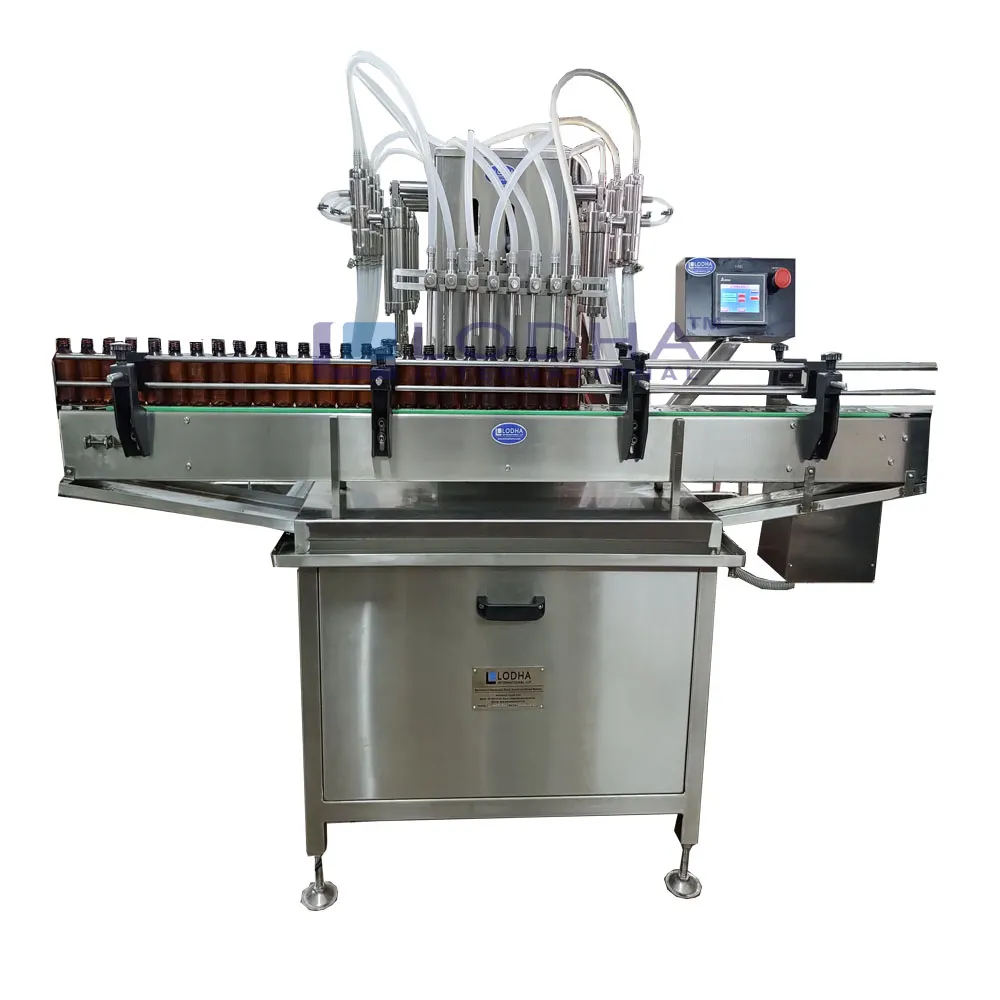

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Food-Grade Polymers and Seals
Gaskets, O-rings, and sealing components require careful material selection based on product compatibility:
- EPDM: Suitable for non-carbonated beverages and water-based products
- Silicone: Preferred for high-temperature applications (hot fill operations up to 200°C)
- PTFE (Teflon): Required for aggressive cleaning chemicals and acidic products
- Viton: Optimal for alcohol-based products and spirits
Frame and Structural Components
Equipment frames constructed from powder-coated carbon steel offer cost advantages for budget-conscious operations. However, stainless steel frames provide superior corrosion resistance in high-humidity environments typical of beverage production facilities.
Application-Specific Material Requirements
Carbonated Beverages (Beer, Kombucha, Soda)
Counter pressure filling systems like the XF4500C require materials rated for elevated pressures. Stainless steel construction ensures durability under repeated pressurization cycles while maintaining sanitary conditions.
High-Temperature/Particulate Products
Specialized equipment such as the XF200HTP incorporates larger flow paths and heat-resistant materials for hot sauce, BBQ sauce, and juice applications. Material selection must account for:
– Thermal expansion coefficients
– Abrasion resistance from particulates
– Chemical compatibility with acidic products
Spirits and Alcohol
Volumetric fillers for distilled spirits require materials resistant to alcohol degradation. Alcohol-compatible seals and gaskets prevent swelling and premature failure.
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
Materials must satisfy regulatory requirements in target markets:
- USA: FDA 21 CFR compliance for food contact materials; TTB regulations for alcohol products
- EU: EC 1935/2004 framework regulation; specific migration limits per EC 10/2011
Material Selection Comparison Table
| Material | Applications | Temperature Range | Chemical Resistance | Relative Cost | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | General beverage contact | -200°C to 870°C | Good | Moderate | FDA/EU compliant |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Acidic products, chloride exposure | -200°C to 870°C | Excellent | High | FDA/EU compliant |
| EPDM Seals | Water-based, non-carbonated | -40°C to 120°C | Moderate | Low | FDA/EU compliant |
| Silicone Seals | Hot fill applications | -60°C to 230°C | Good | Moderate | FDA/EU compliant |
| PTFE Seals | Aggressive chemicals, acids | -200°C to 260°C | Excellent | High | FDA/EU compliant |
| Viton Seals | Alcohol, spirits, oils | -20°C to 200°C | Excellent (solvents) | High | FDA/EU compliant |
| Powder-Coated Carbon Steel | Non-contact frames | Standard ambient | Moderate | Low | N/A (non-contact) |
Procurement Recommendations
- Specify material certificates: Request mill certificates for stainless steel components and material data sheets for polymers
- Evaluate seal replacement costs: Factor ongoing consumable expenses into TCO calculations
- Confirm international voltage compatibility: Equipment manufacturers like XpressFill offer 220V options for European operations
- Assess cleaning chemical compatibility: Match seal materials to your CIP/SIP protocols
Material selection decisions made during procurement directly influence maintenance schedules, product quality consistency, and equipment service life across your production timeline.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for can filling equipment
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Can Filling Equipment
The manufacturing of can filling equipment demands precision engineering and rigorous quality control to ensure reliable performance in demanding production environments. Understanding these processes helps buyers evaluate equipment quality and make informed procurement decisions.
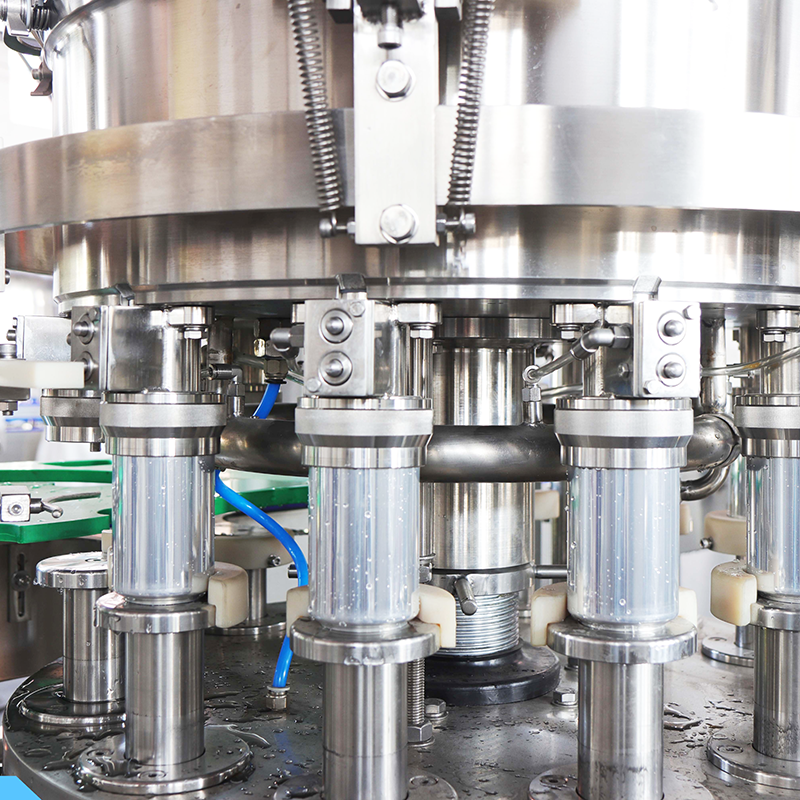

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Process Overview
1. Preparation Phase
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Sourcing food-grade stainless steel (typically 304 or 316), sanitary-grade polymers, and certified electronic components | Traceability documentation, material certificates |
| Design Engineering | CAD modeling, flow path optimization, component specification | Compliance with sanitary design principles |
| Component Procurement | Valves, sensors, pumps, control systems | Vendor qualification, incoming inspection |
Premium manufacturers like XpressFill emphasize handcrafted, custom-made construction, ensuring each unit meets specific application requirements for beer, wine, spirits, and other beverages.
2. Forming and Fabrication
- Sheet metal forming: Precision cutting, bending, and welding of stainless steel frames and housings
- CNC machining: Manufacturing fill heads, nozzles, and valve bodies to tight tolerances
- Surface finishing: Electropolishing internal product contact surfaces to achieve sanitary finishes (≤0.8 µm Ra)
- Welding: Orbital TIG welding for sanitary tube connections; full penetration welds inspected for porosity
3. Assembly
- Subassembly integration: Fill heads, pneumatic systems, control panels
- Electrical wiring: Control systems, digital timers, sensor probes (level detection systems)
- Calibration: Volumetric timing systems calibrated to ±0.01 seconds accuracy
- Pressure testing: Counter-pressure systems validated for carbonated beverage applications
4. Quality Control Checkpoints
| Checkpoint | Testing Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional verification | CMM inspection | Per engineering drawings |
| Weld integrity | Visual/dye penetrant | Zero defects |
| Leak testing | Pressure hold test | No pressure decay |
| Electrical safety | Hi-pot testing | Per UL/CE requirements |
| Functional testing | Production simulation | Consistent fill accuracy |
Quality Standards and Certifications
ISO Compliance:
– ISO 9001:2015: Quality management systems for consistent manufacturing processes
– ISO 22000: Food safety management (critical for beverage industry applications)
Regional Requirements:
– CE Marking: Mandatory for European market entry
– UL/CSA Certification: Electrical safety for North American markets
– 3-A Sanitary Standards: Voluntary certification demonstrating hygienic design
Quality Assurance Best Practices
- Documentation: Complete build records, test reports, and material traceability
- Calibration programs: Regular verification of measurement and control systems
- Final acceptance testing: Customer-witnessed FAT when specified
- Warranty support: Post-delivery technical assistance and parts availability
When evaluating suppliers, request quality documentation, inspection reports, and references from similar applications to verify manufacturing capabilities align with your production requirements.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘can filling equipment’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Can Filling Equipment
Use this comprehensive checklist to systematically evaluate and procure can filling equipment that meets your production requirements and budget constraints.
Phase 1: Define Your Requirements
- [ ] Identify your beverage type
- Carbonated (beer, kombucha, soda) → Counter-pressure or open fillers required
- Still beverages (juice, wine) → Level or volumetric fillers
-
Viscous products (sauces, thick juices) → High-temperature particulate fillers
- [ ] Determine production volume needs
- Current output requirements (cans per hour/day)
- Projected growth over 3-5 years
-
Peak season capacity demands
- [ ] Specify can formats
- Standard can sizes (12oz, 16oz, crowlers)
- Specialty formats
-
Multiple size flexibility requirements
- [ ] Document regulatory compliance needs
- TTB requirements (for alcohol)
- FDA regulations
- Local/regional standards (USA vs. EU)
Phase 2: Technical Evaluation
| Criteria | Questions to Answer |
|---|---|
| Fill Technology | Counter-pressure, volumetric, or level fill? |
| CO2 Retention | Does the system minimize carbonation loss? |
| Fill Accuracy | What tolerance levels are acceptable? |
| Automation Level | Manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic? |
| Power Requirements | 110V or 220V compatibility? |
| Integration | Compatible with existing brite tanks/kegs? |
- [ ] Assess automation features
- Digital timers with precision settings (.01 second accuracy)
- Automatic level sensors
-
Gas purge cycles for oxygen reduction
- [ ] Verify material compatibility
- Food-grade stainless steel construction
- Sanitary design for cleaning protocols
- Chemical resistance for sanitizers
Phase 3: Vendor Qualification
- [ ] Research manufacturer credentials
- Years in business
- Industry specialization
-
Customer references in your sector
- [ ] Evaluate support infrastructure
- Technical support availability
- Spare parts accessibility
-
Training programs offered
- [ ] Confirm logistics capabilities
- Domestic vs. international shipping
- Lead times
-
Installation support
- [ ] Review financing options
- Equipment financing partnerships
- Lease-to-own programs
- Payment terms
Phase 4: Request for Quotation (RFQ)
Include these specifications in your RFQ:
- [ ] Detailed production requirements
- [ ] Can sizes and formats
- [ ] Beverage specifications (carbonation levels, viscosity, temperature)
- [ ] Desired automation level
- [ ] Power supply specifications
- [ ] Timeline requirements
- [ ] Warranty expectations
- [ ] Training and installation needs
Phase 5: Final Selection Criteria
| Priority | Evaluation Factor | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| High | Fill accuracy and consistency | 25% |
| High | Production capacity match | 20% |
| Medium | Total cost of ownership | 20% |
| Medium | Ease of operation/cleaning | 15% |
| Medium | Vendor support quality | 10% |
| Low | Expansion flexibility | 10% |
- [ ] Conduct equipment demonstrations (on-site or virtual)
- [ ] Request sample fills with your actual product
- [ ] Verify warranty terms and service agreements
- [ ] Confirm delivery timeline and installation requirements
Quick Reference: Equipment Type by Application
| Application | Recommended Equipment Type | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Beer/Kombucha/Soda | Counter-pressure can filler | CO2 retention during fill |
| Crowlers | Counter-pressure filler | Large format compatibility |
| High-volume carbonated | Open filler with gas purge | Automatic level sensing |
| Spirits/Juice | Volumetric filler | TTB compliance, precise volumes |
| Hot sauces/Thick liquids | High-temp particulate filler | Large flow path, temperature tolerance |
Next Step: Begin vendor outreach with your completed requirements documentation.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for can filling equipment Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Can Filling Equipment Sourcing
Understanding the complete cost structure of can filling equipment is essential for making informed procurement decisions. This analysis breaks down all cost components and provides actionable strategies to optimize your investment.
Equipment Price Ranges by Category
| Equipment Type | Entry-Level | Mid-Range | Industrial-Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual/Semi-Auto Can Fillers | $3,000–$8,000 | $8,000–$25,000 | $25,000–$75,000 |
| Counter Pressure Fillers (Carbonated) | $5,000–$12,000 | $12,000–$40,000 | $40,000–$150,000+ |
| Level Fill Systems | $4,000–$10,000 | $10,000–$30,000 | $30,000–$100,000 |
| Volumetric Fillers | $4,500–$12,000 | $12,000–$35,000 | $35,000–$120,000 |
| High-Temp Particulate Fillers | $6,000–$15,000 | $15,000–$45,000 | $45,000–$150,000 |
Complete Cost Breakdown
1. Materials and Equipment Costs (60–70% of Total Investment)
Base Unit Components:
– Stainless steel construction (food-grade 304/316)
– Fill heads and nozzles
– Control systems (PLCs, digital timers, sensors)
– Pneumatic or hydraulic systems
– Safety enclosures and guards
Required Accessories:
– CO2/nitrogen purge systems for carbonated beverages
– Foam detection sensors
– Level sensors for automatic shutoff
– Conveyor integration components

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Voltage Considerations:
– Standard 110V units (North America)
– 220V configurations available for European markets (may require custom ordering)
2. Labor Costs (15–25% of Total Investment)
| Labor Component | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Installation & Setup | $1,500–$8,000 |
| Operator Training | $500–$3,000 |
| Initial Calibration | $500–$2,000 |
| Ongoing Maintenance (Annual) | 3–8% of equipment cost |
Labor considerations by region:
– USA: Higher installation labor rates; domestic support readily available
– Europe: Variable rates by country; consider CE compliance verification costs
3. Logistics and Shipping Costs (5–15% of Total Investment)
| Logistics Factor | Domestic (USA/EU) | International |
|---|---|---|
| Freight Shipping | $500–$3,000 | $2,000–$8,000 |
| Customs & Duties | N/A | 5–15% of equipment value |
| Crating & Handling | $200–$800 | $500–$1,500 |
| Insurance (Transit) | 1–2% of value | 2–3% of value |
Note: Many manufacturers offer international shipping with 220V power options—confirm availability during the quotation process.
Hidden Costs to Budget For
- Spare parts inventory: $500–$2,500 initial stock
- Consumables: Gaskets, seals, tubing (annual: $300–$1,500)
- Utility upgrades: Compressed air systems, electrical panel upgrades
- Regulatory compliance: TTB compliance verification (USA), CE marking (Europe)
- Downtime during installation: 2–5 days production loss
Cost-Saving Strategies
Equipment Selection
- Match capacity to actual needs—avoid over-specifying; a 2-head filler may suffice over a 4-head unit
- Choose versatile platforms—units handling both bottles and cans (e.g., counter pressure systems) reduce capital outlay
- Consider volumetric fillers for regulated products—TTB-compliant precision reduces waste and compliance costs
Procurement Tactics
- Request financing options—many manufacturers partner with financing providers for manageable payment terms
- Bundle purchases—negotiate discounts when ordering fillers with seamers or conveyors
- Buy during trade shows—manufacturers often offer promotional pricing at industry events
Operational Efficiency
- Invest in operator training—reduces product waste and equipment damage
- Implement preventive maintenance schedules—extends equipment lifespan by 30–50%
- Stock critical spare parts—minimizes costly emergency shipping
Logistics Optimization
- Consolidate shipments with other equipment orders
- Evaluate regional distributors—may offer lower shipping costs and faster support
- Factor in total cost of ownership (TCO)—cheaper equipment with poor support costs more long-term
ROI Considerations
| Production Volume | Recommended Investment | Expected Payback Period |
|---|---|---|
| <500 cans/day | $3,000–$10,000 | 12–24 months |
| 500–2,000 cans/day | $10,000–$40,000 | 8–18 months |
| 2,000–10,000 cans/day | $40,000–$100,000 | 6–14 months |
| >10,000 cans/day | $100,000+ | 4–12 months |
Key Takeaways
- Total acquisition cost typically runs 15–30% above base equipment price when factoring all components
- Counter pressure fillers command premium pricing but are essential for carbonated beverage quality retention
- European buyers should confirm 220V availability and CE compliance upfront
- Financing partnerships can significantly improve cash flow for growing operations
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing can filling equipment With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Can Filling Equipment With Other Solutions
When evaluating can filling equipment for your beverage operation, understanding how it compares to alternative packaging solutions is essential for making an informed capital investment. This analysis examines can filling systems against two primary alternatives: bottle filling equipment and manual/crowler filling methods.
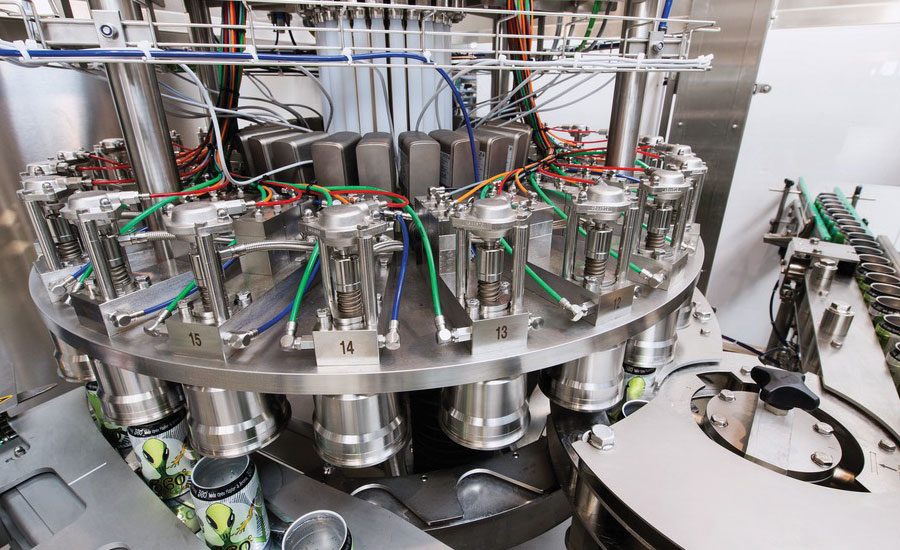

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparison Table
| Factor | Can Filling Equipment | Bottle Filling Equipment | Manual/Crowler Filling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $5,000–$50,000+ | $3,000–$40,000+ | $500–$2,000 |
| Throughput | 10–60+ CPM | 8–50+ BPM | 2–5 units/minute |
| Packaging Material Cost | Lower per unit | Higher per unit | Highest per unit |
| Shelf Life (Carbonated) | 6–12 months | 3–6 months | 24–48 hours |
| Oxygen Ingress | Minimal (sealed seam) | Moderate (crown/cork) | High |
| Shipping Weight | Lighter | Heavier | N/A (on-premise) |
| Consumer Portability | Excellent | Moderate | Limited |
| Sustainability Perception | High (recyclability) | Moderate | Low |
| Equipment Footprint | Moderate | Moderate | Minimal |
| Seaming Complexity | Requires precision seamer | Simple capping | Basic lid application |
Analysis by Alternative
Can Filling vs. Bottle Filling Equipment
Bottle filling systems—whether volumetric fillers for spirits and juices or level fillers for wine—offer flexibility across container sizes and accommodate irregular bottle dimensions. Counter-pressure bottle fillers (such as 2-head or 4-head units) effectively retain CO2 in carbonated beverages.
However, can filling equipment provides distinct advantages for carbonated beverage producers:
- Superior oxygen barrier: Aluminum cans eliminate light exposure and minimize oxygen ingress, extending product freshness
- Lower logistics costs: Cans weigh less and stack efficiently, reducing shipping expenses by 20–40%
- Retail positioning: Cans increasingly dominate craft beer, RTD cocktails, and functional beverage segments
- Faster chilling: Aluminum conducts temperature faster than glass
Best fit: Choose bottle filling when brand positioning requires premium glass presentation or when serving markets with established bottle preferences (wine, premium spirits).
Can Filling vs. Manual/Crowler Filling
Manual crowler filling serves taproom and limited on-premise distribution models. While entry costs remain low, this approach presents significant limitations:
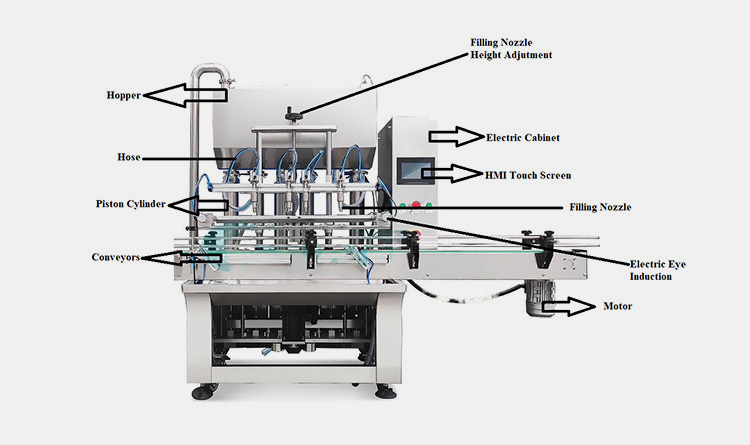
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Inconsistent fills: Manual operation introduces variation in fill levels and dissolved oxygen levels
- Limited shelf life: Crowlers typically maintain quality for 24–48 hours maximum
- Labor intensity: One operator produces 2–5 crowlers per minute versus 20+ cans per minute with automated equipment
- Regulatory constraints: Many jurisdictions restrict off-premise crowler sales
Counter-pressure can fillers with gas purge cycles and automatic level sensors address these limitations while maintaining accessibility for small-batch producers.
Best fit: Manual/crowler filling suits taproom-only operations with minimal to-go volume or businesses testing market demand before equipment investment.
Decision Framework
Select can filling equipment when:
– Distribution extends beyond on-premise sales
– Product shelf life requirements exceed 30 days
– Shipping costs significantly impact margins
– Target retail channels favor canned formats
Select bottle filling equipment when:
– Product category traditionally uses glass (wine, premium spirits)
– Brand positioning emphasizes artisanal or luxury perception
– Existing bottle inventory requires utilization
Select manual/crowler methods when:
– Annual volume remains under 500 cases
– Sales occur exclusively on-premise
– Capital preservation takes priority over operational efficiency
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for can filling equipment
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Can Filling Equipment
Understanding technical specifications and industry terminology is critical when evaluating can filling equipment. This section covers the key properties and trade terms that inform purchasing decisions.
Core Technical Properties
Fill Method Classifications
| Fill Method | Mechanism | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Counter Pressure | Fills under pressure to retain dissolved gases | Carbonated beverages (beer, kombucha, soda) |
| Level Fill | Sensor probe stops fill at predetermined height | Products requiring visual consistency; variable container dimensions |
| Volumetric | Digital timer controls precise liquid volume | Spirits, juices, oils; TTB-regulated products |
| Gravity Fill | Uses gravity for liquid transfer | Still beverages, low-viscosity products |
Critical Performance Specifications
- Fill Accuracy: Typically expressed as ±percentage or ±mL deviation from target volume
- Fill Speed: Containers per minute (CPM) or fills per hour (FPH)
- Pressure Rating: PSI capacity for counter pressure systems
- Temperature Range: Operating limits; high-temp units handle viscous products requiring heat
- Viscosity Compatibility: Measured in centipoise (cP); determines flow path requirements
- Container Range: Minimum/maximum can diameters and heights accommodated
Electrical and Utility Requirements
- Voltage Options: 110V (North America standard) or 220V (European/International)
- Air Supply: Compressed air requirements in PSI and CFM
- CO2 Consumption: Relevant for purge cycles and counter pressure operations
Essential Trade Terminology
Procurement Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity—lowest unit count a supplier will sell |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer—produces equipment under another brand’s label |
| Lead Time | Production and delivery timeframe from order to receipt |
| FOB | Free On Board—indicates where shipping responsibility transfers |
| CIF | Cost, Insurance, Freight—seller covers delivery to destination port |
Equipment Configuration Terms
- Brite Tank Integration: Direct connection to bright beer tanks for carbonated fills
- Keg Compatibility: Ability to fill from kegged product sources
- Purge Cycle: Pre-fill gas displacement to minimize oxygen exposure
- Headspace: Distance between liquid surface and container seal point
- Dwell Time: Duration product remains in contact with fill nozzle
Regulatory and Compliance Terms
- TTB Compliance: Adherence to Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau fill volume standards (U.S.)
- CE Marking: European conformity certification for equipment safety
- Sanitary Design: Construction meeting food-grade hygiene standards
- CIP Compatibility: Clean-In-Place capability for automated sanitization
Specification Comparison Checklist
When requesting quotes, obtain the following from suppliers:
- Fill accuracy tolerance at rated speed
- Maximum and minimum container dimensions
- Changeover time between container formats
- Material construction (304 vs. 316 stainless steel)
- Warranty terms and service availability
- Spare parts lead times and availability
- Training and installation support included
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the can filling equipment Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Can Filling Equipment Sector
Historical Evolution of Can Filling Technology
The can filling equipment sector has undergone significant transformation over the past two decades. What began as industrial-scale operations dominated by high-volume manufacturers has evolved into a diversified market serving producers of all sizes. The craft beverage revolution—particularly in beer, kombucha, and specialty sodas—fundamentally shifted demand patterns, creating opportunities for equipment manufacturers to develop scaled solutions for small and mid-sized operations.
Counter-pressure filling technology, once exclusive to large breweries, has become accessible to craft producers through compact, affordable systems. This democratization has expanded the addressable market considerably, with equipment now available for operations filling as few as hundreds of cans per day.
Current Market Dynamics
| Market Driver | Impact on Sourcing Decisions |
|---|---|
| Craft beverage growth | Increased demand for flexible, lower-volume equipment |
| Canned wine/cocktail expansion | Need for multi-format filling capabilities |
| Labor cost pressures | Preference for automated and semi-automated systems |
| Supply chain localization | Shift toward domestic manufacturing partners |
| Regulatory compliance (TTB) | Requirement for volumetric precision and documentation |
Key sourcing considerations for B2B buyers:
- Flexibility across formats: Equipment capable of handling bottles, standard cans, and crowlers reduces capital expenditure
- Carbonation retention: Counter-pressure filling systems are essential for carbonated beverages to maintain CO2 levels
- Product viscosity range: Operations handling multiple product types (spirits, juices, sauces) require adjustable systems
Sustainability Trends Shaping Procurement
Sustainability has moved from peripheral concern to central procurement criterion:
- Material efficiency: Level-fill sensors and automatic shutoff technology minimize product waste during filling operations
- Energy consumption: 220V options and efficient motor designs reduce operational carbon footprint
- Equipment longevity: Handcrafted, custom-built equipment from specialized manufacturers often delivers longer service life than mass-produced alternatives
- Aluminum can preference: Cans’ superior recyclability versus glass is driving beverage producers toward can-focused filling lines
Regional Sourcing Considerations
North American buyers benefit from domestic manufacturers offering:
– Reduced lead times
– Simplified service and parts logistics
– TTB compliance expertise built into equipment design
European buyers should verify:
– 220V power compatibility
– CE marking and local regulatory compliance
– International shipping and support infrastructure
Strategic Recommendations for Equipment Sourcing
- Assess production trajectory: Select equipment with capacity headroom for 3-5 year growth projections
- Prioritize versatility: Multi-format capability (bottles and cans) provides operational flexibility
- Evaluate total cost of ownership: Consider financing options, maintenance requirements, and consumables costs alongside purchase price
- Verify compliance features: Volumetric precision for TTB-regulated products is non-negotiable for spirits and wine producers
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of can filling equipment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Can Filling Equipment
1. What types of can filling machines are available for different beverage applications?
Can filling equipment falls into several categories based on your product type:
| Filling Type | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Counter Pressure Fillers | Beer, kombucha, soda, carbonated beverages | Fills under pressure to maximize CO2 retention |
| Level Fillers | Wine, hot-fill products | Sensor-based shutoff for consistent fill heights |
| Volumetric Fillers | Spirits, juices, olive oil | Digital timer control for precise volume compliance |
| Open Fillers | Carbonated beverages (high efficiency) | Gas purge cycle with automatic level sensor |
2. Can the same equipment fill both bottles and cans?
Yes, certain models accommodate both formats. For example, counter pressure systems can fill bottles and cans, including crowlers, from kegs or brite tanks. However, dedicated can fillers typically offer higher efficiency for can-only operations. Evaluate your packaging mix before selecting equipment.
3. What should we consider for TTB compliance when filling spirits or regulated beverages?
Volumetric fillers are specifically designed for TTB (Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau) compliance. Key features include:
- Digital timers adjustable to 0.01 seconds
- Consistent fill volume ranges within regulatory tolerances
- Memory storage for fill settings
- Precise volume control regardless of product viscosity
4. Is international voltage compatibility available?
Yes, reputable manufacturers offer 220-volt power options for European and international operations. Confirm voltage requirements and international shipping availability before purchase.
5. How do we handle products with particulates or high viscosity?
Specialized high-temperature particulate fillers accommodate:
- Hot sauce
- Barbeque sauce
- Juices with pulp
- Other viscous liquids
These units feature larger flow paths for smooth filling and can handle both glass and plastic containers.
6. What financing options exist for can filling equipment?
Many equipment suppliers partner with financing companies to offer payment plans. This allows businesses to acquire equipment without significant upfront capital expenditure. Contact manufacturers directly for current financing terms and partner programs.
7. How do level fillers differ from volumetric fillers?
Level Fillers:
– Use sensor probes to detect liquid height
– Ideal for hand-blown or specialty containers with wall thickness variations
– Ensure visual consistency across bottles
– Accept volume variations exceeding 3%
Volumetric Fillers:
– Control fill by timed dispensing
– Ensure consistent volume regardless of container variations
– Required for regulatory compliance (TTB)
– Adjustable for different viscosities
8. What production scale do entry-level can fillers support?
Entry-level commercial can fillers typically range from 2-head to 4-head configurations, suitable for:
- Craft breweries
- Small-batch beverage producers
- Pilot production lines
- Contract packaging startups
Scale up to higher-head-count systems as production demands increase.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for can filling equipment
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion: Can Filling Equipment
Selecting the right can filling equipment represents a critical investment decision that directly impacts production efficiency, product quality, and operational scalability. Throughout this guide, we’ve examined the key factors that drive successful equipment procurement.
Key Takeaways for Buyers
| Priority | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Product Match | Align filler type (counter-pressure, volumetric, level fill) with your beverage characteristics |
| Scale Alignment | Match throughput capacity to current needs while planning for growth |
| Compliance | Ensure equipment meets TTB and regional regulatory requirements |
| Total Cost | Evaluate financing options, maintenance requirements, and operational costs |
Market Outlook
The can filling equipment sector continues evolving toward:
– Greater automation and sensor-based precision
– Flexible systems accommodating multiple container formats
– Enhanced CO2 retention technology for carbonated beverages
– Accessible financing enabling smaller producers to scale
Final Recommendation
Prioritize suppliers offering customizable solutions, international voltage compatibility, and responsive technical support. Request demonstrations with your specific products before committing. The right equipment partner delivers not just machinery, but a foundation for sustainable production growth across North American and European markets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.