The global camera module market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-resolution imaging in smartphones, automotive systems, security, and emerging IoT applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 33.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 53.1 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by technological advancements such as miniaturization, improved sensor performance, and rising adoption of multi-camera setups in consumer electronics. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the automotive sector’s growing reliance on camera modules for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving as a key growth driver. With innovation accelerating across industries, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in volume, R&D investment, and technological capability—shaping the future of imaging worldwide.
Top 9 Camera Module Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Guangzhou Sincere Information Technology Ltd.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cameramodule.com
Key Highlights: IN THE MANUFACTURE AND SALE OF CAMERA MODULE For over 20 years · We own factory area 30,000 square meters. · Our Production capacity reaches 3 million per month….
#2 Infrared Camera Modules, Lenses, & AI Decision Support
Domain Est. 1993
Website: oem.flir.com
Key Highlights: Simplify development with an ecosystem of infrared imaging technologies, AI-powered thermal perception, and world-class technical support….
#3 Camera Modules
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: It is a page about Camera Modules | Application Examples | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd….
#4 Supertek
Domain Est. 2018
Website: supertekmodule.com
Key Highlights: With Supertek, you get customized camera modules, with hardware and software tailored exactly to your needs. Your samples are delivered in just 20 days….
#5 USB Camera Modules
Domain Est. 2020
Website: usb-cameras-modules.com
Key Highlights: Explore JSK Technology’s cutting-edge USB camera modules tailored for precision imaging, including object and facial recognition, biometric analysis, ……
#6 Camera Module Services
Website: camemake.eu
Key Highlights: Camemake delivers complete camera solutions, from custom camera module manufacturing to AI, IoT, and industrial vision systems. We provide MIPI & GMSL ……
#7 Automotive Camera Modules
Domain Est. 1993
Website: global.kyocera.com
Key Highlights: Kyocera develops a wide variety of automotive camera modules based on optical, circuit, software design, and image control technologies….
#8 Get Machine Vision Cameras (GigE, USB 3.0, CoaXPress)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: baslerweb.com
Key Highlights: $35 deliveryHere you’ll find area, line scan, 3D and embedded vision cameras. Get the best machine vision cameras for all your imaging needs….
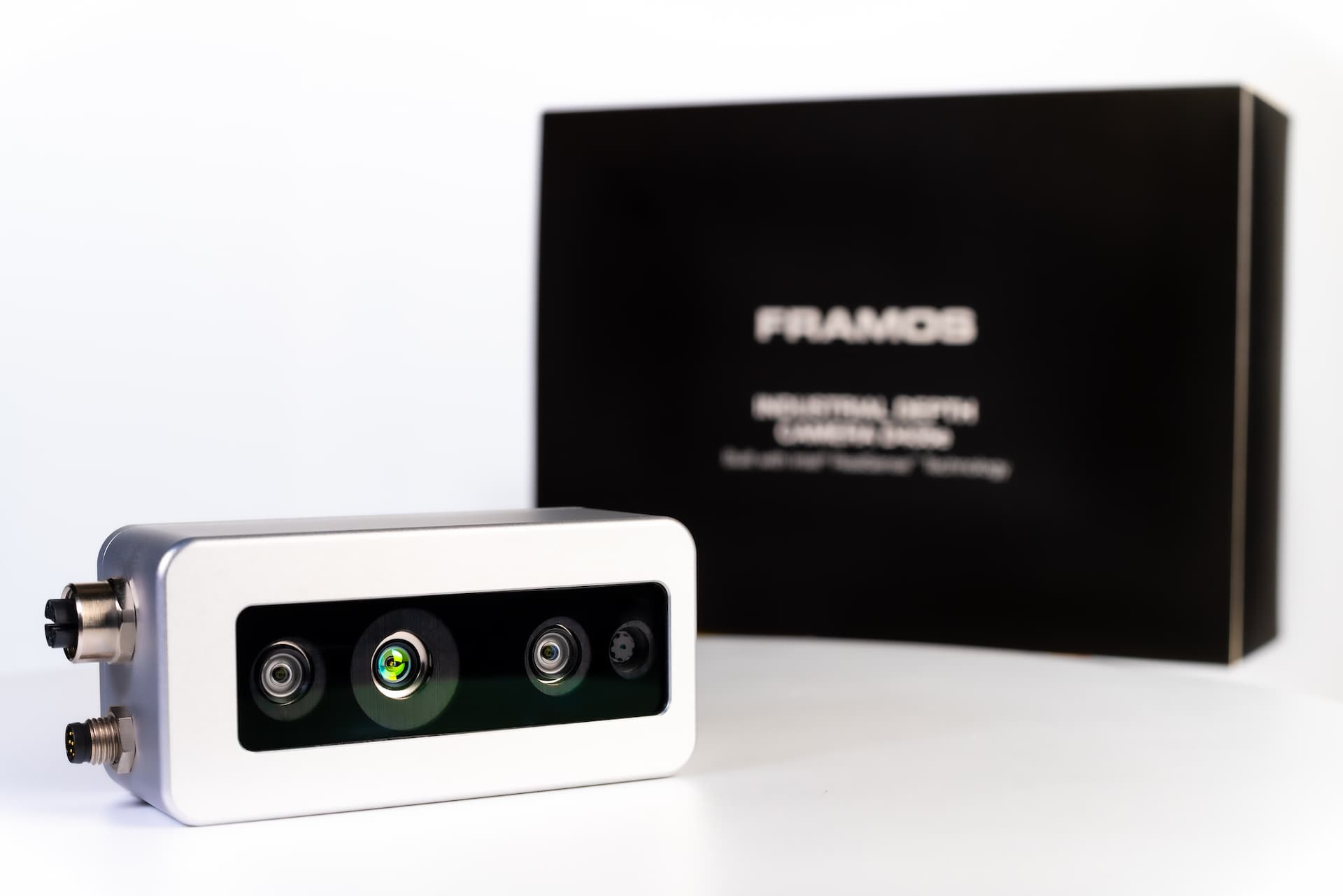
#9 FRAMOS
Domain Est. 2008
Website: framos.com
Key Highlights: FRAMOS combines R&D and manufacturing under one roof and provides scalable manufacturing capacities up to millions of pieces in Europe. Speed Meets Simplicity….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Camera Module

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Camera Modules
The camera module market is poised for transformative growth and technological evolution by 2026, driven by rising demand across consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and industrial applications. Several key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape in the coming years, with innovation, integration, and intelligence at the forefront.
1. Proliferation of Multi-Camera Systems in Smartphones
Smartphones will continue to be the largest end-use segment for camera modules. By 2026, the adoption of triple and quad-camera configurations will become standard, even in mid-range devices. Consumers increasingly value advanced photography features such as ultra-wide-angle, telephoto, macro, and depth-sensing capabilities. This trend is pushing manufacturers to integrate more sophisticated modules with higher resolution (48MP to 200MP sensors), improved low-light performance, and computational photography enhancements.
2. Advancements in Sensor Technology and Pixel Size Reduction
Image sensor technology will evolve rapidly, with continued miniaturization of pixel sizes (below 1.0µm) and adoption of stacked CMOS sensors. Companies like Sony, Samsung, and OmniVision are expected to lead in developing sensors with higher dynamic range, faster readout speeds, and lower power consumption. Backside-illuminated (BSI) and stacked sensors will dominate the market, enabling superior image quality in compact form factors.
3. Growth in Automotive Camera Modules
The automotive sector is emerging as a high-growth market for camera modules. With the expansion of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and the gradual progression toward autonomous driving (Levels 2–4), vehicles will integrate six to ten cameras per unit by 2026. These include front-facing, surround-view, rearview, and driver monitoring systems. Modules will require high reliability, wide dynamic range (WDR), and enhanced performance in low-light and adverse weather conditions. The adoption of AI-powered vision systems will further drive demand for intelligent camera modules.
4. Rise of AI and On-Device Image Processing
Integration of AI directly into camera modules or associated processors will be a key trend. On-device machine learning enables real-time object detection, facial recognition, scene optimization, and low-latency video analytics. This shift reduces reliance on cloud processing, improving privacy and speed. AI-enhanced camera modules will be critical in smartphones, security systems, robotics, and smart home devices.
5. Expansion in Non-Consumer Applications
Beyond smartphones and automotive, camera modules are gaining traction in industrial automation, medical imaging (e.g., endoscopes), drones, AR/VR headsets, and IoT devices. In healthcare, miniaturized camera modules enable less invasive diagnostics. In industrial settings, machine vision systems rely on high-speed, high-resolution modules for quality inspection and robotic guidance. These applications demand rugged, compact, and high-performance solutions.
6. Miniaturization and Wafer-Level Optics (WLO)
To meet space constraints in wearable and mobile devices, manufacturers are investing heavily in wafer-level packaging (WLP) and wafer-level optics. These technologies enable the production of ultra-compact camera modules suitable for applications such as hearables, AR glasses, and medical devices. The WLO market is expected to grow significantly by 2026, driven by demand for thinner and lighter modules.
7. Supply Chain Resilience and Regional Diversification
Geopolitical tensions and past supply chain disruptions have prompted camera module manufacturers to diversify production. China remains a dominant player, but investments are increasing in Southeast Asia (Vietnam, India) and India’s PLI (Production Linked Incentive) scheme is attracting global suppliers. This regional diversification will enhance supply chain resilience and support localized manufacturing.
8. Sustainability and Eco-Design
Environmental concerns are pushing the industry toward sustainable practices. By 2026, OEMs and module makers will focus on recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing, and longer product lifecycles. Regulatory pressures in Europe and North America will accelerate the adoption of eco-design principles in camera module production.
Conclusion
By 2026, the camera module market will be defined by technological sophistication, diversification of applications, and integration of AI. While smartphones remain the primary driver, automotive and industrial applications will emerge as critical growth engines. Companies that innovate in sensor technology, optical design, and intelligent processing—while adapting to regional and environmental challenges—will lead the next phase of market expansion.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Camera Modules: Quality and IP Concerns
Sourcing camera modules for integration into electronic products involves navigating several critical challenges, especially concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product delays, increased costs, legal disputes, or reputational damage.
Poor or Inconsistent Image Quality
One of the most frequent issues is receiving camera modules that fail to meet the required image quality standards. This includes problems such as low resolution, poor low-light performance, color inaccuracy, or inconsistent focus. These issues often stem from suppliers using lower-tier image sensors or inadequate lens assemblies. Additionally, variations in manufacturing processes can result in inconsistent performance across batches, making it difficult to ensure reliable product quality in volume production.
Lack of Quality Control and Testing
Many suppliers, particularly smaller or less-established manufacturers, may lack robust quality control (QC) procedures. Without comprehensive testing—such as optical alignment checks, autofocus calibration, or environmental stress testing—defective modules may pass inspection only to fail in the field. Relying on visual inspection alone is insufficient; structured automated testing protocols are essential to ensure reliability.
Insufficient Technical Documentation and Support
A common pitfall is sourcing from suppliers who provide incomplete or unclear technical documentation. Missing details on electrical specifications, mechanical dimensions, optical parameters, or integration guidelines can delay development and increase engineering effort. Additionally, limited technical support can hinder troubleshooting during prototyping or mass production, especially when firmware or driver issues arise.
IP Infringement and Use of Counterfeit Components
Sourcing camera modules carries significant IP risks, particularly when suppliers use cloned or reverse-engineered image sensors, firmware, or reference designs without proper licensing. This can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated markets. Counterfeit or grey-market components may also be integrated into modules, leading to reliability issues and potential violations of export controls or industry standards.
Hidden Licensing and Royalty Obligations
Some camera modules incorporate third-party IP, such as patented image processing algorithms or compression technologies (e.g., H.264, HDR). Suppliers may not disclose these embedded licenses, leading buyers to unknowingly violate terms or face unexpected royalty payments. It is crucial to verify licensing terms and ensure the supplier has the right to sublicense any included IP.
Dependency on Proprietary Interfaces or Firmware
Certain suppliers lock customers into proprietary communication protocols, firmware, or SDKs. This can limit design flexibility, complicate future sourcing alternatives, and increase long-term dependency on a single vendor. If the supplier discontinues support or goes out of business, it may become impossible to maintain or update the camera functionality.
Inadequate Supply Chain Transparency
Lack of visibility into the component supply chain—such as the origin of the image sensor, lens, or PCB—can create vulnerabilities. Geopolitical risks, export restrictions (e.g., U.S. EAR regulations), or disruptions in key component availability (e.g., due to shortages) can jeopardize production. Ensuring traceability and dual-sourcing options is essential for supply chain resilience.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, demand complete and verifiable technical documentation, perform independent quality testing, and include clear IP indemnification clauses in contracts. Engaging with reputable suppliers and, where possible, sourcing modules based on well-documented, widely supported platforms (e.g., those from Sony, Omnivision, or on standard interfaces like MIPI CSI-2) can significantly reduce risk.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Camera Module
Product Classification & Regulatory Requirements
Camera modules are subject to various international regulations depending on their technical specifications and intended use. Key compliance areas include:
– Export Control: Determine if the module falls under export control regimes such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), especially if it includes high-resolution sensors or encryption capabilities.
– Customs Classification: Accurately classify the product using the Harmonized System (HS) Code. Camera modules typically fall under HS 8525.80 (Transmission apparatus for television) or 8543.70 (Electrical apparatus for line transmission), depending on function.
– Radio Frequency (RF) Compliance: If the module includes wireless transmission (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), ensure certification by relevant bodies such as the FCC (USA), CE-RED (EU), ISED (Canada), or MIC (Japan).
Packaging & Labeling Standards
Proper packaging and labeling are critical for safe transport and customs clearance:
– ESD Protection: Use antistatic packaging (e.g., pink poly bags, conductive foam) to prevent electrostatic discharge damage.
– Labeling Requirements: Include product identifiers (model number, batch/lot), country of origin, RoHS compliance mark, and handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
– Barcoding & Traceability: Implement GS1-compliant barcodes for inventory tracking and customs documentation. Maintain traceability for quality control and recalls.
Transportation & Handling
Ensure safe and efficient global logistics:
– Mode of Transport: Choose air freight for high-value, time-sensitive shipments; sea freight for large volumes. Use temperature-controlled containers if required.
– Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 10–30°C, 30–60% RH) to prevent condensation and component degradation.
– Handling Protocols: Train personnel in ESD-safe handling. Avoid mechanical stress on lens and connector areas during loading and transit.
Environmental & Safety Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations across the product lifecycle:
– RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm the camera module is free of restricted substances (e.g., lead, mercury, phthalates). Maintain compliance documentation for customs and auditors.
– WEEE Directive: Provide take-back and recycling information where applicable.
– Battery Regulations: If the module includes a battery, comply with IEC 62133 (safety) and UN 38.3 (transport) standards.
Documentation & Customs Clearance
Complete and accurate documentation is essential for border crossings:
– Commercial Invoice: Include full product description, HS code, value, origin, and Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP).
– Packing List: Detail quantity, weight, dimensions, and packaging types per shipment.
– Certificates of Compliance: Provide RoHS, REACH, FCC/CE declarations, and any required test reports.
– Export Licenses: Submit required licenses for controlled technology, particularly for destinations under sanctions or embargoes.
Supply Chain Security & Best Practices
Maintain integrity and compliance throughout the logistics chain:
– Authorized Economic Operator (AEO): Partner with AEO-certified logistics providers to expedite customs processing.
– Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: Use tamper-evident packaging and secure serialization to prevent diversion.
– Incident Response Plan: Establish protocols for damaged goods, customs holds, or compliance audits.
Adhering to this guide ensures timely delivery, regulatory compliance, and protection of product integrity for camera module shipments worldwide.
Conclusion for Sourcing Camera Module:
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and market availability, the recommended camera module meets the project’s requirements in terms of resolution, image quality, low-light performance, form factor, and compatibility with the intended application. Multiple suppliers have been assessed for reliability, lead times, scalability, and adherence to quality standards, with the selected vendor offering the best balance of performance, cost-efficiency, and long-term support.
Sourcing this camera module ensures timely integration into the product development cycle, supports future scalability, and aligns with both technical and business objectives. It is advised to proceed with the finalized supplier under agreed-upon terms, including sample testing, volume pricing, and clear service-level agreements to mitigate supply chain risks. Regular performance reviews and ongoing collaboration with the supplier will be essential to maintain quality and responsiveness throughout the product lifecycle.