The global calcium granules market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across agriculture, animal nutrition, and industrial applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the calcium supplements market—which includes granular forms—is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 7.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by increasing awareness of mineral deficiency in livestock and the need for soil enrichment in sustainable farming practices. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the expanding use of calcium-based products in environmental applications, such as flue gas desulfurization, further boosting industrial demand. With Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to intensifying agricultural and manufacturing activities, the supply chain for high-purity calcium granules is rapidly evolving. As quality, consistency, and scalability become critical differentiators, a select group of manufacturers have risen to lead the market. Below are the top six calcium granules manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, global reach, and robust production capabilities.
Top 6 Calcium Granules Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Calcium Carbonate Granular Manufacturer and Supplier …
Domain Est. 2023
Website: richen-nutritional.com
Key Highlights: Richen Nutritional Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer and supplier of top-quality Calcium Carbonate Granular….
#2 Oil
Domain Est. 1996
Website: oildri.com
Key Highlights: Oil-Dri Corporation of America is a leading manufacturer and supplier of specialty sorbent products for consumer and business to business markets….
#3 Calcium Citrate Tetrahydrate FCC Fine Granular, CAS 5785
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jostchemical.com
Key Highlights: Calcium Citrate Tetrahydrate FCC Fine Granular can be used as a dietary ingredient and as a nutrient. Calcium is vital for strong bone and teeth formation….
#4 Calcium Granules
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americanelements.com
Key Highlights: American Elements specializes in producing high purity Calcium Granules in ultra high purity for analytical standards in health and safety research….
#5 Calcium Metal Granular Lab Grade
Domain Est. 2011
Website: laballey.com
Key Highlights: In stock $73.18 deliveryOn-budget and on-time, every time with Lab Alley’s Calcium Metal Granular Lab Grade. Order Lab, tech, and other chemical grades from a trusted partner….
#6
Domain Est. 2012
Website: fredungroup.com
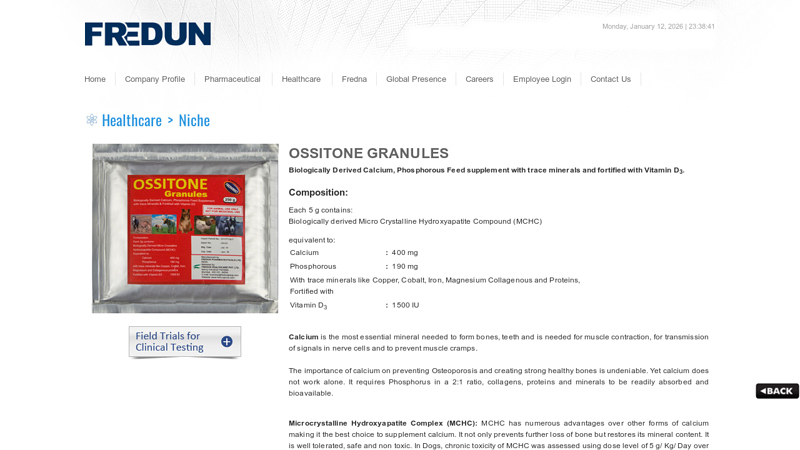
Key Highlights: OSSITONE Granules is a unique blend of Microcrystalline Hydroxyapatite Complex (MCHC) a biologically derived calcium, phosphorus with Vitamin D3. The MCHC ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Calcium Granules

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Calcium Granules
The global calcium granules market is anticipated to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by rising demand across key industrial and agricultural sectors. Several interrelated factors are expected to shape market dynamics, including increasing applications in environmental protection, metal production, and soil treatment.
-
Industrial Demand Expansion
Calcium granules are extensively used in the steel and metallurgical industries as desulfurizing and deoxidizing agents. As global infrastructure development accelerates—particularly in emerging economies like India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa—the demand for high-purity steel is projected to rise. This, in turn, will boost the need for calcium granules in molten metal treatment processes, supporting market expansion through 2026. -
Environmental and Water Treatment Applications
Growing regulatory emphasis on pollution control and wastewater treatment is enhancing the adoption of calcium-based products. Calcium granules are effective in flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems and in neutralizing acidic industrial effluents. With stricter environmental regulations being implemented in regions such as the European Union and North America, demand for calcium granules in eco-friendly technologies is expected to increase significantly by 2026. -
Agricultural Sector Growth
Calcium is a vital nutrient for plant health, and calcium granules are increasingly used as soil amendments to correct calcium deficiencies and improve crop yields. The global push toward sustainable agriculture and enhanced soil health management will drive adoption in agrarian economies. Countries with large-scale farming operations, such as the United States, Brazil, and China, are likely to contribute substantially to market growth. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the calcium granules market by 2026, led by China and India, due to rapid industrialization and expanding agricultural and steel industries. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will maintain stable demand, supported by environmental compliance requirements and technological advancements in material processing. -
Supply Chain and Raw Material Considerations
The availability and pricing of raw materials, primarily limestone and high-purity calcium sources, will influence production costs and market pricing. Investments in mining and refining infrastructure, especially in calcium-rich regions, will be critical to meeting growing demand without significant supply disruptions. -
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Manufacturers are focusing on producing higher-purity calcium granules with controlled particle size and reactivity to meet specialized industrial requirements. Innovations in granulation techniques and coating technologies may enhance product performance and open new application areas, further stimulating market growth.
In summary, the calcium granules market in 2026 is expected to reflect robust growth, underpinned by cross-sector demand, regulatory support for environmental solutions, and ongoing advancements in production technology. Strategic investments in supply chain resilience and product development will be key for stakeholders aiming to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Calcium Granules (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-quality calcium granules, especially for pharmaceutical or high-purity industrial applications, requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to significant operational, financial, and legal risks.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Purity Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is failing to clearly define and verify purity requirements. Calcium granules may contain impurities such as heavy metals (lead, arsenic), residual solvents, or unwanted metal oxides. Sourcing without stringent purity standards (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur., or custom assay limits) can result in product contamination, batch failures, or compliance violations in regulated industries.
Inconsistent Particle Size and Morphology
Calcium granules must often meet specific particle size distribution (PSD) requirements for reactivity, dissolution rate, or processing efficiency. Suppliers may deliver inconsistent granule size or shape due to variable manufacturing processes, leading to performance issues in end-use applications such as metallurgy or chemical synthesis.
Poor Packaging and Handling Leading to Degradation
Calcium is highly reactive with moisture and oxygen. Improper packaging (e.g., non-airtight containers or inadequate desiccants) can result in oxidation or hydrolysis during transit and storage, reducing efficacy and introducing safety hazards. Always verify suppliers use inert atmosphere packaging (e.g., argon-filled containers) and moisture-barrier materials.
Lack of Robust Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
Relying on supplier claims without a detailed, batch-specific CoA is risky. Ensure CoAs include verified test results for identity, assay, impurities, residual solvents, and particle characteristics. Absence of third-party testing or traceable quality control data increases the risk of receiving substandard material.
Unverified Supply Chain and Traceability
Sourcing from intermediaries without transparency into the original manufacturer can mask quality inconsistencies. Untraceable supply chains increase the risk of counterfeit or adulterated materials. Always audit suppliers and require full documentation of raw material sources and manufacturing history.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Manufacturing Processes
Calcium granulation methods, especially those involving specific passivation techniques or alloying agents, may be protected by patents. Sourcing granules produced via patented processes without licensing can expose your organization to infringement claims, particularly in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement.
Use of Proprietary Formulations Without Authorization
Some suppliers offer “enhanced” calcium granules with proprietary coatings or stabilizers designed to improve handling or performance. Using these without understanding the IP status—or without appropriate usage rights—can lead to legal disputes, especially if incorporated into your own patented products.
Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier IP Ownership
Failing to confirm that the supplier owns or has legitimate rights to the technology used in production can result in downstream liability. Conduct IP audits or request warranties from suppliers stating their products do not infringe third-party rights.
Export/Import Compliance and Technology Transfer Restrictions
Certain high-purity or specially processed calcium granules may be subject to export controls (e.g., dual-use regulations) due to their application in sensitive industries. Unauthorized international sourcing may breach technology transfer laws, especially when IP-protected methods are involved.
Inadequate Contractual IP Protections
Purchase agreements often lack clauses addressing IP indemnification, permitted use, and liability for infringement. Ensure contracts clearly allocate IP risks and include provisions for audit rights and compliance certifications.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, compliant sourcing of calcium granules.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Calcium Granules
Overview and Definition
Calcium granules are fine, pelletized forms of elemental calcium or calcium compounds, commonly used in industrial applications such as metallurgy (as a deoxidizer or desulfurizer), water treatment, and chemical synthesis. Proper handling, transport, and regulatory compliance are essential due to their reactive nature, particularly with moisture and acids, which can produce flammable hydrogen gas.
Regulatory Classification
Calcium granules are typically classified under hazardous materials regulations due to their reactivity. Key classifications include:
– UN Number: UN 1406 (Calcium, in granular form)
– Hazard Class: 4.3 (Dangerous when wet – substances liable to spontaneous combustion or emit flammable gas on contact with water)
– Packing Group: II (Medium danger)
– GHS Classification:
– H261: In contact with water releases flammable gases which may ignite spontaneously
– H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
– H318: Causes serious eye damage
Packaging Requirements
Packaging must prevent moisture ingress and physical damage:
– Use hermetically sealed, moisture-resistant containers (e.g., steel drums with polymer liners or double-layered plastic bags inside fiber drums)
– Inner containers must be leak-proof and compatible with calcium (e.g., polyethylene)
– Outer packaging must meet UN performance standards for Packing Group II
– All packages must display proper hazard labels (Class 4.3) and UN number markings
Storage Guidelines
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from sources of moisture, heat, and ignition
- Keep away from oxidizers, acids, halogens, and water-reactive substances
- Use non-combustible flooring and spill containment systems
- Limit storage quantities per local fire code; segregate from incompatible materials
- Use desiccants or humidity control if necessary
Transportation Requirements
- Road (ADR): Comply with ADR regulations for Class 4.3 materials; use approved vehicles with segregation from water sources and oxidizing agents
- Air (IATA): Subject to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations; may require special provisions and approval from the carrier; generally prohibited as passenger aircraft cargo unless excepted in limited quantities
- Sea (IMDG): Must be stowed “away from” sources of heat and moisture; segregation from Class 3, Class 5.1, and Class 8 materials required
- All transport documents must include proper shipping name, UN number, hazard class, and emergency contact information
Handling Procedures
- Use in a controlled environment with engineering controls (e.g., fume hoods, local exhaust)
- Operators must wear appropriate PPE: chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile or neoprene), safety goggles or face shield, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection if dust is generated
- Avoid creating dust; use non-sparking tools
- Never handle with wet hands or in humid conditions
- Ground equipment to prevent static discharge
Emergency Response
- Spill: Do not use water. Smother with dry sand, dry sodium chloride (table salt), or Class D fire extinguishing agent. Collect material carefully and place in a dry, sealed container under inert atmosphere.
- Fire: Use Class D fire extinguishers (e.g., Met-L-X, dry sand, graphite powder). Water or CO₂ will intensify the fire. Evacuate area and call emergency services.
- Exposure:
- Skin contact: Flush with copious amounts of dry cloth to remove granules, then rinse with water; seek medical attention
- Eye contact: Rinse immediately with water for at least 15 minutes; consult a physician
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical help if respiratory irritation occurs
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
- Maintain Safety Data Sheet (SDS) compliant with GHS and local regulations (e.g., OSHA HazCom in the U.S., CLP in the EU)
- Ensure transporters are trained and certified in dangerous goods handling
- Keep records of training, shipments, and safety inspections
- Comply with REACH (EU), TSCA (U.S.), and other chemical control regulations as applicable
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
- Dispose of as hazardous waste in accordance with local, national, and international regulations (e.g., Basel Convention if exported)
- Neutralize under controlled conditions using approved methods (e.g., slow reaction with alcohol under inert atmosphere) before disposal
- Prevent release into sewers, waterways, or soil due to reactivity and environmental hazards
Special Considerations for International Trade
- Verify import/export restrictions; some countries require permits for calcium metal products
- Ensure correct HS Code classification (e.g., 2805.30 for calcium metal, granules)
- Comply with customs documentation, including dangerous goods declaration and SDS
Training and Recordkeeping
- Provide regular training for personnel on hazards, handling, storage, and emergency procedures
- Conduct drills for spill and fire response
- Maintain up-to-date records of safety training, incident reports, and compliance audits
By adhering to this guide, organizations can ensure the safe and compliant logistics management of calcium granules across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Calcium Granules
In conclusion, sourcing calcium granules requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and regulatory compliance. High-purity calcium granules are essential for various industrial applications, including metallurgy, chemical synthesis, and environmental treatment, making supplier credibility and material consistency critical. When selecting a supplier, factors such as product specifications (e.g., particle size, purity level, and packaging), supply chain stability, and adherence to safety and environmental standards must be thoroughly evaluated.
Establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers, preferably those certified under international quality standards (such as ISO), ensures consistent product performance and traceability. Additionally, considering regional availability and logistics can help reduce lead times and transportation costs. As demand for high-performance materials grows, investing in sustainable sourcing practices and exploring alternative supply channels or emerging markets may offer competitive advantages.
Ultimately, a well-informed and proactive sourcing strategy for calcium granules not only supports operational efficiency but also enhances product quality and process reliability across industrial applications.