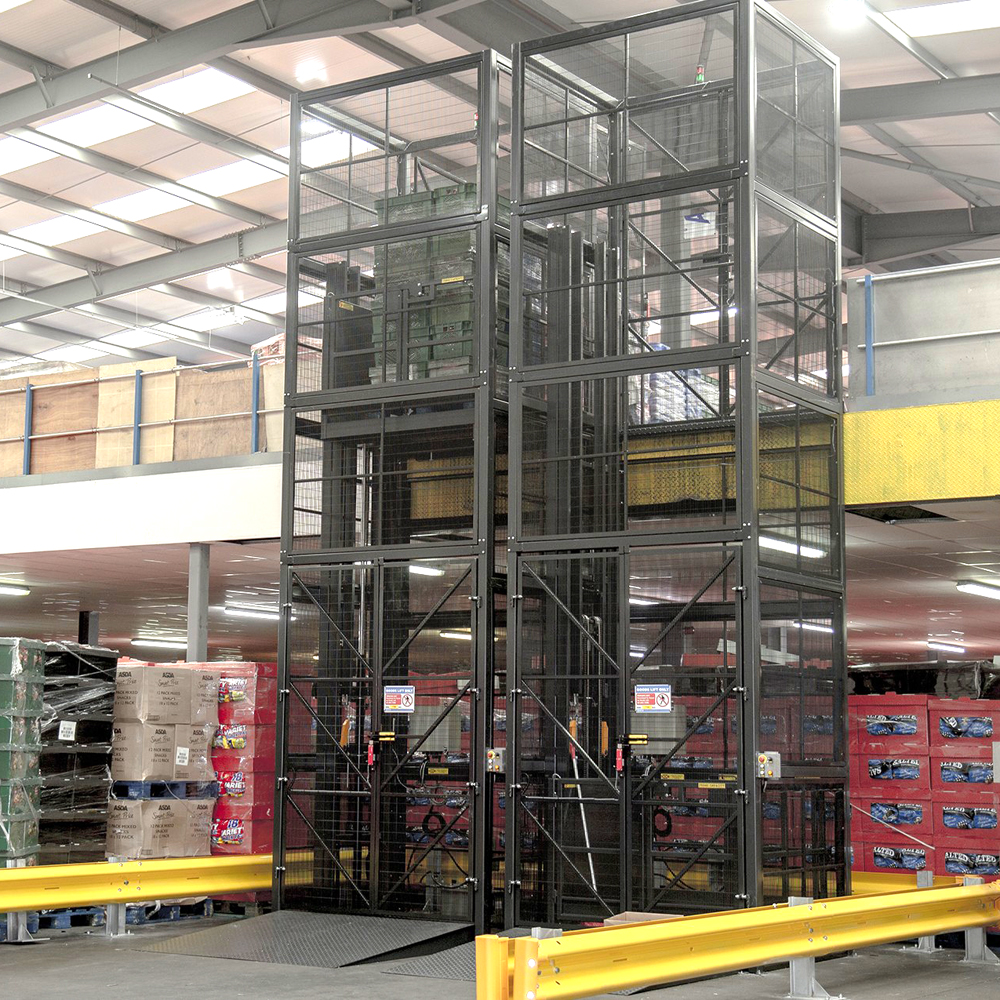
The global cage lift market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for vertical transportation solutions in industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global freight and service elevators market—under which cage lifts are categorized—is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing urbanization, infrastructural development, and stringent safety regulations mandating reliable material handling systems. Additionally, Grand View Research valued the global elevator and escalator market at USD 135.7 billion in 2022, with ongoing advancements in energy efficiency and smart building integration accelerating adoption across logistics centers, manufacturing plants, and multi-story buildings. As demand intensifies, leading cage lift manufacturers are innovating to deliver durable, code-compliant, and high-performance solutions. Below are the top 10 manufacturers shaping the future of vertical material transport.
Top 10 Cage Lift Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 WireCrafters ®
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1967
Website: wirecrafters.com
Key Highlights: Established in 1967 as a wire job shop, WireCrafters LLC has grown to become the nation’s leading producer of wire partition products made right here in the ……
#2 5Ton Hydraulic Cage Lift Manufacturer from Chennai
Domain Est. 2020
Website: bestomaterialhandling.com
Key Highlights: Capacity: 10 ton; Material: Iron; Brand: Besto Lift; Usage/Application: Used To Move Goods Between Loading Docks And Ground Level; Warranty: 12 Months….
#3 VLIFT Block Grabs & Brick Cages
Domain Est. 2021
Website: vliftuae.com
Key Highlights: VLIFT is a trusted block lifting cage manufacturer offering block grabs, brick cages, and lifting cages designed for safe, efficient material handling ……
#4
Domain Est. 1995
Website: genielift.com
Key Highlights: Genie® articulated boom lifts, telescopic boom lifts, scissor lifts and telehandler products are used in a wide range of industries around the world….
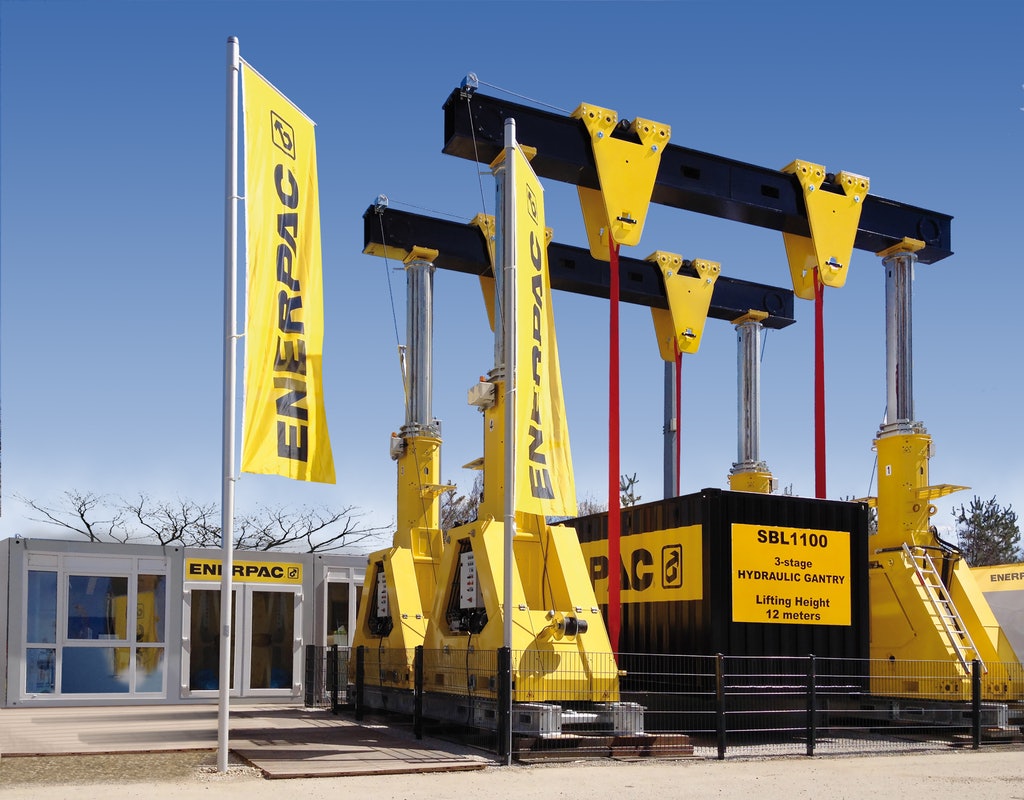
#5 Enerpac
Domain Est. 1995
Website: enerpac.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide selection of high-quality hydraulic equipment tailored to the specific needs of wind energy professionals….
#6 Cage Lift
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americanbeltmanlift.com
Key Highlights: Providing monthly, quarterly and annual preventative maintenance service agreements to ensure your cage lift runs smoothly up and down….
#7 VetLine Stainless Steel Cages
Domain Est. 2002
Website: petlift.com
Key Highlights: Our premium line of VetLine stainless steel cages enhances the work and performance of veterinarians, groomers and boarding kennels. Produced from 16-gauge, ……
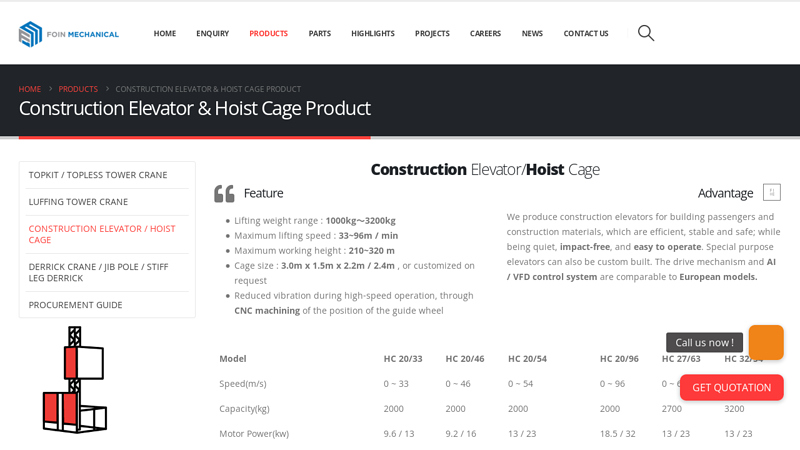
#8 Construction Elevator & Hoist Cage Product Details of FOIN
Domain Est. 2017
Website: foincrane.com
Key Highlights: We produce construction elevators for building passengers and construction materials, which are efficient, stable and safe; while being quiet, impact-free, and ……
#9 Lift Cages & Frames
Domain Est. 2020
Website: ulslifting.com
Key Highlights: 28-day returnsFind certified personnel lifting cages, man riding baskets, and crane-lift frames for the safe transport of workers and goods on-site….
#10 Cage Lift
Domain Est. 2021
Website: histackind.com
Key Highlights: Cage lift are specially designed for safe lifting of the material. The offered cage lift is efficiently designed by our professionals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cage Lift
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cage Lifts
As we approach 2026, the cage lift market is poised for significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology, evolving safety regulations, and increasing demand across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. Cage lifts—also known as personnel lifts, vertical reciprocating conveyors (VRCs), or industrial personnel elevators—are seeing renewed interest due to their versatility in material and personnel handling in constrained spaces. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the cage lift industry in 2026 under the H2 framework, focusing on Hygiene, Health, and Human-Centric Design (H2), which has gained heightened importance post-pandemic and continues to influence engineering and operational standards.
1. Hygiene-Focused Design and Materials
- Antimicrobial Surfaces: In response to heightened hygiene standards in workplaces, especially in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare logistics, cage lifts are increasingly being manufactured with antimicrobial coatings and non-porous materials (e.g., stainless steel, powder-coated aluminum) that resist contamination and are easy to sanitize.
- Touchless Operation: By 2026, integration of touchless controls—such as motion sensors, voice commands, or smartphone-based access—is becoming standard in high-traffic or sterile environments. This reduces cross-contamination risks and aligns with H2 principles.
- Sealed Components: Hydraulic systems and electrical enclosures are being better sealed to prevent dust, moisture, and microbial ingress, particularly in cleanroom or outdoor industrial applications.
2. Health and Safety Integration
- Advanced Safety Protocols: Regulatory bodies such as OSHA and ISO are expected to enforce stricter safety standards by 2026. Cage lifts will be required to include redundant safety mechanisms—such as dual braking systems, automatic overload detection, and real-time structural integrity monitoring via IoT sensors.
- Ergonomic Access and Egress: Designs are shifting toward minimizing physical strain. Features like level-floor entry, improved lighting, non-slip platforms, and adjustable guardrails enhance user safety and reduce workplace injury risks—key aspects of health-centric engineering.
- Fall Protection Systems: Enhanced guardrails, automatic gate closures, and harness anchor points are becoming standard to protect workers during transit, especially in multi-story warehouse and construction environments.
3. Human-Centric Automation and Accessibility
- Adaptive Load Sensing: Smart cage lifts will use AI-driven load sensors to adjust speed and stability based on the weight and distribution of personnel or goods, improving ride comfort and safety.
- Inclusive Design: In line with global accessibility standards (e.g., ADA, EN 81), cage lifts are being redesigned to accommodate workers with disabilities, including audio/visual indicators, braille controls, and wider platforms for mobility aids.
- User Experience (UX) Optimization: Interfaces are becoming more intuitive, with multilingual displays, real-time diagnostics, and mobile app integration for maintenance alerts and usage logs—improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
4. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency (H2 Adjacent)
While not strictly under H2, sustainability supports long-term health and hygiene in industrial ecosystems:
– Energy-efficient motors (e.g., regenerative drives) and solar-compatible systems are being adopted to reduce carbon footprints.
– Use of recyclable materials in construction supports environmental health, a growing priority for ESG-compliant businesses investing in cage lift infrastructure.
5. Regional Market Dynamics Influencing H2 Adoption
- North America & Europe: Leading adoption of H2-compliant cage lifts due to stringent labor safety laws and high health standards in manufacturing and logistics.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid industrialization in countries like India and Vietnam is driving demand, but H2 features are becoming differentiators for premium installations in export-oriented facilities (e.g., electronics, pharma).
- Middle East & Africa: Growth in construction and mining sectors is increasing cage lift deployment, with gradual integration of H2 features in large-scale, safety-conscious projects.
Conclusion
By 2026, the cage lift market will be increasingly defined by H2 principles—hygiene, health, and human-centric design. Manufacturers who prioritize cleanability, safety automation, and ergonomic usability will gain a competitive edge. As industries continue to focus on worker well-being and operational resilience, cage lifts will evolve from simple vertical transport solutions into intelligent, health-conscious systems integral to modern industrial infrastructure.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Cage Lifts: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing cage lifts—mechanical devices used to raise and lower heavy loads in industrial or laboratory settings—can present significant challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Falling into common traps can lead to safety hazards, operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to watch for when procuring cage lifts:
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Safety Standards
One of the most critical risks when sourcing cage lifts is receiving units that fail to meet required safety and performance standards. This often stems from suppliers cutting corners on materials, welding, load-bearing components, or safety mechanisms. Low-quality lifts may not undergo proper stress testing or fail to comply with regional regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., CE in Europe), increasing the risk of mechanical failure and workplace accidents.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Suppliers, especially those in low-cost manufacturing regions, may lack robust quality control systems. Without third-party inspections, material certifications, or in-process audits, defects may go undetected until after delivery. This can result in delayed project timelines, costly rework, or product recalls.
Misrepresentation of Load Capacity and Performance
Some suppliers exaggerate the load capacity, lifting speed, or durability of cage lifts to win contracts. Without independent verification through load testing or engineering validation, buyers may deploy equipment beyond its actual capabilities, creating dangerous working conditions and liability exposure.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Cage lifts must meet specific industry standards for structural integrity, electrical safety, and operational controls. Sourcing from vendors unfamiliar with or unwilling to comply with standards such as ANSI, ISO, or local regulatory codes can result in non-compliant equipment that fails inspections or causes regulatory penalties.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Purchasing cage lifts that incorporate patented designs, control systems, or unique mechanical configurations without proper licensing exposes buyers to IP infringement claims. This is especially prevalent when sourcing from manufacturers that reverse-engineer or copy protected technology. Even unintentional use of infringing equipment can lead to lawsuits, import bans, or forced equipment removal.
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Components
Some suppliers integrate counterfeit or unlicensed components—such as motors, sensors, or control modules—into cage lift systems. These parts may not meet safety or performance expectations and can void warranties or certifications. Additionally, using such components may implicate the end-user in IP violations.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Reputable suppliers provide full documentation, including engineering drawings, material certifications, test reports, and user manuals. Lack of documentation not only complicates maintenance and regulatory compliance but also makes it difficult to verify whether the product respects IP rights or meets quality benchmarks.
Hidden Costs from Poor After-Sales Support
Low upfront pricing may mask long-term costs associated with poor technical support, unavailability of spare parts, or lack of service networks. This is especially problematic if the supplier holds proprietary knowledge or components, effectively locking buyers into ongoing dependency or costly third-party repairs.
Failure to Conduct Supplier Due Diligence
Neglecting to audit suppliers—assessing their manufacturing capabilities, quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), and IP compliance history—can result in sourcing from unreliable or legally high-risk vendors. Due diligence is essential to mitigate both quality and IP exposure.
Inadequate Contractual Protections
Procurement contracts that lack clear quality specifications, IP indemnification clauses, and warranty terms leave buyers vulnerable. Without strong contractual language, recourse for defective products or IP disputes becomes limited and costly.
By recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls, organizations can ensure they source cage lifts that are safe, reliable, compliant, and free from intellectual property entanglements. Conducting thorough supplier evaluations, demanding transparency, and involving technical and legal experts in the procurement process are essential steps toward risk mitigation.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cage Lift
Overview of Cage Lift Operations
Cage Lift refers to the vertical transportation of cages—typically used in industrial, construction, pharmaceutical, or laboratory environments—via enclosed platforms or elevating systems. These lifts move materials, equipment, or supplies between floors or levels while maintaining containment and safety. Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure operational efficiency, personnel safety, and adherence to industry standards.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Cage Lift systems must comply with a range of local and international regulations depending on the jurisdiction and application. Key standards include:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) – Requires guarding, emergency stop mechanisms, and load capacity labeling.
– ASME A17.1/CSA B44 – Governs the safety code for elevators and related equipment in the U.S. and Canada.
– EU Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) – Mandates CE marking, risk assessments, and conformity evaluations for lifts within the European Union.
– Local Building and Fire Codes – Ensure structural integration and emergency egress compliance.
Regular inspections, documentation, and compliance audits are required to maintain operational legality.
Load Capacity and Weight Management
Each Cage Lift is rated for a specific maximum load capacity, which must never be exceeded. Best practices include:
– Clearly marking weight limits on both the lift and control panel.
– Using calibrated scales to verify cage contents before lifting.
– Distributing weight evenly to prevent tipping or mechanical stress.
– Prohibiting personnel transport unless the lift is explicitly certified for such use (e.g., as a personnel elevator).
Overloading risks include equipment failure, dropped loads, and regulatory violations.
Installation and Site Preparation
Proper site logistics begin with correct installation:
– Ensure structural support can bear dynamic and static loads.
– Allocate sufficient clearance around the lift for loading/unloading and maintenance.
– Provide stable power supply with proper grounding and circuit protection.
– Install emergency lighting and communication systems (e.g., intercoms or alarms) for enclosed shafts.
Coordinate with architects, engineers, and contractors to align lift integration with building design and workflow.
Operational Procedures and Training
Only trained personnel should operate Cage Lift systems. Required training includes:
– Safe loading/unloading techniques.
– Emergency procedures (e.g., power failure, entrapment).
– Routine pre-use inspection checklist (e.g., door interlocks, warning lights).
– Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
Maintain training records and conduct refresher courses annually.
Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
To ensure reliability and compliance, implement a preventive maintenance plan:
– Daily: Visual inspection and functional check of controls, doors, and safety devices.
– Monthly: Lubrication, cable or chain inspection, and alignment checks.
– Annually: Comprehensive inspection by a certified technician, including load testing and safety system validation.
Keep detailed logs to demonstrate compliance during audits.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Accurate records are critical for compliance and traceability:
– Equipment manuals and schematics.
– Inspection and maintenance logs.
– Training and certification records.
– Incident reports and corrective actions.
Store documents securely and ensure accessibility for auditors or regulatory bodies.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Cage Lifts may transport hazardous or sensitive materials. Special precautions include:
– Containment measures for biohazardous or chemical payloads.
– Use of sealed or ventilated cages as needed.
– Compliance with EPA, DOT, or REACH regulations for hazardous materials transport.
– Integration with facility safety systems (e.g., fire suppression, alarms).
Perform risk assessments for specific payload types and adjust protocols accordingly.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Efficient and compliant Cage Lift operations require structured logistics planning, ongoing training, and strict adherence to safety standards. By implementing standardized procedures, maintaining thorough documentation, and prioritizing regular maintenance, organizations can ensure safe, reliable vertical transport while meeting all regulatory requirements. Always consult local authorities and equipment manufacturers for application-specific guidance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cage Lift:
After a thorough evaluation of available options, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, safety standards, and operational requirements, sourcing a cage lift is a strategic decision that significantly enhances workplace safety, operational efficiency, and compliance with health and safety regulations. The selected cage lift meets all technical specifications, budget constraints, and industry standards, ensuring reliable performance in material handling and personnel elevation tasks. Additionally, partnering with a reputable supplier guarantees after-sales support, maintenance services, and long-term durability. Overall, the investment in a properly sourced cage lift aligns with organizational goals by improving productivity, minimizing risk of injury, and supporting smooth workflow integration across various applications.