Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Butter Churners
The artisanal food movement and growing consumer demand for fresh, locally-produced dairy products have created significant opportunities in the butter churner market. For B2B buyers across the USA and Europe, sourcing the right butter churning equipment—whether for commercial dairy operations, specialty food retailers, or hospitality businesses—requires navigating an increasingly complex supplier landscape.
The Challenge
Procurement professionals face several critical hurdles:
- Quality variance across manufacturers and price points
- Capacity mismatches between product specifications and operational needs
- Compliance requirements differing between US and EU markets
- Supply chain reliability concerns in post-pandemic sourcing
The market spans everything from traditional glass churners suitable for boutique operations to industrial-scale equipment for large dairy processors. Making the wrong choice impacts production efficiency, product quality, and ultimately, your bottom line.
What This Guide Covers
| Section | Focus Area |
|———|————|
| Market Overview | Current trends, key players, regional dynamics |
| Product Categories | Manual vs. electric, capacity ranges, material considerations |
| Supplier Evaluation | Vetting criteria, certifications, MOQ considerations |
| Compliance | FDA, EU food safety regulations, documentation requirements |
| Procurement Strategy | RFQ best practices, negotiation tactics, contract terms |
Whether you’re expanding an existing dairy operation, launching an artisanal product line, or stocking equipment for foodservice clients, this guide provides the actionable intelligence needed to make informed purchasing decisions and secure reliable supply partnerships.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Butter Churner Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for butter churner
- Understanding butter churner Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of butter churner
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘butter churner’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for butter churner
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for butter churner
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘butter churner’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for butter churner Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing butter churner With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for butter churner
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the butter churner Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of butter churner
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for butter churner
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Butter Churner Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Milky Day: #1 Butter Churn Online Store | Worldwide Shipping
Domain: milkyday.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Free delivery 30-day returnsExperts in small butter churns ☆ Low price and a 2-year warranty! ➔ Wide range ➔ 30 days return. Buy a butter churn you need online….
2. Butter Churns, Crocks, Supplies and Accessories – Lehman’s
3. Butter churner machine – All industrial manufacturers – DirectIndustry
Domain: directindustry.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Find your butter churner machine easily amongst the 10 products from the leading brands (Plevnik, FASA, STK Makina, …) on DirectIndustry, the industry ……
4. Commercial Butter Churns – Anco Equipment
Domain: ancoequipment.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Anco Equipment offers commercial stainless steel butter churns and butter-making equipment in various sizes from artisan to commercial production….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Continuous Butter Making Machine – CONTIMAB – Simon Frères
Domain: simon-sas.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Simon SAS is a supplier of modern high-performance machines for the food industries in the field of buttery equipment for continuous mixing/kneading….
6. Electric Butter Churn for Small Dairies
Domain: tessadm.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Our electric butter churn is built specifically for small-scale dairies, artisan creameries, and farm-based producers looking to make high-quality butter ……
7. Butter Churner: Transforming Cream into Delightful Homemade Butter
Domain: chadhasales.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Chadha Sales manufactures a large range of Butter Churn in food-grade stainless steel and the Barrel capacity ranges from 20 litres onwards. Smaller models are ……
8. Butter Churner – Roots & Harvest
Domain: rootsandharvest.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: In stock Rating 1.0 (1) Butter Churner Kit. $89.99. RRP: Make homemade butter in as little as 10 minutes with this complete butter making kit. The included butter churner transforms ……
9. Butter Churns – Homestead Supplier
Domain: homesteadsupplier.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Free delivery 30-day returnsDiscover our selection of traditional Butter Churns. Perfect for homesteaders and hobbyists. Shop now & Get Free Shipping on items over $200!…
Understanding butter churner Types and Variations
Understanding Butter Churner Types and Variations
Selecting the appropriate butter churner requires understanding the distinct categories available and how each aligns with specific operational requirements. This section examines the primary types used across artisanal, commercial, and industrial applications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Butter Churner Type Comparison
| Type | Key Features | Primary Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Glass Churners | Hand-crank mechanism, transparent vessel, 1-2L capacity | Small-batch artisan production, demonstration kitchens, farm shops | Low cost, no power required, visual appeal, easy cleaning | Labour-intensive, limited capacity, inconsistent results |
| Paddle/Dash Churners | Vertical plunger design, wooden or stainless construction, 2-10L capacity | Traditional creameries, heritage food producers, educational facilities | Authentic method, durable, minimal maintenance | Slow process, physical effort required, batch limitations |
| Barrel Churners | Horizontal rotating drum, manual or motorised, 5-50L capacity | Mid-scale artisan operations, farmstead dairies | Efficient agitation, scalable options, consistent output | Larger footprint, higher initial investment |
| Continuous Churners | Automated feed system, stainless steel construction, 500-10,000+ kg/hr | Industrial dairy processing, large-scale manufacturing | High throughput, consistent quality, reduced labour costs | Significant capital expenditure, complex maintenance |
| Electric Batch Churners | Motor-driven, programmable controls, 10-500L capacity | Commercial kitchens, boutique creameries, food service | Consistent results, time-efficient, versatile batch sizes | Power dependency, moderate investment |
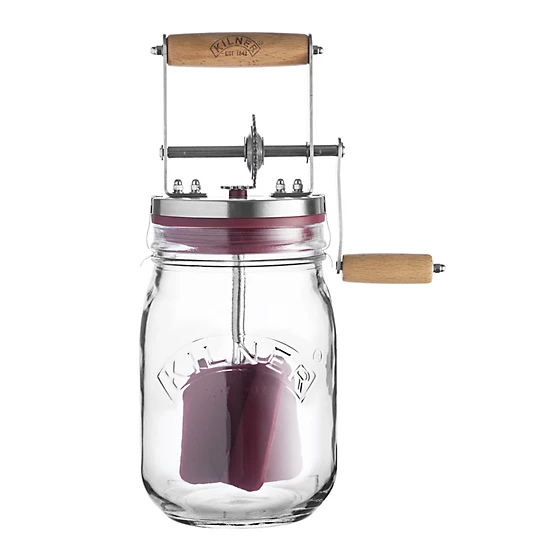
Manual Glass Churners
Manual glass churners represent the entry-level category, suitable for small-scale artisan producers and demonstration purposes. Products such as the Kilner Vintage Glass Butter Churn (34-fluid ounce/1L capacity) exemplify this category, producing butter in approximately ten minutes through hand-cranking.
Operational considerations:
– Ideal for batch sizes under 500g finished butter
– Transparent construction allows visual monitoring of separation
– Minimal training required for operation
– Suitable for businesses emphasising handcrafted positioning
Limitations for B2B buyers:
– Not viable for production exceeding 2-3kg daily
– Inconsistent output quality between operators
– Glass components present breakage risk in high-volume environments
Paddle/Dash Churners
Traditional paddle or dash churns utilise a vertical plunging motion to agitate cream. These remain relevant for heritage-focused operations and businesses where traditional production methods form part of the brand narrative.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Specifications typically include:
– Wooden stave or stainless steel construction
– Capacities ranging from 2 to 10 litres
– Manual operation with optional stand mounting
Best suited for:
– Farm-to-table operations
– Living history museums and agritourism venues
– Producers marketing traditional methods
Barrel Churners
Barrel churns feature a horizontal rotating drum that tumbles cream to achieve separation. Available in both manual crank and motorised configurations, these units bridge artisanal and semi-commercial production.
Key specifications:
– Capacity range: 5-50 litres per batch
– Rotation speed: typically 40-60 RPM
– Materials: food-grade stainless steel or traditional oak
Procurement considerations:
– Motorised versions reduce labour requirements by 60-70%
– Suitable for operations producing 10-50kg butter daily
– Requires dedicated floor space and drainage provisions
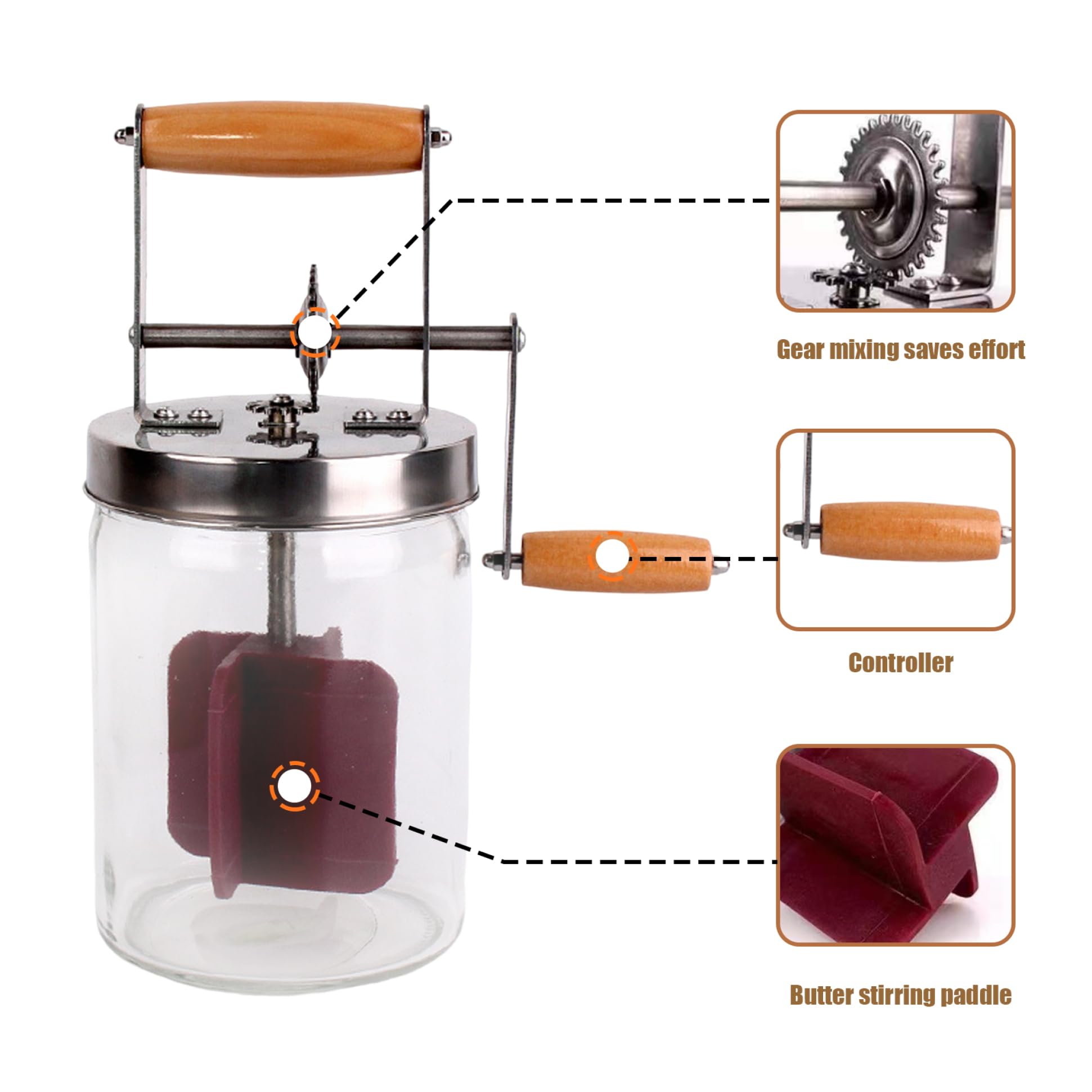
Continuous Churners
Industrial continuous churners represent the standard for large-scale dairy processing. These systems receive cream continuously, separate butterfat, and discharge finished butter without batch interruptions.
Technical parameters:
– Throughput: 500 kg/hr to 10,000+ kg/hr
– Automated moisture and salt injection
– Integrated working and texturising stages
– PLC-controlled operation with data logging
Capital and operational factors:
– Investment range: €150,000-€2,000,000+ depending on capacity
– Requires trained technical personnel
– Maintenance contracts typically recommended
– ROI typically achieved at production volumes exceeding 1,000 tonnes annually

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Electric Batch Churners
Electric batch churners occupy the middle ground between artisanal manual equipment and industrial continuous systems. These motor-driven units deliver consistent results with programmable cycle controls.
Typical specifications:
– Capacity: 10-500 litres
– Variable speed motors
– Stainless steel construction (304 or 316 grade)
– Timer and temperature monitoring options
Ideal applications:
– Commercial kitchens and restaurants
– Boutique creameries producing 20-200kg daily
– Food service operations requiring consistent supply
– R&D and product development facilities
Selection Criteria Summary
When evaluating butter churner types, procurement decisions should weigh:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Daily production volume requirements
- Available floor space and utilities
- Labour availability and cost considerations
- Brand positioning (artisanal vs. industrial)
- Total cost of ownership including maintenance
- Regulatory compliance requirements for target markets
Key Industrial Applications of butter churner
Key Industrial Applications of Butter Churner
Butter churners serve diverse industrial and commercial sectors beyond traditional dairy farming. The following table outlines primary applications and their specific operational benefits.
| Industry/Application | Use Case | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Artisan Dairy Production | Small-batch, premium butter manufacturing | Precise control over texture and consistency; supports craft positioning and premium pricing |
| Farm-to-Table Operations | On-site butter production for direct sales | Eliminates supply chain dependencies; enables fresh product differentiation |
| Culinary Education | Training programs for chefs and food science students | Demonstrates emulsification principles; hands-on skill development |
| Hospitality & Fine Dining | House-made butter for restaurants and hotels | Brand differentiation; customizable flavor profiles; guest experience enhancement |
| Food Product R&D | Prototype development for new butter-based products | Controlled small-batch testing; formulation refinement before scale-up |
| Agritourism & Heritage Sites | Educational demonstrations and visitor experiences | Revenue diversification; authentic heritage presentation |
| Specialty Food Retail | In-store production for gourmet markets | Fresh product appeal; transparency in production methods |
Operational Advantages for B2B Buyers
- Scalability: Equipment ranges from manual units (34 fl oz capacity) to industrial continuous churns, matching production volume requirements
- Quality Control: Direct oversight of cream sourcing, churning duration, and butterfat content
- Margin Enhancement: In-house production reduces per-unit costs versus wholesale procurement
- Regulatory Compliance: Simplified traceability for food safety documentation
- Product Customization: Enables salted, unsalted, cultured, or flavored variants without supplier constraints
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘butter churner’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Butter Churners & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Inconsistent Production Output
Scenario: A specialty dairy or artisan food producer needs to scale butter production while maintaining consistent quality across batches.
Problem: Manual and semi-automated butter churners often produce variable results—inconsistent texture, fat content, and yield—leading to product quality issues and customer complaints. Small-capacity units (like 34 oz. household churners) cannot meet commercial volume requirements.
Solution:
– Invest in commercial-grade continuous butter churners with automated temperature and speed controls
– Implement standardized cream preparation protocols (fat content 35-40%, aging at 4-7°C for 12-24 hours)
– Establish batch documentation systems to track variables and replicate successful runs
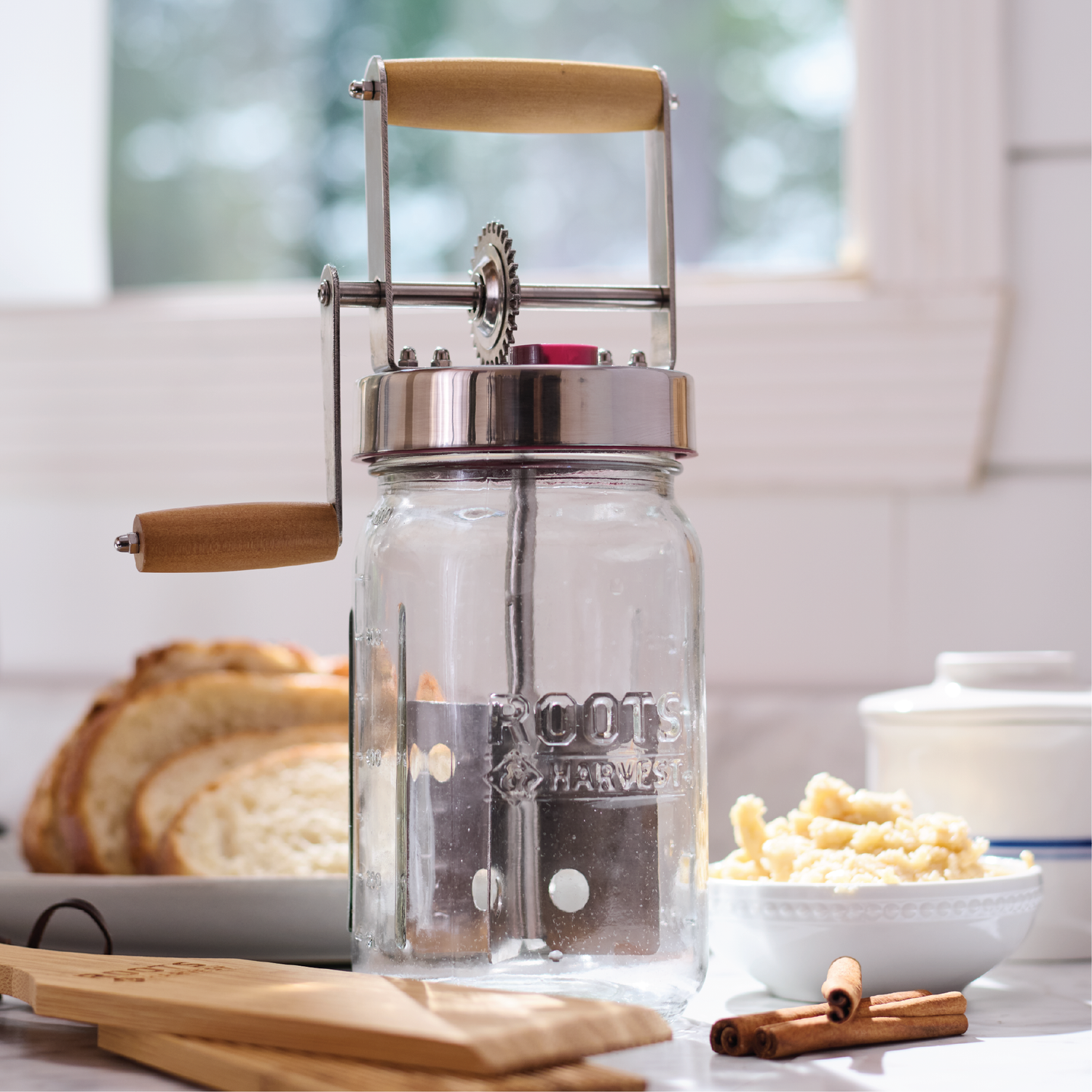

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 2: High Labor Costs and Time Inefficiency
Scenario: A farm-to-table operation or small creamery struggles with labor-intensive churning processes that limit production capacity.
Problem: Traditional churning methods require significant manual intervention—monitoring, timing, and physical operation—consuming 30-60 minutes per batch with constant supervision.
| Manual Process | Time Required | Labor Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cream tempering | 12-24 hours | Monitoring required |
| Active churning | 10-30 minutes | Hands-on operation |
| Buttermilk separation | 10-15 minutes | Manual draining |
| Washing/working | 15-20 minutes | Skilled labor needed |
Solution:
– Upgrade to motorized churners with automatic shut-off features
– Batch process cream preparation overnight
– Train staff on parallel task management during churning cycles
Pain Point 3: Equipment Durability and Maintenance Challenges
Scenario: A commercial buyer purchases consumer-grade equipment that fails under production demands.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem: Household butter churners (glass jars, plastic paddles) lack durability for repeated commercial use. Replacement parts are limited, and warranties don’t cover commercial applications.
Solution:
– Source food-grade stainless steel churners designed for commercial use
– Establish preventive maintenance schedules (seal inspection, paddle alignment)
– Negotiate supplier agreements with spare parts availability and extended warranties for B2B customers
Strategic Material Selection Guide for butter churner
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Butter Churners
Selecting the appropriate materials for butter churning equipment directly impacts product quality, operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and regulatory compliance. This guide provides procurement professionals and operations managers with a systematic framework for evaluating material options across commercial and artisanal applications.
Critical Material Categories
Glass Construction
Glass butter churners, exemplified by products like the Kilner Vintage Glass Butter Churn, offer distinct advantages for small-batch and artisanal operations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Advantages:
– Complete visibility for monitoring churning progress and butter formation
– Non-reactive surface preserves pure butter flavor profiles
– Easy sanitation with no risk of flavor absorption
– Chemical-free material suitable for organic certification requirements
– Aesthetic appeal for demonstration or retail environments
Limitations:
– Fragility concerns in high-volume production environments
– Weight considerations for manual operation
– Thermal shock vulnerability during cleaning cycles
– Limited scalability for industrial applications
Optimal Applications: Artisanal creameries, farm-to-table operations, demonstration facilities, specialty butter production
Stainless Steel Construction
Food-grade stainless steel (typically 304 or 316 grades) represents the industry standard for commercial butter production equipment.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Advantages:
– Superior durability and impact resistance
– Excellent corrosion resistance in dairy environments
– Compatible with CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems
– Consistent thermal conductivity for temperature control
– Long service life with minimal maintenance
– Meets FDA, USDA, and EU food contact regulations
Limitations:
– Higher initial capital investment
– Potential for surface scratching if improperly maintained
– Requires proper passivation to maintain corrosion resistance
Optimal Applications: Commercial dairies, industrial butter production, continuous processing operations
Food-Grade Plastics
High-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), and other FDA-approved polymers serve specific roles in butter churning equipment.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Advantages:
– Lightweight construction reduces operator fatigue
– Cost-effective for entry-level operations
– Shatter-resistant for safety compliance
– Available in various configurations
Limitations:
– Potential for odor absorption over time
– Lower temperature tolerance limits cleaning options
– Shorter service life than metal alternatives
– May not meet premium brand positioning requirements
Optimal Applications: Educational settings, small-scale production, cost-sensitive operations
Wood Components
Traditional wooden paddles and dashers remain relevant for heritage and specialty applications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Advantages:
– Historical authenticity for traditional butter varieties
– Natural antimicrobial properties (certain hardwoods)
– Gentle mechanical action on butter granules
Limitations:
– Complex sanitation requirements
– Moisture absorption concerns
– Not suitable for most commercial regulatory environments
– Requires regular conditioning and replacement
Optimal Applications: Heritage brand production, demonstration purposes, specialty traditional products
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
| Region | Primary Standards | Key Material Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| USA | FDA 21 CFR 177, 3-A Sanitary Standards | Food-contact approved, cleanable surfaces |
| EU | EC 1935/2004, EC 2023/2006 | Migration limits, GMP compliance |
| UK | UK Food Contact Materials Regulations | Post-Brexit alignment with EU standards |
Material Selection Comparison Table
| Criteria | Glass | Stainless Steel | Food-Grade Plastic | Wood |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | Low | Excellent | Moderate | Low-Moderate |
| Initial Cost | Low-Moderate | High | Low | Low |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Low | Moderate | High |
| Sanitation Ease | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Regulatory Compliance | Good | Excellent | Good | Limited |
| Scalability | Limited | Excellent | Moderate | Limited |
| Flavor Neutrality | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Variable |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | Excellent | Limited | Poor |
| Service Life | 2-5 years | 15-25 years | 3-7 years | 1-3 years |
| Typical Capacity Range | 1-10L | 50-5000L+ | 1-50L | 1-20L |
Procurement Recommendations
- Volume Assessment: Match material selection to production scale—glass for under 50L/day, stainless steel for commercial volumes
- Total Cost Analysis: Factor maintenance, replacement cycles, and sanitation costs beyond initial purchase price
- Certification Requirements: Verify material certifications align with target market regulations before procurement
- Supplier Verification: Request material certificates, traceability documentation, and compliance statements from vendors
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for butter churner
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Butter Churners
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols behind butter churners is essential for B2B buyers evaluating potential suppliers. This section provides a comprehensive overview of production methodologies and quality standards that distinguish premium butter churning equipment.
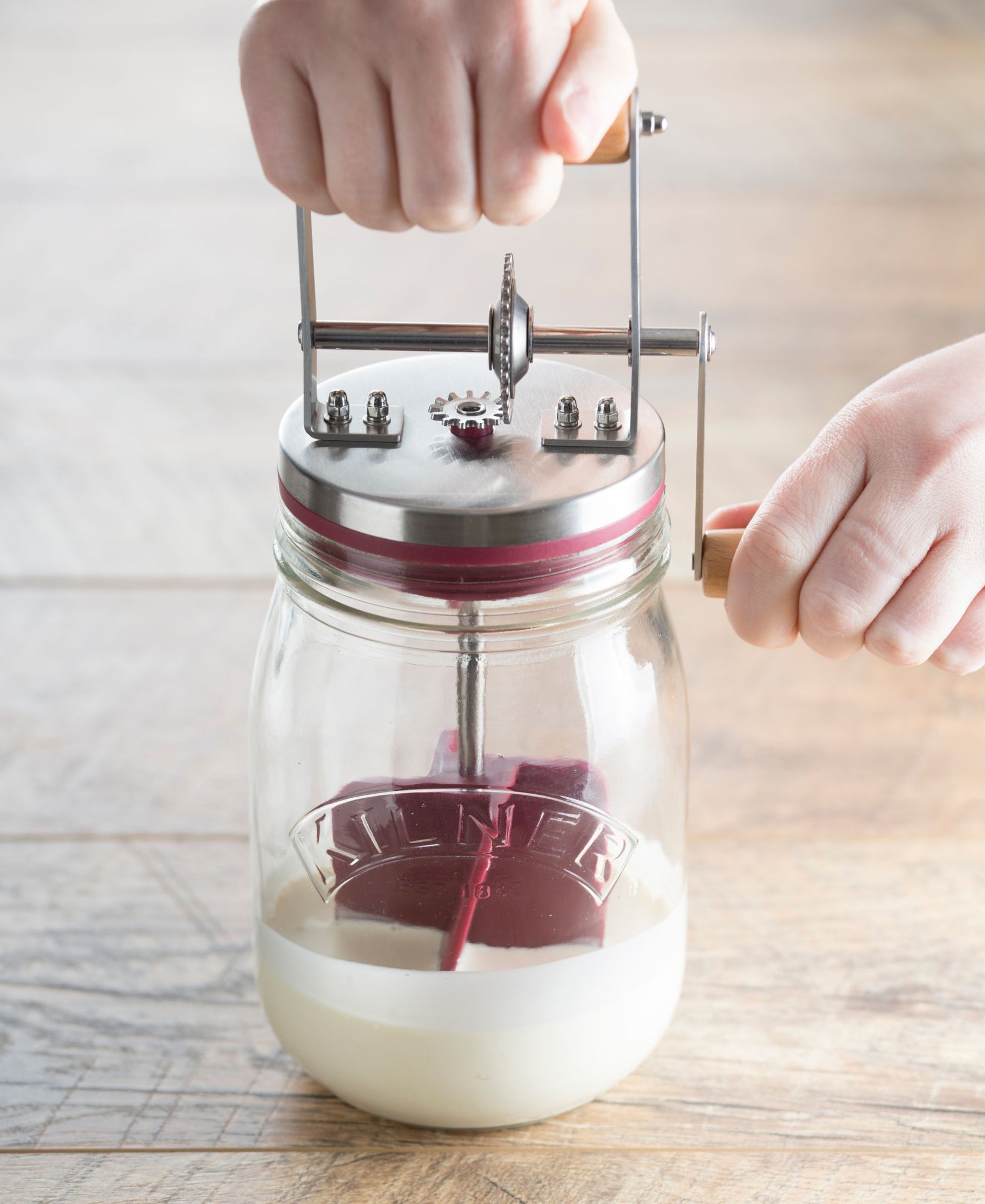

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Process Overview
Butter churner production follows a systematic workflow that varies based on material composition—glass, stainless steel, or food-grade plastics. Below is the standard manufacturing sequence:
1. Preparation Phase
| Process Step | Glass Churners | Stainless Steel Churners | Plastic Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Borosilicate or soda-lime glass | 304/316 food-grade stainless steel | FDA-approved polymers |
| Material Inspection | Optical clarity testing, chemical composition verification | Mill certifications, alloy composition analysis | Resin purity testing, melt flow index verification |
| Pre-processing | Glass batch mixing, cullet preparation | Sheet/tube cutting, degreasing | Pellet drying, colorant blending |
2. Forming Operations
Glass Components:
– Molten glass forming via press-and-blow or blow-and-blow methods
– Annealing at controlled temperatures (typically 500-550°C) to relieve internal stress
– Precision grinding of sealing surfaces
Metal Components:
– Deep drawing or hydroforming for vessel bodies
– CNC machining for paddle assemblies and mechanical components
– Welding (TIG/MIG) for structural joints with full penetration requirements
Plastic Components:
– Injection molding for handles, lids, and gear housings
– Tolerance control within ±0.1mm for critical mating surfaces

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Assembly Sequence
- Sub-assembly preparation – Paddle mechanisms, gear systems, sealing gaskets
- Primary assembly – Vessel integration with mechanical churning systems
- Seal installation – Food-grade silicone or EPDM gaskets
- Hardware attachment – Handles, clamps, adjustment mechanisms
- Functional testing – Rotation smoothness, seal integrity, torque verification
Quality Control Checkpoints
| Stage | Inspection Type | Key Parameters | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incoming Materials | Destructive/Non-destructive | Chemical composition, dimensional accuracy | Per material specification sheets |
| In-Process | Visual + Dimensional | Surface defects, critical dimensions | Zero defects on food-contact surfaces |
| Post-Assembly | Functional | Seal integrity, mechanism operation | 100% pass rate on leak testing |
| Final Inspection | Comprehensive | Cosmetic, functional, packaging | AQL 1.0 for critical defects |
Quality Standards and Certifications
Reputable butter churner manufacturers maintain compliance with the following standards:
Food Safety Standards:
– FDA 21 CFR – Compliance for food-contact materials (USA)
– EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 – Materials in contact with food (Europe)
– LFGB – German food safety certification
Quality Management Systems:
– ISO 9001:2015 – Quality management system certification
– ISO 22000 – Food safety management (for manufacturers serving food processing facilities)
Material-Specific Standards:
– NSF/ANSI 51 – Food equipment materials
– EN 10088 – Stainless steel specifications (Europe)
– ASTM E438 – Glass composition standards

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Supplier Evaluation Criteria
When assessing butter churner manufacturers, B2B buyers should verify:
- Documentation: Material traceability records, test certificates, calibration records
- Facility audits: Clean manufacturing environments, segregated food-grade production areas
- Testing capabilities: In-house laboratory for material verification and functional testing
- Corrective action systems: Documented CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) procedures
Key Takeaways for Procurement
- Request ISO 9001 certificates and food-contact material compliance documentation
- Verify welding certifications for stainless steel products (AWS D18.1 for hygienic applications)
- Confirm batch traceability systems are in place
- Evaluate supplier’s defect rate history and warranty claim data
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘butter churner’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Butter Churners
Pre-Sourcing Assessment
1. Define Your Requirements
– [ ] Determine volume needs (small-batch artisan vs. commercial production)
– [ ] Specify capacity requirements (e.g., 34 fl oz for small-scale; 5-50+ gallons for commercial)
– [ ] Identify material preferences (glass, stainless steel, food-grade plastic)
– [ ] Establish budget parameters per unit and total order value
– [ ] Define lead time requirements
2. Identify Target Markets
– [ ] Confirm end-user profile (restaurants, artisan producers, retail resale, educational)
– [ ] Verify compliance requirements for USA/EU markets
– [ ] Determine packaging and labeling needs
Supplier Identification
| Source Type | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Direct manufacturers | Bulk orders, custom specs | Minimum order quantities (MOQs), longer lead times |
| Wholesale distributors | Mid-volume, faster delivery | Higher unit cost, established logistics |
| Trade platforms (Alibaba, ThomasNet) | Price comparison, variety | Verify supplier credentials |
| Specialty kitchenware suppliers | Premium/branded products | Kilner, Lehman’s, European brands |
3. Supplier Vetting Checklist
– [ ] Request product samples
– [ ] Verify business licenses and certifications
– [ ] Check FDA/EU food-contact compliance documentation
– [ ] Review supplier ratings and trade references
– [ ] Confirm return/warranty policies (note: retail example shows extended return windows)
Negotiation & Order Placement
4. Commercial Terms
– [ ] Negotiate unit pricing based on volume tiers
– [ ] Confirm shipping terms (FOB, CIF, DDP)
– [ ] Establish payment terms (Net 30, LC, escrow for new suppliers)
– [ ] Document quality specifications in purchase agreement
– [ ] Set inspection protocols for incoming goods
5. Logistics Planning
– [ ] Calculate landed costs (product + shipping + duties + handling)
– [ ] Arrange freight forwarding if importing
– [ ] Schedule delivery windows aligned with inventory needs
Post-Order Quality Assurance
- [ ] Inspect samples against agreed specifications
- [ ] Document any defects with photos and formal reports
- [ ] Maintain supplier performance records for future orders
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for butter churner Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Butter Churner Sourcing
Understanding the full cost structure of butter churner procurement enables B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions and negotiate effectively with suppliers. This analysis breaks down pricing components and identifies strategic opportunities for cost optimization.
Market Price Benchmarks
| Product Category | Unit Price Range (USD) | Typical MOQ | Target Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Glass Churns (Consumer-Grade) | $35–$50 | 12–50 units | Retail/Specialty Stores |
| Manual Paddle Churns (Traditional) | $45–$120 | 10–25 units | Artisan/Farm Operations |
| Small Electric Churns | $80–$200 | 5–20 units | Small-Scale Production |
| Commercial Electric Churns | $500–$3,000 | 1–5 units | Dairy Processors |
| Industrial Continuous Churns | $15,000–$100,000+ | 1 unit | Large-Scale Manufacturing |
Reference: Consumer-grade glass churns retail at approximately $42.95–$49.95 per unit (Kilner 34 fl oz capacity), indicating wholesale costs of $25–$35 for similar specifications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cost Component Breakdown
Materials (40–55% of Total Cost)
| Material | Cost Impact | Quality Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Borosilicate Glass | High | Durability, thermal resistance |
| Stainless Steel Components | Medium-High | Food-grade 304/316 certification |
| Food-Grade Plastics (PP/HDPE) | Low-Medium | BPA-free compliance |
| Wooden Elements | Variable | Hardwood vs. composite |
| Silicone Seals/Gaskets | Low | FDA/EU food contact compliance |
Key Cost Drivers:
– Glass thickness and quality grade
– Metal alloy specifications
– Certification requirements (FDA, EU 1935/2004)
– Surface finishing and coating treatments
Labor (15–25% of Total Cost)
| Manufacturing Region | Labor Cost Index | Lead Time Impact |
|---|---|---|
| China | Low ($2–$5/unit) | 30–60 days |
| Eastern Europe | Medium ($8–$15/unit) | 14–30 days |
| Western Europe | High ($20–$40/unit) | 7–21 days |
| USA (Domestic) | Highest ($25–$50/unit) | 5–14 days |
Labor Cost Variables:
– Assembly complexity (manual vs. automated)
– Quality control inspection requirements
– Custom finishing or branding work
– Packaging and kitting services
Logistics (10–20% of Total Cost)
| Shipping Method | Cost per Unit (Asia to USA/EU) | Transit Time |
|---|---|---|
| Sea Freight (FCL) | $1.50–$4.00 | 25–40 days |
| Sea Freight (LCL) | $3.00–$8.00 | 30–50 days |
| Air Freight | $8.00–$25.00 | 5–10 days |
| Express Courier | $15.00–$40.00 | 3–7 days |
Additional Logistics Costs:
– Import duties: 0–6.5% (USA), 0–4.7% (EU) for kitchenware
– Customs brokerage: $150–$500 per shipment
– Warehousing: $0.50–$2.00/unit/month
– Insurance: 0.3–0.5% of cargo value
Overhead and Hidden Costs (10–15% of Total Cost)
- Tooling/Mold Fees: $2,000–$15,000 (amortized over production runs)
- Sample Development: $100–$500 per iteration
- Certification Testing: $500–$3,000 (FDA, CE, food contact)
- Quality Audits: $300–$1,500 per factory visit
- Currency Hedging: 1–3% for international transactions
- Payment Processing: 2–4% for LC/escrow services
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Model
| Cost Category | % of TCO | Optimization Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Product Cost | 55–65% | High |
| Shipping & Logistics | 15–20% | Medium |
| Duties & Taxes | 5–10% | Low-Medium |
| Quality & Compliance | 5–8% | Medium |
| Administrative/Overhead | 5–10% | Medium |
Strategic Cost Reduction Tips
Volume Optimization
- Consolidate Orders: Combine SKUs to reach FCL (Full Container Load) thresholds—typically 2,000–5,000 units for manual churns
- Annual Contracts: Negotiate 8–15% discounts with committed volume agreements
- Group Purchasing: Join buying cooperatives for shared container shipments
Supplier Negotiation Tactics
- Request Tiered Pricing: Secure pricing breaks at 500, 1,000, and 2,500+ unit levels
- Negotiate Payment Terms: Net-60 or 70/30 split reduces working capital requirements
- Bundle Tooling Costs: Amortize mold fees across multi-year agreements
- Benchmark Aggressively: Use multiple supplier quotes to drive competitive pricing
Logistics Efficiency
- FOB vs. DDP: FOB terms typically save 5–10% on smaller shipments
- Consolidation Hubs: Use freight forwarder consolidation in origin countries
- Off-Peak Shipping: Schedule shipments during January–March for lower freight rates
- Nearshoring: Consider Eastern European suppliers for EU markets to reduce transit costs and duties
Specification Optimization
- Value Engineering: Review specifications for over-engineered components
- Standardization: Use common components across product lines
- Packaging Reduction: Minimize packaging dimensions to improve container utilization
- Material Substitution: Evaluate equivalent food-grade materials at lower cost points
Compliance Cost Management
- Pre-Certified Suppliers: Source from factories with existing FDA/EU certifications
- Test Report Sharing: Request existing compliance documentation before commissioning new tests
- Regional Compliance Partners: Use local testing labs in manufacturing regions for 30–50% savings
Price Negotiation Framework
| Order Volume | Expected Discount | Negotiation Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| 100–499 units | 5–10% off list | Payment terms, repeat business |
| 500–999 units | 10–15% off list | Exclusivity, marketing support |
| 1,000–2,499 units | 15–22% off list | Long-term contracts, co-branding |
| 2,500+ units | 20–30% off list | Joint product development, preferred terms |
Regional Sourcing Cost Comparison
| Factor | China | India | Poland | USA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Manufacturing Cost | Lowest | Low | Medium | Highest |
| Quality Consistency | Variable | Variable | High | Highest |
| Lead Time to USA | 45–60 days | 50–70 days | 25–35 days | 7–14 days |
| Lead Time to EU | 35–50 days | 40–55 days | 5–14 days | 25–35 days |
| Minimum Viable Order | 500+ units | 300+ units | 100+ units | 50+ units |
| Communication Ease | Moderate | Moderate | High | Highest |
Recommended Cost Management Actions
- Conduct TCO Analysis: Calculate all-in costs before comparing supplier quotes
- Establish Supplier Scorecards: Weight pricing against quality, reliability, and service
- Build Safety Stock Strategically: Balance inventory carrying costs against stockout risks
- Review Annually: Renegotiate contracts based on volume performance and market conditions
- Diversify Supplier Base: Maintain 2–3 qualified suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and supply continuity
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing butter churner With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Butter Churners With Other Solutions
When evaluating butter production methods for your operation, understanding the trade-offs between different solutions is critical for making informed procurement decisions. Below, we compare traditional manual butter churners with two primary alternatives.
Comparison Matrix
| Factor | Manual Butter Churner (e.g., Kilner Glass Churn) | Electric Stand Mixer with Paddle Attachment | Commercial Continuous Butter Maker |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $40–$100 | $300–$600 | $15,000–$100,000+ |
| Production Capacity | 0.5–1 lb per batch | 1–2 lbs per batch | 200–2,000+ lbs/hour |
| Production Time | 10–20 minutes | 8–15 minutes | Continuous |
| Labor Requirements | High (manual operation) | Low (automated mixing) | Low (automated process) |
| Maintenance | Minimal; hand-wash components | Moderate; motor servicing required | High; specialized technicians needed |
| Scalability | Not scalable | Limited scalability | Highly scalable |
| Consistency | Variable (operator-dependent) | Moderate consistency | High consistency |
| Best Application | Artisan producers, demonstrations, small-batch specialty | Small-to-medium food service, test kitchens | Industrial dairy operations |
Analysis
Manual Butter Churners
Manual churners like the Kilner 34-fluid ounce glass model serve a specific niche: artisan producers prioritizing authenticity, craft demonstrations, or ultra-small-batch production. The low entry cost (~$43–$50) makes them accessible for market testing or specialty product lines. However, labor intensity and batch limitations render them impractical for volume production.
Electric Stand Mixers
For operations producing 5–20 lbs daily, repurposing commercial stand mixers offers a middle-ground solution. The investment leverages multi-use equipment already present in many kitchens, reducing dedicated capital expenditure. Trade-offs include inconsistent texture control and potential equipment wear from non-primary use.
Commercial Continuous Butter Makers
Operations requiring consistent, high-volume output should evaluate continuous butter-making systems. While capital requirements are substantial, the per-unit production cost decreases significantly at scale, and product uniformity meets industrial quality standards.
Recommendation Framework
- <50 lbs/week: Manual churner or stand mixer
- 50–500 lbs/week: Dedicated batch churning equipment
- >500 lbs/week: Continuous commercial systems
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for butter churner
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Butter Churners
Key Technical Specifications
When sourcing butter churners for B2B applications, evaluate these critical parameters:
| Property | Description | Typical Range/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Volume of cream the unit can process per batch | 1-100+ liters (commercial); 0.5-2 liters (artisanal) |
| Material Construction | Body and component materials | Food-grade stainless steel (304/316), borosilicate glass, HDPE plastic |
| RPM Range | Rotational speed of churning mechanism | 20-60 RPM (traditional); 1,000-3,000 RPM (continuous) |
| Power Rating | Motor capacity for electric models | 0.5-15 kW depending on throughput |
| Throughput/Yield | Processing capacity per hour | Measured in kg/hour or liters/hour |
| Fat Recovery Rate | Percentage of butterfat extracted from cream | 98-99.5% (industry standard) |
| Operating Temperature | Optimal cream temperature for churning | 10-15°C (50-59°F) |
Trade Terminology
Procurement Terms:
– MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Lowest unit count per order; typically 1-5 units for commercial equipment, 50-500 for retail/artisanal products
– OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Custom branding/manufacturing under buyer’s label
– ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): Supplier-designed products customizable to specifications
– FOB (Free on Board): Pricing excludes shipping; risk transfers at port of origin
– CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight): Pricing includes delivery to destination port
Product Classification:
– Batch Churners: Process fixed volumes per cycle
– Continuous Churners: Uninterrupted production flow for high-volume operations
– Manual/Hand-Crank: Non-electric, artisanal applications
– Paddle vs. Barrel Design: Internal mechanism configuration
Compliance & Certification:
– FDA 21 CFR (USA)
– EC 1935/2004 (Europe)
– NSF/ANSI certification
– CE marking (European market)
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the butter churner Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Butter Churner Sector
Market Overview and Current Dynamics
The butter churner market has experienced a notable resurgence, driven by intersecting trends in artisanal food production, small-batch manufacturing, and consumer demand for transparency in dairy processing. B2B buyers across the USA and Europe are navigating a market that spans traditional manual churners to industrial-scale continuous butter-making systems.
Key Market Segments:
| Segment | Primary Buyers | Volume Range | Price Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artisanal/Manual | Specialty retailers, farm shops, hospitality | 1-50L capacity | $40-$500 |
| Small Commercial | Craft dairies, restaurants, food service | 50-500L capacity | $2,000-$25,000 |
| Industrial | Large-scale dairy processors | 500L+ continuous | $50,000-$500,000+ |
Historical Context Informing Current Sourcing
The butter churner traces its commercial origins to 19th-century mechanization of dairy production. Today’s market reflects this heritage through two distinct channels:
- Heritage-style products (e.g., Kilner glass churners at ~$43-$50 retail) serve specialty food retailers and hospitality operations seeking authentic presentation
- Modern continuous churners dominate industrial procurement, with European manufacturers (particularly from Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands) leading technological advancement
Sustainability Considerations for B2B Procurement
European and North American buyers increasingly prioritize:
- Material sourcing: Glass and stainless steel over plastic components
- Energy efficiency: Variable-speed motors and heat recovery systems in commercial units
- Longevity: Repairable designs with available replacement parts
- Local manufacturing: Reduced carbon footprint through regional sourcing
Sourcing Recommendations
| Priority | Action |
|---|---|
| Quality assurance | Verify food-grade certifications (FDA, EU 1935/2004) |
| Supply chain resilience | Establish relationships with 2-3 qualified suppliers |
| Total cost analysis | Factor maintenance, energy consumption, and lifespan into procurement decisions |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of butter churner
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Butter Churners
1. What production capacity should I consider when purchasing butter churners for commercial use?
Production capacity depends on your operational scale and throughput requirements. Key considerations include:
| Business Type | Recommended Capacity | Typical Output |
|---|---|---|
| Artisan/Small Batch | 1-5 liters | 10-50 lbs/day |
| Mid-Scale Production | 5-50 liters | 50-200 lbs/day |
| Industrial Operations | 50+ liters | 200+ lbs/day |
Evaluate your daily production targets, peak demand periods, and growth projections before selecting capacity.
2. What are the key differences between manual and electric butter churners for B2B applications?
Manual Churners:
– Lower upfront cost ($40-$500)
– Suitable for artisan/demonstration purposes
– No power requirements
– Higher labor costs per unit produced
Electric/Industrial Churners:
– Higher initial investment ($1,000-$50,000+)
– Consistent output quality
– Reduced labor requirements
– Scalable for volume production
– Requires maintenance contracts
3. What certifications and compliance standards should B2B butter churners meet?
Essential certifications for USA and European markets include:
- FDA compliance (USA food contact materials)
- NSF International certification (commercial food equipment)
- CE marking (European conformity)
- EHEDG certification (European hygienic engineering)
- Food-grade stainless steel (typically 304 or 316 grade)
Request documentation from suppliers verifying compliance with local food safety regulations.
4. What is the typical lead time and MOQ for bulk butter churner orders?
| Order Type | Typical MOQ | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|
| Stock Items | 10-25 units | 1-2 weeks |
| Custom Orders | 50-100 units | 4-8 weeks |
| OEM/Private Label | 100-500 units | 8-16 weeks |
Lead times vary significantly based on manufacturer location, customization requirements, and current supply chain conditions. Request confirmed timelines in writing.
5. What warranty and after-sales support should I expect from suppliers?
Standard B2B warranty provisions include:
- Warranty period: 1-3 years on manufacturing defects
- Parts availability: Minimum 7-10 years post-purchase
- Service response time: 24-72 hours for commercial accounts
- Training: Installation and operator training included
- Spare parts inventory: Confirm supplier maintains adequate stock
Negotiate extended warranty options and service level agreements (SLAs) for high-volume purchases.
6. What materials are preferred for commercial butter churner construction?
Recommended Materials:
– Contact surfaces: Food-grade stainless steel (304/316), borosilicate glass
– Seals/gaskets: FDA-approved silicone or EPDM rubber
– Frames: Powder-coated steel or stainless steel
Avoid:
– Aluminum (reactive with dairy)
– Non-food-grade plastics
– Components containing BPA
Material selection impacts durability, cleaning efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
7. What are the total cost of ownership considerations beyond purchase price?
Calculate TCO including:
- Energy consumption (kWh per production cycle)
- Maintenance costs (annual service, replacement parts)
- Labor requirements (operator hours per batch)
- Cleaning supplies (CIP systems vs. manual cleaning)
- Downtime costs (reliability metrics, MTBF)
- Training expenses (initial and ongoing)
Request operational cost data from suppliers and existing customers during evaluation.
8. Can butter churners be customized for private label or specific production requirements?
Most commercial suppliers offer customization options:
- Branding: Logo placement, custom colors
- Capacity modifications: Adjusted bowl sizes
- Control systems: Programmable settings, IoT integration
- Material upgrades: Enhanced corrosion resistance
- Accessories: Custom attachments, packaging integration
Customization typically requires higher MOQs (100+ units) and extended lead times. Request detailed specifications and prototyping options before committing to large orders.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for butter churner
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion: Butter Churner Procurement
Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers
The butter churner market presents viable sourcing opportunities for foodservice distributors, artisanal producers, and specialty retailers targeting the growing demand for handcrafted dairy products.
Critical Procurement Considerations:
| Factor | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Unit Economics | Entry-level glass churners ($40-50 range) offer accessible inventory positioning |
| Lead Times | Stock availability from established suppliers remains stable |
| Market Demand | Consistent consumer interest (1K+ monthly units on leading platforms) |
| Product Lifecycle | Durable goods with low return rates when properly merchandised |
Forward Outlook
- Growth Drivers: Farm-to-table movement, homesteading trends, and culinary education segments continue expanding
- Margin Opportunity: Premium positioning supports healthy markup potential for specialty kitchen distributors
- Risk Factors: Limited differentiation among suppliers; prioritize vendors with reliable fulfillment and return policies
Recommended Next Steps
- Evaluate supplier terms across multiple distribution channels
- Consider tiered inventory strategy—entry-level glass units alongside commercial-grade options
- Align product offerings with seasonal demand peaks (holiday gifting, spring homesteading)
Strategic sourcing of butter churners represents a low-risk category addition with demonstrated sell-through velocity and alignment with sustainable food production trends.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.