The global electrical connectors market, driven by rising demand in automotive, industrial equipment, and renewable energy sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. Within this expanding landscape, butt splice connectors—critical for reliable wire termination and splicing—have seen increased adoption due to their durability, ease of installation, and performance in high-vibration environments. As infrastructure development and electrification initiatives accelerate worldwide, the demand for high-quality, UL-listed butt connectors has intensified. This growing need has positioned key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and production. Based on market presence, product range, certifications, and customer reviews, we’ve identified the top 9 butt splice connector manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 9 Butt Splice Connectors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Non
Domain Est. 2000
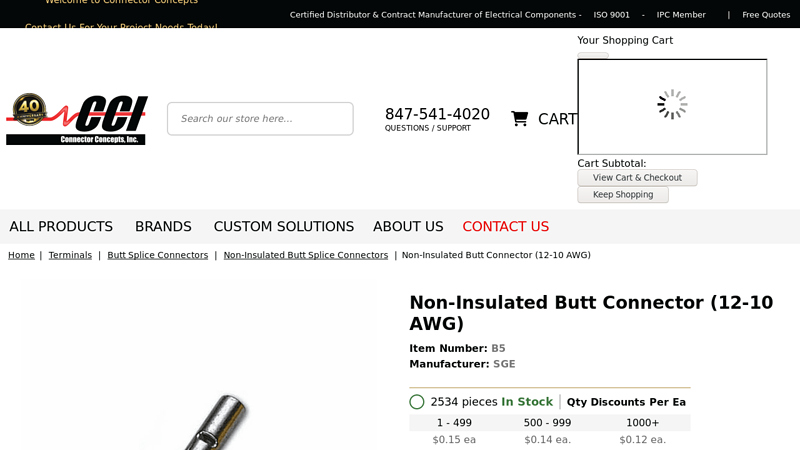
Website: connectorconcepts.com
Key Highlights: Non-Insulated Butt Connector (12-10 AWG). MANUFACTURER: SGE. MANUFACTURER ITEM #:, B5. WIRE RANGE: 12-10 AWG. DIMENSIONS: 3.6 mm Ød, 5.5 mm ØD, 15 mm L. Related ……
#2 Butt Splice Connector
Domain Est. 2014
Website: sgeterminals.com
Key Highlights: Crimp-on connectors are attached by inserting the stripped end of a standard wire into a portion of the connector, which is then mechanically deformed……
#3 PIDG Butt Splices
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsOur pre-insulated diamond grip (PIDG) butt splices are insulated splices with a closed barrel for discrete or regular wire….
#4 Butt Connectors, Crimp Connectors and Splice Connectors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: waytekwire.com
Key Highlights: Butt Splice Connectors and Crimp Connectors offer a simple, effective way of completing a wide range of electrical wiring projects. Shop Waytek today!…
#5 Butt Splice Connectors
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nelcoproducts.com
Key Highlights: Utilizing ultra-efficient chambered barrel ends, these simple-to-use butt splice connectors ensure quick and easy wire insertion in virtually any environment….
#6 Butt Splice Connectors
Domain Est. 2003
Website: catalog.scfastening.com
Key Highlights: Browse Butt Splice Connectors in the SC Fastening Systems catalog including Item #,Price,Item Name,Units Per Package….
#7 Butt Splices Archives
Domain Est. 2004
Website: nsiindustries.com
Key Highlights: All Butt Splices ; Nylon Butt Splice for 12-10 AWG. #B12-N ; 12-10 Nylon Butt Splice-Bulk. #B12-N-BULK ; 12-10 Vinyl Butt Splice, 50 Per Pack. #B12-V ; 12-10 Vinyl ……
#8 Butt Splices
Domain Est. 2008
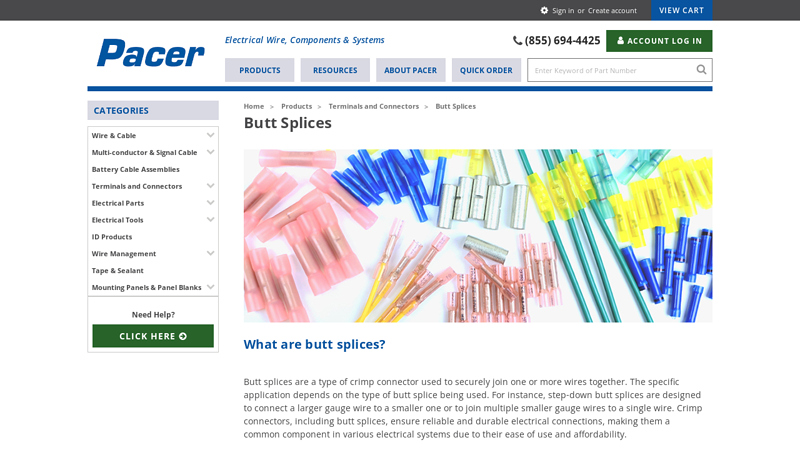
Website: pacergroup.net
Key Highlights: Pacer offers a wide selection of butt splices, including heat shrink, nylon, vinyl, and non-insulated types, each offering unique advantages….
#9 Butt
Domain Est. 2012
Expert Sourcing Insights for Butt Splice Connectors

2026 Market Trends for Butt Splice Connectors
The butt splice connector market is poised for steady growth and technological evolution by 2026, driven by increasing demand across key industries, advancements in materials and design, and a strong focus on efficiency and reliability. Here are the dominant trends shaping the market:
H2: Electrification and Automation Driving Demand
The most significant force propelling the butt splice connector market is the global surge in electrification and automation. The rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) is creating substantial demand for high-reliability, high-current connectors essential for battery packs, power distribution units, and motor systems. Butt splices, particularly insulated and heat-shrink varieties, are critical for secure, durable wire splicing in these high-vibration, high-stress environments. Similarly, industrial automation continues to grow, requiring robust wiring solutions in robotics, control panels, and machinery. Butt splices offer a quick, reliable method for joining control and power wires, supporting the need for efficient installation and maintenance in smart factories. The renewable energy sector, especially solar and wind installations, also relies heavily on butt splices for connecting cables in combiner boxes, inverters, and power transmission, further amplifying market demand.
H2: Shift Towards Higher Performance and Specialized Solutions
As applications become more demanding, the market is shifting from basic, commodity-style butt splices towards higher-performance and specialized products. Key trends include:
- Enhanced Materials: Increased use of tinned copper for superior corrosion resistance, especially in automotive and marine applications. Development of high-temperature rated insulating sleeves (using materials like nylon or advanced polyolefins) to withstand under-hood or industrial environments.
- Improved Design: Focus on designs offering higher pull-out strength, lower insertion force, and better environmental sealing. Heat-shrink butt splices with adhesive lining are gaining significant traction due to their superior moisture, dust, and vibration resistance compared to standard vinyl-insulated versions.
- Specialization: Growth in connectors designed for specific needs, such as ultra-compact sizes for space-constrained electronics, connectors rated for extreme temperatures (e.g., aerospace), or versions optimized for automated crimping processes in high-volume manufacturing.
- Focus on Reliability and Safety: Stringent regulations and the critical nature of electrical connections are pushing demand for connectors meeting higher safety standards (e.g., UL, CSA, TÜV) and offering consistent, verifiable crimp quality.
H2: Efficiency, Automation, and Sustainability Pressures
Manufacturers and end-users are increasingly prioritizing efficiency and sustainability:
- Production Efficiency: Demand is rising for butt splices compatible with automated crimping and wire processing equipment to reduce labor costs and improve consistency in high-volume industries like automotive and appliance manufacturing. Pre-stripped wires with integrated connectors are also gaining interest.
- Sustainability: Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing the market. This includes the development of RoHS-compliant connectors (lead-free solder, halogen-free insulation), recyclable packaging, and a focus on product longevity to reduce waste. The shift towards EVs itself is a major driver of sustainable technology, indirectly boosting the market for the connectors enabling it.
- Supply Chain Optimization: The global nature of manufacturing is leading to a focus on reliable supply chains and cost-effective sourcing, particularly in the competitive Asian markets where much of the production and consumption occurs.
H2: Competitive Landscape and Regional Dynamics
The market remains competitive, with established players (e.g., TE Connectivity, Molex, Amphenol, 3M) competing alongside numerous regional and specialized manufacturers, particularly in Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea). The APAC region is expected to maintain its position as the largest and fastest-growing market, fueled by massive automotive production, industrialization, and infrastructure development. North America and Europe will see steady growth, driven primarily by the EV transition, industrial automation upgrades, and renewable energy investments. Competition will center on innovation in materials, design for automation, cost optimization, and providing comprehensive technical support and quality assurance. Consolidation within the supplier base may occur to achieve economies of scale and broader product portfolios.
In conclusion, the butt splice connector market in 2026 will be characterized by robust growth fueled by electrification, particularly in transportation and energy. Success will depend on offering high-performance, reliable, and increasingly specialized solutions that meet the demands of automation, enhance safety, and align with sustainability goals, all while navigating a competitive and globally distributed landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Butt Splice Connectors (Quality, IP)
Poor Crimp Quality and Inconsistent Dimensions
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing butt splice connectors is inconsistent or substandard crimp quality. Low-cost manufacturers may use inferior dies or poorly maintained machinery, resulting in weak crimps that compromise electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. Inconsistent barrel dimensions can lead to loose wire fits, increasing resistance and the risk of overheating or connection failure.
Use of Substandard Materials
Many low-quality butt splices are made from impure or non-copper conductive tubes (e.g., brass or low-grade copper alloys), which reduce conductivity and increase resistance. Similarly, the heat shrink tubing used may lack proper thickness, UV resistance, or adhesion properties—especially critical in outdoor or harsh environments. This undermines the connector’s durability and environmental protection.
Misleading or Inaccurate IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
A major pitfall is assuming all heat-shrink butt splices offer reliable environmental sealing. Some suppliers falsely claim high IP ratings (e.g., IP67 or IP68) without third-party certification. In reality, poorly designed seals, inadequate adhesive lining, or thin wall tubing can result in moisture ingress, leading to corrosion and electrical failure.
Lack of Compliance and Certification
Sourcing connectors without proper certifications (such as UL, CSA, RoHS, or ISO) poses significant risks, especially in regulated industries. Non-compliant products may not meet safety or performance standards, resulting in liability, warranty issues, or field failures.
Inadequate Temperature and Voltage Ratings
Some generic butt splices are not rated for the full range of operating conditions they may encounter. Using connectors with insufficient temperature ratings (e.g., rated only for 85°C in a 105°C environment) can lead to insulation degradation, shrink-back, or short circuits.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Products
In global supply chains, counterfeit connectors are a growing concern. These may mimic reputable brands but fail under load or environmental stress. Buyers may unknowingly receive products that do not match specifications, leading to systematic reliability issues.
Poor Packaging and Handling
Bulk-packaged or poorly stored connectors can suffer from bent terminals, damaged insulation, or contamination (dust, moisture). This affects ease of use and long-term reliability, especially in automated production environments.
Overlooking Application-Specific Requirements
Not all butt splices are suitable for every application. For example, automotive, marine, or solar installations demand specific performance characteristics. Sourcing generic connectors without considering vibration resistance, salt spray tolerance, or UV stability can result in premature failure.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence—choosing reputable suppliers, verifying certifications, requesting samples for testing, and ensuring specifications match actual application demands.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Butt Splice Connectors
Product Overview
Butt splice connectors are electrical components used to join two wires end-to-end, providing a secure and insulated connection. They are commonly used in automotive, marine, aerospace, and industrial electrical systems. These connectors typically feature a metal barrel crimped to the wire and a heat-shrink or vinyl insulation sleeve for protection.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
Butt splice connectors sold in the European Union and many other global markets must comply with RoHS directives. This restricts the use of hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE). Ensure all connectors are labeled RoHS-compliant and accompanied by a Declaration of Conformity (DoC).
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals)
Manufacturers and importers must verify that chemicals used in the production of butt splice connectors (e.g., in insulation materials or plating) are registered under REACH regulations. Avoid substances of very high concern (SVHCs) listed on the REACH Candidate List.
UL and CSA Certification
For use in North America, butt splice connectors should carry certification marks from recognized bodies such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) or Canadian Standards Association (CSA). These certifications confirm that the product meets safety standards for electrical performance, flammability, and mechanical durability.
CE Marking
Products placed on the European market must bear the CE marking, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. CE marking is mandatory for electrical accessories under the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive where applicable.
Conflict Minerals Compliance (Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502)
If supplying to companies in the United States, ensure your supply chain does not source tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold (3TG minerals) from conflict-affected areas, particularly the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Submit an annual Conflict Minerals Report (CMR) if required.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Product Labeling
Each package of butt splice connectors must include:
– Manufacturer or brand name
– Part number and specifications (e.g., wire gauge range, insulation type)
– Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, UL, CE)
– Date of manufacture and batch/lot number
– Country of origin
Packaging Requirements
Use anti-static and moisture-resistant packaging where applicable, especially for connectors with sensitive plating (e.g., tin or silver). Packaging should protect against crushing and environmental exposure during transit. Bulk packaging must be clearly labeled with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”).
Shipping and Logistics
International Shipping Documentation
Ensure all shipments include:
– Commercial invoice with detailed product description, HTS code (e.g., 8536.90 for electrical connectors), and declared value
– Packing list with item quantities and weights
– Certificate of Origin (required for preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– RoHS/REACH/UL compliance documentation upon request
Hazardous Materials Classification
Butt splice connectors are generally not classified as hazardous materials. However, verify that packaging materials (e.g., adhesives, coatings) do not contain substances regulated under IATA, IMDG, or ADR. Most connectors can be shipped via standard freight (air, sea, or ground) without hazardous goods declarations.
Import/Export Controls
Check destination country regulations. Some countries may require:
– Product certification (e.g., CCC in China, KC in South Korea)
– Pre-shipment inspection
– Electrical safety testing reports
Engage local customs brokers to ensure smooth clearance.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Batch Traceability
Maintain records linking each production batch to raw material sources, manufacturing dates, and test results. This enables effective recalls and compliance audits.
Testing and Inspection
Conduct regular quality checks including:
– Crimp pull strength testing
– Electrical continuity and resistance measurement
– Insulation integrity (dielectric strength test)
– Visual inspection for defects
Provide test reports upon request from distributors or end customers.
Storage and Handling
Storage Conditions
Store butt splice connectors in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (10°C to 30°C) away from direct sunlight and corrosive substances. Avoid prolonged exposure to high humidity, which may degrade insulation materials.
Shelf Life
Most butt splice connectors have a recommended shelf life of 2–5 years. Monitor expiration dates for heat-shrink variants, as adhesive and sleeve materials may degrade over time.
Disposal and Environmental Responsibility
End-of-Life Management
Butt splice connectors are typically recyclable. The metal (usually copper or brass) can be reclaimed, and plastics should be processed according to local e-waste regulations. Encourage customers to dispose of used connectors through certified electronic waste recyclers.
WEEE Compliance (EU)
If selling in the EU, comply with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive by registering with national authorities and providing take-back options for end-of-life products.
Conclusion
Adhering to logistics and compliance standards ensures the safe, legal, and sustainable distribution of butt splice connectors globally. Maintain accurate documentation, partner with certified suppliers, and stay updated on evolving regulations to support market access and customer trust.
Conclusion for Sourcing Butt Splice Connectors:
Sourcing the right butt splice connectors is essential for ensuring reliable, durable, and safe electrical connections in various applications, from automotive and marine to industrial and residential wiring. When selecting butt splice connectors, key factors such as material quality (e.g., copper construction, tin or nylon insulation), proper size and gauge compatibility, ease of installation (crimp vs. solder), and environmental resistance (e.g., waterproof or heat-shrink variants) must be carefully evaluated.
Procuring connectors from reputable suppliers ensures compliance with industry standards (such as UL, RoHS, or ISO), consistent performance, and long-term reliability. Additionally, considering cost-efficiency without compromising quality helps balance budget constraints with operational safety and effectiveness. Bulk purchasing from trusted manufacturers or distributors can also lead to cost savings and supply chain stability.
In summary, a strategic sourcing approach that prioritizes quality, compatibility, and supplier reliability will ensure optimal performance of butt splice connectors, minimizing maintenance issues and enhancing the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.