The global butchery equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising meat consumption, advancements in food safety regulations, and increasing automation in meat processing facilities. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% through 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights expanding demand from both commercial butcheries and retail meat departments, with innovations in hygiene, energy efficiency, and precision cutting technologies accelerating adoption. As the industry evolves, leading manufacturers are positioning themselves through R&D investment, sustainable design, and smart equipment integration. In this competitive landscape, the following ten companies have emerged as key players, setting benchmarks in reliability, innovation, and global reach.
Top 10 Butchery Equipment Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meat & Butchery
Domain Est. 2013
Website: cmpsol.com
Key Highlights: CM Process Solutions is a leading supplier of material handling, industrial washing, sanitizing, and personal hygiene equipment for the meat and butchery ……
#2 Meat Processing Equipment & Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hobartcorp.com
Key Highlights: Elevate your food prep with Hobart meat processing equipment. Explore the lineup of commercial meat grinders, mixer-grinders, saws, accessories and more….
#3 Butcher Boy
Domain Est. 1998
Website: butcherboymachines.com
Key Highlights: EQUIPMENT & SUPPLIES · Meat Band Saws · Meat Grinder · Meat Flaker · Meat Mixer Blender · Meat Mixer Grinder · Material Handling · Butcher Boy Machines Manual ……
#4 Alaska Butcher Supply
Domain Est. 2007
Website: alaskabutcherequip.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsWe have the vacuum packaging supplies for fish and game, as well as processing equipment such as knives and cutlery, tenderizers, stuffers, mixers and more….
#5 Butcher Supply Company
Domain Est. 2009
Website: butchersupplycompany.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsWe’re honored to carry on the legacy that began in ’79, supplying restaurants, processors, hunters & artisans alike with both new & used equipment + retail ……
#6 Weston Brands
Domain Est. 2015
Website: westonbrands.com
Key Highlights: Weston’s thoughtfully designed and easy-to-use meat grinders, slicers, saws, sausage stuffers, jerky tools, and vacuum sealers….
#7 MEAT! Your Maker
Domain Est. 2017
Website: meatyourmaker.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsIndustry leading meat grinders, vacuum sealers, food dehydrators, and more. Yes, we love meat processing equipment so much we named our brand after it….
#8 High
Domain Est. 2019
Website: srbutchersupply.com
Key Highlights: Explore top-tier butcher supplies and professional meat processing equipment at Snake River Butcher Supply. From knives and seasonings to advanced machinery ……
#9 Dave’s Butcher Supply – Meat Supplies
Domain Est. 2020
Website: davesbutchersupply.net
Key Highlights: Here at Dave’s Butcher Supply, we have all the meat supplies you need! From seasonings to casings and more, be sure to contact us today!…
#10 Butcher
Domain Est. 2022
Website: maxwellmeats.com
Key Highlights: Highly knowledgeable of cuts, trims, de-boning, ties, grinds, portion sizing, shrinkage, and curing and smoking of meats processed. Supervises, motivates, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Butchery Equipment

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Butchery Equipment
The global butchery equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving consumer demands, and heightened regulatory and sustainability pressures. Key trends shaping the industry include:
1. Automation and Smart Technology Integration:
By 2026, automation will move from niche adoption to mainstream implementation. Smart equipment embedded with IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and machine learning will enable predictive maintenance, real-time performance monitoring, and optimized cutting precision. Automated portioning systems, robotic deboning arms, and self-cleaning conveyors will reduce labor dependency and increase operational efficiency—critical amid persistent labor shortages in the meat processing sector.
2. Emphasis on Food Safety and Hygiene:
Stringent food safety regulations and consumer awareness will accelerate demand for hygienic design. Equipment featuring seamless stainless steel surfaces, antimicrobial coatings, and CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems will dominate. Traceability-enabled tools that integrate with digital tracking platforms will ensure compliance with HACCP and FSMA standards, minimizing contamination risks and enhancing supply chain transparency.
3. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
Sustainability will be a core purchasing criterion. Manufacturers will prioritize energy-efficient motors, water-saving cleaning systems, and recyclable materials in equipment design. Demand will rise for equipment that reduces waste through precise portion control and yield optimization. Additionally, eco-conscious processors will favor vendors offering lifecycle assessments and take-back programs.
4. Customization and Modular Design:
As butchers and processors cater to diverse meat products—from traditional cuts to plant-based hybrids—flexible, modular equipment will gain traction. Systems allowing quick reconfiguration for different cuts, protein types, or production volumes will be in high demand, enabling small to mid-sized operations to remain competitive and responsive to market shifts.
5. Growth in Emerging Markets and Artisanal Segments:
While mature markets in North America and Europe focus on upgrading to advanced systems, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will see rising demand due to expanding meat consumption and modernization of food retail infrastructure. Simultaneously, artisanal butchers will invest in compact, high-precision tools that support craft butchery while maintaining hygiene and efficiency.
6. Digitalization and Data-Driven Operations:
Cloud-connected equipment will empower operators with real-time data on throughput, equipment health, and yield analytics. Integration with ERP and MES systems will streamline inventory management, production planning, and quality control—turning butchery operations into data-driven enterprises.
In summary, the 2026 butchery equipment market will be defined by intelligent, sustainable, and adaptable solutions that enhance productivity, ensure safety, and support evolving consumer and regulatory landscapes. Companies that innovate at the intersection of technology, hygiene, and sustainability will lead the next phase of industry growth.
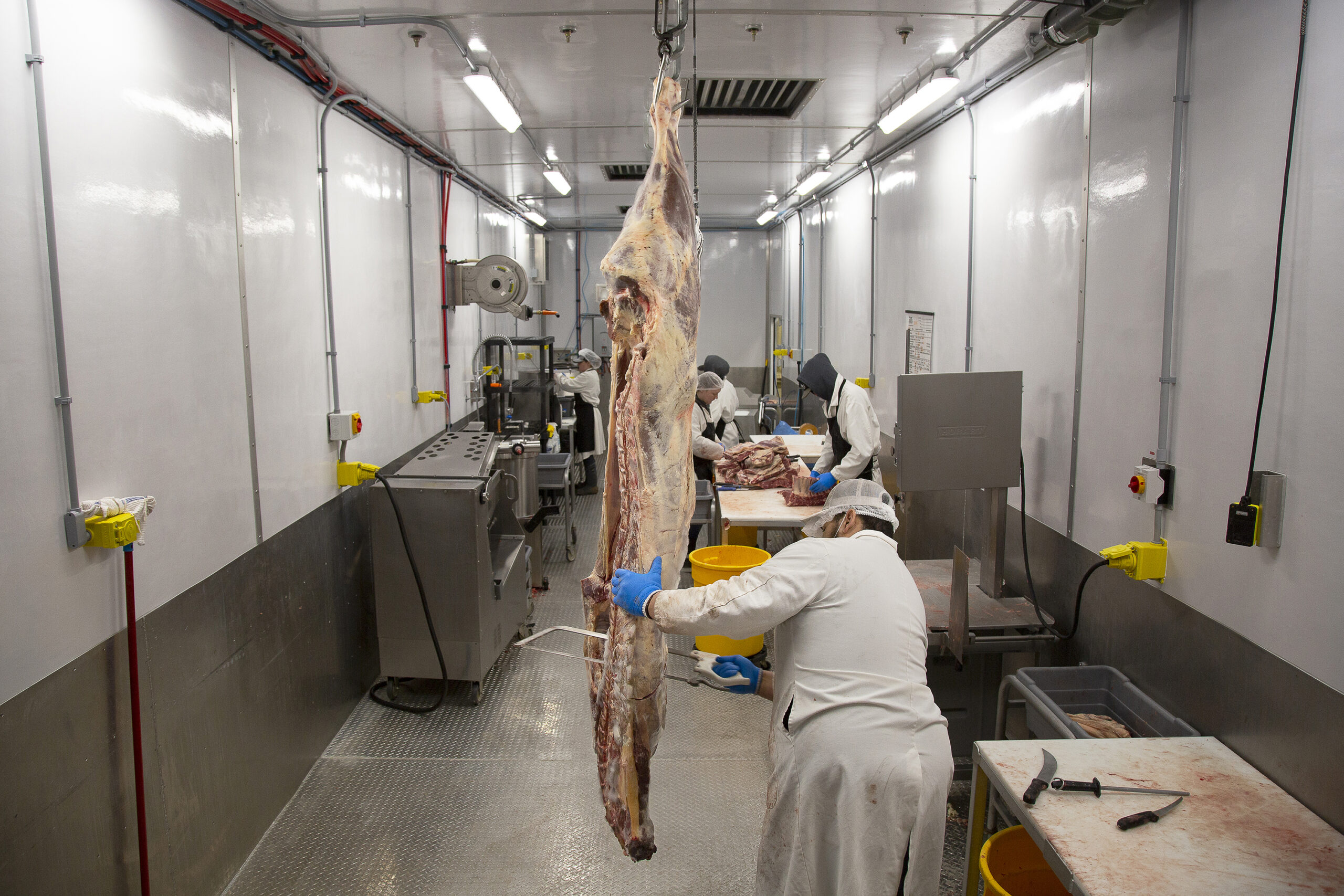

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Butchery Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing butchery equipment involves more than just finding the lowest price. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) issues can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Equipment Quality and Material Standards
Low-cost butchery equipment may use substandard materials such as non-food-grade stainless steel, inferior blades, or weak mechanical components. This compromises food safety, accelerates wear and tear, and increases maintenance costs. Always verify compliance with food safety standards (e.g., NSF, CE, or 3-A Sanitary Standards) and ensure materials are corrosion-resistant and easy to clean.
Lack of Certification and Regulatory Compliance
Equipment lacking proper certifications may not meet regional health and safety regulations. Using uncertified machinery can result in failed inspections, facility shutdowns, or fines. Confirm that suppliers provide documented proof of compliance with local and international standards relevant to food processing environments.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Choosing suppliers with limited technical support or long lead times for spare parts can halt production. Verify the supplier’s service network, warranty terms, and spare parts inventory before purchase. Reliable post-purchase support is critical for minimizing downtime.
Counterfeit or Clone Equipment Infringing IP Rights
Some suppliers offer equipment that replicates patented designs or trademarks without authorization. Purchasing such items exposes buyers to intellectual property infringement claims, even if unintentional. This can result in legal liability, equipment seizure, or forced replacement—costing time and money.
Insufficient Verification of Supplier Authenticity
Working with unauthorized distributors or counterfeit manufacturers increases the risk of receiving knock-off equipment. Conduct due diligence: verify the supplier’s legitimacy, check references, and, if possible, inspect manufacturing facilities. Direct engagement with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) reduces IP and quality risks.
Overlooking Design and Functional Imitations
Even if equipment isn’t a direct copy, subtle design elements (e.g., blade configurations, safety mechanisms, or control systems) may still infringe on existing patents. Request technical documentation and conduct IP screening, especially for custom or high-value machinery.
Failure to Protect Custom or Proprietary Designs
If sourcing custom-designed equipment, ensure contracts include clear IP ownership clauses. Without proper agreements, the supplier may retain rights to the design or reuse it for competitors, undermining your competitive advantage.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, insistence on certifications, and attention to both technical specifications and legal compliance. Investing time upfront ensures safe, reliable, and legally sound butchery operations.
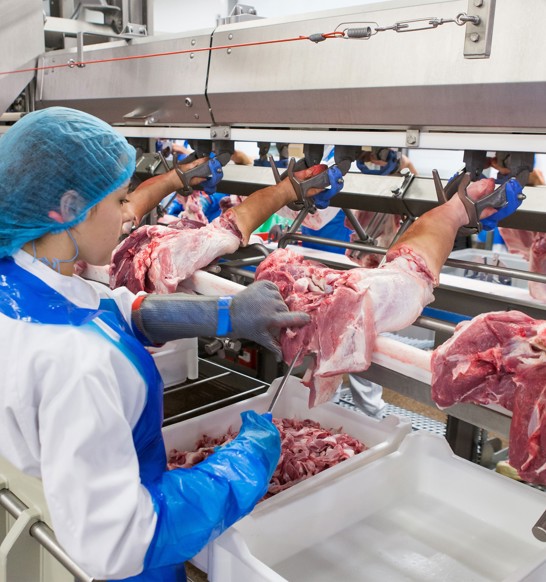

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Butchery Equipment
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations when transporting, installing, and operating butchery equipment. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, food safety, and worker safety across the supply chain—from manufacturer to end-user.
Equipment Classification & Regulatory Framework
Butchery equipment includes saws, grinders, mixers, slicers, vacuum sealers, and refrigeration units. These are subject to multiple regulations based on jurisdiction and application. Key regulatory bodies include:
– FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) – For food contact surfaces and sanitation standards.
– USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) – For meat processing equipment in federally inspected facilities.
– CE Marking (European Union) – Compliance with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Hygiene of Foodstuffs regulations.
– Health Canada & CFIA (Canadian Food Inspection Agency) – For food safety and equipment standards in Canada.
– Local Health & Safety Agencies – Local codes for electrical, plumbing, and workplace safety.
Ensure all equipment meets applicable standards before shipment or installation.
Transportation & Logistics Planning
Proper handling during transit protects both equipment integrity and regulatory compliance.
-
Packaging Requirements
Use protective, moisture-resistant, and tamper-evident packaging. Include desiccants for stainless steel parts to prevent corrosion. Clearly label fragile components and food-contact surfaces. -
Temperature & Environmental Control
Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or contaminants during transit. Refrigerated or climate-controlled transport may be needed for sensitive electronic components. -
Freight Mode Selection
Choose appropriate freight methods (air, sea, or ground) based on equipment size, delivery timelines, and destination. Oversized items (e.g., band saws, processing tables) may require special handling and permits. -
Customs & Import Documentation
Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and equipment conformity declarations (e.g., CE, FDA compliance). Include HS codes specific to meat processing machinery (e.g., 8438.20 for mincing machines).
Installation & Site Compliance
Proper installation ensures equipment performance and adherence to health and safety codes.
-
Facility Readiness
Verify floor load capacity, ventilation, drainage, and utility connections (electrical voltage, water, compressed air). Install slip-resistant flooring and adequate lighting. -
Sanitary Design Principles
Equipment must comply with 3-A Sanitary Standards or EHEDG (European Hygienic Engineering and Design Group) guidelines. Key features include: - Smooth, non-porous surfaces (e.g., #304 or #316 stainless steel)
- No crevices, dead zones, or hard-to-clean joints
- Sloped surfaces for drainage
-
Removable parts for cleaning and inspection
-
Utility Compliance
Confirm electrical systems meet local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S.). Ground all equipment and use GFCI protection where water is present. Plumbing must prevent cross-connection and backflow.
Operational Compliance & Maintenance
Ongoing compliance ensures food safety and extends equipment life.
-
HACCP & Preventive Controls
Integrate equipment cleaning and maintenance into your HACCP plan or FDA’s Preventive Controls for Human Food (PCHF). Identify critical control points (CCPs) such as blade sanitation or temperature monitoring in chillers. -
Cleaning & Sanitation Procedures
Follow manufacturer-recommended cleaning protocols. Use food-grade, non-toxic cleaners. Document cleaning schedules and verification (e.g., ATP swab testing). -
Calibration & Maintenance Logs
Maintain logs for blade sharpness, motor performance, temperature sensors, and pressure systems. Schedule preventive maintenance per OEM guidelines. -
Worker Training & Safety
Train staff on safe operation, lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and PPE requirements. Display safety signage near hazardous equipment.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Retention of accurate records is essential for audits and regulatory inspections.
- Compliance Documentation
Keep on file: - Equipment manuals and schematics
- Certificates of Conformity (CE, NSF, 3-A)
- Sanitation and maintenance logs
- Calibration records
-
Employee training records
-
Traceability
Maintain serial numbers and service history for each piece of equipment to support recalls or incident investigations.
Disposal & End-of-Life Compliance
Retired equipment must be disposed of in accordance with environmental and data security standards.
-
Decontamination
Thoroughly clean and sanitize equipment before decommissioning to prevent cross-contamination. -
Recycling & E-Waste
Recycle metals (especially stainless steel) and dispose of electronic components through certified e-waste handlers. -
Data Protection
For equipment with digital controls or data logging, securely erase any stored operational data.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for butchery equipment reduces risk, ensures food safety, and supports regulatory readiness. By following this guide—from shipping and installation to operation and disposal—businesses can maintain high standards of hygiene, safety, and legal compliance throughout the equipment lifecycle.
In conclusion, sourcing butchery equipment requires careful consideration of quality, functionality, durability, and cost-effectiveness to ensure efficient and safe operations in any meat processing environment. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their reputation, product range, compliance with food safety standards, and after-sales support. Whether sourcing new or refurbished equipment, conducting thorough research and comparing options will help in making informed decisions that align with operational needs and budget constraints. Investing in reliable, well-maintained butchery equipment not only enhances productivity and hygiene but also contributes to long-term sustainability and success in the meat industry.