The global demand for industrial safety solutions has surged in recent years, driven by stricter environmental regulations and increasing emphasis on workplace safety—trends reflected in the steady growth of the burn container market. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global hazardous waste management market, a key driver for burn container adoption, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by rising industrial activity, stringent EPA and OSHA compliance requirements, and the need for controlled waste incineration in sectors ranging from oil and gas to pharmaceuticals. As companies prioritize efficient and compliant waste disposal methods, burn containers have emerged as essential equipment for safe, on-site combustion of oily rags, PPE, and other combustible waste. With North America currently leading in market adoption due to robust regulatory frameworks, manufacturers are innovating to deliver durable, code-compliant solutions. Based on market presence, product quality, and compliance with safety standards, here are the top 9 burn container manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 9 Burn Container Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Air Burners Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: airburners.com
Key Highlights: Our air curtain burners are a cost-efficient, environmentally-friendly solution to eliminate unwanted wood and vegetative waste 40x faster than an open burn….
#2 CPSC Warns Consumers to Immediately Stop Using Fuel Bottles …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cpsc.gov
Key Highlights: CPSC is warning consumers to immediately stop using refillable fuel bottles sold by Shenzhen Pink Vine Technology because they pose a risk of poisoning and ……
#3 Burns & McDonnell
Domain Est. 1995
Website: burnsmcd.com
Key Highlights: We provide engineering, architecture, construction, environmental and consulting solutions. We plan, design, permit, construct and manage facilities….
#4 Ports of Indiana receives U.S. Customs approval to establish first …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: portsofindiana.com
Key Highlights: US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) has approved a proposal from Ports of Indiana-Burns Harbor to establish the first international sea cargo container ……
#5 Richard S. Burns & Company
Domain Est. 2000
Website: burnscompany.net
Key Highlights: The Richard S. Burns Company is Philadelphia’s only fully permitted and LEED staffed materials and waste recycling facility….
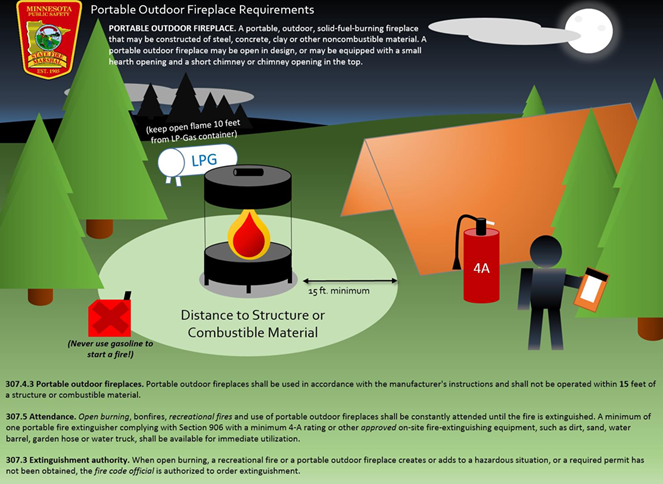
#6 Outdoor burning
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cdphe.colorado.gov
Key Highlights: There are three types of outdoor burning that may require a smoke permit: Open burns are small burns typical for wood piles, vegetation, and yard waste….
#7 Sec. 88.171 MN Statutes
Domain Est. 2005
Website: revisor.mn.gov
Key Highlights: No person shall conduct, cause, or permit open burning of rubber, plastics, chemically treated materials, or other materials which produce excessive or noxious ……
#8 Outdoor Burning Regulations
Domain Est. 2022
Website: rdmfire.org
Key Highlights: Burning is allowed beginning at 8 AM daily. Campfires, warming fires, and cooking fires, in approved fire rings or appliances, are allowed year-round….
#9 Open Burn
Domain Est. 2023
Website: boxeldercountyut.gov
Key Highlights: Every year there are two open burning windows for residents to burn yard debris ie: leaves, branches weeds, and such, this does not include garbage, tires, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Burn Container

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Burn Containers
As we approach 2026, the market for burn containers—specialized systems used for the safe and controlled incineration of waste, biohazardous materials, or industrial byproducts—is expected to undergo significant transformation driven by regulatory, environmental, and technological factors. Below is an analysis of key trends shaping the burn container market in 2026.
1. Stricter Environmental Regulations Driving Innovation
By 2026, global emissions standards are expected to become more stringent, particularly in North America and the European Union. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Environment Agency (EEA) are anticipated to enforce tighter controls on particulate matter, dioxins, and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions from combustion processes. This will push manufacturers to develop next-generation burn containers equipped with advanced emission control systems, including catalytic converters, secondary combustion chambers, and real-time emissions monitoring.
2. Growth in Healthcare and Biohazard Waste Management
The healthcare sector’s continued expansion, especially post-pandemic, will increase the volume of biohazardous waste requiring safe disposal. Burn containers designed for medical waste incineration are expected to see higher demand in hospitals, research labs, and remote clinics. In 2026, modular and mobile burn units could become increasingly popular, providing scalable and compliant solutions for decentralized waste management.
3. Adoption of Smart and IoT-Enabled Burn Containers
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into burn container systems is expected to gain momentum by 2026. Smart burn containers with remote monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, and automated combustion optimization will improve operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. These systems will allow facility managers to track burn cycles, fuel consumption, and emissions data in real time, supporting sustainability reporting and audit readiness.
4. Shift Toward Sustainable and Alternative Fuels
Environmental concerns and rising fossil fuel costs will drive innovation in fuel sources for burn containers. By 2026, we anticipate increased adoption of burn containers designed to run on biofuels, waste-derived syngas, or hybrid systems that reduce reliance on diesel or propane. This transition aligns with broader corporate sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
5. Expansion in Developing Markets
Emerging economies in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America will see growing investments in waste management infrastructure. As urbanization and industrial activity increase, governments and private entities will deploy burn containers to manage municipal, agricultural, and industrial waste in areas lacking access to centralized incineration facilities. This presents a significant growth opportunity for manufacturers offering cost-effective, durable, and low-maintenance units.
6. Emphasis on Portability and Rapid Deployment
In response to disaster relief and military logistics needs, the demand for portable and rapidly deployable burn containers is expected to rise. By 2026, lightweight, trailer-mounted, or containerized incineration units will be increasingly used in emergency response scenarios, remote mining operations, and humanitarian missions.
7. Increased Focus on Carbon Footprint Reduction
With global net-zero targets influencing procurement decisions, burn container manufacturers will prioritize carbon footprint reduction in design and operation. This includes improved thermal efficiency, heat recovery systems, and integration with carbon offset programs. Third-party certifications such as ISO 14001 and carbon-neutral designations will become key differentiators in the market.
Conclusion
The burn container market in 2026 will be shaped by the convergence of environmental regulation, technological innovation, and expanding global waste management needs. Companies that invest in cleaner, smarter, and more adaptable incineration solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities across healthcare, industrial, and municipal sectors. Strategic partnerships with waste management firms, government agencies, and environmental consultants will be critical for market leadership in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Burn Container (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a burn container—typically used for controlled disposal of sensitive materials, especially in defense, aerospace, or data security sectors—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these aspects can lead to safety risks, legal liabilities, and compromised operations.
Poor Material and Construction Quality
One of the most frequent issues is selecting a burn container made from substandard materials or with inadequate fabrication. Low-quality steel may warp or fail under high temperatures, posing serious safety hazards. Containers lacking proper welding, corrosion resistance, or heat dispersion design can result in structural failure, emissions leaks, or incomplete combustion.
Key risks:
– Use of thin-gauge or non-compliant steel
– Inadequate insulation or heat shielding
– Poor weld integrity leading to cracks or leaks
– Non-compliance with environmental or safety standards (e.g., EPA, OSHA)
Best practice: Require certified material test reports (MTRs), third-party inspections, and adherence to recognized standards (e.g., ASME, ASTM).
Lack of Design Verification and Testing
Many suppliers offer burn containers based on generic designs without validating performance under real-world conditions. Without proper testing for thermal stress, combustion efficiency, and emissions control, the container may not perform as expected, especially when processing classified or hazardous materials.
Key risks:
– Unverified burn efficiency leading to incomplete destruction
– Excessive smoke or toxic byproducts
– Overheating damaging surrounding infrastructure
Best practice: Demand performance data, burn test results, and validation under load conditions similar to your operational needs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Burn container designs—especially those used in government or defense applications—may be protected by patents, technical data rights, or export controls. Sourcing from vendors who replicate proprietary designs without authorization exposes your organization to IP litigation and compliance violations.
Key risks:
– Procuring containers that infringe on patented designs or technical drawings
– Receiving counterfeit or reverse-engineered equipment
– Violating ITAR or EAR regulations when handling sensitive tech
Best practice: Vet suppliers for IP compliance, request design ownership documentation, and ensure contracts include IP indemnification clauses.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Missing or falsified documentation undermines quality assurance and IP integrity. Without traceable records—such as manufacturing logs, material certifications, or design approvals—it becomes difficult to verify compliance or defend against liability in case of failure.
Key risks:
– Inability to prove regulatory compliance
– Challenges in maintenance, repair, or replacement
– Exposure during audits or legal inquiries
Best practice: Require full documentation packages, including as-built drawings, compliance certificates, and chain-of-custody records for materials and design.
Choosing Vendors Without Domain Expertise
General industrial fabricators may lack the specialized knowledge required for secure, high-temperature burn applications. This can result in design flaws, improper safety features, or failure to meet mission-critical requirements.
Key risks:
– Misunderstanding operational environment (e.g., field deployment vs. fixed site)
– Overlooking security features (e.g., tamper-proof access, surveillance integration)
– Poor integration with existing disposal protocols
Best practice: Source from vendors with proven experience in defense, classified material destruction, or certified waste incineration systems.
By addressing these common pitfalls—prioritizing quality construction, verifying design integrity, protecting intellectual property, ensuring documentation, and selecting specialized vendors—organizations can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, compliant operation of burn containers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Burn Container
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations when using a burn container for waste disposal. Proper handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence are critical to ensure safety, environmental protection, and legal compliance.
Purpose of a Burn Container
A burn container is a secure, enclosed metal unit designed for the controlled combustion of waste materials, typically used in remote locations, industrial sites, or emergency response scenarios. It helps minimize open burning risks and contains ash and emissions.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local, state, federal, and environmental regulations is mandatory when operating a burn container.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Regulations: Open burning and incineration may be restricted under the Clean Air Act. Check EPA guidelines on acceptable burn materials and emission standards.
- State and Local Permits: Many jurisdictions require permits for burning operations. Contact your state environmental agency or local fire department for approval.
- Prohibited Materials: Do not burn hazardous waste, medical waste, plastics, rubber, treated wood, or materials emitting toxic fumes. Only clean, untreated wood, paper, and natural debris are typically allowed.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain logs of burn dates, materials burned, weather conditions, and permit numbers for inspection purposes.
Site Selection and Setup
Choose a safe and compliant location for the burn container.
- Clearance: Place the container at least 50 feet from structures, vegetation, and combustible materials.
- Stable Surface: Position on a non-combustible surface such as gravel, concrete, or bare earth.
- Wind Direction: Set up the container so prevailing winds carry smoke away from inhabited areas.
- Fire Safety Equipment: Keep a fire extinguisher, water source, or shovel nearby to manage emergencies.
Logistics and Transportation
Transporting a burn container or waste materials requires planning and adherence to safety standards.
- Container Transport: Secure the container on a trailer or flatbed using chains or straps. Ensure it’s empty and cooled before moving.
- Waste Handling: Store waste in designated non-combustible bins prior to burning. Avoid stockpiling combustible materials near the container.
- Loading and Unloading: Use proper lifting equipment or personnel to prevent injury. Confirm the container is stable before and after placement.
Operational Best Practices
Follow safe procedures during burn operations.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid burning during high winds, droughts, or fire bans.
- Ignition: Use approved fire-starting materials (e.g., kindling, fire starters). Never use accelerants like gasoline.
- Supervision: Maintain constant supervision during burning. Do not leave the fire unattended.
- Extinguishing: Fully extinguish the fire with water after burning. Stir ashes and check for hot spots before leaving.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Minimize impact on air quality and surrounding ecosystems.
- Smoke Management: Burn only during favorable atmospheric conditions to reduce smoke nuisance.
- Ash Disposal: Allow ashes to cool completely. Dispose of in non-combustible containers; consider recycling if metal residues are present.
- Wildlife Protection: Avoid burning near habitats of endangered species or sensitive ecosystems.
Inspection and Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures safe and compliant operation.
- Inspect Container: Check for rust, cracks, or structural damage before each use.
- Clean Regularly: Remove ash buildup to maintain airflow and efficiency.
- Replace When Needed: Retire containers showing significant wear or deterioration.
Emergency Procedures
Prepare for unexpected incidents.
- Fire Escalation: If the fire spreads, evacuate immediately and call emergency services.
- Injury Response: Have a first aid kit accessible and train personnel in basic emergency response.
- Spill or Leak: In case of fuel or chemical exposure, follow HAZMAT protocols and report to authorities if required.
Training and Documentation
Ensure all operators are trained and procedures are documented.
- Operator Training: Provide instruction on safe operation, emergency response, and compliance requirements.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and distribute clear guidelines for use.
- Audit Readiness: Keep permits, training records, and burn logs organized for regulatory audits.
By following this guide, organizations can safely and legally utilize burn containers while minimizing environmental and safety risks. Always consult with local authorities before initiating any burning operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Burn Container
After evaluating various options for sourcing a burn container, it is clear that selecting the right solution requires balancing safety, regulatory compliance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. A properly sourced burn container must meet local environmental and fire safety regulations, particularly if used for controlled waste burning or in industrial, agricultural, or emergency response applications. Key considerations include material construction (such as thick-gauge steel with heat resistance), appropriate size and accessibility, and features like vents, lids, and stability mechanisms.
Sourcing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers ensures quality control and adherence to safety standards. Additionally, prefabricated models offer reliability and consistency, while custom-fabricated options may better suit specific operational needs. Environmental responsibility and long-term maintenance should also factor into the decision-making process.
In conclusion, investing time and resources into sourcing a high-quality, compliant burn container not only enhances operational efficiency and safety but also mitigates legal and environmental risks. A well-sourced burn container is a critical component in safe and responsible combustion practices.