The global trisodium phosphate (TSP) market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industrial cleaning, water treatment, and food processing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global phosphate chemicals market was valued at USD 26.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030, with TSP playing a significant role in this upward trajectory. This growth is fueled by increasing industrialization, stricter hygiene standards, and the compound’s effectiveness as a degreaser and emulsifier. As demand intensifies, particularly in North America and Asia-Pacific, sourcing reliable bulk TSP suppliers has become critical for manufacturers and formulators seeking consistent quality and scalable supply chains. In this context, identifying leading producers with proven production capacity, regulatory compliance, and global distribution networks is essential for maintaining competitive advantage. Below, we spotlight the top 8 bulk trisodium phosphate manufacturers shaping the current market landscape.
Top 8 Bulk Trisodium Phosphate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Trisodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wegochem.com
Key Highlights: Wego Chemical Group is an industrial distributor and supplier of Trisodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate, providing supply chain, logistics and warehousing ……
#2 Monosodium Disodium Trisodium Phosphate Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2005
Website: mubychem.com
Key Highlights: We serve it all. Specifications, Safety Data Sheet, Manufacturing process details, Wholesale retail buy sell prices, Uses etc available on line in these pages ……
#3 Trisodium Phosphate
Domain Est. 2024
Website: nationalchemicalind.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer, supplier, exporter of Trisodium Phosphate offered by NATIONAL CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES at the latest price from Thane, Maharashtra….
#4 Trisodium Phosphate Supplier and Distributor
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gjchemical.com
Key Highlights: GJ Chemical offers Trisodium Phosphate. Available in various grades, packaging and quantities from LTL to Bulk. Speak to one of our technical experts today!…
#5 Trisodium Phosphate (TSP)
Domain Est. 2001
Website: qualitychemical.com
Key Highlights: Removes hard to clean dirt and prepares surfaces for repainting. Ideal for most residential cleaning uses. Easily remove mold or mildew from tight corners….
#6 Trisodium Phosphate Supplier
Domain Est. 2004
Website: silverfernchemical.com
Key Highlights: Trisodium Phosphate 7601-54-9 is in stock, get a quote today. Silver Fern is your reliable supplier of Trisodium Phosphate….
#7 Trisodium Phosphate Suppliers USA
Domain Est. 2012
Website: americanchemicalsuppliers.com
Key Highlights: We have compiled a list of Trisodium Phosphate suppliers in the USA, the companies listed have a genuine United States presence….
#8 Trisodium Phosphate
Domain Est. 2014
Website: covalentchemical.com
Key Highlights: Covalent Chemical offers Trisodium Phosphate – TSP. Available in various grades, packaging and quantities from LTL to Bulk. Speak to one of our technical ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bulk Trisodium Phosphate

H2: Market Trends for Bulk Trisodium Phosphate in 2026
As the global industrial and consumer markets evolve, the demand for bulk trisodium phosphate (TSP) is expected to reflect a complex interplay of regulatory, environmental, and sector-specific dynamics by 2026. While TSP has historically been a key ingredient in detergents, cleaning agents, and industrial applications, its market trajectory is being reshaped by sustainability initiatives, technological advancements, and shifting regional demands.
-
Regulatory Pressure and Environmental Restrictions
By 2026, stringent environmental regulations—particularly in North America and Western Europe—are anticipated to continue limiting the use of phosphates in household detergents due to concerns over eutrophication in water bodies. These restrictions are expected to constrain traditional TSP markets, especially in consumer cleaning products. However, industrial and institutional applications, where phosphate use is less regulated or exempt, may provide stable demand. -
Shift Toward Industrial and Niche Applications
The bulk trisodium phosphate market is projected to pivot toward industrial uses, including metal cleaning, water treatment, and food processing (where food-grade TSP is permitted). The construction and manufacturing sectors, particularly in emerging economies, are expected to drive demand for TSP as a degreaser and surface preparation agent. Additionally, its use in ceramic production and as a pH regulator in various chemical processes may sustain market relevance. -
Geographic Market Shifts
While demand in mature markets like the U.S. and EU remains subdued due to environmental policies, growth in Asia-Pacific—especially in India, Southeast Asia, and parts of China—is expected to offset declines elsewhere. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and less restrictive regulations in certain regions are likely to support increased consumption of bulk TSP for commercial and industrial cleaning. -
Competition from Alternatives
By 2026, alternative builders such as zeolites, citrates, and silicates are expected to dominate the eco-friendly detergent segment, further pressuring TSP’s market share in household products. However, in high-efficiency industrial cleaning where performance is critical, TSP’s superior cleaning and emulsifying properties may preserve its niche utility. -
Price Volatility and Supply Chain Dynamics
Fluctuations in raw material costs—particularly phosphoric acid and soda ash—may contribute to price volatility in the bulk TSP market. Geopolitical factors affecting phosphate rock supply, primarily sourced from regions like Morocco and China, could influence production costs and availability. Companies investing in supply chain resilience and regional sourcing are likely to gain competitive advantages. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Growing emphasis on the circular economy may prompt innovation in phosphate recovery and recycling technologies. While not yet mainstream for TSP, advancements in recovering phosphates from wastewater could impact long-term supply dynamics and reduce dependency on mined resources, potentially altering cost structures by 2026.
Conclusion
The bulk trisodium phosphate market in 2026 is expected to be characterized by contraction in traditional consumer applications and steady demand in industrial sectors. Geographic shifts, regulatory landscapes, and competition from alternatives will be key determinants of market performance. Producers who adapt to sustainable practices, target high-growth industrial segments, and expand in less-regulated regions are likely to maintain or grow their market share despite overarching environmental challenges.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bulk Trisodium Phosphate (Quality and Intellectual Property Considerations)
Sourcing bulk trisodium phosphate (TSP) can present several challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply, regulatory compliance, and protection against legal exposure.
1. Inconsistent Product Quality
A major pitfall is receiving TSP that does not meet specified purity or technical standards. Variability may arise from:
– Differences in manufacturing processes across suppliers.
– Contamination with impurities such as heavy metals, silicates, or insoluble residues.
– Inadequate quality control protocols, especially with low-cost or unverified suppliers.
Impact: Poor-quality TSP can compromise end-product performance in applications like cleaning agents, water treatment, or food processing.
2. Misrepresentation of Grade (Technical vs. Food/Pharmaceutical Grade)
Suppliers may label industrial-grade TSP as food or reagent grade without proper certification.
Risk: Using misrepresented TSP in regulated industries can lead to non-compliance, recalls, or safety issues. Always verify compliance with standards such as FCC (Food Chemicals Codex), USP, or ISO.
3. Lack of Certifications and Documentation
Failure to obtain proper documentation—such as Certificate of Analysis (CoA), Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS), or regulatory compliance statements—can lead to supply chain vulnerabilities.
Best Practice: Require batch-specific CoAs and audit supplier quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
While trisodium phosphate itself is a commodity chemical and generally not patented, sourcing may involve IP pitfalls when:
– Purchasing under a branded formulation or proprietary blend protected by trademarks or process patents.
– Using TSP in a patented application or process without proper licensing.
Example: A cleaning product formulation incorporating TSP may be protected under a patent; sourcing TSP for such use without due diligence could expose the buyer to contributory infringement claims.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Source Verification
Opaque supply chains may hide sub-tier suppliers using unethical practices or non-compliant manufacturing methods. This increases the risk of counterfeit or adulterated material entering the supply chain.
Recommendation: Conduct supplier audits and favor vertically integrated or certified suppliers.
6. Regulatory and Environmental Compliance Issues
TSP is restricted or regulated in some regions due to environmental concerns (e.g., eutrophication from phosphate runoff). Sourcing from jurisdictions with weak environmental oversight may result in non-compliant material or reputational damage.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Vet suppliers rigorously, focusing on quality systems and regulatory compliance.
– Require full documentation and conduct independent testing when necessary.
– Conduct IP due diligence, especially when integrating TSP into proprietary or patented applications.
– Monitor evolving regulations related to phosphate use and environmental impact.
Proactive management of quality and IP considerations ensures reliable, compliant, and legally sound sourcing of bulk trisodium phosphate.
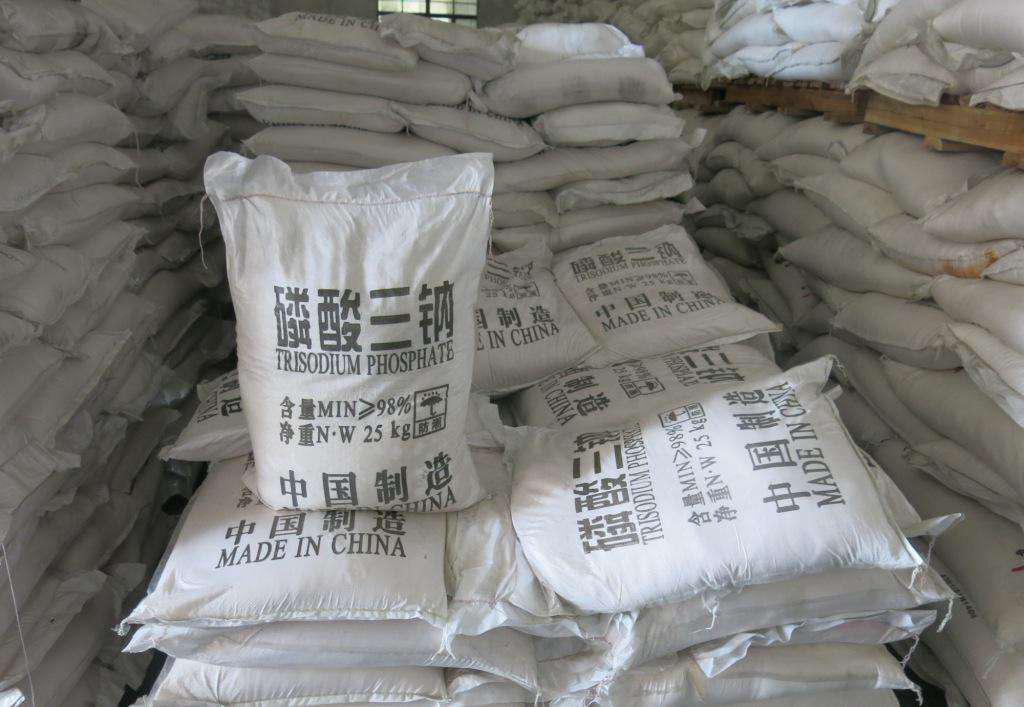

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bulk Trisodium Phosphate (TSP)
1. Chemical Overview
Trisodium Phosphate (TSP)
– Chemical Formula: Na₃PO₄
– CAS Number: 7601-54-9
– UN Number: 1389
– Classification: Non-hazardous for transport under normal conditions (may vary by formulation and concentration), but classified as an irritant (GHS)
– Appearance: White, granular or crystalline powder
– Uses: Industrial cleaning, water treatment, food additive (E339), metal degreasing, and ceramic manufacturing
2. Regulatory Classification & Compliance
GHS Classification (Globally Harmonized System)
- Skin Irritation: Category 2
- Eye Damage/Irritation: Category 1
- Hazard Statements:
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H318: Causes serious eye damage
- H335: May cause respiratory irritation
- Precautionary Statements:
- P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume
- P280: Wear protective gloves/eye protection/face protection
- P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
Transport Regulations
- IMDG Code (Marine): Not regulated as dangerous goods when transported in bulk (UN 1389 – may be exempt depending on form and packaging)
- ADR (Road – Europe): Not classified as hazardous for transport (check regional variations)
- 49 CFR (USA – DOT): Not regulated as a hazardous material in bulk when dry and non-reactive
- IATA (Air): Generally permitted as non-hazardous; however, carriers may impose restrictions due to alkalinity or dust generation
Note: Always verify the specific form (anhydrous vs. hydrated) and purity with safety data sheets (SDS) prior to shipment.
3. Packaging & Handling Requirements
Bulk Packaging Options
- FIBCs (Flexible Intermediate Bulk Containers): 500–1000 kg capacity; UV-resistant, UN-certified if required
- Bulk Bags with Liners: To prevent moisture absorption and contamination
- Big Bags on Pallets: For forklift handling
- Railcars or Tank Containers: For very large volumes (dry bulk pneumatic tankers)
Handling Precautions
- Use dust-suppression methods (ventilation, misting) during loading/unloading
- Operators must wear PPE: gloves (nitrile or neoprene), safety goggles, respirators (N95 or equivalent), and protective clothing
- Avoid contact with acids – may generate toxic fumes
- Keep dry – TSP is hygroscopic and can cake if exposed to moisture
4. Storage Guidelines
- Location: Dry, well-ventilated, cool area
- Conditions: Relative humidity < 60%; temperature between 15–30°C (59–86°F)
- Compatibility: Store away from acids, ammonium salts, and moisture sources
- Shelving: On pallets, off concrete floors to prevent damp absorption
- Segregation: Not required for non-hazardous classification, but prudent to separate from incompatible chemicals
5. Transportation Logistics
Modes of Transport
- Road: Use covered trucks or containers to prevent moisture ingress and dust dispersion
- Rail: Bulk hopper cars suitable for dry, free-flowing powders
- Marine: In FIBCs or in bulk holds (if vessel permits); ensure cargo is secured and protected from sea moisture
- Air: Possible in non-hazardous classification; notify carrier in advance due to alkalinity
Documentation
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Required (GHS-compliant, Section 14 – Transport Information)
- Commercial Invoice & Packing List: Detail net/gross weights, packaging type, and UN number (if applicable)
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): For quality and regulatory assurance
- Customs Declarations: HS Code: 2835.31.00 (inorganic phosphates)
6. Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Ecotoxicity: Harmful to aquatic life; avoid release into waterways
- Spill Response:
- Contain spill, avoid raising dust
- Sweep or vacuum with HEPA-filtered equipment
- Dampen only if necessary (may cake)
- Dispose of in accordance with local regulations
- Waste Disposal: Classified as non-hazardous waste in many jurisdictions, but check local rules. Neutralize before disposal if required
7. Import/Export Compliance
- REACH (EU): Registered under REACH; ensure downstream user compliance
- TSCA (USA): Listed; no significant restrictions
- Customs Requirements:
- Verify import permits (especially in countries with strict chemical controls)
- Confirm labeling in local language (e.g., Spanish in Latin America, Chinese in China)
- FDA (if food-grade): Must comply with 21 CFR 182.1778 if intended for food use
8. Best Practices Summary
- Always use up-to-date SDS (rev. 16 or later)
- Conduct regular training for handlers on safe practices
- Label all containers with GHS pictograms and hazard statements
- Monitor for caking or moisture during long-term storage
- Partner with freight forwarders experienced in bulk chemical logistics
For the most accurate compliance, always consult the latest regulatory databases (e.g., ECHA, OSHA, DOT) and involve a chemical logistics specialist when planning international shipments.
In conclusion, sourcing bulk trisodium phosphate (TSP) requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure cost-effectiveness, quality, and regulatory compliance. It is essential to identify reliable suppliers with a proven track record of providing high-purity TSP suitable for your intended application, whether industrial cleaning, metal treatment, or other uses. Evaluating suppliers based on certification standards, logistical capabilities, and pricing structures can help secure a consistent and sustainable supply. Additionally, compliance with environmental and safety regulations—especially due to TSP’s impact on water systems—must be factored into sourcing decisions. By conducting thorough due diligence and maintaining strong supplier relationships, businesses can efficiently source bulk trisodium phosphate while minimizing risks and optimizing operational performance.