The global halal meat market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for certified halal products across both Muslim-majority and non-Muslim countries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the halal food market—including meat and poultry—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.3% from 2023 to 2028, with halal meat representing a significant share due to rising religious compliance awareness and expanding diaspora populations. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, estimating the global halal meat market size to reach USD 1.87 billion by 2030, fueled by stringent certification standards and growing e-commerce distribution. As demand surges, sourcing from reliable, large-scale manufacturers has become critical for importers, retailers, and foodservice providers. Based on production capacity, global reach, certifications, and export volume, the following are the top 10 bulk halal meat manufacturers leading this expanding market.
Top 10 Bulk Halal Meat Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Halal Factory
Domain Est. 2023
Website: halalfactoryco.com
Key Highlights: Quality halal meat. Ethically produced. From farm to freezer. Discover our antibiotic-free selection of chicken and hand-selected halal meat cuts….
#2 Purchase Halal Meat Wholesale & Bulk Online
Domain Est. 2007
Website: marxfoods.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $399Our wholesale halal meat includes beef, lamb, and goat, as well as wholesale chicken and bulk quail meat. 81 Products. Sort & Filter….
#3 A & A Halal Distributors
Domain Est. 2009
Website: aahalal.com
Key Highlights: The #1 Wholesaler for all your Halal Meats. · Contact Us · Customer Information Form · Click here for a full list of our PRODUCTS. · About Us….
#4 Saad Wholesale Meats
Domain Est. 2011 | Founded: 1976
Website: saadmeats.com
Key Highlights: Saad Wholesale Meats – Serving quality halal meats since 1976. Free local delivery on orders of $150 or more. Recognized as the largest halal meat provider in…
#5 WHOLESALE
Domain Est. 2018
#6 Halal Foundry
Domain Est. 2022
Website: halalfoundry.com
Key Highlights: Halal Foundry delivers wholesale halal meat directly to your doorstep. Our meat is exclusively 100% hand-slaughtered zabiha halal….
#7 Chaudhry Halal Meats
Domain Est. 2022
Website: chaudhrymeats.com
Key Highlights: Chaudhry Halal Meats provides USDA inspected harvest and processing service. We have more than 20 years of experience in the industry, and proudly supply….
#8 Premier Halal Butchers
Domain Est. 2023 | Founded: 1965
Website: premierhalalmeats.com
Key Highlights: Your first-choice destination for exceptional quality halal meat in East London. Since 1965, we’ve upheld a commitment to ethical farming and premium sourcing….
#9 MCH Halal Meat Packing
Domain Est. 2024
Website: mchhalalmeat.com
Key Highlights: We focus on delivering the freshest halal meat to your doorstep. Grass Fed, USDA Inspected, No GMO Prime and Organic.We guarantee no hormones, no antibiotics, ……
#10 Al
Domain Est. 2020
Website: almadinausa.com
Key Highlights: Al Madina is the top source for quality Halal meat. All of our products are raised from local farms that adhere to the strictest guidelines….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bulk Halal Meat

2026 Market Trends for Bulk Halal Meat
As global demand for ethically sourced, religiously compliant food continues to rise, the bulk halal meat market is poised for significant growth by 2026. Driven by demographic shifts, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of halal certification standards, this sector is transforming into a strategic focus area for producers, distributors, and retailers worldwide. The following analysis outlines key trends expected to shape the bulk halal meat market in 2026.
Expansion of Global Halal Demand
The Muslim population, currently over 1.9 billion and projected to reach 2.2 billion by 2030, remains the primary driver of halal meat consumption. By 2026, regions with large Muslim communities—including Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and parts of Europe—will continue to lead demand. In addition, non-Muslim consumers are increasingly choosing halal meat due to perceptions of higher quality, hygiene, and ethical animal treatment, expanding the market beyond religious necessity.
Supply Chain Modernization and Traceability
In 2026, bulk halal meat supply chains will be increasingly digitized to ensure transparency and compliance. Blockchain technology and smart labeling solutions will gain traction, enabling real-time tracking from farm to fork. This enhances trust in halal certification and reduces the risk of fraud—critical factors for importers and retailers operating in regulated markets such as the European Union and North America.
Growth in Halal Meat Exports
Countries with strong halal infrastructure—such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Brazil, Australia, and New Zealand—are expected to increase exports to meet international demand. Free trade agreements and halal-friendly policies will facilitate cross-border transactions. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, in particular, are projected to remain major importers due to limited domestic production and high per capita consumption.
Premiumization and Value-Added Products
The bulk halal meat market will see a shift toward premium and value-added segments. Processed halal meats, ready-to-cook cuts, marinated products, and organic halal options are gaining popularity. By 2026, bulk buyers—including hotels, restaurants, and institutional caterers—will increasingly seek convenience and consistency, driving innovation in packaging, preservation, and product variety.
Regulatory Harmonization Efforts
A major trend by 2026 will be the ongoing effort to standardize halal certification across countries. Initiatives led by organizations such as the World Halal Council and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) aim to create mutual recognition agreements between national halal bodies. This harmonization will reduce trade barriers, lower compliance costs, and streamline bulk procurement for multinational foodservice operators.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Environmental and animal welfare concerns will influence halal meat production practices. Producers will adopt sustainable farming methods, reduce carbon footprints, and emphasize humane slaughter practices aligned with Islamic principles. Bulk buyers will prioritize suppliers who demonstrate both halal compliance and environmental responsibility, reflecting broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) trends.
Technological Advancements in Production
Automation and biotechnology will play a crucial role in scaling halal meat production. AI-driven livestock management, precision slaughter systems, and cold chain innovations will improve efficiency and safety. While lab-grown halal meat remains in early stages, 2026 may see initial regulatory approvals and pilot commercialization, potentially disrupting traditional meat supply models in the long term.
Conclusion
By 2026, the bulk halal meat market will be characterized by increased globalization, technological integration, and consumer-driven innovation. As demand grows across both Muslim-majority and multicultural markets, stakeholders must adapt to evolving standards, embrace traceability, and invest in sustainable practices to remain competitive. The convergence of faith-based requirements with modern food industry trends positions bulk halal meat as a dynamic and resilient segment of the global protein economy.
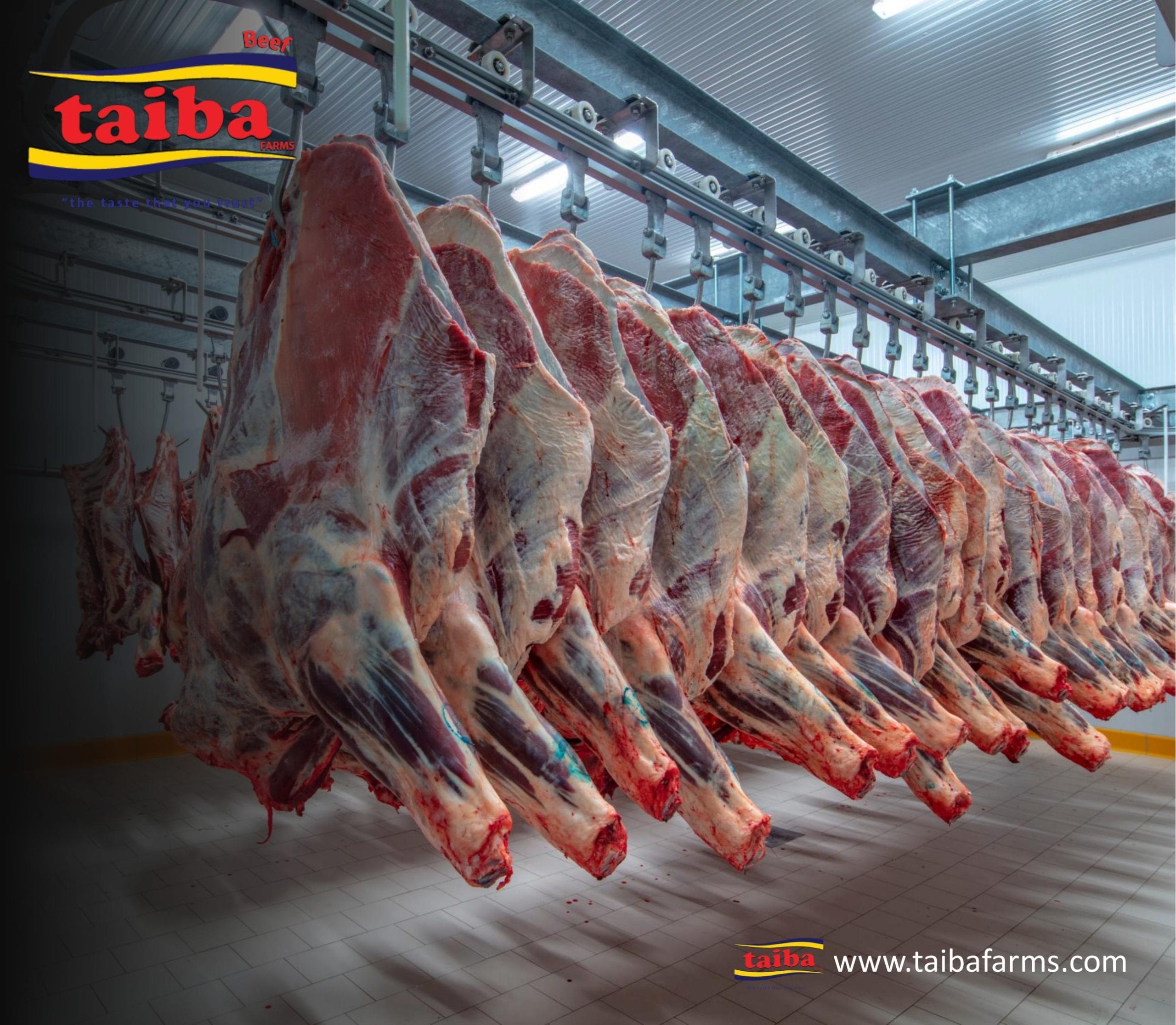

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bulk Halal Meat (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing bulk Halal meat presents unique challenges that go beyond standard procurement. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to reputational damage, regulatory issues, financial loss, and consumer trust erosion. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for food manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent or Non-Compliant Slaughter Practices
One of the most critical pitfalls is assuming that a Halal certification automatically guarantees consistent, high-quality slaughter methods. Variations in stunning policies (pre- vs. post-cut), knife sharpness, bleed-out duration, and worker training across different abattoirs can impact both meat quality (e.g., blood retention, stress-induced meat deterioration) and authentic Halal compliance. Failing to audit slaughterhouses directly can result in substandard or non-compliant product.
Lack of Traceability and Transparency
Bulk sourcing often involves complex supply chains. Without robust traceability systems—from farm to final packaging—buyers risk receiving meat from unapproved sources or mixed batches (e.g., conventional meat inadvertently mixed with Halal). This lack of transparency undermines Halal integrity and increases the risk of contamination or mislabeling.
Inadequate Cold Chain Management
Halal meat, like all perishable protein, requires strict temperature control. During bulk transport and storage, lapses in the cold chain (e.g., improper refrigeration during transit or at distribution hubs) can lead to bacterial growth, spoilage, and compromised product safety and shelf life—damaging both quality and consumer health.
Variable Meat Quality and Specifications
Bulk suppliers may offer inconsistent meat quality in terms of marbling, fat content, tenderness, or cut uniformity. Without clearly defined quality specifications and regular batch testing, buyers may receive product unsuitable for their intended use (e.g., processed foods vs. premium retail cuts), leading to waste or customer complaints.
Misleading or Fraudulent Halal Certification
Not all Halal certifications are equally rigorous. Some certifications may be issued by non-accredited or biased bodies. Buyers who fail to verify the credibility of the certifying organization risk sourcing from suppliers with fraudulent or questionable Halal claims—an issue that has led to major recalls and legal actions in various markets.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Branding and Certification Marks
Suppliers may misuse registered Halal certification logos or mimic well-known Halal brand identifiers without authorization. Sourcing bulk meat bearing such marks without proper licensing exposes the buyer to IP infringement claims, especially if the product is rebranded or resold. Buyers must ensure all Halal symbols used are legitimately licensed.
Copying of Product Formulations and Processes
When working with co-manufacturers or private-label suppliers on customized Halal meat products (e.g., seasoned cuts, ready meals), there’s a risk the supplier replicates the formulation or production process for other clients. Without strong non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and IP clauses in contracts, proprietary recipes and methods can be exploited, diluting competitive advantage.
Lack of Contractual Clarity on IP Ownership
In custom development scenarios (e.g., creating a new Halal product line), contracts often fail to specify who owns the resulting IP—the buyer, the supplier, or both. This ambiguity can lead to disputes over usage rights, resale, or future innovation, especially if the supplier attempts to market a similar product independently.
Geographic Indications and Misrepresentation
Some Halal meat products are marketed with claims about origin (e.g., “Australian Lamb,” “Scottish Beef”) to imply quality or authenticity. Sourcing bulk meat with such claims without verifying geographic sourcing can lead to IP misuse and accusations of false advertising, particularly if protected designations are involved.
Counterfeit Supply Chains
Organized counterfeiters sometimes infiltrate bulk supply chains, repackaging lower-grade or non-Halal meat with authentic Halal branding. This not only violates IP rights but also breaches religious and food safety standards. Buyers without anti-counterfeiting measures (e.g., batch tracking, forensic tagging) are vulnerable to receiving and distributing these illegal products.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, partner with reputable and audited suppliers, demand third-party Halal certification from accredited bodies, implement strong contractual protections, and invest in supply chain transparency technologies such as blockchain or RFID tracking.
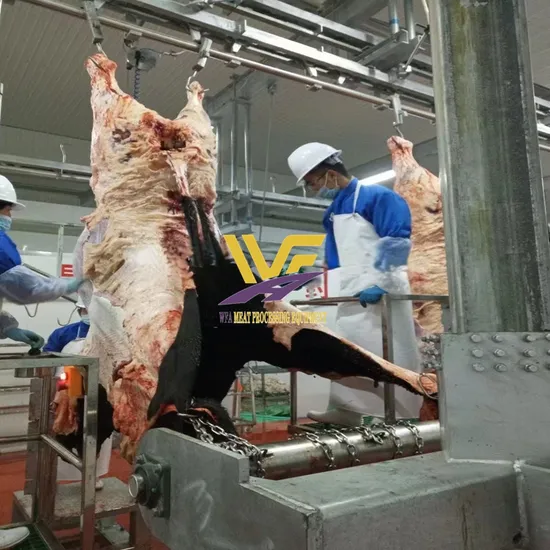

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bulk Halal Meat
Overview of Halal Meat Logistics
Handling bulk halal meat requires strict adherence to both logistical efficiency and religious compliance. The supply chain—from sourcing and slaughter to transportation, storage, and delivery—must maintain halal integrity at every stage. This guide outlines key protocols to ensure compliance with Islamic dietary laws while preserving product quality and safety.
Sourcing and Certification
All halal meat must originate from certified halal suppliers or slaughterhouses approved by a recognized Islamic authority (e.g., Halal Monitoring Committee, IFANCA, or JAKIM). Verify that the supplier holds valid halal certification, which should be renewed regularly and available for audit. The animals must be healthy at the time of slaughter and slaughtered by a sane adult Muslim who recites the Tasmiyah (Bismillah) during dhabihah (the halal slaughter method).
Slaughter and Processing Standards
The slaughtering process must follow halal principles: a swift, deep cut to the throat with a sharp knife, severing the trachea, esophagus, and blood vessels while leaving the spinal cord intact. Complete drainage of blood is essential. Processing facilities must ensure no cross-contamination with non-halal products, including the use of dedicated equipment and production lines where feasible.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Bulk halal meat must be packaged in tamper-evident, food-grade materials. Each package must be clearly labeled with:
– The halal certification mark and issuing body
– Product name and cut type
– Batch number and slaughter date
– Storage conditions and expiry date
– Country of origin and facility details
Labels must not contain any non-halal ingredients or references. Multilingual labeling may be required for export compliance.
Cold Chain Management
Maintaining a consistent cold chain is critical. Bulk halal meat must be stored and transported at or below -18°C (0°F) for frozen products or 0–4°C (32–39°F) for chilled meat. Use refrigerated containers (reefers) with real-time temperature monitoring and data logging. Any temperature deviation must be documented and assessed for halal and safety implications.
Transportation and Handling
Use dedicated halal transport vehicles or implement segregation protocols if shared. Vehicles must be cleaned and sanitized before loading to prevent contamination. Drivers and handlers should be trained in halal handling procedures. Documentation, including the halal certificate and temperature logs, must accompany the shipment at all times.
Import/Export Compliance
For international trade, ensure compliance with destination country regulations. This may include:
– Official halal certification recognized by the importing country
– Veterinary health certificates
– Customs documentation with accurate commodity descriptions
– Adherence to sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures under WTO agreements
Work with customs brokers familiar with halal product regulations to avoid delays.
Storage and Inventory Control
Warehouses must have segregated halal storage zones with clear signage. Implement a first-expiry, first-out (FEFO) system to manage stock rotation. Regular audits should verify halal compliance, pest control, and temperature maintenance. Unauthorized access to halal storage areas should be restricted.
Audits and Documentation
Maintain comprehensive records for traceability, including:
– Supplier halal certificates
– Slaughter logs and batch records
– Temperature monitoring reports
– Transportation and delivery documentation
Conduct regular internal and third-party audits to verify compliance with halal standards and food safety regulations (e.g., HACCP, ISO 22000).
Crisis Management and Recalls
Establish a halal compliance incident response plan. In case of non-compliance (e.g., cross-contamination, certification lapse), initiate a product hold or recall immediately. Notify relevant halal certifiers and authorities promptly. Transparent communication with customers and stakeholders is essential to maintain trust.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics of bulk halal meat requires a holistic approach that integrates religious compliance, food safety, and supply chain efficiency. By following this guide and maintaining rigorous standards, businesses can ensure the integrity of halal meat from farm to consumer.
Conclusion for Sourcing Bulk Halal Meat
Sourcing bulk halal meat requires a strategic and informed approach to ensure compliance with Islamic dietary laws, maintain product quality, and meet the growing demand from Muslim consumers and halal-conscious markets. A successful sourcing strategy hinges on partnering with certified halal suppliers, verifying slaughter practices, and maintaining full traceability throughout the supply chain. Additionally, considerations such as animal welfare, geographical sourcing, pricing, and logistical efficiency are crucial for long-term sustainability.
By establishing relationships with reputable halal-certified producers and adhering to strict auditing and certification standards—such as those from recognized bodies like the Halal Food Authority (HFA) or Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America (IFANCA)—businesses can ensure authenticity and build consumer trust. Furthermore, bulk purchasing offers significant cost advantages and supply stability, especially for foodservice providers, retailers, and manufacturers targeting halal markets.
In conclusion, sourcing bulk halal meat is not only a logistical decision but also a commitment to ethical, religious, and quality standards. With the global halal food market expanding rapidly, businesses that prioritize transparency, certification, and responsible sourcing will be well-positioned to succeed in this dynamic and faith-driven industry.