The global cement market continues to expand, driven by rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and increasing construction activities—particularly across Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global cement market was valued at approximately USD 435 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth trajectory is underpinned by government-led infrastructure investments and the rising demand for affordable housing. With such momentum, identifying the leading bulk cement manufacturers becomes critical for construction firms, distributors, and procurement professionals seeking reliable supply, competitive pricing, and quality assurance. The following list highlights the top 10 bulk cement producers worldwide, ranked based on production capacity, global reach, and market influence.
Top 10 Bulk Cement Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ash Grove Cement
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ashgrove.com
Key Highlights: Ash Grove, a CRH Company, is one of North America’s leading cement manufacturers, with a legacy of innovation and excellence dating back to 1882. The Company ……
#2 Products & Solutions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: cemex.com
Key Highlights: High-quality customized cement products. Whether in bags or in bulk, we provide our customers with high-quality cement products and services. Our knowledge ……
#3 Leading Supplier of Concrete & Building Materials
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cemexusa.com
Key Highlights: Trusted building materials supplier and concrete supplier, Cemex US delivers ready-mix concrete, aggregates, and sustainable solutions nationwide for ……
#4 Lehigh White Cement Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lehighwhitecement.com
Key Highlights: Our company produces, imports and markets white cement throughout North America. Lehigh White Cement takes artistic expression to new heights, ……
#5 GCC
Domain Est. 1997
Website: gcc.com
Key Highlights: GCC produces cement, concrete, aggregates and innovative products for the construction industries in Mexico, the United States, Latin America and Canada….
#6 CTS Cement
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ctscement.com
Key Highlights: Your quarterly concrete guides include information and resources on new construction, repairs and restoration, and decorative concrete….
#7 Cement Solutions & Operations
Domain Est. 2000
Website: holcim.com
Key Highlights: We offer an extensive line of innovative and low-carbon cements and hydraulic binders, including bag and bulk products….
#8 Dangote Cement
Domain Est. 2003
Website: dangotecement.com
Key Highlights: Dangote Cement Plc is Sub-Saharan Africa’s leading cement company, with a production capacity of 52.0 million tonnes per year across ten countries….
#9 Dragon Alfa Cement Ltd
Domain Est. 2006
Website: dragonalfacement.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Dragon Alfa Cement | Leading cement import company in the UK | High-quality bagged and bulk cement with exceptional customer service | View our ……
#10 Heidelberg Materials North America
Domain Est. 2022
Website: heidelbergmaterials.us
Key Highlights: In North America, Heidelberg Materials is a leading supplier of cement, aggregates, ready mixed concrete, and asphalt with more than 450 locations and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bulk Cement
H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Bulk Cement
As the global construction and infrastructure sectors continue to evolve, the bulk cement market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by urbanization, government infrastructure initiatives, technological advancements, and sustainability mandates, the bulk cement industry is adapting to meet changing demands. This analysis explores key trends shaping the 2026 bulk cement market landscape.
1. Rising Infrastructure Investment in Emerging Economies
Developing regions—particularly in South Asia, Africa, and Southeast Asia—are expected to be primary drivers of bulk cement demand in 2026. Countries such as India, Nigeria, Indonesia, and Bangladesh are investing heavily in road networks, affordable housing, and smart city projects. India’s National Infrastructure Pipeline and Indonesia’s continued urban expansion are projected to increase bulk cement consumption significantly. This infrastructure boom supports sustained demand for bulk cement, favoring large-scale producers with logistics capabilities.
2. Shift Toward Sustainable and Low-Carbon Cement
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing cement manufacturers to adopt greener alternatives. By 2026, the adoption of low-carbon cements—such as Portland Limestone Cement (PLC), blended cements with fly ash or slag, and emerging carbon capture technologies—is expected to grow. The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and similar policies in North America are influencing global supply chains, compelling producers to reduce emissions. Bulk cement suppliers investing in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) or alternative fuels will gain a competitive edge.
3. Digitalization and Supply Chain Optimization
The integration of digital technologies in cement logistics is reshaping bulk distribution. By 2026, advanced tracking systems, IoT-enabled bulk transporters, and predictive analytics will enhance efficiency in cement delivery. Real-time monitoring of silo levels and automated dispatch systems allow for just-in-time delivery, reducing inventory costs for construction firms. Major producers are partnering with logistics tech firms to streamline bulk cement supply chains, particularly in densely populated urban centers.
4. Consolidation and Vertical Integration
Market consolidation is expected to accelerate by 2026 as large cement producers acquire regional players to expand geographic reach and secure raw material supplies. Vertical integration—controlling everything from limestone quarries to grinding stations and distribution networks—will improve cost efficiency and supply reliability. This trend is especially evident in markets like China and Turkey, where scale economies are critical for competitiveness in the bulk segment.
5. Regional Supply-Demand Imbalances and Trade Flows
Global bulk cement trade will be influenced by regional imbalances. While the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) regions maintain surplus production capacity, regions with rapid construction growth but limited local production (e.g., West Africa) will rely more on bulk imports via maritime shipping. China’s cement export volumes may stabilize or decline due to domestic demand shifts, opening opportunities for producers in Turkey, Vietnam, and Egypt to capture market share.
6. Price Volatility and Input Cost Pressures
Energy costs, particularly for coal and electricity, remain a critical factor influencing bulk cement pricing. Geopolitical tensions and energy transition policies may cause volatility in input costs through 2026. Producers investing in alternative fuels (e.g., biomass, waste-derived fuels) and energy-efficient kilns will be better positioned to manage margins. Additionally, fluctuations in global shipping rates could impact the competitiveness of exported bulk cement.
7. Growth of Ready-Mix Concrete and On-Site Bulk Handling
The expansion of ready-mix concrete (RMC) plants, especially in urban areas, is increasing demand for bulk cement deliveries. RMC operators prefer bulk supply due to its cost-effectiveness and consistency. Simultaneously, large construction projects are adopting on-site bulk storage silos, reducing reliance on bagged cement and improving construction efficiency. This trend supports continued investment in bulk logistics infrastructure.
Conclusion
By 2026, the bulk cement market will be shaped by a confluence of infrastructure development, environmental regulations, technological innovation, and evolving supply chain dynamics. Producers who prioritize sustainability, digital integration, and logistical efficiency will be best positioned to capitalize on growth opportunities. While challenges such as energy costs and regional volatility persist, the long-term outlook for bulk cement remains positive—especially in high-growth emerging markets with rising urbanization rates.
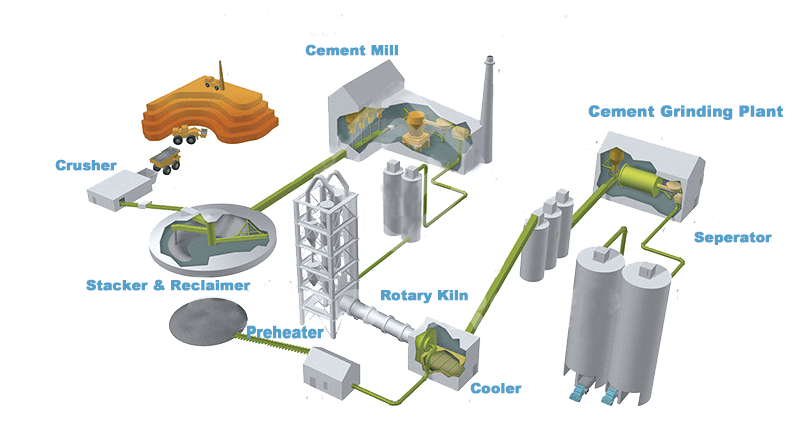
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bulk Cement (Quality, IP)
Sourcing bulk cement presents unique challenges beyond simple price negotiation. Focusing solely on cost can lead to significant risks related to product quality, project timelines, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding and mitigating these common pitfalls is crucial for successful procurement.
Quality Inconsistency and Non-Compliance
One of the most critical risks is receiving cement that fails to meet required specifications or standards. Bulk shipments from large suppliers, especially in international sourcing, can suffer from batch-to-batch variability. Differences in raw materials, kiln processes, or blending can alter key properties like strength development, setting time, and sulfate resistance. Sourcing from suppliers without rigorous quality control (QC) systems increases the likelihood of non-compliant cement, potentially leading to structural failures, costly rework, and project delays. Always verify that the supplier adheres to recognized standards (e.g., ASTM, EN, or local equivalents) and conducts regular third-party testing.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Bulk cement often moves through complex supply chains involving multiple handlers, making traceability difficult. Without proper documentation, it becomes nearly impossible to track the origin of a batch, its manufacturing date, or test results. This lack of traceability complicates quality investigations if problems arise on-site and can hinder compliance with regulatory or project-specific requirements. Ensure suppliers provide comprehensive mill test certificates (MTCs) for each shipment and maintain a clear chain of custody.
Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure in Custom Formulations
When sourcing specialized or custom-blended cement formulations (e.g., for high-performance concrete or specific environmental conditions), there’s a risk of IP exposure. Sharing proprietary mix designs or performance requirements with suppliers may inadvertently disclose sensitive technical information. Unscrupulous suppliers could reverse-engineer the formulation or use the knowledge to serve competitors. Always use robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and limit the disclosure of only essential specifications, avoiding revealing exact proportions or unique additives.
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Due Diligence
Choosing a supplier based primarily on price or convenience without thorough due diligence can lead to significant issues. Overlooking a supplier’s production capacity, logistical capabilities, financial stability, or environmental compliance increases the risk of supply disruptions, missed deadlines, or reputational damage. Conduct comprehensive audits, including site visits and reviews of past performance, to ensure the supplier can consistently deliver quality cement and meet contractual obligations.
Poor Logistics and Handling Leading to Contamination
Bulk cement is susceptible to contamination and degradation during transport and storage. Moisture ingress during shipping or improper handling at transfer points can cause pre-hydration, reducing cement efficacy. Using unclean or shared transport vehicles (e.g., trucks previously carrying other powders) introduces foreign materials. Ensure logistics contracts specify sealed, dedicated transport and proper storage conditions (dry, ventilated silos) to preserve cement integrity.
Misalignment on Testing Protocols and Acceptance Criteria
Disputes often arise due to ambiguous or unagreed-upon testing procedures. Differences in sampling methods, testing labs, or interpretation of results can lead to rejected shipments and strained supplier relationships. Clearly define acceptance criteria, sampling protocols, and the governing testing standards in procurement contracts. Consider using independent third-party inspectors to validate quality at the point of loading or delivery.
Overlooking Long-Term Supply and Contractual Flexibility
Bulk cement projects often span months or years. Locking into long-term contracts without price adjustment mechanisms or supply guarantees exposes buyers to market volatility and potential shortages. Conversely, suppliers may lack incentive to maintain quality if future business is uncertain. Build flexibility into contracts with performance incentives, review clauses, and clear exit strategies to protect both parties.
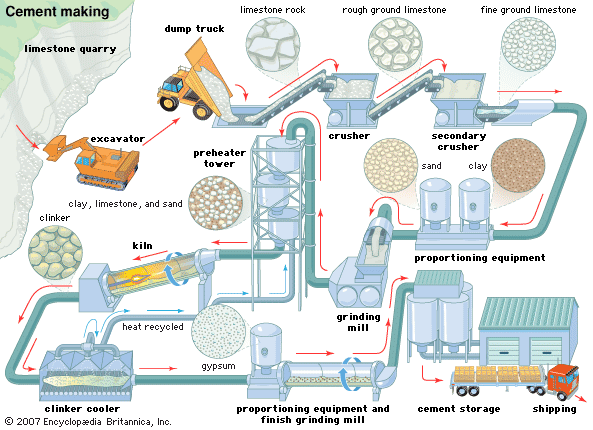
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bulk Cement
Overview of Bulk Cement Transportation
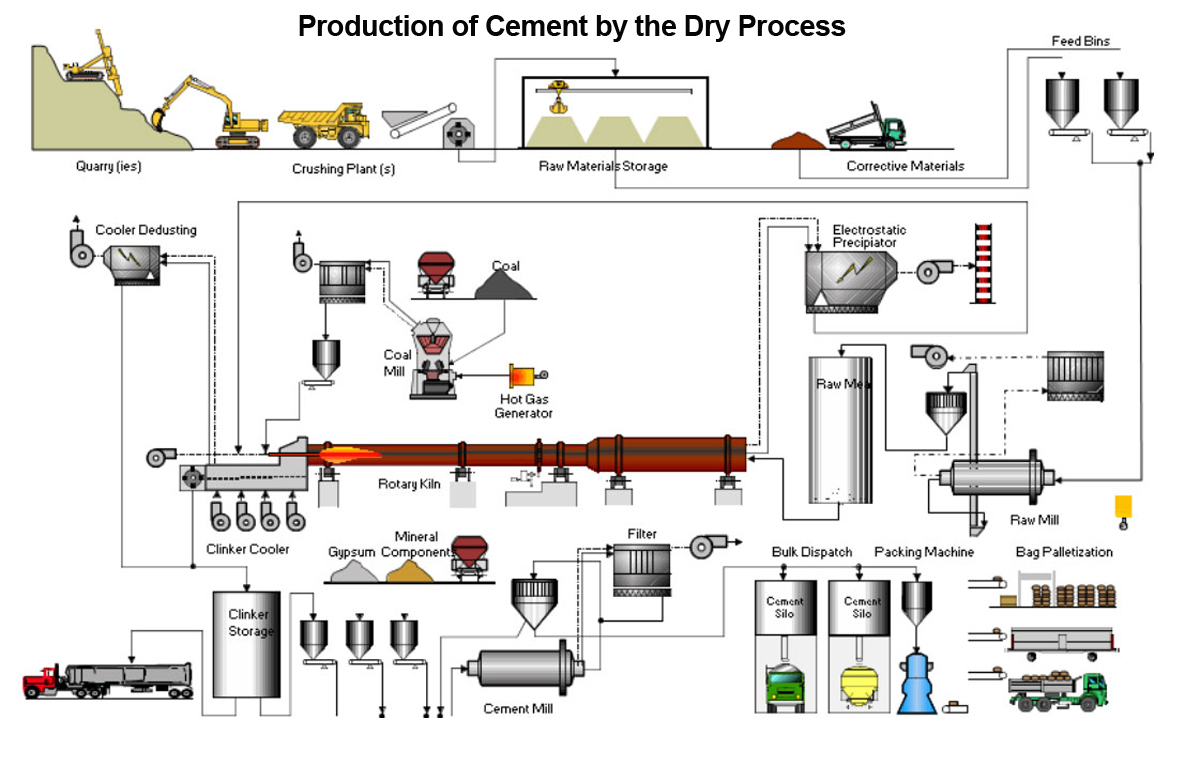
Bulk cement is a critical construction material transported in large quantities, typically via specialized dry bulk carriers such as pneumatic tank trucks, railcars, or bulk vessels. Due to its fine particulate nature, hygroscopic properties, and environmental and safety concerns, the logistics and compliance requirements for bulk cement are stringent. This guide outlines best practices and regulatory considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant movement of bulk cement from manufacturer to end-user.
Transportation Modes and Equipment
Road Transport – Pneumatic Tank Trucks
Pneumatic tank trucks are the most common method for moving bulk cement over land. These vehicles use compressed air to fluidize and discharge cement powder. Key requirements include:
– Use of DOT-approved, ASME-coded tanks designed for dry bulk materials.
– Regular inspection and maintenance of pressure relief valves, filters, and discharge systems.
– Drivers must be trained in handling pressurized systems and emergency procedures.
Rail Transport – Covered Hopper Cars
Rail is cost-effective for long-distance or high-volume shipments. Covered hopper cars must:
– Be dedicated or thoroughly cleaned to prevent contamination.
– Feature sealed lids and discharge systems to prevent dust emissions.
– Comply with AAR (Association of American Railroads) standards.
Maritime Shipping – Bulk Carriers
For international or coastal transport, bulk cement is shipped in dedicated bulk carriers or containerized in flexitanks within dry containers. Requirements include:
– Use of moisture barriers and ventilation control to prevent hydration.
– Compliance with IMO and SOLAS regulations for cargo stability and safety.
– Proper documentation under the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes (IMSBC) Code.
Handling and Storage Requirements
Loading and Unloading Procedures
- Loading must be conducted in controlled environments to minimize dust emissions using dust collection systems.
- Unloading should occur at designated silo facilities with proper venting and filtration.
- Operators must verify moisture content and material consistency prior to transfer.
On-Site Storage
- Cement should be stored in sealed silos or enclosed facilities to prevent exposure to moisture and contamination.
- Silos must be equipped with level indicators, dust collectors, and pressure relief mechanisms.
- Regular inspection for clinker build-up, corrosion, and structural integrity is essential.
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
- EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): Bulk cement handling is subject to National Emissions Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) and New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) for particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5).
- Dust suppression measures such as enclosed systems, filters, and wet suppression may be required.
- Facilities must comply with Clean Air Act standards and report emissions if applicable.
Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA)
- Workers must be protected from respiratory hazards; use of NIOSH-approved respirators and proper ventilation is mandatory.
- Hazard Communication (HazCom) standards require SDS (Safety Data Sheets) for cement, which is alkaline and can cause skin/eye irritation.
- Confined space entry procedures must be followed when inspecting or cleaning silos.
DOT and Transportation Safety
- In the U.S., DOT 407 or 412-specification tanks are required for hazardous material transport (cement is generally non-hazardous but regulated as a bulk commodity).
- Vehicles must display appropriate placards if carrying other regulated materials; cement itself does not require hazard placards unless contaminated.
- Pressure systems must be tested and certified periodically.
International Standards
- IMDG Code (International Maritime Dangerous Goods): Applies if cement is shipped in containers (non-hazardous, but packaging requirements apply).
- REACH and CLP (EU): Cement is classified under CLP as Skin Corrosion/Irritation Category 1B; suppliers must provide compliant labels and SDS in EU member states.
- Customs and Import Regulations: Importers must ensure conformity with local building material standards (e.g., ASTM C150 in the U.S., EN 197-1 in Europe).
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Product Specifications
- Cement must meet relevant standards (e.g., ASTM, EN, ISO) for composition, fineness, setting time, and strength.
- Batch testing and certification should accompany each shipment.
Required Documentation
- Bill of Lading (BOL) specifying type, quantity, and destination.
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA) or Mill Test Report.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) compliant with GHS.
- Customs declarations and import permits (for international shipments).
Risk Management and Emergency Preparedness
Spill and Dust Control
- In case of spillage, dry cleanup methods (e.g., industrial vacuums) should be used; avoid water to prevent hazardous reactions.
- Dust clouds pose explosion risks; facilities must follow NFPA 652 (Combustible Dust Standard).
Emergency Response
- Facilities must have spill kits, PPE, and response plans for leaks or over-pressurization events.
- Local emergency services should be informed of bulk cement storage locations and hazards.
Sustainability and Best Practices
- Optimize transport routes to reduce carbon emissions.
- Recycle dust collected from filters.
- Invest in energy-efficient pneumatic systems and electric-powered loading equipment.
Conclusion
Efficient and compliant logistics for bulk cement require careful coordination across transportation modes, strict adherence to environmental and safety regulations, and robust quality control. By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure the safe delivery of bulk cement while minimizing operational risks and regulatory non-compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Bulk Cement:
Sourcing bulk cement requires a strategic approach that balances cost-efficiency, quality assurance, reliable supply, and logistical feasibility. By establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers, conducting thorough due diligence, and securing long-term contracts where appropriate, businesses can ensure a consistent and high-quality cement supply. Key considerations such as transportation, storage capabilities, regional availability, and market price fluctuations must be carefully evaluated to minimize risks and optimize project timelines and budgets. Ultimately, effective bulk cement sourcing contributes significantly to the success and sustainability of large-scale construction and infrastructure projects.