The global buck-boost transformer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient voltage regulation in commercial, industrial, and renewable energy applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global transformer market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, with buck-boost transformers playing a critical role in addressing voltage fluctuations in aging electrical infrastructure and distributed energy systems. The rise in industrial automation, coupled with expanding renewable energy installations, continues to amplify the need for reliable and cost-effective voltage correction solutions. As grid modernization efforts gain momentum worldwide, the demand for high-performance buck-boost transformers is expected to rise in parallel. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of leading manufacturers that combine innovation, efficiency, and scalability. Based on market presence, product range, and technical capabilities, the following nine companies represent the top buck-boost transformer manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 9 Buck-Boost Transformer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electrical
Domain Est. 2012
Website: temcoindustrial.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 365-day returnsFederal Pacific – K1XGF16-1 – 1 Phase – 120×240 Volts Primary – 16/32 Volts Secondary – 1 kVA – Buck Boost Transformer – 60 Hz – Copper – NEMA 3R….
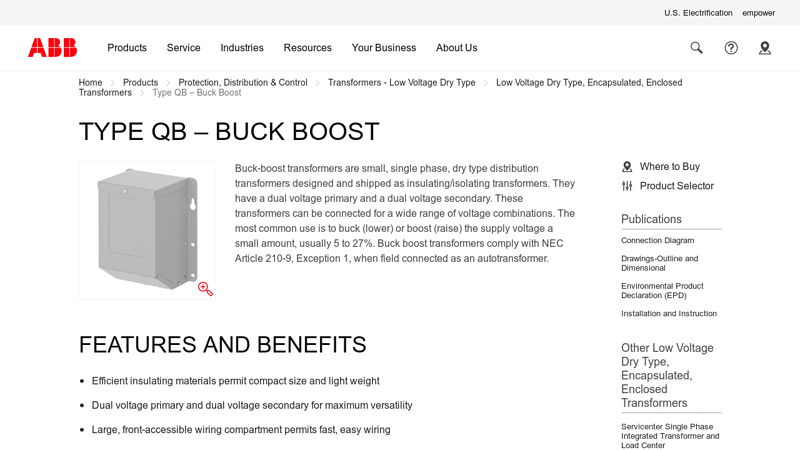
#2 Buck Boost Transformer Type QB
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: Buck-boost transformers are small, single phase, dry type distribution transformers designed and shipped as insulating/isolating transformers….
#3 Buck
Domain Est. 1995
Website: store.hubbell.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsT181051. Buck-Boost Transformer – Single Phase, 120 X 240 – 12/24V, 500VA. $249.54. Add To Cart. Compare. Buck-Boost Transformer – Single Phase, ……
#4 Buck Boost Transformers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hubbell.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsExplore our buck boost transformers, ideal for adjusting voltage levels in electrical circuits to enhance device performance and ensure stability….
#5 Buck boost
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton’s buck boost, low-voltage transformers are ideally suited to applications where the available voltage needs to be slightly increased (“boosted”) or ……
#6 Buck Boost Transformers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: crescentelectric.com
Key Highlights: 3–9 day delivery 60-day returnsBuck boost transformers are single phase transformers that adjust voltages which are applied to alternating current systems. By increasing or ……
#7 Buck Boost Transformers, Low Voltage General Purpose
Domain Est. 1997
Website: se.com
Key Highlights: Schneider Electric USA. Browse our products and documents for Buck Boost Transformers, Low Voltage General Purpose – Economical space-saving design for ……
#8 Buck
Domain Est. 2000
Website: americas.hammondpowersolutions.com
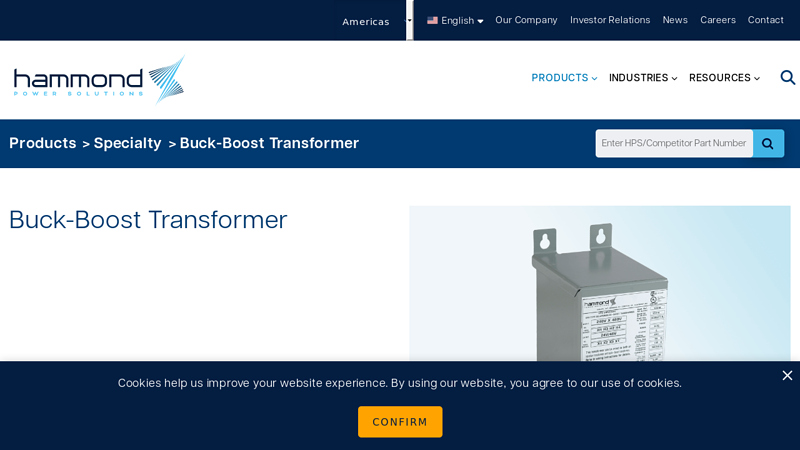
Key Highlights: The HPS line of buck-boost transformers is an economical way to both raise supply voltage caused by line drop or lower voltage caused by increased system ……
#9 Tormach Mill Upgrade
Domain Est. 2002
Website: tormach.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $250 60-day returnsThe Buck-Boost Transformer is recommended for minor increases of stable line voltages less than 230VAC to eliminate performance degradation….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Buck-Boost Transformer

H2: Buck-Boost Transformer Market Trends in 2026
The global buck-boost transformer market is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by evolving energy demands, infrastructure modernization, and technological advancements. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the industry in 2026:
1. Rising Demand for Voltage Regulation in Industrial and Commercial Sectors
Buck-boost transformers are increasingly being deployed to stabilize voltage in commercial buildings, manufacturing facilities, and data centers. Fluctuating power supplies due to aging grids and variable loads are pushing industries to adopt cost-effective voltage correction solutions. By 2026, this demand is expected to grow significantly, especially in regions with unreliable grid infrastructure.
2. Expansion of Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of solar and wind power into existing grids often causes voltage instability. Buck-boost transformers play a critical role in managing these fluctuations by adjusting voltage levels to match grid or load requirements. With renewable energy capacity projected to expand globally by 2026, the need for ancillary equipment like buck-boost transformers will rise in tandem.
3. Growth in Smart Grid and Microgrid Deployments
Smart grid initiatives and the proliferation of microgrids—especially in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific—are creating new applications for buck-boost transformers. These systems require precise voltage control to maintain efficiency and reliability. Transformers with enhanced monitoring and control capabilities are expected to gain traction, supporting the trend toward intelligent power management.
4. Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Manufacturers are focusing on developing compact, energy-efficient buck-boost transformers with improved thermal performance and lower electromagnetic interference. The incorporation of digital monitoring features, such as IoT-enabled sensors for real-time diagnostics, is anticipated to be a major differentiator in the 2026 market landscape.
5. Regional Infrastructure Investments
Government-led infrastructure projects in emerging economies—particularly in India, Southeast Asia, and Africa—are driving demand for reliable power distribution equipment. Buck-boost transformers are being increasingly specified in new construction and retrofit projects to address under-voltage issues common in developing power networks.
6. Shift Toward Standardized and Modular Designs
To reduce installation time and costs, there is a growing preference for pre-wired, modular buck-boost transformer systems. Standardized solutions that can be easily scaled or reconfigured are expected to dominate the market by 2026, especially in commercial HVAC and lighting applications.
7. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Compliance
With increasing emphasis on energy conservation, regulatory bodies are tightening efficiency standards for electrical equipment. Buck-boost transformers with higher energy efficiency ratings and compliance with standards such as DOE (U.S. Department of Energy) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) will be preferred, influencing procurement decisions across sectors.
8. Supply Chain Optimization and Local Manufacturing
Following post-pandemic disruptions, manufacturers are reshoring or regionalizing production to mitigate risks. By 2026, localized manufacturing hubs are expected to improve delivery times and reduce logistics costs, especially in high-demand regions like North America and Southeast Asia.
In conclusion, the buck-boost transformer market in 2026 will be shaped by the convergence of energy transition, digitalization, and infrastructure development. Companies that innovate in efficiency, connectivity, and scalability will be best positioned to capture growth opportunities in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Buck-Boost Transformers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing buck-boost transformers involves more than just matching voltage and current ratings. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, and legal complications. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Testing
One of the most frequent issues is assuming that all transformers meet the same quality standards. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners on materials and testing, leading to premature failure or inconsistent performance. Always verify that the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality standards such as ISO 9001 and provides test reports for dielectric strength, temperature rise, and insulation resistance. Lack of proper certification increases the risk of field failures and safety incidents.
Ignoring Insulation Class and Temperature Rating
The insulation class (e.g., Class B, F, or H) directly impacts the transformer’s ability to withstand thermal stress. Using a transformer with an insufficient insulation class in a high-temperature environment can result in degraded insulation, short circuits, or fire hazards. Ensure the insulation system matches the application’s operating conditions and ambient temperature. Never assume a standard insulation class is suitable for all installations.
Overlooking UL, CSA, or Other Safety Certifications
For use in North America, buck-boost transformers typically require UL 1561 or CSA C22.2 No. 66 certification. Sourcing non-certified units—even if they appear identical—can violate electrical codes, void insurance, and create liability risks. Verify that the exact model is listed in the certification database, as certification is model-specific and not transferable between manufacturers.
Counterfeit or Clone Products with IP Violations
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “equivalent” buck-boost transformers that closely mimic branded designs. These may infringe on patents, trademarks, or copyrighted designs. Using such products can expose your company to legal action, especially in regulated industries. Always source from authorized distributors or manufacturers with clear IP compliance and avoid products with suspiciously low prices or ambiguous branding.
Poor Core and Winding Material Quality
The efficiency and longevity of a buck-boost transformer depend heavily on core material (e.g., grain-oriented silicon steel) and copper winding quality. Substandard materials increase losses, generate excess heat, and reduce efficiency. Request material specifications and inspect samples for build quality. Be cautious of transformers using aluminum windings marketed as copper—they often underperform and overheat.
Inadequate IP (Ingress Protection) Rating for Environment
While not always labeled with an IP code like enclosures, the physical construction of the transformer must suit its environment. Transformers used in dusty, humid, or outdoor locations need sealed windings and protective varnishes. Failure to consider environmental exposure can lead to moisture ingress, corrosion, and insulation breakdown. Confirm with the manufacturer the suitability for indoor/outdoor, NEMA, or other environmental ratings where applicable.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide batch traceability, test data, and full technical documentation. Without these, troubleshooting field issues or proving compliance during audits becomes difficult. Ensure the supplier maintains records and can provide certificates of conformance upon request. Avoid vendors who cannot supply detailed product documentation or lack a clear manufacturing history.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, buyers can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection from legal and operational risks when sourcing buck-boost transformers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Buck-Boost Transformer
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe and legal handling, transportation, and installation of buck-boost transformers.
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure all buck-boost transformers are correctly classified under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for international shipping (e.g., 8504.23 or 8504.31, depending on specifications). Maintain accurate technical documentation, including nameplate data, test reports, and manufacturer certifications, to support customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Buck-boost transformers must be securely packaged in robust, moisture-resistant materials to prevent damage during transit. Use wooden crates or strong corrugated boxes with internal bracing. Clearly label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack,” and include the transformer’s model number, kVA rating, input/output voltages, and net weight.
Transportation and Storage Conditions
Transport units in dry, temperature-controlled environments to avoid condensation and insulation degradation. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures (typically outside -25°C to +55°C) and high humidity. During storage, keep transformers in a clean, indoor area on a level surface, away from corrosive substances, vibrations, and direct sunlight. Elevate units off the floor using pallets to prevent moisture absorption.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify compliance with destination country regulations, including conformity assessment procedures and certification marks (e.g., CE for Europe, UKCA for the United Kingdom, EAC for Eurasia). For the U.S., ensure compliance with Department of Energy (DOE) efficiency standards under 10 CFR Part 431. Confirm adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations where applicable.
Electrical Safety and Installation Standards
Buck-boost transformers must conform to recognized electrical safety standards such as:
– UL 5085 (U.S. Standard for Safety of Transformers)
– CSA C22.2 No. 66 (Canada)
– IEC 61558-2-16 (International Standard for Safety of Transformers for Power Supplies)
Installation must follow National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 450 in the U.S. or equivalent local codes, including proper overcurrent protection, grounding, and ventilation requirements.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Dispose of failed or obsolete units in compliance with local environmental regulations. Buck-boost transformers may contain insulating oil or materials subject to hazardous waste rules (e.g., PCB testing if manufactured before 1979). Recycle metal components in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions.
Certification and Labeling
All units must bear permanent labels indicating:
– Manufacturer name and location
– Model and serial number
– kVA rating
– Primary and secondary voltages
– Frequency (Hz)
– Efficiency rating (per DOE or equivalent)
– Safety certification marks (UL, CSA, CE, etc.)
Ensure labels are legible and resistant to wear and environmental exposure.
Training and Technical Support
Provide installers and logistics personnel with access to product manuals and safety data sheets (SDS) if applicable. Offer technical support to ensure correct application and connection of buck-boost transformers, particularly in autotransformer configurations, to prevent hazardous voltage conditions.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Maintain records of purchase orders, shipping documents, compliance certifications, and inspection reports for a minimum of seven years to support audits, warranty claims, and regulatory inquiries. Implement a serial-number tracking system for full supply chain traceability.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Buck-Boost Transformer
In conclusion, sourcing a buck-boost transformer requires careful consideration of electrical requirements, load characteristics, environmental conditions, and compliance standards. These transformers offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for minor voltage adjustments in both industrial and commercial applications, ensuring equipment operates within acceptable voltage ranges and preventing potential damage due to overvoltage or undervoltage conditions.
Key factors in the sourcing process include accurate load assessment, selection of the appropriate configuration (buck or boost), proper kVA rating, input/output voltage specifications, and adherence to relevant safety and regulatory standards such as UL, CSA, or IEC. Additionally, partnering with reputable suppliers or manufacturers ensures product reliability, technical support, and warranty coverage.
By thoroughly evaluating technical needs and aligning them with quality sourcing practices, organizations can enhance power system stability, improve energy efficiency, and extend the lifespan of connected equipment. Ultimately, a well-sourced buck-boost transformer contributes to a more resilient and dependable electrical infrastructure.