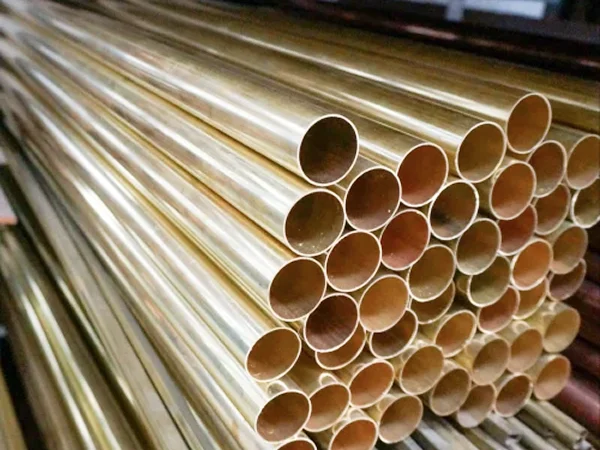
The global brass water pipe market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising urbanization, infrastructure development, and increasing demand for corrosion-resistant plumbing solutions. According to Grand View Research, the global copper and brass plumbing tubes and pipes market was valued at USD 59.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects continued demand for brass piping systems in residential, commercial, and industrial applications, particularly in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific and Latin America. With durability, antimicrobial properties, and high thermal conductivity making brass a preferred material for water distribution, sourcing from reliable manufacturers has become critical for project success. In this landscape, identifying top-performing brass water pipe manufacturers ensures access to quality, compliance, and innovation. Here’s a data-informed look at the leading manufacturers shaping the industry.
Top 10 Brass Water Pipe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mueller Industries
Domain Est. 1996
Website: muellerindustries.com
Key Highlights: Mueller Industries, Inc. is an industrial manufacturer that specializes in copper and copper alloy manufacturing while also producing goods made from aluminum, ……
#2 Cerro Flow Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cerro.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Cerro Flow Products LLC®. We manufacture world-class copper tube and supply fittings for the Plumbing, HVAC/Refrigeration, and Industrial markets….
#3 Brass Pipe Manufacturer & Distributor
Domain Est. 2017
Website: avivametals.com
Key Highlights: Aviva Metals offers an extensive collection of brass pipe for a variety of industry applications. Browse our selection today!…
#4 BrassCraft
Domain Est. 1995
Website: brasscraft.com
Key Highlights: This is Our Craft. BrassCraft produces high quality products plumbers depend on to make their business a success….
#5 T&S Brass
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tsbrass.com
Key Highlights: T&S Brass offers a full range of top quality foodservice, commercial, laboratory, and pet market faucets and fittings….
#6 Brass
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meritbrass.com
Key Highlights: Explore brass piping components (leaded & lead-free) for your inventory or next installation of a piping system….
#7 Service Brass
Domain Est. 2000
Website: muellercompany.com
Key Highlights: Mueller Co. provides utility and plumbing contractors with one of the broadest product lines of water service connections for distribution mains, service lines ……
#8 Royal Brass Incorporated
Domain Est. 2002
Website: rbisj.com
Key Highlights: Royal Brass Incorporated is your one-stop hose company in San Jose, CA for hose accessories and hose repair. Contact our hydraulic hose shop for all of your ……
#9 Midland Industries
Domain Est. 2011
Website: midlandindustries.com
Key Highlights: NEW TANKLESS WATER HEATER VALVES. NOW IN STOCK. • Lead-Free Brass Forged Bodies • Full Port 3/4″ Drain Outlets • Ready to ship from Midland. Shop New Tankless ……
#10 Wolverine Brass
Website: wolverine-brass.com
Key Highlights: Discover high-quality plumbing products at Wolverine Brass. Explore our extensive range of durable fittings and fixtures designed for superior performance….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Brass Water Pipe
H2: Market Trends for Brass Water Pipes in 2026
The global market for brass water pipes is expected to witness moderate growth by 2026, driven by urbanization, infrastructure development, and increasing demand for corrosion-resistant plumbing materials. Key trends shaping the brass water pipe market in 2026 include:
-
Growing Demand in Residential and Commercial Construction
Urban expansion and rising investments in housing, hotels, and commercial complexes—especially in emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa—are boosting demand for durable plumbing solutions. Brass water pipes, known for their longevity and resistance to microbial growth, are increasingly preferred in high-end residential and commercial projects. -
Emphasis on Water Quality and Safety
Regulatory standards around lead content in plumbing materials are tightening globally. In 2026, the market is seeing a shift toward low-lead or lead-free brass alloys (e.g., DZR—Dezincification Resistant brass) to comply with health and environmental regulations such as NSF/ANSI 61 and the U.S. Reduction of Lead in Drinking Water Act. This shift is encouraging manufacturers to innovate with safer brass formulations. -
Replacement of Outdated Plumbing Systems
Aging infrastructure in North America and Europe is prompting large-scale retrofits and rehabilitation projects. Brass water pipes are being selected for replacements due to their durability, ease of installation, and compatibility with modern plumbing systems, supporting market growth despite competition from PEX and CPVC alternatives. -
Competition from Plastic and Composite Pipes
Although brass offers superior strength and temperature resistance, plastic alternatives like PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) and HDPE are gaining popularity due to lower cost and easier installation. However, brass maintains a niche in applications requiring high reliability, such as in hospitals, laboratories, and high-rise buildings. -
Sustainability and Recycling Trends
Brass is 100% recyclable without loss of quality, aligning with global sustainability goals. By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly adopting circular economy practices, using recycled brass to reduce environmental impact and production costs. This sustainability advantage is improving brass’s appeal among environmentally conscious developers and municipalities. -
Technological Advancements and Smart Plumbing Integration
The integration of smart building technologies is influencing plumbing material choices. While brass pipes themselves are not “smart,” their compatibility with sensor-equipped fittings and smart water monitoring systems enhances their utility in intelligent building designs. -
Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific: China, India, and Southeast Asian countries are leading demand due to rapid urbanization and government infrastructure programs.
- North America and Europe: Steady demand from renovation projects and regulatory compliance drives market stability.
- Middle East and Africa: Increased investment in water infrastructure supports brass pipe adoption, especially in desalination and district cooling systems.
In summary, the brass water pipe market in 2026 is characterized by steady demand, regulatory evolution, and competition from alternative materials. While facing pressure from plastics, brass continues to hold a strong position in applications where performance, safety, and longevity are paramount.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Brass Water Pipe (Quality, IP)
Sourcing brass water pipe for plumbing, industrial, or potable water applications requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) compliance. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly failures, legal issues, and reputational damage. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Non-Compliance
One of the biggest risks when sourcing brass water pipe—especially from low-cost suppliers—is receiving substandard material that fails to meet required specifications.
-
Incorrect Brass Alloy Composition: Not all brass is suitable for water applications. Using low-zinc or leaded brass (e.g., non-lead-free C36000) in potable water systems violates regulations such as NSF/ANSI 61 and the U.S. Safe Drinking Water Act. Sourcing pipes made from non-compliant alloys like C37700 (foundry brass) instead of approved lead-free alternatives (e.g., C46400, C69300, or DZR brass) can result in lead leaching and health hazards.
-
Inadequate Corrosion Resistance: Dezincification-resistant (DZR or DR brass) is essential in aggressive water conditions. Standard brass pipes may suffer from dezincification, leading to premature pipe failure. Buyers often fail to specify DZR compliance, especially in regions with soft or acidic water.
-
Poor Manufacturing Standards: Pipes with inconsistent wall thickness, surface cracks, improper temper (hardness), or poor threading can compromise system integrity. Sourcing from manufacturers without ISO 9001 certification or third-party testing increases risk.
-
Lack of Certifications and Traceability: Reputable suppliers provide mill test certificates (MTCs), material traceability, and compliance documentation (e.g., NSF, WRAS, ACS). Accepting pipes without verifiable documentation exposes buyers to liability and compliance failures.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing brass water pipe often involves technical designs, proprietary manufacturing processes, or branded product lines—making IP a critical but frequently overlooked concern.
-
Counterfeit or Knockoff Products: Some suppliers may offer pipes branded as “equivalent” to well-known manufacturers (e.g., Uponor, Viega, or Wirsbo) but are unauthorized replicas. These may infringe on trademarks, patented designs, or trade dress, exposing the buyer and end-user to legal liability.
-
Patented Technologies: Certain brass pipe systems incorporate proprietary connection methods (e.g., press-fit, push-fit, or sealing technologies) protected by patents. Sourcing unlicensed versions—even if the base material is brass—can lead to infringement lawsuits, especially in markets like the U.S. or EU.
-
Use of Unauthorized Branding or Markings: Pipes improperly marked with certification logos (e.g., NSF, WRAS, CSA) without authorization constitute IP and regulatory fraud. Buyers may unknowingly distribute non-compliant or counterfeit products.
-
Failure to Verify Licensing Agreements: When sourcing from third-party manufacturers producing “compatible” fittings or pipes, ensure they have proper licensing from the IP holder. Lack of due diligence can result in supply chain disruptions and legal action.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Specify exact material standards (e.g., ASTM B43, EN 12165) and require lead-free, DZR-compliant brass.
– Demand full certification packages and conduct independent material testing.
– Vet suppliers thoroughly—prioritize those with ISO certifications and a transparent supply chain.
– Conduct IP due diligence: verify trademarks, check patent databases, and request proof of licensing for branded or patented systems.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
By addressing both quality and IP concerns proactively, buyers can ensure safe, compliant, and legally secure sourcing of brass water pipe.
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Brass Water Pipe
Importing, transporting, and distributing brass water pipe requires strict adherence to technical, safety, and regulatory standards to ensure product integrity, environmental protection, and market access. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations.
H2: Product Classification & Regulatory Standards
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Accurately classify brass water pipe for customs. Common codes include:
- 7411.10: Pipes and Tubes, seamless, of copper (may apply if brass content is high copper).
- 7411.21 / 7411.22: Pipes and Tubes, having circular cross-sections, of copper, with fittings (consider brass as copper alloy). Confirm precise code based on alloy composition (e.g., % zinc), dimensions, and application with customs authorities.
- Key Compliance Standards:
- NSF/ANSI 61 (Drinking Water System Components): MANDATORY in the US, Canada, and many other regions. Certifies materials are safe for contact with drinking water, limiting leaching of lead and other contaminants. Products must be certified by an accredited body (e.g., NSF International, IAPMO).
- NSF/ANSI 372: Certifies compliance with “lead-free” requirements (<0.25% weighted average lead content in wetted surfaces) mandated by the US Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) and similar regulations globally.
- ASTM B43: Standard Specification for Seamless Red Brass Pipe and Tube (85% Cu–15% Zn). Specifies dimensions, mechanical properties, and testing.
- ASTM B88: Standard Specification for Seamless Copper Water Tube. While for copper, brass pipe for water often references dimensional standards within B88.
- Local Plumbing Codes: Must comply with national/regional codes (e.g., IPC, UPC in the US; National Building Code in Canada; WRAS in the UK; DVGW in Germany). These often mandate NSF/ANSI 61/372 certification.
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals. Brass components must comply with substance restrictions, particularly concerning lead and other SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern).
- RoHS (EU & others): Restriction of Hazardous Substances. While primarily for electronics, ensure no restricted substances are present in platings or markings if applicable.
H2: Packaging, Handling & Storage
- Packaging:
- Protect against physical damage (dents, scratches), corrosion, and contamination.
- Use sturdy, moisture-resistant materials (e.g., plastic end caps, shrink-wrapping, wooden crates, or steel strapping on pallets).
- Clearly label packages with product details, HS code, country of origin, weight, handling instructions (“Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Moisture”), and compliance marks (NSF, WRAS, etc.).
- Include Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) if required by transport regulations (generally not hazardous, but SDS clarifies composition).
- Handling:
- Use appropriate equipment (forklifts, cranes) to avoid dropping or impacting pipes.
- Prevent kinking or bending during loading/unloading.
- Avoid contact with dissimilar metals to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Storage:
- Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area, off the ground (on pallets).
- Protect from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and moisture to prevent tarnishing or corrosion.
- Segregate from chemicals, acids, or salt-laden environments.
- Maintain organized inventory to prevent damage from stacking.
H2: Transportation & Logistics
- Mode Selection:
- Ocean Freight: Primary mode for international shipments. Use standard dry containers. Ensure proper dunnage and blocking/bracing within containers to prevent shifting.
- Rail Freight: Suitable for long domestic/international overland routes. Follow similar securing principles as ocean freight.
- Road Freight: Essential for final delivery. Use enclosed trailers to protect from weather. Secure loads effectively.
- Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice: Detail product description, HS code, value, origin.
- Packing List: Itemize contents per package, weights, dimensions.
- Bill of Lading (BOL) / Air Waybill (AWB): Contract of carriage.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariffs (e.g., USMCA, EU agreements).
- Compliance Certificates: NSF/ANSI 61 & 372 certificates are CRITICAL. Include copies with shipping documents. WRAS, DVGW, etc., as required by destination market.
- Phytosanitary Certificate: May be required if wooden packaging is used (ISPM 15 compliant pallets usually suffice).
- Customs Clearance:
- Provide complete and accurate documentation.
- Be prepared for customs inspections, especially verification of “lead-free” compliance and NSF certification.
- Understand and budget for applicable duties, taxes, and fees based on the HS code and origin.
H2: Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS) Considerations
- Material Safety: Brass is generally not classified as hazardous for transport (UN numbers typically not required). However, brass dust generated during cutting/threading can be hazardous if inhaled. Provide SDS and recommend PPE (respirators, gloves) for fabrication.
- Lead Exposure: Strictly manage lead content per NSF/ANSI 372 and local regulations. Implement controls during manufacturing and handling to prevent lead dust exposure.
- Waste Management: Recycle scrap brass efficiently. Dispose of packaging materials according to local regulations.
- Spill Response: While liquid spills are unlikely, have procedures for cleaning up significant brass dust or debris.
H2: Key Compliance Verification Checklist
- Certification: Confirm valid, up-to-date NSF/ANSI 61 and NSF/ANSI 372 certification (or equivalent like WRAS, DVGW) for the specific brass water pipe product.
- Lead Content: Verify product meets “<0.25% lead” requirement for wetted surfaces (NSF 372).
- Markings: Ensure pipes are permanently marked with manufacturer, alloy, size, compliance standard (e.g., “NSF-pw”), and potentially lot number.
- Documentation: All required certificates (NSF, CoO) and accurate shipping docs (Invoice, PL, BOL) are prepared.
- Packaging: Secured against damage and moisture, properly labeled.
- HS Code: Verified as correct for the specific product with customs broker.
- Destination Regulations: Confirmed compliance with all relevant local plumbing and environmental codes.
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Regulations vary significantly by country and change frequently. Always consult with legal counsel, customs brokers, and certification bodies specific to your origin and destination markets for definitive requirements.
Conclusion on Sourcing Brass Water Pipes:
Sourcing brass water pipes requires a careful evaluation of quality, compliance, cost, and supplier reliability. Brass remains a preferred material for water distribution systems due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and antimicrobial properties. When sourcing, it is essential to ensure that the brass pipes meet relevant international standards such as NSF/ANSI 61, ASTM B88, or EN 1254, particularly with respect to lead content (e.g., low-lead or lead-free brass compliant with regulations like the U.S. Safe Drinking Water Act).
Key considerations include selecting reputable suppliers with proven manufacturing capabilities, verifying certifications, and assessing the total cost of ownership—including freight, tariffs, and lead times. While domestic suppliers may offer shorter delivery times and easier communication, overseas suppliers—particularly from regions like Asia—can provide cost advantages if quality control and logistical challenges are effectively managed.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of brass water pipes involves balancing quality assurance, regulatory compliance, cost efficiency, and supply chain resilience. Conducting thorough supplier audits, requesting material test reports, and establishing long-term partnerships can help ensure a reliable supply of high-performance brass piping for plumbing and industrial applications.